Patient Positioning in Neurosurgery and Principles of Making a Craniotomy. Presenter: Dr. Shashank Ramdurg
|
|
|
- Ashlyn Watkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Patient Positioning in Neurosurgery and Principles of Making a Craniotomy Presenter: Dr. Shashank Ramdurg
3 Introduction Patient positioning critical and vital Control of bleeding and ventilation Sir Victor Horsley in 1906 used fork rest of professor Frazier Head rest an extension attached to the operating table Horsley and Krause also proposed the use of lateral position for posterior fossa surgeries
4 Schede in 1905 used sitting position with patient leaning far forward de Martel in 1913 used sitting position and took credit for its routine use in posterior fossa surgeries He introduced a special chair and head fixation holder Theoretical advantage of lowering ICP and venous bleeding with risk of syncope and the inability to disarrange the draping from this position Bailey
5 The correct position
6 In early years trial and error Today though standardized, not absolute Factors associated: 1. Age 2. Site and nature of lesion 3. Head position in relation to heart 4. Position of anesthesiologist/ nurse 5. Microscope and other imaging equipment Pediatric patients present a different set of considerations Some operations have more than one acceptable position
7 Supine
8 Indications Most of the cranial procedures Anterior cervical spine Anterior approaches to the lumbar spine Carotid endarterctomies
9 Upper extremities- adducted Knees flexed- sciatic nerve injury Compressive stocking sequential compression foot board Head : 0-45 degrees Neck rotation> 45 degrees-raise shoulder Head beyond table Head rest: horse shoe, cupped, three or four pronged head fixation Head elevation: reverse trendlenburg, flex table
10
11 Positioning Extreme turning of head causes: vertebral compression brainstem ischemia jugular compression raised ICP, brain swelling an bleeding Pressure on the ulnar nerve least in supine position Prielipp et al ulnar nerve pressure. Influence of arm position and relationship to somatosensory evoked potential. Anesthesiology: 91: : 1999 Avoid prolonged pressures, stretching Pin sites not on sinus regions, with at least one dependant
12 Lateral position
13 Indications Temporal craniotomies Skull base procedures Posterior fossa explorations Lateral approaches to the cervical spine Trans thoracic and retroperitoneal approaches to the thoracic and lumbar spine Extremely obese or kyphotic patients Unilateral herniated discs offending side up Lumboperitoneal, syringoperitoneal shunts
14 Patients trunk support: tapes, brace, straps hand in hanging or ventral position Pillow positioned between legs Three point fixation Dependant extremity -axillary artery -brachial plexus injury Shoulder/ elbow abducted and flexed respectively resting on a pillow or padded board Horse shoe rest: axillary role Operating table flexed, kidney rest Dependant leg flexed: avoid pressure -fibular head and peroneal nerve
15 Positioning Dependant portion outstretched in front of patient Upper arm on a pillow or air plane arm rest, or along the upper torso with shoulder taped park bench position This position advocated by Dr. Cone Gilbert RGB et al: specific intracranial operations. In anesthesia for neurosurgery; 1966,
16 Prone position
17 Indications Posterior fossa surgeries Sub occipital regions Posterior approaches to the spine
18
19
20 Technique Femoral, distal pulses checked Genitalia should lie free Extremes of head rotation and neck extension to be avoided In cases cord compromise patient may be placed in halo frame before turning him
21 Kneeling position Advantage: IVC pressure lowest in kneeling position Disadvantages: More time to position Mechanical injuries Difficulty in changing curvature Hypotension Rarely: DVT Pulmonary embolism Renal failure Post operative pain
22 Concorde position Variant of prone position Occipital trans-tentorial, supra cerebellar infratentorial approach Head higher than heart Three point fixation Variant of prone position Less venous embolism fatigue Complications as in prone Head flexed with extension of thoraco-lumbar region
23 Sitting position
24 Indications Posterior fossa Cervical cord Sub temporal approaches
25
26 Somato sensory monitoring Monitoring: Doppler, TEE, CVP, fraction excretion of nitrogen capnography, continuous capnography, per-cutaneous oxygen measurement
27 Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages: Midline lesions Low ICP Improved venous drainage Drainage of blood and CSF Unobstructed view of patients face Less cerebellar retraction Complications: air embolism, hypotension, postoperative tension pneumocephalus, sub dural hematoma, quadriplegia and discomfort in upper extremities
28 Other complications Both brain and spinal cord at increased risk of cerebral ischemia in the presence of mass lesions Ernst PS et al intracranial and spinal cord hemodynamics in the sitting position in dogs in the presence and absence of ICP: Anesthesia analgesia: 1990 Precautions: echocardiography, CVP, slow positioning, antigravity suit inflated with air Other rare complications: supra tentorial hematoma, cerebellar hemorrhages, peripheral nerve palsies, traumatic elbow dislocations
29 Three quarter prone
30 Indications AKA semi prone/ lateral oblique Parieto occipital regions Posterior fossa/ CP angle Pineal and vermian region Advantage: comfortable for the surgeon with less risk for embolism, Less retraction
31 Brachial plexus Supine in semi sitting/ semi fowler s position Head turned to opposite side Ipsilateral arm patients side, abducted 50 deg, arm rest Place roll beneath medial aspect of scapula
32 Trans sphenoidal procedures Supine horse shoe rest, c arm fluoroscopy, head tilt of degrees 10 degree head elevation with indwelling LP drain Banerji AK et al: trans nasal approach to pituitary adenomas. Neurol india: 34: 183: 1986
33 Complications Position Supine Prone Complications excessive head rotation, pressure sores, alopecia pressure sores, vascular compromise, brachial plexus injuries, stretch injuries, blindness, embolism, anesthetic problems Concorde Three quarter prone Lateral Awake same same brachial plexus injuries, stretch injuries, pressure palsies aspiration, asphyxiation, pressure palsies
34 Sitting vs prone position Sitting Prone Advantages: Low ICP face Improved venous drainage Drainage of blood and CSF Unobstructed view of patients Less cerebellar retraction Complications: air embolism(30-60%), hypotension, postoperative tension pneumocephalus, sub dural hematoma, quadriplegia and discomfort in upper extremities Easy to position Good access to lesion Comfortable Less complications pressure sores, vascular compromise, brachial plexus injuries, stretch injuries, blindness, embolism (<5%), anesthetic problems
35 Craniotomy principles
36 Skin flaps historical perspective
37 Skin flaps Neolithic period in 2000 B.C Trepanations made followed by scrapings of the skull till holes 19 th century trephines 1889 Wagner first osteoplastic bone flap Gigli saw for craniotomy Obalinski in 1897 Electric and gas powered high speed drills
38 Anatomic and neurovascular considerations 5 layers of scalp: Skin Subcutaneous tissue Galea loose areolar tissue periosteum
39 Nasion Bregma Lambda Inion Pterion: Middle meningeal artery Asterion: Transverse sigmoid junction Land marks
40 Nerves Fronto temporal branch: anterior branch middle branch posterior branch Middle division: 1 cm anterior to superficial temporal artery, subgaleal pad of fat dissect between superficial and deep layers of superficial temporalis fascia
41 Blood supply Superficial temporal artery Occipital artery Posterior auricular artery Supra orbital and trochlear vessels
42 Planning Position of lesion Position of important structures Contingency plan for enlarging incision Obtain adequate closure
43 Principles General principals: 1. surgical exposure of the lesion 2. neuro vascular supply 3. cosmetic effect Types: Random pattern Based on named vessel Length not > 1.5 times base Integrity of major vascular flap to be maintained Incision in hair containing region No crossed incisions
44 Principles Skin incised with galea Pressure over the scalp Periosteum raised with scalp or separately Raney s clips, bipolar, Dandy s clamps Adequate retraction Inner surface protected with moistened gauze Roller gauze Dissect in interfascial fat which is encountered in 4 cm of orbital rim
45 Bicoronal/ Souttar flaps
46 Bicoronal/ Souttar flaps Large exposures of anterior cranial fossa and sella Fronto temporal lesions and cranial base Superior to zygomatic arch, 1 cm anterior to tragus extends over the bregma to the corresponding site on the opposite side Reflect up to orbit rim Supraorbital/ trochlear vessels
47 Frontal flap Exposes anterior frontal lobe Begins along coronal suture and curves anteriorly along the midline preferably ending at hair line
48 Temporal flap Anterior temporal lobe and sub temporal access Based on zygoma Goes behind the ear Extends anteriorly just behind the superior temporal line to the hair line
49 Fronto temporal flap Used for most pterional craniotomies Combines frontal and temporal skin flaps Extends from zygoma to 1 2 cm off the frontal midline following a curve behind the natural hair line Temporalis muscle either dissected or reflected as a separate layer In the later instance a cuff is left superiorly so as to suture it
50 Question mark skin flap Cranial trauma Exposure to whole hemisphere Based on zygoma Blood supply from superior temporal and supra orbital vessels Curves around 3.5 cm posterior to external auditory meatus Anterior limb extends to hair line
51 Horse shoe skin flap Expose any portion of cerebral convexity Inverted U shaped with base directed towards vascular supply Subtemporal exposure: anterior limb 1 cm anterior to the tragus For anterior transcallosal approaches: over coronal suture
52 Mitre skin flap Mitre hats worn by bishops Occipital lobe, posterior falx and superior tentorial surface Inion to vertex: vertical limb Upper limb then falls over posterior parietal region towards the ear Blood supply from the occipital artery
53 Linear and curvilinear incisions Limited exposures Simplicity E.g..: MLSOC RMSOC Hockey stick incisions Linear incisions for temporal lobe and sub temporal access
54 Principles of craniotomy Preoperative review of patient Preparation of scalp Positioning of patient on the table Scalp toilet Marking of the incision Draping
55 Types of craniotomies Flap craniotomy Trephine craniotomy Flap craniotomy: Osteoplastic Free bone flap
56 Bone flaps Most direct access to target For cerebral convexity directly centered over the lesion Skull base lesions should be at the cranial base Number of burr holes varies Separation of underlying dura Beveling effect
57 If dura is lacerated during cutting, saw should be turned of and removed backwards via entrance hole Air cells opened: remove the mucosa pack with betadine soaked spongstan pack with bone wax cover it up with vascularized tissue
58 Proposed bony cuts over the sinuses should be done lastvascularity adherence Cut sinus can be sewn/ tamponade Bony bleeds stopped with bone wax Penfield s retractors to separate dura Epidural tacking sutures to control epidural bleeding before opening dura Others don t in order to protect cortical blood vessels with an intervening brain spoon Tailor to avoid dural venous channels
59 Opening of Dura mater Manually palpate the dura Dura opened as straight, curved or flap like incisions Flaps based towards sinuses Opened with sharp hook and knife Incision further opened with dural scissors Placement of cottonoid along the intended incision Suitable cuff of dura around the bone for suturing later
60 Closure Closure in layers Check for BP valsalva maneuver Hitch suture Water tight but not tension Bone flap replacement Skin closed in two layers
61 Frontal/ Bifrontal bone flaps Skin incisions: frontal, hockey stick, three quarters souttar Suitable for frontal lobe, sub frontal approaches to anterior skull base, and trans cortical access to ventricles Burr holes: key point, anterior midline just above skull base, multiple holes placed close together at midline Avoid entering orbit If orbit breached: bipolar cautery and close with bone wax Last burr hole place posterior to key burr hole
62 An extended frontal or bi frontal craniotomies for exposure of sella, anterior cranial base Supine with head extended for these Holes placed on either sides of sagittal sinus and intervening bone is removed with roneguers or drill Either removed as single piece or conversion of frontal flap to bi frontal flap Combining a frontal flap with pterional flap
63 Goals of surgery dictate the craniotomy Bilateral orbital craniotomies may be added to minimize frontal lobe retraction Dural openings for a unilateral frontal craniotomy usually consist of flap reflected towards sagittal sinus For bi frontal access transverse incision will suffice Superior sagittal sinus will have to be ligated on both sides
64 Fronto temporal (pterional) bone flap Popularized by Yasargil Most useful for aneurysms of anterior circulation, basilar top, also tumors of retro orbital, parasellar and subfrontal areas Usually performed through right side Supine position with head end elevated to 30 degrees and rotated by the same to opposite side Skin incision through standard fronto temporal ski incisions
65 Temporalis muscle dissected or reflected Bone flap centered over the pterion Key burr hole, frontal burrhole, posterio burr hole, last burr hole just above the zygoma Further bone may be removed from the inferior temporal squama To improve vision, drill the sphenoid ridge Dural flap based on the orbit
66 Addition of orbito zygomatic craniotomy will allow for a more lower and anterior approach Suited for para sellar, inter peduncular lesions Pterional+ anterior temporal craniotomy= upper basilar aneurysm
67 Krause during all operations upon the brain, care must be exercised to avoid undue pressure on the thorax and abdomen which might interfere with respirations. Top of the table must be arranged to allow change of position operating room should be warm while operating on the cerebrum shoulders and thorax too be elevated to little less than 45 degrees. On operating on the side or posterior aspect of the head it is best to posture the patient on his side and allow his head to extend beyond the edge of the table. In all instances the assistant holds the head firmly with the fingers opposed to the jaws and cheeks. Surgery of the brain and spinal cord on personal experiences
68 Cushing In his report to chief surgeon: ordinary pillows and sand bags are desirable. In order to get proper elevation of the head so that it can stand free of the surrounding, one or two sandbags, measuring 8*8*3 inches covered with rubber sheet, will be found convenient. A secure arrangement to prevent there slipping in the course of prolonged operation is essential He also used a horseshoe head rest to allow for access to patients head and neck in the prone position
69 Awake craniotomies
70 CP angle tumors Supine Lateral Three quarters prone Prone Sitting
71 Indications and Technique Mapping speech, motor sensory cortex Intractable epilepsy Tumors in eloquent areas Stereo tactic biopsies, DBS, chronic SDH, thermocoagulation of brain lesions
72 Technique Simple head rest or pin fixation may be used Maintenance of airway paramount importance Possibility of venous air embolism Monitoring of ETCO2 by nasal catheter Appropriate padding Catheterization
73 Nerves Occipital branch of posterior auricular nerve superior nuchal line no deficits Supra orbital nerve notch In 8 53% of patients foramenopen it up Supra trochlear nerve Temporal scalp supplied by auricular temporal branch of mandibular nerve Greater occipital nerve supplies upto vertex
74 Thank you
5. COMMON APPROACHES. Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2.
 5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH
 5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
5.5. RETROSIGMOID APPROACH The retrosigmoid approach provides good access to the cerebellopontine angle. It is by far simpler and faster with much less need for bone removal than other more extensive lateral
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
The SCALP. Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery
 COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the
 Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery
 Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery The Review Committee has made the following changes to the CPT code mappings: The following previously untracked CPT codes
Case Log Mapping Update: April 2018 Review Committee for Neurological Surgery The Review Committee has made the following changes to the CPT code mappings: The following previously untracked CPT codes
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Pathologies, Procedures and Room Set-Up
 Pathologies, Procedures and Room Set-Up Degenerative diseases - arthritis, osteoperosis Most common cause for neck pain and back pain Herniated disks or bulging disk Commonly occur at L4-5, L5-S1 Spinal
Pathologies, Procedures and Room Set-Up Degenerative diseases - arthritis, osteoperosis Most common cause for neck pain and back pain Herniated disks or bulging disk Commonly occur at L4-5, L5-S1 Spinal
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
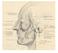 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
Transfemoral Amputation Preop This 26 year old male sustained a gunshot wound to the left thigh. He was treated emergently with revascularization and fasciotomies. He was transferred to our regional trauma
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
OHSU Neurological Surgery Education. Neurosurgical Basics. Copyright Oregon Health & Science University Department of Neurological Surgery
 OHSU Neurological Surgery Education Neurosurgical Basics Chapter 1 Basic Principles: Cranial Three-Point Head Fixation Proper and safe application of a three-point rigid cranial fixation device provides
OHSU Neurological Surgery Education Neurosurgical Basics Chapter 1 Basic Principles: Cranial Three-Point Head Fixation Proper and safe application of a three-point rigid cranial fixation device provides
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop. Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP
 OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
OMT Without An OMT Table Workshop Dennis Dowling, DO FAAO Ann Habenicht, DO FAAO FACOFP Cervical Somatic Dysfunction (C5 SR RR) - Seated 1. Patient position: seated. 2. Physician position: standing facing
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition
 Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Knee Disarticulation Amputation
 Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures
 9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
4The head basic anatomy and physiology
 Hene_Ch04.qxd 8/30/04 2:47 AM Page 108 108 THE HEAD BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 4The head basic anatomy and physiology The scalp Anatomists describe the SCALP as having five layers: Skin, Subcutaneous
Hene_Ch04.qxd 8/30/04 2:47 AM Page 108 108 THE HEAD BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 4The head basic anatomy and physiology The scalp Anatomists describe the SCALP as having five layers: Skin, Subcutaneous
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Regional Anesthesia. Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology
 Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
Regional Anesthesia Fatiş Altındaş Dept. of Anesthesiology Regional anesthesia - Definition Renders a specific area of the body, e.g. foot, arm, lower extremities insensating to stimulus of surgery or
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
In Situ Fusion L5 to S1
 Chapter 2 In Situ Fusion L5 to S1 Stuart L. Weinstein, M.D. DIAGNOSIS Spondylolisthesis COMMON INDICATIONS n In symptomatic low grade Spondylolysis and listhesis of less than 30 % n Pain unresponsive to
Chapter 2 In Situ Fusion L5 to S1 Stuart L. Weinstein, M.D. DIAGNOSIS Spondylolisthesis COMMON INDICATIONS n In symptomatic low grade Spondylolysis and listhesis of less than 30 % n Pain unresponsive to
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017
 OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
We describe some of the conceptual nuances and
 Suprasellar Meningiomas Ivan Ciric, M.D., Sami Rosenblatt, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare, Evanston Hospital, Northwestern University Medical School, Evanston, Illinois
Suprasellar Meningiomas Ivan Ciric, M.D., Sami Rosenblatt, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare, Evanston Hospital, Northwestern University Medical School, Evanston, Illinois
Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience
 80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
F OR several years we have used a linear. Limited exposure in cerebral surgery. Technical note. trephine aid drill. Technique
 Technical note DONALD H. WILSON, M.D. Section o/ Neurosurgery, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Hanover, New Hampshire ~' A limited exposure is possible, and perhaps preferable, for most cerebral surgery.
Technical note DONALD H. WILSON, M.D. Section o/ Neurosurgery, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Hanover, New Hampshire ~' A limited exposure is possible, and perhaps preferable, for most cerebral surgery.
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Module 1, Stomatology
 Module 1, Stomatology Department of operative surgery and topographic anatomy Test questions for self training for passing Module 1, writing part Paractical questions with images The patient has been scheduled
Module 1, Stomatology Department of operative surgery and topographic anatomy Test questions for self training for passing Module 1, writing part Paractical questions with images The patient has been scheduled
SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
 Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
IOM at University of. Training for physicians. art of IOM. neurologic. injury during surgery. surgery on by IOM. that rate is.
 Topics covered: Overview of science and art of IOM IOM at University of Michigan Hospital and Health Systems What is the purpose of Intraoperative monitoring? Training for physicians Overview of science
Topics covered: Overview of science and art of IOM IOM at University of Michigan Hospital and Health Systems What is the purpose of Intraoperative monitoring? Training for physicians Overview of science
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY
 NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
NIDCD NATIONAL TEMPORAL BONE, HEARING AND BALANCE PATHOLOGY RESOURCE REGISTRY Guidelines for Removal of Temporal Bones for Pathological Study The temporal bones should be removed as soon as possible. If
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Wunzi Strapping Applications
 Wunzi Strapping Applications In addition to the basic garment set(s), all Wunzi product configurations now include limb cuff and strapping options that attending therapists can use to achieve higher levels
Wunzi Strapping Applications In addition to the basic garment set(s), all Wunzi product configurations now include limb cuff and strapping options that attending therapists can use to achieve higher levels
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. Surgical approaches Review
 Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. Surgical approaches Review Hirotoshi Sano Dept. of Neurosurgery Fujita Health University Introduction There are two main types of approaches for anterior communicating
Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms. Surgical approaches Review Hirotoshi Sano Dept. of Neurosurgery Fujita Health University Introduction There are two main types of approaches for anterior communicating
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
The Upper Limb III. The Brachial Plexus. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip. Joseph H. Dimon
 Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
