Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density Using Unenhanced Computed Tomography
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article pissn: , eissn: Yonsei Med J 54(1):28-33, 213 Evaluation of the Effect of Hemoglobin or Hematocrit Level on Dural Sinus Density Using Unenhanced Computed Tomography Seung Young Lee, 1 Sang-Hoon Cha, 1 Sung-Hyun Lee, 2 and Dong-Ick Shin 2 Departments of 1 Radiology and 2 Neurology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. Received: October 17, 211 Revised: March 5, 212 Accepted: March 9, 212 Corresponding author: Dr. Seung Young Lee, Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, 776, 1st sunwhan-ro, Heungdeok-gu, Cheongju , Korea. Tel: , Fax: lsyrad@chungbuk.ac.kr The authors have no financial conflicts of interest. Purpose: To identify the relationship between hemoglobin (Hgb) or hematocrit (Hct) level and dural sinus density using unenhanced computed tomography (UECT). Materials and Methods: Patients who were performed UECT and had records of a complete blood count within 24 hours from UECT were included (n=122). We measured the Hounsfield unit (HU) of the dural sinus at the right sigmoid sinus, left sigmoid sinus and 2 points of the superior sagittal sinus. Quantitative measurement of dural sinus density using the circle regions of interest (ROI) method was calculated as average ROI values at 3 or 4 points. Simple regression analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between mean HU and Hgb or mean HU and Hct. Results: The mean densities of the dural sinuses ranged from to HU (mean, HU). There was a strong correlation between mean density and Hgb level (r=.832) and between mean density and Hct level (r=.84). Conclusion: Dural sinus density on UECT is closely related to Hgb and Hct levels. Therefore, the Hgb or Hct levels can be used to determine whether the dural sinus density is within the normal range or pathological conditions such as venous thrombosis. Key Words: Dural sinus, density, CT, hemoglobin, hematocrit INTRODUCTION Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 213 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non- Commercial License ( licenses/by-nc/3.) which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Pathological conditions involving the dural sinuses are uncommon, but cases of dural sinus thrombosis (DST) or cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), with an annual incidence of 3 to 4 cases per million adults, are not unusual. 1 These cases account for approximately 1-2% of all strokes in adults and affect all age groups. 2 DST often presents with highly variable symptoms such as headache, dizziness, visual disturbance, focal neurologic deficits, seizures, and impaired consciousness. 3-7 DST has a wide clinical spectrum and onset is often subacute; therefore, the average delay from the onset of symptoms to diagnosis is 7 days. 1,8 Unenhanced computed tomography (UECT) is the first imaging modality for patients presenting with variable neurologic symptoms. One direct sign of DST, the cord sign is defined as a homogeneous, hyperattenuated appearance of intravenous thrombi in dural sinuses or veins which reflects newly-formed thrombi within 1 week of disease onset. The cord sign is visualized in less than 25% of DST 28 Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January 213
2 The Effect of Hgb and Hct Level on Dural Sinus Density cases. The qualitative signs of CVT have been described in some studies However, hyperattenuation is a qualitative and subjective finding. We are usually able to observe the variability of dural sinus density using UECT in routine practice. Therefore, a noticeably high or low density of dural sinuses can confuse normality with pathologic conditions. To our knowledge, only three studies have focused on quantitative measurement of the density of normal superior sagittal sinus (SSS) However, SSS cannot be representative of the whole dural sinus. In this study, we quantitatively measured the density of dural sinus including the sigmoid sinuses (SS) in normal populations and evaluated the effect of hemoglobin (Hgb) or hematocrit (Hct) on variability of dural sinus density on UECT. MATERIALS AND METHODS Inclusion and exclusion criteria The 122 patients included in this study were admitted to our institution between January 29 and, April 29. Inclusion criteria consisted of patients with UECT of the brain and a complete blood count (CBC) test acquired within a 24-hour period, regardless of patient symptoms or signs. However, patients who were clinically suspected to have DST were excluded. Exclusion criteria included intracranial hemorrhage or skull fracture adjacent to dural sinuses, an increased intracranial pressure condition such as hydrocephalus, severe brain swelling, intra-axial or extra-axial mass, recent interventional or surgical treatment, intravenous or intraarterial iodinated contrast media administration within the previous 24 h. Patients receving a blood transfusion within the previous 24 h were also excluded. roview 5.3 (Infinitt Co., Seoul, Korea) Picture Archiving and Communication System by one neuroradiologist to eliminate inter-operator variability. Axial scans that showed the fewest beam hardening artifacts were selected for analysis. The dural sinus densities were measured using the circle regions of interest (ROI) method at 3 or 4 points including the right SS, left SS and 2 points of the SSS (upper 1/2 and lower 1/2 of dorsal SSS) on axial sections. One or both SS were required for use in the ROI measurement. The ROI area was set to a limit of 1-2 mm 2 and we used a circular ROI area as large as possible that could be measured at three or more points. Identical circular ROIs in one patient were used by copying and pasting (Fig. 1). The exclusion criteria of UECT during image interpretation were as follows: cases in which the ROI could not be measured in both SS and in at least 3 points because of significant artifacts such as beam hardening or partial volume, undifferentiated sinuses with brain parenchyma, or small dural sinuses <1 mm 2. The mean value of sinus density measured at 3 or 4 points was calculated. Laboratory data CBC results were obtained from the electronic in-hospital data base of clinical records. Only patients who had the results of CBC results acquired within 24 h before or after UECT were included in this study. If one or more CBC results were available from that 24 h period, the data with the shortest time interval from UECT was used. Hgb and Hct UECT imaging protocol UECT was performed using a 64-detector row CT scanner (Brilliance 64, Philips Medical Systems, Best, the Netherlands) using axial or helical methods. In the axial method, the gantry tilt was parallel to the orbito-meatal line, and in helical method, the images were reconstructed parallel to the line. The following parameters were used: a peak kilovoltage of 12 kvp, variable tube currents ( ma) from an automatic exposure system, section thickness of 5 mm, and a reconstruction increment of 5 mm. Image interpretation Axial UECT scan were retrospectively reviewed using Ma- Fig. 1. The region of interests (ROI) measured at 3 or 4 points including right sigmoid sinus (SS), Lt. SS and 2 points of superior sagittal sinus. One or both sigmoid sinus must be included in ROI measurement. Identical, circular ROI in one patient were used by copying and pasting method. Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January
3 Seung Young Lee, et al. levels were also collected. Statistical methods Simple regression analysis, multiple regression analysis, Mean ROI (HU) Fig. 2. Frequency graph of mean Hounsfield unit (HU) values. The mean densities ranged from to HU with a mean of The mean densities in 97 patients (79.5%) were included within range from 35 HU to 5 HU. Mean ROI (HU) <25 Fig. 3. Graph illustrating the correlation between mean HU and Hgb. There was a strong correlation between mean HU and Hgb levels (r=.832). HU, Hounsfield unit; ROI, regions of interest; Hgb, hemoglobin. Mean ROI (HU) < Frequency 1 Correlation between mean ROI and Hgb Hgb (g/dl) 3 Hct (%) Fig. 4. Graph illustrating the correlation between mean HU and Hct. There was a strong correlation between mean HU and Hct levels (r=.84). HU, Hounsfield unit; ROI, regions of interest; Hct, hematocrit. 15 Correlation between mean ROI and Hct 4 Mean ROI Mean ROI correlation analysis and independent sample t-test using SPSS 12. (SPSS company, Chicago, IL, USA) were performed. Simple regression analysis was used to evaluate the correlation between mean HU and Hgb or mean HU and Hct. Correlation analyses and independent sample t- tests were used to evaluate the effect of age and sex, respectively. Multiple regression analyses were performed to evaluate the relationship between mean HU and Hct according to age or sex. RESULTS The total population (n=122) consisted of 71 men and 51 women (range, years; mean age, 53 years). The mean circular ROI area was 14.5 mm 2 ( mm 2 ). ROI measurements were available in bilateral SS in 7 patients and only in unilateral SS in 52 patients. In addition, mean ROIs were calculated at 4 points in 7 patients and at 3 points in 52 patients. The mean density of dural sinuses ranged from to HU with a mean of with standard deviation (SD) of 5.82 (Fig. 2). Hgb levels ranged from 6.6 g/ dl to 16.5 g/dl with a mean of 13.17±2.18 and Hct levels ranged from 2.3% to 48.2% with a mean of 38.89±6.22. There was a strong correlation between mean HU and Hgb level (r=.832) (Fig. 3), so it may be possible to use regression equation such as mean HU= Hgb (p<.1). There was also a strong correlation between mean HU and Hct level (r=.84) (Fig. 4), so it may be possible to use regression equation such as mean HU= Hct (p<.1). The difference between mean density and Hct ranged from 3.1 to 12.8 with a mean of 4.39 and SD of 3.4. The seven patients (5.7%, 5 females, 2 males) showed a difference of more than 1 between mean ROI and Hct levels. The densities in the SS (mean HU in the right SS, and HU in the left SS) were higher than those in the SSS (mean-42.8 HU in the upper portion of SSS, HU in the lower portion). The densities of the right or left SS were higher than the SSS densities in 19 of 122 cases (89.3%) and the difference between SS density and SSS density ranged from -2.5 to 14 with a mean of 3.68±3.13. The mean density of dural sinuses was HU with a SD of 5.43 in males and HU with SD of 5.84 in females. The difference of the mean HU between the sexes was statistically significant (p=.1), but there was no difference in orrelation between mean HU and Hct levels by sex (p=.87). There was a negative correlation between 3 Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January 213
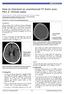
4 The Effect of Hgb and Hct Level on Dural Sinus Density mean HU and age but no difference in correlation between mean HU and Hct level according to the age. In our cohort, the highest mean density was HU with an Hgb of 15.9 g/dl and an Hct level of 47.1% in a 47-year-old male who was previously healthy and presented with a headache (Fig. 5). The lowest mean density was HU in 28-year-old female with an Hgb of 8.4 g/dl and an Hct of 24.3%. She was pregnant and had underlying Wilson s disease and liver cirrhosis (Fig. 6). In a 31-year old male who presented with a headache, UECT showed a grossly hyperdense dural sinus, but quantitatively, the mean ROI measured as 51 HU and was wellcorrelated with an Hgb level of 15.7 g/dl and an Hct level of 47.2%. In addition, the dense cortical vein observed at the frontal sulcus measured as 62 HU. CT angiography and MRI revealed CVT without evidence of DST (Fig. 7). In a 49-year-old male who presented with multiple fractures of long bone in a traffic accident without head trauma, the mean density of the dural sinus on initial preoperative brain CT was 46 HU with an Hgb of 14.1 g/dl and an Hct of 41.9%, but postoperative CT performed after 5 days showed a mean density of HU. This patient did not receive a blood transfusion in operation, at which time, the Hgb was 1.1 g/dl and the Hct was 3.1% (Fig. 8). DISCUSSION MRI with MR venography is commonly considered, the noninvasive gold standard in diagnosing CVT 3,6 Howev- er, DST often presents with highly variable symptoms, so UECT is usually the first imaging modality for most of them. The hyperattenuating signs in UECT are occasionally observed when an acute clot has formed in a vessel and can be seen in various vascular diseases, including acute arterial occlusion, acute arterial dissection, aneurysm rupture and acute venous thrombosis. 15 As a thrombus retracts, water content decreases, Hct concentration increase, and its attenuation value subsequently increase to 5-8 HU. 16,17 In our study, the mean densities ranged from to HU with a mean of 43.28, and these results showed a relatively low attenuation compared with previous quantitative study of SSS (32-69 HU) by Black, et al. 14 One study of a pediatric population found that SSS attenuation measurements ranged between 5 and 68 HU. 13 Another study of adults revealed the attenuation values were distributed with a mean of 5 HU and SD of In our study, the densities of the right or left SS were higher than the SSS densities in 19 of 122 cases (89.3%), so HU differences between our study and others may not be caused by addition of SS to the mean density measurement but, rather, to the patient population. In an earlier report, Fanous, et al. 12 suggested that the lack of a strong correlation between attenuation values and Hgb levels may be due to the dural sinus complexity. The lateral venous lacunae and cavernous spaces contribute to structural heterogeneity. Therefore, if the dural sinus attenuations are measured at larger and more numerous points, then the mean values will be more precise. The dural sinuses were very close to the skull, which may have resulted in inevitable partial volume averaging and Fig. 5. In our cohort, the highest mean density was HU with an Hgb of 15.9 g/dl and an Hct level of 47.1% in a 47-year-old male who was previously healthy and presented with a headache. There was no clinical suspicion of dural sinus thrombosis in this patient. HU, Hounsfield unit; Hgb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit. Fig. 6. The lowest mean density was HU in 28-year-old female with an Hgb of 8.4 g/dl and an Hct of 24.3%. She was pregnant and had underlying Wilson s disease and liver cirrhosis. HU, Hounsfield unit; Hgb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit. Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January
5 Seung Young Lee, et al. A B C Fig. 7. A 31-year-old male presented with headache. The UECT (A) showed grossly hyperdense dural sinus, but mean density was measured as 51 HU and was well correlated with an Hgb level of 15.7 g/dl and an Hct level of 47.2%. The dense cortical vein observed at the frontal sulcus measured as 62 HU (white arrow). Additionally performed CT angiography (B) not showed filling defects in dural sinuses suggesting thrombosis and MRI (C) revealed cortical vein thrombosis (black arrow). UECT, unenhanced computed tomography; HU, Hounsfield unit. A Fig. 8. A 49-year-old male presented with multiple fractures of long bone without head trauma. The mean density of dural sinus on initial preoperative UECT (A) was 46 HU with an Hgb of 14.1 g/dl and an Hct of 41.9%, but postoperative UECT (B) performed after 5 days showed a mean desntiy of HU, at which time, the Hgb was recorded to 1.1 g/dl and Hct was 3.1%. UECT, unenhanced computed tomography; HU, Hounsfield unit; Hgb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit. female patients had a history of chronic disease such as liver cirrhosis or chronic renal failure and none presented with active bleeding. There was no statistically significant difference in the correlation between mean HU and Hct level between the sexes (p=.87), but more complex factors such as hydration may have influenced the dural sinus density in females. Collins, et al. 18 demonstrated that aortic attenuation on abdomen CT is capable of providing a reliable indicator of the presence of anemia and that an averaged aortic attenuation value >5 HU in males and >45 HU in females is conbeam hardening artifacts. Therefore, we thought that the SS was suitable for the ROI measurement because it has a larger area than the SSS, which made avoidance of the beam hardening artifact possible. In our study, the difference between mean HU and Hct ranged from -3.1 to 12.8 with a mean of 4.39 and SD of 3.4. Seven patients (5.7%, 5 females, 2 males) had a difference above 1 between mean HU and Hct levels. One of two male patients had underlying liver cirrhosis that presented with variceal bleeding and the other presented with traumatic abdominal bleeding. However, none of the five B 32 Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January 213
6 The Effect of Hgb and Hct Level on Dural Sinus Density sistent with the absence of anemia. The relationship between thoracic UECT and anemia has been described in other reports Those studies reported a threshold of 35 HU, similar to the report by Fanous, et al. 12 that suggested SSS attenuation was an indicator of anemia. We could know the importance of quantitative assessment in the case of Fig. 7. The dural sinuses that grossely showed hyperattenuation and so was suspected DST, finally normal hyperdense sinus without thrombosis on CTV. The hyperattenuation of dural sinuses (51 HU) caused by high Hgb level (15.7 g/dl) of the patient. In the case of Fig. 8, we thought that the dural sinus density on UECT may reflect a recent change of Hgb and Hct status to some degree although cannot reflect active bleeding. This study has some limitations. First, this is a retrospective study, so clinical information was obtained from chart review and the electronic in-hospital database of clinical records without real time data about hydration or medication. Second, the ROIs were measured by a single neuroradiologist for consistency, so inter-observer variability in ROI measurement was not calculated. Third, DST underdiagnosed by neurologist and subacute or chronic DST not showing high density on UECT can be included in this study. In conclusion, dural sinus density on UECT is closely related to Hgb and Hct levels. Therefore, Hgb or Hct level can be used to determine whether the dural sinus density is within the normal range or pathologic conditions such as venous thrombosis, polycythemia vera or severe anemia. Quantitative assessment of the dural sinuses is easy and less time-consuming work in clinical practice without additional radiation exposure, therefore, when grossly hypodense or hyperdense dural sinuses are observed on UECT, radiologists should measure dural sinus attenuation and check Hgb or Hct levels. REFERENCES 1. Linn J, Pfefferkorn T, Ivanicova K, Müller-Schunk S, Hartz S, Wiesmann M, et al. Noncontrast CT in deep cerebral venous thrombosis and sinus thrombosis: comparison of its diagnostic value for both entities. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29;3: Bogousslavsky J, Pierre P. Ischemic stroke in patients under age 45. Neurol Clin 1992;1: Linn J, Ertl-Wagner B, Seelos KC, Strupp M, Reiser M, Brück- mann H, et al. Diagnostic value of multidetector-row CT angiography in the evaluation of thrombosis of the cerebral venous sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27;28: Tehindrazanarivelo AD, Bousser MG. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and cerebral dural sinus thrombosis. Am J Med 1994;97: Leker RR, Steiner I. Features of dural sinus thrombosis simulating pseudotumor cerebri. Eur J Neurol 1999;6: Renowden S. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Eur Radiol 24;14: Ferro JM, Canhão P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F; ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 24;35: Sidani CA, Ballourah W, El Dassouki M, Muwakkit S, Dabbous I, Dahoui H, et al. Venous sinus thrombosis leading to stroke in a patient with sickle cell disease on hydroxyurea and high hemoglobin levels: treatment with thrombolysis. Am J Hematol 28;83: Wendling LR. Intracranial venous sinus thrombosis: diagnosis suggested by computed tomography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1978;13: Patronas NJ, Duda EE, Mirfakhraee M, Wollmann RL. Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis diagnosed by computed tomography. Surg Neurol 1981;15: Virapongse C, Cazenave C, Quisling R, Sarwar M, Hunter S. The empty delta sign: frequency and significance in 76 cases of dural sinus thrombosis. Radiology 1987;162: Fanous R, Leung A, Karlik S. Quantitative assessment of the superior sagittal sinus on unenhanced computed tomography. Eur J Radiol 21;75: Osborn AG, Anderson RE, Wing SD. The false falx sign. Radiology 198;134: Black DF, Rad AE, Gray LA, Campeau NG, Kallmes DF. Cerebral venous sinus density on noncontrast CT correlates with hematocrit. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 211;32: Morita S, Ueno E, Masukawa A, Suzuki K, Machida H, Fujimura M. Hyperattenuating signs at unenhanced CT indicating acute vascular disease. Radiographics 21;3: New PF, Aronow S. Attenuation measurements of whole blood and blood fractions in computed tomography. Radiology 1976; 121(3 Pt. 1): Swensen SJ, McLeod RA, Stephens DH. CT of extracranial hemorrhage and hematomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1984;143: Collins AJ, Gillespie S, Kelly BE. Can computed tomography identify patients with anaemia? Ulster Med J 21;7: Doppman JL, Rienmuller R, Lissner J. The visualized interventricular septum on cardiac computed tomography: a clue to the presence of severe anemia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1981;5: Foster M, Nolan RL, Lam M. Prediction of anemia on unenhanced computed tomography of the thorax. Can Assoc Radiol J 23;54: Title RS, Harper K, Nelson E, Evans T, Tello R. Observer performance in assessing anemia on thoracic CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 25;185: Yonsei Med J Volume 54 Number 1 January
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign
 Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
 Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of
 L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis
 Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 4(2): 284-289, 2009 2009, INSInet Publication The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 1 Mohamed Abdel
Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 4(2): 284-289, 2009 2009, INSInet Publication The Role of Multidetector CT Venography in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 1 Mohamed Abdel
Thrombotic occlusions of the cerebral veins and sinuses occur
 Published February 12, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1451 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J. Linn T. Pfefferkorn K. Ivanicova S. Müller-Schunk S. Hartz M. Wiesmann M. Dichgans H. Brückmann Noncontrast CT in Deep Cerebral Venous
Published February 12, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1451 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J. Linn T. Pfefferkorn K. Ivanicova S. Müller-Schunk S. Hartz M. Wiesmann M. Dichgans H. Brückmann Noncontrast CT in Deep Cerebral Venous
Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:787 791, May 2004 Case Report Multisection CT Venography of the Dural Sinuses and Cerebral Veins by Using Matched Mask Bone Elimination Charles B. L. M. Majoie, Marcel van Straten,
Case Post traumatic cerebral venous thrombosis
 Case 12382 Post traumatic cerebral venous thrombosis AMMOR H Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2015, Jan. 20 Patient: 16 year(s), male Authors' Institution Hôpital Moulay El Hassan Ben El. Mehdi. Laayoune.
Case 12382 Post traumatic cerebral venous thrombosis AMMOR H Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2015, Jan. 20 Patient: 16 year(s), male Authors' Institution Hôpital Moulay El Hassan Ben El. Mehdi. Laayoune.
It has been demonstrated that postmortem MDCT, or virtual
 Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Cortical vein thrombosis in adult patients of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis correlates with poor outcome and brain lesions: a retrospective study
 Liang et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:219 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0995-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cortical vein thrombosis in adult patients of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis correlates with poor outcome
Liang et al. BMC Neurology (2017) 17:219 DOI 10.1186/s12883-017-0995-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cortical vein thrombosis in adult patients of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis correlates with poor outcome
Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients
 Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients Poster No.: C-2616 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: H. F.Termes, J. Puig, J. Daunis-i-Estadella,
Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients Poster No.: C-2616 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: H. F.Termes, J. Puig, J. Daunis-i-Estadella,
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Sinus Venous Thrombosis
 Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
Research Article Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis, a Nonenhanced CT Diagnosis?
 Radiology Research and Practice Volume 215, Article ID 581437, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/581437 Research Article Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis, a Nonenhanced CT Diagnosis? Ali Alsafi, Amish
Radiology Research and Practice Volume 215, Article ID 581437, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/581437 Research Article Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis, a Nonenhanced CT Diagnosis? Ali Alsafi, Amish
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1
 Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
1998 Plenary Session: Imaging Symposium
 1998 Plenary Session: Imaging Symposium LEARNING OBJECTIVE Understand the characteristic imaging findings of acute cerebral infarction and dural sinus thrombosis and be familiar with the current best imaging
1998 Plenary Session: Imaging Symposium LEARNING OBJECTIVE Understand the characteristic imaging findings of acute cerebral infarction and dural sinus thrombosis and be familiar with the current best imaging
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
Hemorrhagic infarction due to transverse sinus thrombosis mimicking cerebral abscesses
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 2 Hemorrhagic infarction due to transverse sinus thrombosis mimicking cerebral abscesses N Barua, M Bradley, N Patel Citation N Barua, M Bradley,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 5 Number 2 Hemorrhagic infarction due to transverse sinus thrombosis mimicking cerebral abscesses N Barua, M Bradley, N Patel Citation N Barua, M Bradley,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Correlation of Computed Tomography findings with Glassgow Coma Scale in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2014, Vol-10, No-2 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE To correlate Computed Tomography (CT) findings with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) in patients with acute traumatic brain injury
Etiology, clinical profile in cortical venous thrombosis
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Pazare AR et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Oct;5(5):xxx-xxx http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183365
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Pazare AR et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Oct;5(5):xxx-xxx http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20183365
Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Dural sinus thrombosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound
 https://doi.org/10.15441/ceem.17.237 Dural sinus thrombosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound Laura T. Director, David C. Mackenzie Department of Emergency Medicine, Maine Medical Center, Portland,
https://doi.org/10.15441/ceem.17.237 Dural sinus thrombosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound Laura T. Director, David C. Mackenzie Department of Emergency Medicine, Maine Medical Center, Portland,
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Case Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer
 Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Case 12305 Acute ascending thoracic aortic rupture due to penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer Lopes Dias J, Costa NV, Leal C, Alves P, Bilhim T Section: Chest Imaging Published: 2014, Dec. 19 Patient: 68
Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.2.RD10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Role of Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Accidents. Rishikant Sinha 1, Ahmad Rizwan Karim 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Evaluation of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis by CT, MRI and MR Venography
 16 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 65 November 2017 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis by CT, MRI and MR Venography Pratibha Issar 1, Sirasapalli Chinna 2,
16 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 65 November 2017 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis by CT, MRI and MR Venography Pratibha Issar 1, Sirasapalli Chinna 2,
THE INNOCUOUS HEADACHE THAT TURNED SINISTER
 CHAPTER 54 THE INNOCUOUS HEADACHE THAT TURNED SINISTER K. RAVISHANKAR, MD Case History A 42-year-old businessman was seen in our Headache Clinic with complaints of near-daily, continuous head pain for
CHAPTER 54 THE INNOCUOUS HEADACHE THAT TURNED SINISTER K. RAVISHANKAR, MD Case History A 42-year-old businessman was seen in our Headache Clinic with complaints of near-daily, continuous head pain for
Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Child with headache and otomastoiditis. Diagnosis Dural venous thrombosis secondary to mastoiditis Discussion The cerebral
Transverse Dural Sinus Thrombosis Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Child with headache and otomastoiditis. Diagnosis Dural venous thrombosis secondary to mastoiditis Discussion The cerebral
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
The cortical contrast accumulation from brain computed tomography after endovascular treatment predicts symptomatic hemorrhage
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The cortical contrast accumulation from brain computed tomography after endovascular treatment predicts symptomatic hemorrhage J.-M. Kim a, K.-Y. Park a, W. J. Lee b, J. S. Byun b, J.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The cortical contrast accumulation from brain computed tomography after endovascular treatment predicts symptomatic hemorrhage J.-M. Kim a, K.-Y. Park a, W. J. Lee b, J. S. Byun b, J.
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Potential Mimic of Primary Traumatic Brain Injury in Infants
 Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective Krasnokutsky Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Infants Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective Michael V. Krasnokutsky 1 Krasnokutsky MV Keywords: abusive head injury,
Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective Krasnokutsky Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Infants Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective Michael V. Krasnokutsky 1 Krasnokutsky MV Keywords: abusive head injury,
Role of MRI in Evaluation of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 6 Ver. 11 (June. 2018), PP 06-12 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in Evaluation of Cerebral
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 6 Ver. 11 (June. 2018), PP 06-12 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in Evaluation of Cerebral
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA
 Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Michael Horowitz, MD Pittsburgh, PA Introduction Cervical Artery Dissection occurs by a rupture within the arterial wall leading to an intra-mural Hematoma. A possible consequence is an acute occlusion
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM)
 Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) Clinical Profile and Radiological
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) Clinical Profile and Radiological
Internal Carotid Artery Dissection
 May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
May 2011 Internal Carotid Artery Dissection Carolyn April, HMS IV Agenda Presentation of a clinical case Discussion of the clinical features of ICA dissection Discussion of the imaging modalities used
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Intrasinus Thrombolysis by Mechanical and Urokinase for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis : A Case Report
 122 Intrasinus Thrombolysis by Mechanical and Urokinase for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis : A Case Report Wen-Sou Lin 1, Hung-Wen Kao 2, Chun-Jen Hsueh 2, Chun-An Cheng 3 Abstract- Purpose: Cerebral
122 Intrasinus Thrombolysis by Mechanical and Urokinase for Severe Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis : A Case Report Wen-Sou Lin 1, Hung-Wen Kao 2, Chun-Jen Hsueh 2, Chun-An Cheng 3 Abstract- Purpose: Cerebral
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy. John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
 Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
 Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes
 Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 12/18/08 REVISED DATE: 12/17/09, 03/17/11, 05/19/11, 05/24/12, 05/23/13, 05/22/14
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CT (COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY) PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies
 Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies Michael N. Patlas, MD, FRCPC (1), Christine O. Menias, MD (2), Douglas S. Katz, MD, FACR (3), Ania Z. Kielar, MD, FRCPC (4), Alla M. Rozenblit, MD (5), Jorge
Traumatic and Non Traumatic Adrenal Emergencies Michael N. Patlas, MD, FRCPC (1), Christine O. Menias, MD (2), Douglas S. Katz, MD, FACR (3), Ania Z. Kielar, MD, FRCPC (4), Alla M. Rozenblit, MD (5), Jorge
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Overview
 Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
Overview Tutorial Script 1 Script for the Virtual Stroke Lab Tutorial Overview http://www.ilstu.edu Background and Vocabulary This podcast provides an overview of The Virtual Stroke Lab, a free virtual
Background. Recommendations for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
 for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association An Scientific Statement from the Stroke Council, American Heart Association and American Stroke Association
for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association An Scientific Statement from the Stroke Council, American Heart Association and American Stroke Association
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Disclosure. + Outline. What is a stroke? Role of imaging in stroke Ischemic stroke Venous infarct Current topics
 + Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 + Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Thank you
+ Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 + Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Thank you
Role of magnetic resonance venography in evaluation of cerebral veins and sinuses occlusion
 Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 29 34 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of magnetic resonance venography in
Alexandria Journal of Medicine (2012) 48, 29 34 Alexandria University Faculty of Medicine Alexandria Journal of Medicine www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of magnetic resonance venography in
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents
 Research Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents Acta Radiologica Open 7(10) 1 6! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2018 Article reuse guidelines:
Research Discrepancies in interpretation of night-time emergency computed tomography scans by radiology residents Acta Radiologica Open 7(10) 1 6! The Foundation Acta Radiologica 2018 Article reuse guidelines:
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CEREBRAL VENOUS SINUS THROMBOSIS: A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 220 EST FRIN MEDIL JOURNL May 2010 East frican Medical Journal Vol. 87 No. 5 May 2010 ERERL VENOUS SINUS THROMOSIS: REPORT OF TWO SES. K. Onyambu, Mh, MMed (Diag. Radiol), Lecturer, Department of Diagnostic
220 EST FRIN MEDIL JOURNL May 2010 East frican Medical Journal Vol. 87 No. 5 May 2010 ERERL VENOUS SINUS THROMOSIS: REPORT OF TWO SES. K. Onyambu, Mh, MMed (Diag. Radiol), Lecturer, Department of Diagnostic
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
 WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE
 CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry:
 Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry: Influence of Low Dose CT Technique 1 Tae Gyu Lee, M.D. 2, Myung Jin Chung, M.D., Sung Bum Cho, M.D. 2, Jae Min Cho, M.D., Seog Joon Kim, M.D. 2, Sang Hyun Baik,
Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry: Influence of Low Dose CT Technique 1 Tae Gyu Lee, M.D. 2, Myung Jin Chung, M.D., Sung Bum Cho, M.D. 2, Jae Min Cho, M.D., Seog Joon Kim, M.D. 2, Sang Hyun Baik,
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Scientific Exhibit. Authors: D. Takenaka, Y. Ohno, Y. Onishi, K. Matsumoto, T.
 The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH. Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015
 TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015 IN CASE YOU MISSED THE REFERENCE HEADACHES IN THE ED Account for approximately 2% of ED visits 1% of these are due to SAH Approximately
TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015 IN CASE YOU MISSED THE REFERENCE HEADACHES IN THE ED Account for approximately 2% of ED visits 1% of these are due to SAH Approximately
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Improving the diagnostic quality of CT venography - a question of timing gone wrong?
 Improving the diagnostic quality of CT venography - a question of timing gone wrong? Poster No.: C-0432 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. Al-Chalabi, K. Mankad, H. S. CHANDRASHEKAR,
Improving the diagnostic quality of CT venography - a question of timing gone wrong? Poster No.: C-0432 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. Al-Chalabi, K. Mankad, H. S. CHANDRASHEKAR,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke
 Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Place for Interventional Radiology in Acute Stroke Dr Lakmalie Paranahewa MBBS, MD(Radiology), FRCR Consultant Interventional Radiologist Asiri Group of Hospitals Objectives Imaging in Stroke Neurovascular
Digital tomosynthesis (DT) has been well described as a
 Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Etiology, clinical manifestation and radiological findings in cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Journal of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Research, 2012, Vol 6, No 2, 105-110 www.jpccr.eu Etiology, clinical manifestation and radiological findings in cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Journal of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Research, 2012, Vol 6, No 2, 105-110 www.jpccr.eu Etiology, clinical manifestation and radiological findings in cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
 Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Prevalence of venous sinus stenosis in Pseudotumor cerebri(ptc) using digital subtraction angiography (DSA) Dr.Mohamed hamdy ibrahim MBBC,MSc,MD, PhD Neurology Degree Kings lake university (USA). Fellow
Case Report Delay in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous and Sinus Thrombosis: Successful Use of Mechanical Thrombectomy and Thrombolysis
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 815618, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/815618 Case Report Delay in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous and Sinus Thrombosis: Successful Use of Mechanical Thrombectomy
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2011, Article ID 815618, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/815618 Case Report Delay in Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous and Sinus Thrombosis: Successful Use of Mechanical Thrombectomy
l' ".'"` va" Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation
 136 -. i 'sit'' -k tz#. / e, = r + -e l' ".'"` va" "t 'hua th ;] fteqhiv.r'" ' Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation in the region of the
136 -. i 'sit'' -k tz#. / e, = r + -e l' ".'"` va" "t 'hua th ;] fteqhiv.r'" ' Fig. 1 Patient 1. Precontrast computed tomographic scans demonstrating areas of increased attenuation in the region of the
CASE PRESENTATION. Key Words: cerebral venous thrombosis, internal jugular vein stenosis, thrombolysis, stenting (Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2005;21:527 31)
 Treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL VENOUS THROMBOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH BILATERAL INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN STENOSIS USING DIRECT THROMBOLYSIS AND STENTING: A CASE REPORT
Treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL VENOUS THROMBOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH BILATERAL INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN STENOSIS USING DIRECT THROMBOLYSIS AND STENTING: A CASE REPORT
