Original Article Surgical treatment for ruptured dural arteriovenous fistula with large intracranial hematoma
|
|
|
- Sheila Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Surgical treatment for ruptured dural arteriovenous fistula with large intracranial hematoma Xianwang Ye 1*, Haifeng Wang 2,3*, Yi Huang 2,3, Shengjun Zhou 2,3, Xiang Gao 2,3 1 Department of Radiology, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo Hospital, Zhejiang University, Ningbo, Zhejiang , China; 2 Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo Hospital of Zhejiang University, Ningbo, Zhejiang , China; 3 Zhou Liangfu Academician Workstation, Neurosurgery Ningbo Branch of Shanghai Huashan Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang , China. * Equal contributors. Received September 13, 2014; Accepted November 24, 2014; Epub December 15, 2014; Published December 30, 2014 Abstract: The rupture of dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) is a serious complication endangering the lives of patients. It is difficult to treat such ruptured DAVF with large intracranial hematoma since lacking of early diagnostic methods. Meanwhile, there was no consensus of how to surgically treat these patients in early stage. In this study, we tried to use 4D-CTA to diagnose DAVF and guide surgical treatment. Based on the result of 4D-CTA, we attempted to eliminate DAVF at the same time we removed hematoma. The result was encouraging. 7 patients with ruptured DAVF presented as large spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage were included in this research between May, 2010 and August, 2012 in our hospital. 4D-CTA was performed in all cases. All results of 4D-CTA inspections were studied by both neurosurgeon and neuroradiologist. The therapeutic options were evaluated based on the clinical and angiographic results. All fistulas of seven patients were eliminated at the same time the hematoma being evacuated. 4D-CTA was sufficient for detecting and recognizing basic vessel angioarchitecture of DAVF to guide surgical treatment. Main arterial supplies, fistula location and CVDs found during surgery are consistent with the results 4D-CTA. All seven cases achieved completely fistula occlusion in operation without new neurological complication. We favor one stage surgical treatment for ruptured DAVF with large intracranial hemorrhage. 4D-CTA plays an important role in preoperative emergent inspection for its safety, rapidity and accuracy. However, it still needs further and larger investigations to optimize such treatment methods and to find out other potential risks. Keywords: DAVF, 4D-CTA, intracranial hemorrhage, surgical treatment Introduction Dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) is an obstinate cerebral vascular disease [1]. Intracranial hemorrhage, the most dangerous complication of DAVF caused by its rupture in venous ends, would seriously endanger patients lives [2]. So far, there is no consensus of how to deal such patients with huge intracranial hematoma [3]. In this study, 4D-CTA was used as a dynamic image method to diagnose DAVF [4]. One stage resection of DAVF was performed at the same time we made emergent evacuation of intracranial hematoma. Satisfactory outcome was achieved. Methods Patients 7 patients with ruptured DAVF presented as large spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage were included in this research between May, 2010 and August, 2012 in our hospital. Detail information such as hemorrhage location, preoperative condition, fistula location, arterial supply, venous drainage, etc, were summarized in Table 1. The pre-operative conditions of these patients were all in emergent status. After intracranial hemorrhage detected by computed tomography, patients with irregular shape of hematoma, non-basal ganglia hemorrhage, young patients (age below 40), no underlying diseases such as hypertension and/or diabetes were advised to run further inspection due to suspicion of DAVF or other cerebral vascular malformations. Because of their unconscious or restless pre-operative condition, DSA examination was not performed. 4D-CTA as an only screening method was used in such emergent situation. After inspections completed, all results of 4D-CTA were discussed by neurosur-
2 Table 1. Detail information of 7 patients with dural arteriovenous fistula presented as intracranial hemorrhage Patient no. Age/ Sex Hemorrhage location and volume (ml) Pre-operative condition (GCS) Fistula location Arterial supply (4D-CTA) Borden Treatment Angiographic results of review (DSA/4D-CTA) Outcome; follow up (mouth)/kps 1 70/M (R) F; (40) GCS 8 (R) frontal cranial base (L) OA III HE + FR (-)/cure asymptomatic; 12/ /F (L) F; (40) GCS 10 (L) frontal cranial base (L + R) OA III HE + FR (-)/cure asymptomatic; 9/ /M (R) T + O; (40) GCS 8 (R) occipital dural (R) ECA III HE + FR (-)/cure asymptomatic; 8/ /M (R) F; (35) GCS 10 (R) frontal cranial base (R) MMA III HE + FR (-)/cure asymptomatic; 9/ /M (R) P + O; (40) GCS 10 (left paralysis) (R) superior sagittal sinus (L + R) MMA + (L + R) PMA + (L + R) OCA III HE + FR cure/cure left paralysis; 8/ /M (R) F; (40) GCS 8 (R) frontal cranial base (R) OA III HE + FR (-)/cure asymptomatic; 10/ /M (L) T + P; (40) GCS 5 (right paralysis) (-) = no result of this inspection. (L) middle cranial base (L) MMA II HE + FR (-)/cure right paralysis; 31/ Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
3 Figure 1. Case 1 had intracranial hemorrhage in right frontal lobe (A). Before surgical treatment, lateral projection of 4D-CTA showed frontal fistula (hollow arrow) on the base of anterior fossa base with arterial feeder supplied by OA (white triangle) (B). Review of 4D-CTA after surgical treatment in the same projection, abnormal blood flow was disappeared (C). geons and neuroradiologists. The therapeutic options were evaluated based on the clinical and angiographic results. 4D-CTA examination It was performed by Aquilion ONE multi-detector CT scanner of Toshiba Medical Systems, which equips mm detector rows covering 16 cm of volume per rotation sufficient to cover whole brains. The manner of performing imaging was followed by the procedures below. First, injection of 60 ml intravenous infusion of nonionic contrast medium, with 20 ml of saline, was followed by a dynamic acquisition sequence (22 dynamic volumes each protocol, 80 kvp, 120 mas) with a gantry rotation (one mask volume, 80 kvp, 300 mas) speed of 1 rotation per second. After subtracting the mask volume from the dynamic volumes, a total of 7,040 (22 dynamic volume 320 slice) images (temporal resolution 3 frames per second, spatial resolution ) were stored as 22 DICOM file. Finally, by using these files, the standard scanner software generated time-resolved (arterial to venous) MIPs at different viewing 5246 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
4 angles. These general manners and steps have been previously described and accepted [5, 6]. Surgical treatment All the patients underwent surgical treatment. After dural disclosed, partial hematoma was removed to lower the intracranial pressure. The area around the hematoma was explored carefully. In non-sinus-type fistula, the operative strategy consisted of sole interruption of arterialized leptomeningeal vein either by coagulation or clipping, shortly after the dural entry/exit point. No attempt was made to coagulate meningeal feeding arteries or to excise the arterialized dural. In sinus-type fistula, both the meningeal feeding arteries and the arterialized leptomeningeal vein were cut. Results All patients had 4D-CTA examinations, there were 4 fistulas in frontal cranial base, 1 in middle cranial base, 1 in superior sagittal sinus and 1 in occipital. The hematoma evacuation and fistula elimination were performed at the same time. The fistulas were all confirmed by the intra-operative finding. For case 5 with superior sagittal sinus DAVF, the supplying arteries from occipital and middle meningeal cerebral artery branches were cut, and the cortical venous reflux from the fistula was disconnected. For the other cases, only arterialized leptomeningeal veins were cut. There was no mortality or new neurological deficit. Follow-ups All seven cases had post-operative follow-up, mean months. The follow-up examinations included DSA and/or 4D-CTA. There was no presence of initial fistula re-opening. There was no new neurological complication. Case 1 This 70-year-old man had a sudden headache and quickly lost his consciousness, he was in coma with GCS 8 when he was sent to our hospital. An emergent CT scan showed a right frontal hematoma (Figure 1). An additional 4D-CTA revealed right frontal base DAVF. During operation, the fistula was found in the anterior frontal fossa base. It was cut. Post-operative review of 4D-CTA in the same projection identified the complete occlusion of the fistula following coagulation of the leptomeningeal vein. Case 2 A 55-year-old male felt headache and had paralysis in his left limbs. He was in a restless condition with GCS 10 at admission to hospital. First CT scan proved a hematoma nearly 40 ml in his parietal and occipital lobe (Figure 2). Preoperative 4D-CTA displayed a DAVF with arterial feeders from left anterior, middle meningeal and occipital arteries, which had reflux into superior sagittal sinus though several CVDs. During operation, these arterial supplies and CVDs were cut. Follow-up review by 4D-CTA demonstrated that DAVF had disappeared. Case 3 A 50-year-old male was transported to our hospital due to a mild headache and vomit. Unfortunately, he suddenly got into coma with left pupil dilating and GCS 5. The initial CT scan found a giant hematoma in temporal lobe. Since highly suspicious of cerebral vascular malformation, an emergent 4D-CTA was performed. It demonstrated a left temporal fossa base vascular ectasia and was diagnosed of a DAVF. In operation, a large cortical arterialized vein was found in middle fossa base, and it was cut. During his follow-up by 4D-CTA, no abnormal blood flow was detected (Figure 3). Discussion Dural arteriovenous fistula is abnormal arteriovenous anastomosis occurred between dural arteries and dural veins, cerebral venous sinus and cortical veins, responsible for nearly 10%- 15% [7] of intracranial vascular malformations. The symptoms of DAVF were related to the location of lesion and pattern of venous drainage [8]. Pulsatile tinnitus [9] is a common and benign symptom of non-cavernous sinus DAVF. Regretfully, it has been usually neglected until severe presentations including intracranial hemorrhage and/or non-hemorrhagic neurological deficits have been found [10]. It is difficult to diagnose ruptured DAVF with huge intracranial hematoma. CT and MR imaging are usually predominant in initial radiological evaluation which can only reflect indirect signs of DAVF such as edema and/or dilated 5247 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
5 Figure 2. Case 5 with parietal and occipital hemorrhage (A). Before surgical treatment, 4D-CTA displayed superior sagittal sinus DAVF with the enlarging leptomeningeal vein and fistula (hollow arrow) supplied by middle meningeal and occipital arteries (B). During operation, both arterial supplies and fistula were cut. Follow-up by 4D-CTA and DSA found no abnormal blood flow (C). vessels. Non-contrast CT is used to rule out intracranial hemorrhage or space occupying lesions but unable to make differential diagnosis of vascular pathogenesis. MR imaging is superior to CT in diagnosing vascular malformation. For instance, dilated venous structures, vascular enhancement, and venous hypertension can be demonstrated in high-grade lesions [11]. However, it is hard for CT and MR to make definite diagnosis of DAVF with large hemorrhage. In order to make up precise vascular angioarchitecture and to differentiate DAVF with other vascular malformation, dynamic CTA, MRA or DSA must be considered [12]. For now, the criterion standard for DAVF diagnosis remains DSA [13] despite of its invasion and risks of both silent and symptomatic embolic events [14]. Time-resolved MRA techniques are promising and may be reliable for DAVF screening and surveillance [15]. Reinacher et al [16] had pointed out that DAVF can be correctly graded by time-resolved MRA, which is essential for therapeutic decision-making though small feeders may be overlooked. And it seems especially suitable to ascertain whether fistula has been occluded completely during follow-up Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
6 Figure 3. Case 7 with temporal and parietal hemorrhage was highly suspicious of DAVF rupture (A). 4D-CTA reflected left temporal base fistula (hollow arrow) fed by MMA (B). Diagnosis of DAVF was confirmed by intra-operative findings. During his follow-up by 4D-CTA, no abnormal blood flow was detected (C). But for coma and restless patients with severe intracranial hemorrhage, it is difficult to run time-consumed examinations, such as DSA or MRA carefully. Recently, as the representative of dynamic CTA, 4D-CTA has highlighted its potential value to correctly diagnose AVM [4] and DAVF [5, 17] with full head coverage, less invasiveness and more rapidity. In the previous study of DAVF by Willems et al [18] whose images were independently read by two blinded observers, 10 of 11 cases were full agreement between DSA and 4D-CTA and only one small slow-flow DAVF was missed by 4D-CTA. In Beijer et al [19] cases, the result indicated that 4D-CTA correctly differentiated distinct patterns of venous drainage and made precise classification of Borden type I, II and III, as confirmed by DSA. In our cases, 4D-CTA successfully detected fistulas and CVDs in all patients, which was confirmed by intra-operative findings. It is worth noting that all our cases were in high grade which was more sensitive to CTA. However, CVDs were not shown in every case, which might be caused by the compression of large hematoma. Despite the nonselective nature of 4D-CTA and its lower spatial and temporal resolution compared with DSA, it is able to provide the correct information in high-grade case. We believe 4D-CTA is a very useful method in DAVF examination, especially in emergent situation. Treatment methods of DAVF include interventional treatment, surgery and radiation therapy. There is still no consensus of how to deal patients with huge intracranial hematoma due to DAVF rupture. Interventional treatment by intravenous or arterial route is the main choice to cure DAVF and has satisfactory occlusion rate. But it is less reported to be used in acute patients with huge intracranial hematoma. Houdart et al [20] had indicated that surgical treatment should be applied when space occupying effect of intracranial hematoma exists due to DAVF rupture. There were two different options: only making evacuation of intracranial hematoma, or resecting vascular malformation while cleaning intracranial hematoma. Leaving DAVF intact would put patients in danger of its re-rupture during the rest time. Duffau et al [21] 5249 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
7 reported that CVDs draining to the transverse sinus present a high risk of rupture and re-rupture. Meanwhile, the second operation to eliminate the fistula would be difficult since the adherence of cerebral tissue inheriting from the first operation and containing more complications. One stage treatment of hematoma and DAVF has the advantage of avoiding those potential disasters. Our experience suggested that the early surgical treatment of DAVF was safe and suitable for patients with huge hematoma needing emergent evacuation. For patients with mild hematoma and condition, we prefer elaborate and adequate inspections, for deciding therapeutic strategy, including embolization and/or surgery, even radiation therapy. According to the available reports, surgical treatment for DAVF was mainly applied in lesions in anterior, middle cranial fossa or involving superior sagittal sinus. Our cases are all in these regions. For ruptured-davf involving the transverse sinus, sigmoid sinus and cavernous area which was difficult for microsurgery, staged treatment should be considered. Conclusions Acute rupture is the most serious presentation of cerebral DAVF and carries high morbidity and mortality. 4D-CTA could play an important role in preoperative inspection for emergent cases due to its safety, rapidity and accuracy. Following initial diagnosis with 4D-CTA, we favor one stage surgical treatment for patients with severe intracranial hemorrhage from DAVF rupture. Not only did it make evacuation of hematoma, but also prevented the high risk of re-rupture. It still needs further and larger investigations to optimize such treatment methods and to find out other potential risks. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Xiang Gao or Yi Huang, Department of Neurosurgery, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo Hospital of Zhejiang University, Ningbo, Zhejiang , China. Tel: ; Fax: ; qinyuecui@163.com (XG); huangy102@gmail.com (YH) References [1] Hacein-Bey L, Konstas AA and Pile-Spellman J. Natural history, current concepts, classification, factors impacting endovascular therapy, and pathophysiology of cerebral and spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2014; 121: [2] Peng T, Liu A, Jia J, Jiang C, Li Y, Wu Z and Yang X. Risk factors for dural arteriovenous fistula intracranial hemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci 2014; 21: [3] Novakovic RL, Lazzaro MA, Castonguay AC and Zaidat OO. The diagnosis and management of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurol Clin 2013; 31: [4] Willems PW, Taeshineetanakul P, Schenk B, Brouwer PA, Terbrugge KG and Krings T. The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 2012; 54: [5] Brouwer PA, Bosman T, van Walderveen MA, Krings T, Leroux AA and Willems PW. Dynamic 320-section CT angiography in cranial arteriovenous shunting lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010; 31: [6] Salomon EJ, Barfett J, Willems PW, Geibprasert S, Bacigaluppi S and Krings T. Dynamic CT angiography and CT perfusion employing a 320-detector row CT: protocol and current clinical applications. Klin Neuroradiol 2009; 19: [7] Daniels DJ, Vellimana AK, Zipfel GJ and Lanzino G. Intracranial hemorrhage from dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical features and outcome. Neurosurg Focus 2013; 34: E15. [8] Koyanagi M, Sakai N, Adachi H, Ueno Y, Kunieda T, Imamura H and Kikuchi H. Looplike formation in the cortical venous reflux of dural arteriovenous fistula with intracranial hemorrhage. J Neuroradiol 2013; [Epub ahead of print]. [9] Bink A, Berkefeld J, Kraus L, Senft C, Ziemann U and du Mesnil de Rochemont R. Long-term outcome in patients treated for benign dural arteriovenous fistulas of the posterior fossa. Neuroradiology 2011; 53: [10] Yeh SJ, Tsai LK and Jeng JS. Clinical and carotid ultrasonographic features of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in patients with and without Pulsatile Tinnitus. J Neuroimaging 2010; 20: [11] Cohen SD, Goins JL, Butler SG, Morris PP and Browne JD. Dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Laryngoscope 2009; 119: [12] Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS and Chang KH. MR imaging findings of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: relations with venous drainage patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005; 26: [13] Fujiwara H, Momoshima S, Akiyama T and Kuribayashi S. Whole-brain CT digital subtraction angiography of cerebral dural arteriove Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
8 nous fistula using 320-detector row CT. Neuroradiology 2013; 55: [14] Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Johnstone DM and Terbrugge KG. Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and classification with timeresolved MR angiography at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009; 30: [15] Sakamoto S, Shibukawa M, Kiura Y, Matsushige T, Abe N and Kurisu K. Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas of cavernous sinus before and after endovascular treatment using timeresolved MR angiography. Neurosurg Rev 2010; 33: ; discussion [16] Reinacher PC, Stracke P, Reinges MH, Hans FJ and Krings T. Contrast-enhanced time-resolved 3-D MRA: applications in neurosurgery and interventional neuroradiology. Neuroradiology 2007; 49 Suppl 1: S3-13. [17] Siebert E, Bohner G, Dewey M, Masuhr F, Hoffmann KT, Mews J, Engelken F, Bauknecht HC, Diekmann S and Klingebiel R. 320-slice CT neuroimaging: initial clinical experience and image quality evaluation. Br J Radiol 2009; 82: [18] Willems PW, Brouwer PA, Barfett JJ, terbrugge KG and Krings T. Detection and classification of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas using 4D-CT angiography: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011; 32: [19] Beijer TR, van Dijk EJ, de Vries J, Vermeer SE, Prokop M and Meijer FJ. 4D-CT angiography differentiating arteriovenous fistula subtypes. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013; 115: [20] Houdart E, Saint-Maurice JP, Chapot R, Ditchfield A, Blanquet A, Lot G and Merland JJ. Transcranial approach for venous embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 2002; 97: [21] Duffau H, Lopes M, Janosevic V, Sichez JP, Faillot T, Capelle L, Ismail M, Bitar A, Arthuis F and Fohanno D. Early rebleeding from intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: report of 20 cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 1999; 90: Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations
 Neuroradiology (2012) 54:123 131 DOI 10.1007/s00234-011-0864-0 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations Peter W. A. Willems & Patamintita
Neuroradiology (2012) 54:123 131 DOI 10.1007/s00234-011-0864-0 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The use of 4D-CTA in the diagnostic work-up of brain arteriovenous malformations Peter W. A. Willems & Patamintita
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
The diagnosis of a cranial dural arteriovenous fistula
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.I. Farb R. Agid R.A. Willinsky D.M. Johnstone K.G. terbrugge Cranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Diagnosis and Classification with Time-Resolved MR Angiography at 3T BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.I. Farb R. Agid R.A. Willinsky D.M. Johnstone K.G. terbrugge Cranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Diagnosis and Classification with Time-Resolved MR Angiography at 3T BACKGROUND AND
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention
 52 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention Chun-Yu Lee, Shin-Joe Yeh, Li-Kai Tsai, Sung-Chun Tang, Jiann-Shing Jeng Abstract-
52 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Status Epilepticus Treated Successfully with Endovascular Intervention Chun-Yu Lee, Shin-Joe Yeh, Li-Kai Tsai, Sung-Chun Tang, Jiann-Shing Jeng Abstract-
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) have long
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal. Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:1123 1127, 2016 Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly cured intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas Sudheer Ambekar, MD, Brandon G. Gaynor, MD, Eric C. Peterson,
SDAVFs are rare acquired vascular lesions predominantly
 CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
Research Article Total Bolus Extraction Method Improves Arterial Image Quality in Dynamic CTAs Derived from Whole-Brain CTP Data
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 603173, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/603173 Research Article Total Bolus Extraction Method Improves Arterial Image Quality in Dynamic CTAs Derived from
BioMed Research International, Article ID 603173, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/603173 Research Article Total Bolus Extraction Method Improves Arterial Image Quality in Dynamic CTAs Derived from
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
CASE PRESENTATION. Key Words: cerebral venous thrombosis, internal jugular vein stenosis, thrombolysis, stenting (Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2005;21:527 31)
 Treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL VENOUS THROMBOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH BILATERAL INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN STENOSIS USING DIRECT THROMBOLYSIS AND STENTING: A CASE REPORT
Treatment of cerebral venous thrombosis SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL VENOUS THROMBOSIS ASSOCIATED WITH BILATERAL INTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN STENOSIS USING DIRECT THROMBOLYSIS AND STENTING: A CASE REPORT
Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.106 Case Report Fluoroscopy-guided Combined (Surgical/Endovascular) Treatment
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona
 clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report
 Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage
 CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
CT angiography and its role in the investigation of intracranial haemorrhage RD Magazine, 39, 458, 29-30 Dr M Igra Radiology SPR Leeds General Infirmary Dr I Djoukhadar Research fellow Wolfson Molecular
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 2643-2649, 2017 Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study GUOQUAN CAO, WEIJIAN CHEN, HOUZHANG SUN, XIANZHONG GUO, YUNJUN
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: 2643-2649, 2017 Whole brain CT perfusion imaging using increased sampling intervals: A pilot study GUOQUAN CAO, WEIJIAN CHEN, HOUZHANG SUN, XIANZHONG GUO, YUNJUN
Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center Cohort of 12 Patients
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
Original Article Dual-energy CT angiography for the diagnosis of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):7802-7808 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004905 Original Article Dual-energy CT angiography for the diagnosis of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula Yuanxing Guo
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):7802-7808 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004905 Original Article Dual-energy CT angiography for the diagnosis of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula Yuanxing Guo
Original Article Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after microsurgical clipping of intracranial aneurysms: diagnosis and treatment a review of 13 cases
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3681-3686 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012155 Original Article Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after microsurgical clipping of intracranial aneurysms: diagnosis and treatment
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3681-3686 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012155 Original Article Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after microsurgical clipping of intracranial aneurysms: diagnosis and treatment
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
I-iodoamphetamine single photon emission computed tomography
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:110 117, 2015 Cerebral hemodynamic disturbance in dural arteriovenous fistula with retrograde leptomeningeal venous drainage: a prospective study using 123 I-iodoamphetamine
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas. Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients
 J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
J Neurosurg 71:352-358,1989 Complex dural arteriovenous fistulas Results of combined endovascular and neurosurgical treatment in 16 patients STANLEY L. BARNWELL, M.D., PH.D., VAN V. HALBACH, M.D., RANDALL
A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: 38 42 Online September 11, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2017-0056 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment.
 Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Role of the Radiologist
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Diagnosis and Treatment of Blunt Cerebrovascular Injuries NORDTER Consensus Conference October 22-24, 2007 Clint W. Sliker, M.D. University of Maryland Medical Center R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center
Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations.
 Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography.
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: the value of Carotid Ultrasonography. Poster No.: C-2199 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Filipe, T. Parreira, C. Andrade, R. Santos, E. Azevedo;
Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
The surgical strategy of hypertensive thalamus hemorrhage. Lu Ma, Chao You Dept. of Neurosurgery, West China Hospital
 The surgical strategy of hypertensive thalamus hemorrhage Lu Ma, Chao You Dept. of Neurosurgery, West China Hospital Preface Spontaneous Intracranial hemorrhage (SICH) Spontaneous thalamus hemorrhage---hypertensive
The surgical strategy of hypertensive thalamus hemorrhage Lu Ma, Chao You Dept. of Neurosurgery, West China Hospital Preface Spontaneous Intracranial hemorrhage (SICH) Spontaneous thalamus hemorrhage---hypertensive
Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15921-15927 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022273 Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage Xielin Tang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15921-15927 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022273 Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage Xielin Tang
Methods. Treatment options for intracranial arteriovenous malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations is often extensive
 NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
NOVEMBER, 1974 ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE OCCIPITAL LOBE* By B. TODD TROOST, M.D.,t and THOMAS H. NEWTON, M.D4 T HE blood supply of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization after coil embolization of visceral artery aneurysms
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
Sinus Venous Thrombosis
 Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Sinus Venous Thrombosis Joseph J Gemmete, MD FACR, FSIR, FAHA Professor Departments of Radiology and Neurosurgery University of Michigan Hospitals Ann Arbor, MI Outline Introduction Medical Treatment Options
Treatment of brain AVMs includes different modalities
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij S. Jacobs M. Sluzewski B. van der Pol G.N. Beute M.E. Sprengers Curative Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Onyx: Patient Selection, Embolization Technique,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij S. Jacobs M. Sluzewski B. van der Pol G.N. Beute M.E. Sprengers Curative Embolization of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations with Onyx: Patient Selection, Embolization Technique,
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR?
 Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis.
 Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Normal Variations and Artifacts in MR Venography that may cause Pitfalls in the Diagnosis of Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. Poster No.: R-0005 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis
 Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
DAVFs and AVMs are cerebral vascular malformations
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.T. Le N.J. Fischbein J.B. André C. Wijman J. Rosenberg G. Zaharchuk Identification of Venous Signal on Arterial Spin Labeling Improves Diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.T. Le N.J. Fischbein J.B. André C. Wijman J. Rosenberg G. Zaharchuk Identification of Venous Signal on Arterial Spin Labeling Improves Diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas and
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Cerebral Aneurysms: Accuracy of 320 Detector Row Nonsubtracted and Subtracted Volumetric CT Angiography for Diagnosis 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Wenhua Chen, MD Wei
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Wenhua Chen, MD Wei
Rapidly Progressive Dementia Caused by a Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
 Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 22-26, 2015 apidly Progressive Dementia Caused by a Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case eport yoko IMAZEKI *1, Kazumitsu AMAI *2, Tomoko
Tokai J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 40, No. 1, pp. 22-26, 2015 apidly Progressive Dementia Caused by a Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case eport yoko IMAZEKI *1, Kazumitsu AMAI *2, Tomoko
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic dural arteriovenous fistula with perimedullary hypertension: case report
 Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh Amin Hanjani MD, Fady Charbel MD, Victor Aletich MD.
 Endovascular Approach and Technique for Treatment of Transverse Sigmoid Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Cortical Reflux: The Importance of Venous Sinus Sacrifice Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh
Endovascular Approach and Technique for Treatment of Transverse Sigmoid Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Cortical Reflux: The Importance of Venous Sinus Sacrifice Andrew Carlson MD, Ali Alaraj MD, Sepideh
S. Inagawa, N. Yoshimura, Y. Ito; Niigata/JP spinal sacral areteriovenous fistulae, CTA, MRA /ecr2010/C-2581
 Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus
 337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
337 Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus Van V. Halbach1 Randall T. Higashida 1 Grant B. Hieshima 1 Mark Rosenblum 2 Les Cahan 3 We report the diagnosis
Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: transarterial Onyx embolization experience and technical nuances
 Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona, USA Correspondence to Dr C G McDougall, Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow
The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines
 Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 91 96 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines Roland Mark M GIGATARAS MD,
Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 91 96 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines Roland Mark M GIGATARAS MD,
The standard examination to evaluate for a source of subarachnoid
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3478 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Use of CT Angiography and Digital Subtraction Angiography in Patients with Ruptured Cerebral Aneurysm: Evaluation of a Large
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease
 Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus. Disclosures. Pulsatile Tinnitus: Differential Diagnosis. Pulsatile Tinnitus
 Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sprengers, M. E. S.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sprengers, M. E. S.
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Lecture Outline: 1/5/14
 John P. Karis, MD Lecture Outline: Provide a clinical overview of stroke: Risk Prevention Diagnosis Intervention Illustrate how MRI is used in the diagnosis and management of stroke. Illustrate how competing
John P. Karis, MD Lecture Outline: Provide a clinical overview of stroke: Risk Prevention Diagnosis Intervention Illustrate how MRI is used in the diagnosis and management of stroke. Illustrate how competing
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
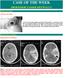 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are acquired abnormal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Retrospective analytical six months study of vascular abnormalities of brain
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20160185 Retrospective analytical
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20160185 Retrospective analytical
Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients
 ngiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Pictorial Essay M E E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:75 84 0361 803X/06/1861 75 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O John M.
ngiography of Neurovascular Lesions in Pediatric Patients Pediatric Imaging Pictorial Essay M E E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:75 84 0361 803X/06/1861 75 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y O John M.
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
