Inverted papilloma of the maxillary sinus and endoscopic endonasal medial maxillectomy
|
|
|
- Evangeline James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 9, January - March 2013 ORIGINAL STUDY Inverted papilloma of the maxillary sinus and endoscopic endonasal medial maxillectomy Philippe Eloy ENT&HNS Department, Cliniques Universitaires de Mont-Godinne, Université Catholique de Louvain, Yvoir, Belgium ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. A medial maxillectomy (MM) consists of a complete resection of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus. Traditionally, the surgery is performed via an open approach. With more familiarity and expertise in endoscopic sinus surgery, the endonasal approach is feasible. OBJECTIVE. To expose the surgical technique and report the results of endonasal endoscopic medial maxillectomy in a series of 9 consecutive patients with inverted papilloma involving the maxillary sinus. MATERIAL AND METHODS. From August 2006 to December 2012, 9 patients with an inverted papilloma involving the maxillary sinus have been operated on with this procedure. There were 8 men and 1 female. The mean age was 64.5 years old (range: 43-83). In 4 cases, it was a primary surgery, whereas in the other 5 cases it was a revision surgery. In the latter group, 2 patients underwent a mini Caldwell Luc procedure and the others underwent an ethmoidectomy associated with a middle antrostomy (n=2) or an inferior meatotomy (n=1). The delay between the previous surgery and the present surgery varies from 3 years to 30 years. Results. All the patients are free of disease at the time of writing with a mean follow-up of 37 months (range: 5 77). This has been confirmed by a nasal endoscopy and CT scans. In one case, we have had a posterior bleeding requiring a sphenopalatine artery ligation. There were no other major per- or postoperative complications. Patients suffered from crusting for at least 3 months postoperatively, necessitating daily nasal douches. One patient is still complaining of intermittent epiphora when he is exposed to wind. 2 patients had an opacification of the ipsilateral frontal sinus. In one case, a reopening of the frontal ostium was performed. Conclusion. Endoscopic medial maxillectomy can be successfully performed for the resection of inverting papilloma involving the maxillary sinus and/or the intersinonasal wall. Compared to open approaches, this kind of surgery seems to be equally effective, with less postoperative morbidity. An important technical point is to do the anterior osteotomy in front of the nasolacrimal duct in order to expose the prelacrimal recess that is typically an area for recurrence. Exact determination of the tumor attachment during the surgery is another key point for success. Long follow-up is required, as the inverted papilloma can be a very slow growing tumor, particularly when it is in the maxillary sinus. Keywords: inverted papilloma, maxillary sinus, endonasal medial maxillectomy, extended endoscopic surgery, radical surgery INTRODUCTION Medial maxillectomy (MM) consists of a complete resection of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus. The limits are inferiorly the nasal floor, superiorly the ethmoid sinus, anteriorly the anterior maxillary wall, including the nasolacrimal duct, and posteriorly the vertical plate of the palatine bone 1. Figure 1 illustrates the procedure on a cadaver. Typically, a complete ethmoidectomy is also performed during the same surgical procedure tailored to the type and extension of the disease. The indications for such an extended surgery are 2 : 1. Benign tumors (e.g. inverted papilloma) with involvement of the lateral nasal wall, the ostiomeatal complex and the medial maxillary wall. 2. Recurrent inverted papillomas, confined to the Corresponding author: Philippe Eloy, MD, Professor, ENT&HNS Department, Cliniques Universitaires de Mont-Godinne, Université Catholique de Louvain, Avenue Thérasse, 1, 5530, Yvoir, Belgium. philippe.eloy@uclouvain.be
2 12 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 9, January - March 2013 Figure 1 Medial maxillectomy cadaver demonstration - yellow structure: nasolacrimal duct; red structure: sphenopalatine artery; blue line: limits of the resection. maxillary sinus, which cannot be completely removed with a more conservative approach. 3. Malignant tumors confined to the medial wall of the maxillary sinus. 4. Access to the lateral or posterior walls of the maxillary sinus or to the infratemporal fossa. An illustrative indication is the removal of a juvenile angiofibroma extended to the infratemporal fossa. In the past, the procedure was performed via an open approach (a Rouge-Denker, a lateral rhinotomy or a midfacial degloving approach) 3,4. Since the late 1990s, thanks to a greater familiarity and expertise in endoscopic endonasal surgery, the endonasal approach was proposed as an alternative to the open approach 2,5-13. The authors report herein their 6 years experience with the endonasal endoscopic medial maxillectomy (EMM), describe the surgical technique and comment their results of surgery of inverted papilloma involving the maxillary sinus. MATERIAL AND METHODS 9 patients were operated on between August 2006 and December 2012 (Table 1). There were 8 men and 1 female. The mean age of this cohort of patients was 64.5 years old (range: 43-83). There was a primary surgery in 4 cases, and a revision surgery in the 5 other cases. In the latter group, 2 patients previously underwent a mini Caldwell-Luc and 3 patients an ethmoidectomy associated with a middle antrostomy (n=2) or an inferior antrostomy (n=1). All the patients had a complete preoperative assess- Table 1 No. Patient Age (years) Type of surgery 1 st surgery Last surgery Follow-up(months) 1 V.M. 58 Primary surgery Left Ethmoidectomy & MM 77 2 T.D. 58 Primary surgery 1996 Standard FESS X Revision: Left MM 57 3 C.M. 43 Primary surgery 2006 Mini Caldwell-Luc 2008 Revision: Right ethmoidectomy + MM 53 4 H.F. 59 Primary surgery 1999 FESS - antrostomy 2008 Revision: Left MM 52 5 M.J. 83 Primary surgery 2004 FESS + bimeatotomy 2009 Revision: Left MM 36 6 M.J.C. 64 Primary surgery Mini Caldwell Luc in the 80s Left ethmoidectomy & MM 25 7 S.K.A 58 Primary surgery - Left ethmoidectomy & MM 22 8 C.E. 76 Primary surgery - Left ethmoidectomy & MM 9 9 P.F. 83 Primary surgery - Right ethmoidectomy & MM 5
3 Eloy Inverted papilloma of the maxillary sinus and endoscopic endonasal medial maxillectomy 13 ment including a biopsy, a computed tomography of the sinuses and a magnetic resonance imaging. In any case, there was an infiltration of either the lateral or anterior walls of the maxillary sinus. No patient had a malignant transformation concomitant to the inverted papilloma (IP). Surgical technique The surgery was conducted under general anaesthesia, the patient in a recumbent position. Neurosurgical cottonoids soaked in a solution of adrenalin (1mg of adrenalin mixed into 40 ml of saline) were placed in the nasal cavities for at least 10 minutes before the surgery. The lateral nasal wall was infiltrated with a solution of Lidocain 1% plus adrenalin (1/10000). The procedure started with a dacryocystorhinostomy performed in a high position, as described by PJ Wormald in The lacrimal pathway was cut at the junction of the lacrimal sac and the nasolacrimal duct. Then the tumor was removed from the middle meatus and the upper part of the maxillary sinus with conventional Blakesley forceps. The sphenopalatine artery was then coagulated with a bipolar cautery. The inferior turbinate was completely removed with a scissor and the microdebrider (XPS - Medtronic tricut blade). Afterwards, osteotomies were done with a hammer and a chisel. One was performed very anteriorly at the level of the maxillary crest, in front of the nasolacrimal eminence; the other was performed inferiorly and horizontally, parallel to the junction of the nasal floor and the medial wall of the maxillary sinus. With such a wide access and using angulated telescopes (45 and 70 telescopes) and forceps, the IP and the sinus mucosa adjacent to its implantation were completely removed. The dissection was made in a subperiosteal plane. Drilling of the site of attachment was done with a diamond drill, transnasally. A sublabial approach through the canine fossa was never used in this cohort of patients. Frozen sections were done to ensure that all the tissue margins were free of tumor. A bicanalicular silicone tube was put in place for 3 months postoperatively and a nasal packing for 2 days. The patient received broad-spectrum antibiotics for 5 days postoperatively. He was informed to clean his nose with nasal douches comprising a saline solution and to put a nasal ointment 3 times a day as long as crusting persists. Postoperative cares under endoscopic guidance with removal of the crusts were done 3 times, postoperatively (day 2, 9 and 21) and later on if crusting was persistent. A computed tomography of the sinuses was ordered 6 months after surgery and after 2 or 3 years. The follow-up consultation was made every 3 months during the first postoperative year, and every 6 months for the next 5 years. RESULTS The mean follow-up period is 37 months (range 5 to 77 months). All the patients are free of disease at the time of writing, based on an endoscopic evaluation and radiologic studies. On the postoperative CT scan, a common finding was a thickening of the soft tissue on either the lateral, inferior or superior walls of the maxillary sinus. 1 patient was complaining of crusting 11 months postoperatively. 1 patient presented an epiphora when he was exposed to the wind. We had one case of posterior bleeding necessitating a coagulation of the sphenopalatine artery. We had no other major complications, particularly no CSF leakage. 2 patients had an opacification of the ipsilateral frontal sinus. In one case, a specific procedure directed to the frontal sinus was performed. The pathological examination of the surgical specimen confirmed that the tissue margins were free of disease in all cases. There was no malignant transformation concomitant to the IP. Figure 2 illustrates one clinical case. DISCUSSIONS A medial maxillectomy (MM) is a radical surgery indicated for the removal of expanding processes involving the maxillary sinus or the intersinonasal wall, which cannot be completely removed with a more conservative procedure. One of the most common indications is surgery for inverted papillomas (IPs) confined to the maxillary sinus. IPs are benign tumors characterized by high recurrence rates, tendency toward multicentricity, a capacity to erode adjacent bones, to extend to the orbit or intracranial cavity, and associated with a risk of malignant transformation in 5% to 15% of the case 4,15. The sole treatment for IPs is surgery. The goal is to achieve a complete resection of the tumor and surrounding mucosa with minimal cosmetic deformities and functional disabilities. In the past, the golden standard was the lateral rhinotomy combined with an open medial maxillectomy 3,4. Even if this approach was highly effective, providing the surgeon an excellent visualization of the tumor attachments and the possibility to extend the approach to adjacent areas (orbit, cranial vault, frontal and contralateral ethmoid sinus), tailored by the tumor extension, the open approach was associated with a significant postoperative morbidity: numbness of the upper lip, hypoesthesia of the cheek and in the area of the trigeminal nerve (V2), lacrimal problems (epiphora and dacryocystitis 16 ). Blindness was also reported 17. With the advances in endonasal endoscopic sur-
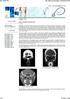
4 14 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 9, January - March 2013 gery, the endonasal approach was proposed as an alternative to the open approach. A complete ethmoidectomy associated with a middle antrostomy and/or a sphenoidotomy was then performed successfully by numerous surgeons for a large number of inverted papillomas. This was well reported in a meta-analysis conducted by Busquet and published in Nevertheless, 2 localizations remain a challenge: the lateral portion of the frontal sinus and the maxillary sinus 19,20. In 2000, in the Belgian ENT journal 19, the authors pointed out that recurrences of IPs were much more frequent in the maxillary sinus than in the ethmoid sinus, when the patients have undergone first an ethmoidectomy and a middle antrostomy. Our series of patients confirmed this assertion, as 3 patients had a recurrence of IP in the maxillary sinus after a complete ethmoidectomy associated with a middle antrostomy (2 cases) and a bimeatotomy (1 case). This can be explained by different factors. The first one is that the surgeon might have confused FESS and ESS. FESS means functional endoscopic sinus surgery. It was first dedicated for the treatment of inflammatory sinonasal lesions. The background of FESS is a maximal preservation of the healthy mucosa. For IPs, the surgery must be radical, consisting of a complete resection of the tumor and the surrounding mucosa 5. Another explanation is that the surgeon underestimated the true extension of the IP within the maxillary sinus, leading to an inadequate (too limited) surgical procedure. At this time, it is important to remind the conclusion of an anatomic study published in 2003 by Sadeghi N 9. The author reported that 64% of the A C B D Figure 2 A: nasal endoscopy inverted papilloma extruding from the middle meatus B: MRI showing a complete involvement of the left maxillary sinus C & D: postoperative CT scans showing a maxillary sinus free of disease.
5 Eloy Inverted papilloma of the maxillary sinus and endoscopic endonasal medial maxillectomy 15 volume of the maxillary cavity is below the lateral attachment of the inferior turbinate on the lateral nasal wall and 10 to 15% of the volume of the maxillary sinus cavity is located in the prelacrimal recess. This anatomic study pointed out that a wide opening is mandatory to have an optimal vision on all the walls and recesses of the maxillary sinus and on the sites of tumor origin and attachments during the surgery 21. A middle antrostomy, even a large one, combined or not with an inferior antrostomy or a mini-caldwell-luc, do not provide an optimal vision on the entire maxillary cavity and so, are certainly not the best option of treatment for IPs extended to the lateral portion of the maxillary sinus or to the intersinonasal wall. As a result of this, the Belgian report recommended to perform a true Caldwell-Luc procedure 19. Nevertheless, when the medial maxillary wall or the inferior turbinate are infiltrated by the IP, a complete resection of the inter - sinonasal wall (Denker procedure) must be done 7-13,21. When the lateral portion of the tumor is not reachable through the endonasal approach, a limited external approach through the canine fossa can be combined with the endonasal approach 7,10. Once more, this limited external approach must allow a complete extirpation of the base of insertion of the IP. When this is not the case, recurrence is possible. 2 patients in this series had been operated on with a limited Caldwell Luc procedure and experienced recurrence some years later. Another important issue is the duration of the follow-up for a patient operated for an IP. As illustrated by our series, recurrence in the maxillary sinus can be symptomatic 10 years after an endonasal conventional surgery. This can be explained by the fact that the maxillary sinus is a large cavity in which the papilloma can grow slowly without clinical symptoms. This is not the case for other localizations such as the ethmoid or the sphenoid sinuses, which are symptomatic sooner and easily visualized by the nasal endoscopy. A very long and close follow-up is therefore mandatory for all patients with an IP. An endoscopy through the surgical opening is mandatory every 6 months for at least 5 years. From this point of view, a medial maxillectomy has the advantage of providing a large and permanent vision in the maxillary sinus, making easier and earlier the detection of recurrences with the nasal endoscopy. The management of the recurrences is still a controversial issue in the literature, taking into account that the behaviour of the tumor may be more aggressive and the association with a squamous cell carcinoma more frequent 5,8,22. Therefore, most authors prefer to do an external approach, whereas others opt for an endonasal approach, with the possibility to combine it with a limited external approach when needed. In our limited number of cases, we used the endonasal approach only. The patient was informed before the surgery of a possible switch to an external approach if necessary. The dissection was done in a subperiosteal plane. All the different walls of the maxillary sinus and the sites of attachment of the IP were clearly visualized using angulated telescopes. The site of implantation of the tumor was meticulously drilled out. We did not find any malignant transformation of the IP or infiltration of the anterior and lateral maxillary walls. Concerning the surgical technique, there are two different ways to do a medial maxillectomy. The first one consists of en bloc resection and the other is a sequential fragmental resection. Based upon Busquet s metaanalysis, there is no statistically significant difference in the recurrent rates between these 2 modalities 18. That is the reason why we preferred to do a sequential resection and a step by step surgical approach. All the procedure was then performed with a permanent visual control and a bloodless surgical field. A crucial technical point is to do the osteotomy very anteriorly, in front of the lacrimal crest, in order to expose the prelacrimal recess, area of possible recurrence. The postoperative morbidity after such an extended surgery is low and far less important compared to the one observed after an external approach. Crusting remains the major problem for a period of minimum 6 months. No change in the voice quality was observed. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, an ENT surgeon dealing with primary or recurrent inverted papilloma involving significantly the maxillary sinus must be able to perform a medial maxillectomy. It is an extended radical surgical procedure that is safe, reproducible and very effective. We recommend doing a step by step procedure, allowing a complete extirpation of the tumor and the sinus mucosa, in a bloodless surgical field, with an optimal exposure and vision of the origin and attachments of the tumor. A sublabial approach can be combined to remove a tumor extension in the anterolateral recess or the anterior maxillary wall. Malignant transformation of IP in the lateral portion of the maxillary sinus is a contraindication for a pure endonasal technique. A precise determination of the origin and site of attachment of the IP intraoperatively is of upmost importance for a successful surgery. Postoperatively, a very close and long follow-up is necessary to detect any recurrence. Copyright. All the authors certify that the manuscript has not been submitted for publication in another journal. We disclose any financial or commercial support that could lead to a conflict of interest.
6 16 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 3, No. 9, January - March 2013 REFERENCES 1. Tanna N., Edwards J.D., Aghdam H., Sadeghi N. - Maxillectomy as the initial oncologic approach to sinonasal neoplasms: the anatomic basis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg., 2007;133(11): Kountakis Stilanos E., Önerci M. - Endoscopic medial maxillectomy. Rhinologic and Sleep Apnea Surgical Techniques, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2007;6: Bielamowicz S., Calcaterra T.C., Watson D. - Inverting papilloma of the head and neck: the UCLA update. Otolaryngol head neck Surg., 1993;109(1): Phillips P.P., Gustafson R.O., Facer G.W. - The clinical behaviour of inverting papilloma of the nose and paranasal sinuses: report of 112 cases and review of the literature. Laryngoscope, 1990;100(5): Myers E.N., Fernau J.L., Johnson J.T., Tabet J.C., Barnes E.L. - Management of inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope., 1990;100: Han J.K., Smith T.L., Loehrl T., Toohill R.J., Smith M.M. - An evolution in the management of sinonasal inverting papilloma. Laryngoscope., 2001;111(8): Wormald P.J., Ooi E., van Hasselt C.A., Nair S. - Endoscopic removal of sinonasal inverted papilloma including medial maxillectomy. Laryngoscope., 2003;113(5): Kraft M., Simmen D., Kaufmann T., Holzmann D. - Long-term results of endonasal sinus surgery in sinonasal papillomas. Laryngoscope., 2003;113(9): Sadeghi N., Al-Dhahri S., Manoukian J.J. - Transnasal endoscopic medial maxillectomy for inverting papilloma. Laryngoscope, 2003;113(4): Tomenzoli D., Castelnuovo P., Pagella F., Berlucchi M., Pianta L., Delù G., Maroldi R., Nicolai P. - Different endoscopic surgical strategies in the management of inverted papilloma of the sinonasal tract: experience with 47 patients. Laryngoscope, 2004;114(2): Krouse J.H. - Evolution in the management of inverted papilloma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg., 2009;140(3): Lane A.P. - The role of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of sinonasal inverted papilloma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg., 2009;17(1): Lawson W., Patel Z.M. - The evolution of management for inverted papilloma: an analysis of 200 cases. Otolaryngol Head neck Surg., 2009;140(3): Tsirbas A., Wormald P.J. - Mechanical endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy with mucosal flaps. Br J Ophthalmol., 2003;87(1): Kaufman M.R., Brandwein M.S., Lawson W. - Sinonasal papillomas: clinicopathologic review of 40 patients with inverted and oncocytc schneiderian papillomas. Laryngoscope., 2002;112(8Pt1): Eloy P., Bachy V., Grulois V., Bertrand B. - Pyocele of the lachrymal sac a late and unusual complication after surgery for a juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Clin Ophthalmol., 2008;2(1): Kalavagunta S., Roy D., Fish B., Jackson S. - Blindness following medial maxillectomy. Rhinology, 2002;40(4): Busquet J.M., Hwang P.H. - Endoscopic resection of sinonasal inverted papilloma: a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg., 2006;134(3): Bertrand B., Eloy P., Jorissen M., et al. - Surgery of inverted papillomas under endoscopic control. Acta Otolaryngol Belg., 2000;542: Mortuaire G., Arzul E., Darras J.A., Chevalier D. - Surgical management of sinonasal inverted papillomas through endoscopic approach. Eur Arch Otolaryngol, 2007;264(12): Sukenik M.A., Casiano R. - Endoscopic medial maxillectomy for inverted papilloma of the paranasal sinuses: value of the intraoperative endocopic examination. Laryngocope, 2000;110: Lee T.J., Huang S.F., Lee L.A., Huang C.C. - Endoscopic surgery for recurrent inverted papilloma. Laryngoscope, 2004;114(1):
Endoscopic medial maxillectomy
 Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology (2010) 21, 111-116 Endoscopic medial maxillectomy Kelly Cunningham, MD, Kevin C. Welch, MD From the Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, Loyola University
Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology (2010) 21, 111-116 Endoscopic medial maxillectomy Kelly Cunningham, MD, Kevin C. Welch, MD From the Department of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, Loyola University
Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases
 Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Original article: Inverted papilloma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a study of 20 cases 1 Dr. Vijay Kumar Kalra, 2 Dr. Samar Pal Singh Yadav, 3 Dr. Swati 1Assistant Professor, 2 Senior Professor
Endoscopic Resection of Anterolateral Maxillary Sinus Inverted Papillomas
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Endoscopic Resection of Anterolateral Maxillary Sinus Inverted Papillomas Nichole R. Dean, DO; Elisa A. Illing,
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Endoscopic Resection of Anterolateral Maxillary Sinus Inverted Papillomas Nichole R. Dean, DO; Elisa A. Illing,
Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Transnasal Endoscopic Medial Maxillary Sinus Wall Transposition With Preservation of Structures Alice Z.
Intranasal location of lacrimal sac in Thai cadavers
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Toho University, Omori-Nishi, Ota-ku, Tokyo , Japan
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 952923, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/952923 Case Report Endoscopic Modified Medial Maxillectomy for Resection of an Inverted Papilloma Originating
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 952923, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/952923 Case Report Endoscopic Modified Medial Maxillectomy for Resection of an Inverted Papilloma Originating
Exposure techniques in endoscopic skull base surgery: Posterior septectomy, medial maxillectomy, transmaxillary and transpterygoid approach
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 284 288 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE Exposure techniques in endoscopic skull base surgery: Posterior
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 284 288 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE Exposure techniques in endoscopic skull base surgery: Posterior
Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis
 THIEME Original Research 159 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Ponnaiah Thulasidas 1 Venkatraman Vaidyanathan 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head
THIEME Original Research 159 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in Persistent Chronic Maxillary Sinusitis Ponnaiah Thulasidas 1 Venkatraman Vaidyanathan 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology Head
Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting. dacryocystorhinostomy with and
 Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Original Research Article Study of success rates in endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with and without stenting Kirti Ambani 1, Niraj Suri 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Assistant Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL SURGERY FOR RESECTION OF BENIGN SINONASAL TUMORS: EXPERIENCE WITH 107 PATIENTS
 Arch Iranian Med 2006; 9 (3): 244 249 Original Article ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL SURGERY FOR RESECTION OF BENIGN SINONASAL TUMORS: EXPERIENCE WITH 107 PATIENTS Mohammad-Hossein Baradaranfar MD, Payman Dabirmoghaddam
Arch Iranian Med 2006; 9 (3): 244 249 Original Article ENDOSCOPIC ENDONASAL SURGERY FOR RESECTION OF BENIGN SINONASAL TUMORS: EXPERIENCE WITH 107 PATIENTS Mohammad-Hossein Baradaranfar MD, Payman Dabirmoghaddam
The modified endoscopic pre-lacrimal approach: how I do it
 Specialty Techniques Page 1 of 6 The modified endoscopic pre-lacrimal approach: how I do it Leslie T. Koh 1, Rataphol C. Dhepnorrarat 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Changi General
Specialty Techniques Page 1 of 6 The modified endoscopic pre-lacrimal approach: how I do it Leslie T. Koh 1, Rataphol C. Dhepnorrarat 2 1 Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Changi General
BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas
 Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(1):26-30. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas Ana Maria Almeida de Sousa 1, Alcioni Boldrini Vicenti 2, José Speck Filho
Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;78(1):26-30. ORIGINAL ARTICLE BJORL Retrospective analysis of 26 cases of inverted nasal papillomas Ana Maria Almeida de Sousa 1, Alcioni Boldrini Vicenti 2, José Speck Filho
Endoscopic management of maxillary sinus inverted papilloma attachment sites to minimize disease recurrence
 Wu et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0271-1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Endoscopic management of maxillary sinus inverted papilloma
Wu et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0271-1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Endoscopic management of maxillary sinus inverted papilloma
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in persistent chronic maxillary. sinusitis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 3 2014 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in persistent chronic maxillary sinusitis Thulasidas P ¹ Venkatraman V ² ¹ Sinus and Nose Hospital, Chennai, India,
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 3 2014 Role of Modified Endoscopic Medial Maxillectomy in persistent chronic maxillary sinusitis Thulasidas P ¹ Venkatraman V ² ¹ Sinus and Nose Hospital, Chennai, India,
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions. Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology
 Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Reasons for Failure and Surgical Revisions Stil Kountakis, MD, PhD Professor and Chief, Division of Rhinology Medical College of Georgia of Georgia Regents University Department of Otolaryngology / Head
Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K.
 05 Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K. Gananathan Introduction...75 General Principles...76 Tips and Tricks in Ventral
05 Tips and Tricks in Ventral Skull Base Dissection Narayanan Janakiram, Dharambir S. Sethi, Onkar K. Deshmukh, and Arvindh K. Gananathan Introduction...75 General Principles...76 Tips and Tricks in Ventral
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
KEY WORDS prelacrimal recess; endoscopic sinus surgery; schwannoma; pterygopalatine fossa; infratemporal fossa; surgical technique
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1068 1073, 2016 The intranasal endoscopic removal of schwannoma of the pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossae via the prelacrimal recess approach Bing Zhou, D, 1 Qian
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1068 1073, 2016 The intranasal endoscopic removal of schwannoma of the pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossae via the prelacrimal recess approach Bing Zhou, D, 1 Qian
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery
 Reda kamel, Cadaveric dissection 1 Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery Cadaver Dissection Guide For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Cairo University Egypt Reda Kamel Professor of Rhinology Cairo University
Reda kamel, Cadaveric dissection 1 Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery Cadaver Dissection Guide For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Cairo University Egypt Reda Kamel Professor of Rhinology Cairo University
PROBLEM RECOMMENDATION
 PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
Considerations in Oncologic Resection (mandible & maxilla)
 Considerations in Oncologic Resection (mandible & maxilla) Jeeve Kanagalingam MA, FRCS (ORL-HNS), FAMS Consultant ENT / Head & Neck Surgeon Tan Tock Seng Hospital Assistant Professor Lee Kong Chian School
Considerations in Oncologic Resection (mandible & maxilla) Jeeve Kanagalingam MA, FRCS (ORL-HNS), FAMS Consultant ENT / Head & Neck Surgeon Tan Tock Seng Hospital Assistant Professor Lee Kong Chian School
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
Surgical Risk Factors for Recurrence of Inverted Papilloma
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Surgical Risk Factors for Recurrence of Inverted Papilloma David Y. Healy Jr., MD, CDR, MC, USN; Nipun Chhabra,
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Surgical Risk Factors for Recurrence of Inverted Papilloma David Y. Healy Jr., MD, CDR, MC, USN; Nipun Chhabra,
Juvenile Angiofibroma
 Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING
 RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
Original Article Modified transnanal endoscopic maxillectomy: a novel surgery style of maxillary malignant tumor
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):11361-11366 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024060 Original Article Modified transnanal endoscopic maxillectomy: a novel surgery style of maxillary malignant tumor Yonghua
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):11361-11366 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024060 Original Article Modified transnanal endoscopic maxillectomy: a novel surgery style of maxillary malignant tumor Yonghua
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013
 FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
FRONTAL SINUPLASTY P R E P A R E D A N D P R E S E N T E D B Y : D R. Y A H Y A F A G E E H R 4 16/ 12/ 2013 ANATOMY: FRONTAL SINUS Not present at birth Starts developing at 4 years Radiographically visualized
Skull Base Volume 12 Month. Patients. Anterior/Midline. Pituitary CSF Leak. Lateral. Craniocervical Junction
 UC SF 2 11/7/2009 Skull Base Surgery in 2009 Ivan El-Sayed MD, FACS Director- Otolaryngology Minimally Invasive Skull Base Surgery Program Department Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of
UC SF 2 11/7/2009 Skull Base Surgery in 2009 Ivan El-Sayed MD, FACS Director- Otolaryngology Minimally Invasive Skull Base Surgery Program Department Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of
Benign Neoplasms of the Nose
 Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Pursuing Wellness Through Teaching, Learning and Healing Benign Neoplasms of the Nose Ivan El Sayed, MD Disclosure Principal Investigator: Grant Support
Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Pursuing Wellness Through Teaching, Learning and Healing Benign Neoplasms of the Nose Ivan El Sayed, MD Disclosure Principal Investigator: Grant Support
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Frontal sinus disease continues to be one of the great
 Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS
 Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent Sinuses in Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
Computed Tomographic Staging and the Fate of the Dependent es in Revision Endoscopic Surgery Neil Bhattacharyya, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objectives: To determine the patterns of disease recurrence in chronic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the Anterior Ethmoid
 Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the nterior Ethmoid Long-term Results ORIGINL RTICLE Toru Kikawada, MD; Masao Fujigaki, MD; Mikino
Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the nterior Ethmoid Long-term Results ORIGINL RTICLE Toru Kikawada, MD; Masao Fujigaki, MD; Mikino
A comprehensive study on complications of endoscopic sinus surgery
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY John M. DelGaudio, MD Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Emory University School
COMPLICATIONS IN ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY John M. DelGaudio, MD Professor and Vice Chair Chief of Rhinology and Sinus Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Emory University School
ROLE OF ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SELECTED MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL NEOPLASMS OF THE NASO-ETHMOIDAL COMPLEX
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SELECTED MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL NEOPLASMS OF THE NASO-ETHMOIDAL COMPLEX Piero Nicolai, MD, 1 Paolo Castelnuovo, MD, 2 Davide Lombardi, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF SELECTED MALIGNANT EPITHELIAL NEOPLASMS OF THE NASO-ETHMOIDAL COMPLEX Piero Nicolai, MD, 1 Paolo Castelnuovo, MD, 2 Davide Lombardi, MD,
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Case Report
 Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses
 14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
The cribriform plate. ethmoid bone. Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths.
 ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
Traditional open surgery for advanced benign nasal tumours in an era of endoscopy: review of 38 cases.
 Traditional open surgery for advanced benign nasal tumours in an era of endoscopy: review of 38 cases. Akeem O Lasisi* and Aderemi A Adeosun Department of Otorhinolaryngology College of Medicine, University
Traditional open surgery for advanced benign nasal tumours in an era of endoscopy: review of 38 cases. Akeem O Lasisi* and Aderemi A Adeosun Department of Otorhinolaryngology College of Medicine, University
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT
 NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
NASAL SEPTUM ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA: A CASE REPORT Shu-Yu Tai, 1 Chen-Yu Chien, 2 Chih-Feng Tai, 2,4 Wen-Rei Kuo, 2,4 Wan-Ting Huang, 3 and Ling-Feng Wang 2,4 Departments of 1 Family Medicine, 2 Otolaryngology
Sinonasal Tumors. Objectives. Objectives. Incidence of Paranasal Sinus Tumors. Demographics of Paranasal Sinus Tumors. Paranasal Sinus Tumors
 Sinonasal Tumors Objectives Incidence and demographics of sinonasal tumors Separating tumors from inflammatory changes Common and notable histologic types of sinonasal tumors Staging of sinonasal tumors
Sinonasal Tumors Objectives Incidence and demographics of sinonasal tumors Separating tumors from inflammatory changes Common and notable histologic types of sinonasal tumors Staging of sinonasal tumors
Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Surgery for Frontal Sinusitis
 Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Surgery for Frontal Sinusitis Ralph Metson, MD; Richard E. Gliklich, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the efficacy of endoscopic surgery for chronic frontal sinusitis.
Clinical Outcome of Endoscopic Surgery for Frontal Sinusitis Ralph Metson, MD; Richard E. Gliklich, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the efficacy of endoscopic surgery for chronic frontal sinusitis.
Total Maxillectomy. A review. Dr T Balasubramanian
 Total Maxillectomy A review Dr T Balasubramanian Maxillectomy a review Introduction: The concept of maxillectomy was first described by Lazars in 1826. After this description it took nearly three years
Total Maxillectomy A review Dr T Balasubramanian Maxillectomy a review Introduction: The concept of maxillectomy was first described by Lazars in 1826. After this description it took nearly three years
ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY has. Endoscopic Transnasal Approach to the Pterygopalatine Fossa ORIGINAL ARTICLE. John M. DelGaudio, MD
 Endoscopic Transnasal Approach to the Pterygopalatine Fossa John. DelGaudio, D ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To describe an endoscopic transnasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF). Design: Case
Endoscopic Transnasal Approach to the Pterygopalatine Fossa John. DelGaudio, D ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To describe an endoscopic transnasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF). Design: Case
By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F2
 20.03.2017 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F2 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Literature Review Conclusion Introduction Topical delivery to the paranasal
20.03.2017 By: Abdulrahman A. Al-Humaizi Rhinology Fellow, F2 Objectives Introduction Materials and methods Results Discussion Literature Review Conclusion Introduction Topical delivery to the paranasal
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
M. PIEMONTE SOC O.R.L. Az. Ospedaliero-Universitaria S.M.M., Udine
 M. PIEMONTE SOC O.R.L. Az. Ospedaliero-Universitaria S.M.M., Udine LIMITS OF ENDOSCOPIC RESECTIONS IN ANTERIOR SKULL BASE TUMORS Limiti delle resezioni endoscopiche nei tumori della rinobase anteriore
M. PIEMONTE SOC O.R.L. Az. Ospedaliero-Universitaria S.M.M., Udine LIMITS OF ENDOSCOPIC RESECTIONS IN ANTERIOR SKULL BASE TUMORS Limiti delle resezioni endoscopiche nei tumori della rinobase anteriore
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 st International Advanced Sinus Dissection Course, 30 th - 31 st March 2017, Berlin. in Berlin
 1 st International Advanced Sinus Dissection Course, 30 th - 31 st March 2017, Berlin in Berlin Dear colleagues, We are very happy to invite you to the 1 st International Advanced Sinus Dissection Course
1 st International Advanced Sinus Dissection Course, 30 th - 31 st March 2017, Berlin in Berlin Dear colleagues, We are very happy to invite you to the 1 st International Advanced Sinus Dissection Course
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Intranasal Localization of the Lacrimal Sac
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Intranasal Localization of the Lacrimal Sac Mustafa Orhan, MD; Canan Y. Saylam, MD; Raşit Midilli, MD Objective: To optimize the approach to the lacrimal sac during intranasal dacryocystorhinostomy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Intranasal Localization of the Lacrimal Sac Mustafa Orhan, MD; Canan Y. Saylam, MD; Raşit Midilli, MD Objective: To optimize the approach to the lacrimal sac during intranasal dacryocystorhinostomy.
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF NASAL AND. Frontier Steven D. Schaefer, MD, FACS
 PRINCIPLES OF ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF NASAL AND SKULL : A New Frontier Steven D. Schaefer, MD, FACS Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology New York keye and dear Infirmary New York Medical College
PRINCIPLES OF ENDOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF NASAL AND SKULL : A New Frontier Steven D. Schaefer, MD, FACS Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology New York keye and dear Infirmary New York Medical College
January th, 2012
 Basic Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Residents & Novices and 1st International Advanced Course in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery & Skull Base Surgery January 17-20 th, 2012 January 17 th, 2012: Basic Endoscopic
Basic Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Residents & Novices and 1st International Advanced Course in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery & Skull Base Surgery January 17-20 th, 2012 January 17 th, 2012: Basic Endoscopic
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
The surgical approach to the sphenoid sinus continues to
 A comparison of two sphenoidotomy approaches using a novel computerized tomography grading system Heitham Gheriani, F.R.C.S.C., F.R.C.S.I., David Flamer, B.Sc., Trent Orton, M.D., Brad Mechor, F.R.C.S.C.,
A comparison of two sphenoidotomy approaches using a novel computerized tomography grading system Heitham Gheriani, F.R.C.S.C., F.R.C.S.I., David Flamer, B.Sc., Trent Orton, M.D., Brad Mechor, F.R.C.S.C.,
ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE
 30 th International Course on ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE Ghent (Belgium) 29 August-1 September 2018 INTERNATIONAL FACULTY Claus Bachert (Ghent, Belgium) Philippe Gevaert (Ghent,
30 th International Course on ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES & SKULL BASE Ghent (Belgium) 29 August-1 September 2018 INTERNATIONAL FACULTY Claus Bachert (Ghent, Belgium) Philippe Gevaert (Ghent,
Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2007) 137, 492-496 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma Nilvano A. Andrade, PhD, José Antonio Pinto, MD, Mônica
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2007) 137, 492-496 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma Nilvano A. Andrade, PhD, José Antonio Pinto, MD, Mônica
Research Article Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal Treatment of Primary Intracranial Tumors within the Paranasal Sinuses
 ISRN Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 129780, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129780 Research Article Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal Treatment of Primary Intracranial Tumors within
ISRN Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 129780, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129780 Research Article Expanded Endoscopic Endonasal Treatment of Primary Intracranial Tumors within
14.25 UBC SINUS & SKULL BASE COURSE 2018 STANDARD COURSE : AUG (FRI-SAT) SKULL BASE COURSE : AUG 12 (SUN) ubccpd.ca CESEI CENTRE VANCOUVER, BC
 14.25 MOC SECTION 1 UBC SINUS & SKULL BASE COURSE 2018 STANDARD COURSE : AUG 10 11 (FRI-SAT) SKULL BASE COURSE : AUG 12 (SUN) CESEI CENTRE VANCOUVER, BC WHO SHOULD ATTEND Surgeons Advanced Trainees Fellows
14.25 MOC SECTION 1 UBC SINUS & SKULL BASE COURSE 2018 STANDARD COURSE : AUG 10 11 (FRI-SAT) SKULL BASE COURSE : AUG 12 (SUN) CESEI CENTRE VANCOUVER, BC WHO SHOULD ATTEND Surgeons Advanced Trainees Fellows
Chapter Six. 1 of 6 11/3/2008 2:21 PM.
 1 of 6 11/3/2008 2:21 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Six FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 6 11/3/2008 2:21 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Six FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgical Treatment of Sinus Disease Description of Procedure or Service Sinusitis refers to infection or inflammation of the sinuses, which are small openings in the bones of the
Corporate Medical Policy Surgical Treatment of Sinus Disease Description of Procedure or Service Sinusitis refers to infection or inflammation of the sinuses, which are small openings in the bones of the
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision
 THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
POST-DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN RHINOLOGY
 POST-DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN RHINOLOGY DURATION OF THE COURSE : 2 YEARS Aim of the Course To provide a broad experience in surgical and evaluative Rhinology. Background: Rhinology is an area of
POST-DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN RHINOLOGY DURATION OF THE COURSE : 2 YEARS Aim of the Course To provide a broad experience in surgical and evaluative Rhinology. Background: Rhinology is an area of
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in the Pediatric Age Group
 Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in the Pediatric Age Group Scott C. Manning Endoscopic Sinus Surgical Preparation and Technique Surgical Risks Every decision for therapy involves a risk-benefit analysis and a
Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in the Pediatric Age Group Scott C. Manning Endoscopic Sinus Surgical Preparation and Technique Surgical Risks Every decision for therapy involves a risk-benefit analysis and a
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A STUDY OF CALDWELL-LUC APPROACH IN VARIOUS ETIOLOGIES Minutha R 1, Sriram Nathan 2
 A STUDY OF CALDWELL-LUC APPROACH IN VARIOUS ETIOLOGIES Minutha R 1, Sriram Nathan 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Minutha R, Sriram Nathan. A study of Caldwell-luc approach in various etiologies. Journal of
A STUDY OF CALDWELL-LUC APPROACH IN VARIOUS ETIOLOGIES Minutha R 1, Sriram Nathan 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Minutha R, Sriram Nathan. A study of Caldwell-luc approach in various etiologies. Journal of
Richard J. Harvey 26 Wall of the Maxillary Sinus Christos C. Georgalas and Wytske J. Fokkens 27 Pterygopalatine Space...
 Contents............................................................ viii Preface......................................................................... xi Acknowledgments.............................................................
Contents............................................................ viii Preface......................................................................... xi Acknowledgments.............................................................
TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION
 TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION CC-BY-NC 3.0 Johan Fagan Total maxillectomy refers to surgical resection of the entire maxilla. Resection includes the floor and medial wall of the orbit and the
TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION CC-BY-NC 3.0 Johan Fagan Total maxillectomy refers to surgical resection of the entire maxilla. Resection includes the floor and medial wall of the orbit and the
The advent of high-resolution computerized tomography
 An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
Research Article Length and Geometric Patterns of the Greater Palatine Canal Observed in Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 International Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 292753, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2010/292753 Research Article Length and Geometric Patterns of the Greater Palatine Canal Observed in Cone Beam Computed Tomography
International Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 292753, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2010/292753 Research Article Length and Geometric Patterns of the Greater Palatine Canal Observed in Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN: 2250-0359 Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report *SUNIL JANARDHANAN *KULOTHUNGAN *VINOD FELIX * KERF ENT HOSPITAL TRIVANDRUM KERALA Abstract: Schwannomas of the nasal
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN: 2250-0359 Schwannoma of the nasal septum-a case report *SUNIL JANARDHANAN *KULOTHUNGAN *VINOD FELIX * KERF ENT HOSPITAL TRIVANDRUM KERALA Abstract: Schwannomas of the nasal
Dacryocystorhinostomy Stent Insertion in Initial Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy
 SV Manjunatha Rao, MM Rajshekar Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1284 Dacryocystorhinostomy Stent Insertion in Initial Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy 1 SV Manjunatha Rao, 2 MM Rajshekar ABSTRACT
SV Manjunatha Rao, MM Rajshekar Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1284 Dacryocystorhinostomy Stent Insertion in Initial Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy 1 SV Manjunatha Rao, 2 MM Rajshekar ABSTRACT
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Non-endoscopic Mechanical Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy
 Surgical Technique Non-endoscopic Mechanical Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy Mohammad Etezad Razavi 1, MD; Morteza Noorollahian 2, MD; Alireza Eslampoor 1, MD 1 Khatam-al-Anbia Eye Research Center, Mashhad
Surgical Technique Non-endoscopic Mechanical Endonasal Dacryocystorhinostomy Mohammad Etezad Razavi 1, MD; Morteza Noorollahian 2, MD; Alireza Eslampoor 1, MD 1 Khatam-al-Anbia Eye Research Center, Mashhad
Extended Draf IIb Procedures in the Treatment of Frontal Sinus Pathology
 Original rticle linical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 8, No. 1: 34-38, March 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.1.34 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Extended raf IIb Procedures in the
Original rticle linical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 8, No. 1: 34-38, March 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.1.34 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Extended raf IIb Procedures in the
Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Page 1 of 9 Today News Reference Education Log In Register Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Author: Ankit Patel, MD; Chief Editor: Arlen D Meyers, MD, MBA more... Updated: Apr 30, 2012 Overview Introduction
Page 1 of 9 Today News Reference Education Log In Register Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Author: Ankit Patel, MD; Chief Editor: Arlen D Meyers, MD, MBA more... Updated: Apr 30, 2012 Overview Introduction
What is head and neck cancer? How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated? How is head and neck cancer treated?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
FESS imaging - the role of MDCT
 FESS imaging - the role of MDCT Poster No.: C-0179 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Plascak, K. Makaruha, B. Klasic, L. Kavur, V. Vidjak; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Image verification,
FESS imaging - the role of MDCT Poster No.: C-0179 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Plascak, K. Makaruha, B. Klasic, L. Kavur, V. Vidjak; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Image verification,
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
SINUS SURGERY. Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS
 SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
SINUS SURGERY Dr Zenia Chow MBBS(hons), FRACS Facial Plastic & Reconstructive Surgeon Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgeon ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY/FESS What are sinuses The sinuses are a connected system
Assessing symptoms of empty nose syndrome in patients following sinonasal and anterior skull base resection
 Research Article Page 1 of 5 Assessing symptoms of empty nose syndrome in patients following sinonasal and anterior skull base resection Joel Hardman 1,2, Julie Ahn 3, Arjuna Nirmalananda 2 1 University
Research Article Page 1 of 5 Assessing symptoms of empty nose syndrome in patients following sinonasal and anterior skull base resection Joel Hardman 1,2, Julie Ahn 3, Arjuna Nirmalananda 2 1 University
Nasal Polyposis. DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore
 Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Challenges in the Management of Inverted Papilloma: A Review of 72 Revision Cases
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Challenges in the Management of Inverted Papilloma: A Review of 72 Revision Cases Gwijde F. J. P. M. Adriaensen,
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Challenges in the Management of Inverted Papilloma: A Review of 72 Revision Cases Gwijde F. J. P. M. Adriaensen,
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
 This Page Intentionally Left Blank ISBN: 0-8247-0743-5 Marcel Dekker, Inc., and the author make no warranty with regard to the accompanying software, its accuracy, or its suitability for any purpose other
This Page Intentionally Left Blank ISBN: 0-8247-0743-5 Marcel Dekker, Inc., and the author make no warranty with regard to the accompanying software, its accuracy, or its suitability for any purpose other
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY ENDOSCOPIC DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hisham Wasl, Darlene Lubbe Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY ENDOSCOPIC DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR) SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Hisham Wasl, Darlene Lubbe Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical
DOWNLOAD OR READ : THE ENDOSCOPIC APPROACH TO VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMAS AND POSTEROLATERAL SKULL BASE PATHOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : THE ENDOSCOPIC APPROACH TO VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMAS AND POSTEROLATERAL SKULL BASE PATHOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 the endoscopic approach to vestibular schwannomas and posterolateral
DOWNLOAD OR READ : THE ENDOSCOPIC APPROACH TO VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMAS AND POSTEROLATERAL SKULL BASE PATHOLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 the endoscopic approach to vestibular schwannomas and posterolateral
