Brain and other natriuretic peptides: molecular aspects
|
|
|
- Nora Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) Brain and other natriuretic peptides: molecular aspects Marc Vanderheyden*, Jozef Bartunek, Marc Goethals Cardiovascular Center, Onze Lieve Vrouwziekenhuis, Moorselbaan 164, 9400 Aalst, Belgium Abstract Received 23 December 2003; accepted 13 January 2004 Natriuretic peptides have emerged as important candidates for development of diagnostic tools and therapeutic agents in cardiovascular disease. The family contains of three major peptides ANP, BNP, CNP that participate in cardiovascular and cardiorenal homeostasis. Each of these natriuretic peptides binds differentially to specific receptors that signal through different mechanisms. They are cleared enzymatically by neutral endopeptidase as well as by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Because of its fast induction and specific expression in overt heart failure, BNP seems the most promising natriuretic peptide. It is predominantly synthesized in the cardiac ventricles, released as pre-probnp and then enzymatically cleaved to BNP and the N- terminal portion of BNP(NT-proBNP). Blood measurements of BNP and NT-proBNP have been shown to identify patients with LV dysfunction. This review focuses on the physiology of natriuretic peptides as a group and brain natriuretic peptide in more detail, its structure and regulation as well as its effects at the cellular level European Society of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: 1. Introduction Natriuretic peptides; Heart failure Though it is well known that neurohormones are activated and released into the circulation in patients with heart failure, the therapeutic importance of this observation has only emerged in the past years. To counter-balance the effects of vasoconstrictor-mitogenic-sodium-retaining neurohormones, released by the sympathetic nervous system and the RAAS, and to maintain circulatory homeostasis the body produces a family of vasodilator antiproliferative natriuretic peptides that have an important role in heart failure both as counter-regulatory hormones and as potential exogenous therapy. In 1981 de Bold and colleagues observed that extracts of atrial tissue infused into rats caused a copious diuresis w1x. Subsequent isolation and purification quickly revealed that a new peptide called atrial natriuretic peptide was the mediator of this diuretic response w1x. Ten years following the description of atrial natriuretic peptide, a second compound of the family of natriuretic *Corresponding author. Tel.: q ; fax: q address: marc.vanderheyden@olvz-aalst.be (M. Vanderheyden). peptides was described. This was called brain natriuretic peptide because of it first isolation from porcine brain w2x. Over the past decade, it has been demonstrated that this peptide has great pathophysiological importance in diagnosing heart failure w3,4x as well as in risk stratification and guiding heart failure therapy w5x. This review focuses on natriuretic peptides as a group and brain natriuretic peptide in more detail, its structure and regulation as well as its effects at the cellular level. 2. The natriuretic peptide family Four distinct natriuretic peptides have been described (Table 1). They all have a characteristic 17 amino-acid residue ring structure formed by an intramolecular disulfide bridge between two cysteine residues w6x. The amino- and carboxyl terminal tails varies between the different peptides leading to polypeptides of 28 amino acids (ANP), 32 amino acids (BNP), 53 amino acids (CNP) and 38 amino acids for D-type w7x. They all also exist as a pro-hormone with a relatively high molecular weight that is cleaved before release into the circulation w8x. The ANP and BNP precursor peptide genes reside in tandem on the distal short arm of chromosome /04/$ - see front matter 2004 European Society of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.ejheart
2 Table 1 Characteristics of the natriuretic peptides ANP BNP CNP DNP BNP NT-proBNP Human chromosomal 1p36.2 1p36.2 1p unk location Components Ct-ANP(28 AA) BNP(32 AA) Nt fragment (1 76) CNP-22 DNP-like peptide Nt-ANPt (98 AA) NT-proBNP (1 108) CNP-53 in humans Hormonally active endocrineyparacrine endocrineyparacrine paracrine unk Genesis Cleavage from pro-anp Cleavage form pro-bnp Release from Cleavage from pro-cnp unk ventricular myocytes Half-life 20 min 120 min Clearance mechanism Neutral endopeptidase Neutral endopeptidase Renal clearance Neutral unk endopeptidase Clearance receptor Clearance receptor Clearance receptor NPR-C NPR-C NPR-C Approved cutoff for CHF unk 100 pgyml Age-75 years: 125 pgyml diagnosis Age)75 years: 450 pgyml Tissue distribution Cardiac atria Brain Brain Brain, ovary, uterus Snake venom and ventricles Cardiac ventricles Cardiac ventricles Testis epidydimis Principal phenotype Salt-sensitive Myocardial fibrosis Myocardial fibrosis Dwarfism unk of knockout mice Hypertension Early death Ct means carboxy-terminal, Nt amino-terminal, AA aminoacid and unk unknown. 262 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) Downloaded from at Pennsylvania State University on February 23, 2013
3 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) w9xwhereas the CNP precursor peptide gene is localized on chromosome 2 w9x. The gene encoding DNP has not been cloned w10x Atrial natriuretic peptide The messenger RNA transcript for atrial natriuretic peptide is approximately 1 kb in size and encodes a precursor protein (pro-atrial natriuretic peptide) of 126 amino acids. Human pro-atrial natriuretic peptide is proteolytically cleaved to a 98-amino-acid amino-terminal fragment and a 28-amino-acid carboxy-terminal fragment that represents biologically active ANP w11x. Both fragments as well as other fragments of the aminoterminal molecule circulate in plasma. Several data suggest that these pro-anp fragments may be as or even more important than ANP as a natriuretic hormone w12x. Atrial natriuretic peptide is present in the ventricular tissue of fetuses and neonates, in hypertrophied ventricles as well as in low concentrations in normal ventricles. However, the atria are the main source in the adult normal heart w7x. A separate natriuretic 32-amino-acid peptide pro-anp fragment called urodilatin has been identified in human urine w13x. Plasma levels of urodilatin are negligible since it is produced within the kidney by a unique processing pathway. Distal nephron cells have been shown to secrete an ANP pro-hormone that could be the precursor of urodilatin. Urodilatin appears to be more resistant to neutral endopeptidases (NEP). Its role in heart failure, if any, is still not very clear w14x Brain natriuretic peptide Human BNP is encoded by a single copy gene consisting of three exons and two introns. Its mrna has a characteristic feature by virtue of the presence of four AUUUAA repeat sequences within the 39 untranslated region that is considered to produce mrna stability w8x. The post-translational processing of the BNP precursor gene is different from that of the human ANP precursor. Regulation of ANP seems to occur at the level of release from storage granules whereas BNP regulation takes place during gene expression w15x. Human brain natriuretic peptide is produced in bursts in the heart as 108 amino acid precursor (pro-bnp) w16x. Further processing releases a mature biologically active 32-amino-acid molecule BNP, which corresponds to the C-terminal sequence of the human BNP precursor and a 76 aminoacid N-terminal fragment (NT-proBNP)(Fig. 1) w17x. The biologically active BNP, the intact 108 amino acid probnp and the remaining part of the prohormone NT-proBNP all circulate in the plasma and can be measured by immunoassay. Circulating BNP consists of 32 amino acids with a characteristic ring closed by a Fig. 1. Structure of brain natriuretic peptide and its activation site. disulfide bond between two cysteine residues, an aminoterminal tail of nine amino acids, and a carboxylterminal tail of six amino-acids w8x. Although atrial and to a greater extent ventricular cardiomyocytes constitute the major source of BNP related peptides, recent data demonstrated that other cells such as cardiac fibroblasts can also produce BNP. In addition, various neurohormones may stimulate cardiac BNP production in interplay between different cardiac cell types. In normal subjects the plasma concentrations of NTproBNP and BNP are similar. Both are continuously released from the heart and are detectable at picomolar concentrations in the venous blood of healthy subjects. With a half life of approximately 22 min in blood w8x, BNP can accurately reflect pulmonary capillary wedge pressure changes every 2 h. The plasma half-life of NTproBNP is 120 min suggesting that meaningful changes in hemodynamics could be reflected by this test approximately every 12 h w18x. However, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction NT-proBNP levels rise more than BNP with plasma concentration 2 10 times higher than BNP. The exact mechanism responsible for this relative change in peptide levels remains undetermined. Shifts in cardiac secretion andyor clearance mechanisms are thought to play a role. Taken together the greater rise in NT-proBNP during heart failure may make it a better marker as compared to BNP w19x. The correlation between BNP and estimated glomerular filtration rate is approximately rsy0.20. This implies a higher cutoff for BNP in the diagnosis of CHF when kidney disease advances. Nevertheless using this approach, BNP maintains a high level of diagnostic utility w20x. NT-proBNP has a stronger correlation with egfr of approximately rsy0.60, and is influenced by the normal age-related decline in renal function. Therefore, below an egfr of 60 mlyminy1.73 m, which is 2 common in the elderly, the cutoff of NT-proBNP for detecting CHF might be less accurate w21x. This tight relationship to renal function has led some investigators to suggest that NT-proBNP reflects cardiorenal instead of cardiac function w18x.
4 264 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) C-type natriuretic peptide A third natriuretic peptide, C-type NP is expressed primarily in the central nervous system and vascular tissues and, unlike ANP and BNP, is nearly non-existent in cardiac tissue w22x. The gene encoding CNP is localized to human chromosome 2 and contains two exons separated by an intron. The NPCC gene encodes a 126-residu CNP precursor peptide pro-cnp that is processed to generate 22- (CNP-22) and 53-amino acid peptides (CNP-53). CNP-22 is more widely and abundantly expressed and is more potent than C-53 peptide w7x. CNP has remarkable similarity to ANP in its amino acid sequence but lacks the Carboxy-terminal tail of ANP w23x. The low almost undetectable levels of CNP suggests that this peptide acts primarily as a neurotransmitter in a paracrine way w24x, while ANP and BNP function more as true counter-regulatory hormones w25x. Nevertheless, CNP does play an important role in cardiovascular physiology as a potent vasorelaxant, as well as an inhibitor of vascular smooth muscle proliferation and endothelial cell migration w17x. Recent data also reported a lusitropic and negative inotropic effect of CNP infusion in isolated papillary muscle w26x D-type natriuretic peptide Dendroaspis natriuretic peptide (DNP), a 38-aminoacid peptide is the newest of the natriuretic peptides. It was isolated from the venom of the Green Mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps) and has structural similarities to the three known human cardiac natriuretic peptides w27x, It shares the characteristic 17-aminoacid disulfide ring with all natriuretic peptides but is structurally different in its N- and C-terminal regions. Human data about this NP are scarce: The gene for DNP has not been cloned neither in the snake nor in any mammal in contrast to the other natriuretic peptides. Recently, a DNP-like peptide has been isolated from human plasma and human atria, yet conclusive evidence about its presence in man remains controversial. Some authors suggest DNP is a primitive, ancestral cardiac natriuretic peptide, an evolutionary precursor to ANP and BNP w10x. 3. Natriuretic peptide receptors The natriuretic peptides are ligands for three different cell surface receptors named natriuretic peptide receptor (NPR) A, NPR-B and NPR-C that mediate their physiological effects. Each of these receptors contains a single transmembrane domain and an extracellular binding domain w28x. Natriuretic peptide receptor A and B are structurally similar, with approximately 44% homology in the ligand-binding extracellular domain w29x. Although both receptors are found in the adrenal gland and the kidney, NPR-A is most abundant in large blood vessels in contrast to NPR-B that predominates in the brain, particularly in the pituitary gland w8x. ANP and BNP bind preferentially to NPR-A that dimerizes and uses a chloride ion to hold itself in the open position. The receptor is linked to a cyclic guanylate monophosphate (c-gmp)-dependent signaling cascade that mediates most of its biological activity w24x. Mice lacking this functional NPR-A receptor exhibit hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy and dilatation and die suddenly before the age of 6 months w30x. The relatively low affinity of BNP for NPR-A with a potency approximately 10-fold lower than that of ANP w31x, has led to the speculation that an additional BNPspecific guanylate cyclase receptor might play a role w26x. Of note in NPR-A knockout mice testis and adrenal glands retain significant high-affinity response to BNP that can only be accounted for by the presence of a novel receptor in these tissues that prefers BNP over ANP. Although the physiological significance and the biochemical components of this receptor remains to be established, its existence does reinforce the notion that ANP and BNP are likely to carry out at least some independent actions w26x. CNP does not act through NPR-A but selectively activates NPR-B a second guanylate cyclase receptor w26x. As previously mentioned, this receptor is similar to NPR-A. Nevertheless, it is only weakly sensitive to ANP and BNP w24x. In contrast to NPR-A and NPR-B the NPR-C is devoid of guanyl cyclase activity and contains 37 amino acid cytoplasmatic domain that contains a G proteinactivating sequence w24x. They are the most widely and abundantly expressed natriuretic peptide receptors and are located in several tissues including vascular endothelium, smooth muscle, heart, adrenal glands and kidney w32x. As demonstrated by studies performed in NPR-C knockout mice, it serves as a clearance receptor for ANP, BNP and CNP w33x. All three natriuretic peptides bind to this receptor in the order of ANP) CNP)BNP w34x, are internalized and enzymatically degraded, after which the C-receptor returns to the cell surface w7x. In addition, recent data indicate that the NPR-C alters target cell function through Gi proteincoupled inhibition of membrane adenylate cyclase activity w24x. The lower affinity of NPR-C for BNP with an interaction partly accounts for the longer plasma halflife of BNP as compared to ANP in man w24x. 4. Clearance of natriuretic peptides Although the rate of synthesis and release of natriuretic peptides is a major regulator of plasma concentrations, the rate of removal of the peptides from the
5 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) Fig. 2. Action of natriuretic peptides at target cells. GC means guanyl cyclase, NPR-A natriuretic peptide receptor A, NPR-B natriuretic peptide receptor B, NPR-C natriuretic peptide receptor C, NEP neutral endopeptidase, aldo aldosterone, OSorthosympathetic system. circulation is also important w35x. The clearance involves two main pathways: enzymatic degradation by neutral endopeptidase and as previously mentioned receptormediated endocytosis followed by lysosomal degradation via the natriuretic peptide receptor C (or clearance receptor) (Fig. 2) w6x. Renal clearance plays a lesser role at least for active C-terminal peptides. NEP, a zinc metallopeptidase is widely distributed on the surface of endothelial cells, smooth-muscle cells, cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts and is particularly concentrated at the brush border membranes in the proximal tubule of the kidney w17x. It cleaves the natriuretic peptides and opens the ring structure, thus inactivating the peptides w8x. The NPR-C is the most widely and abundantly expressed natriuretic peptide receptor and is located in several tissues including vascular endothelium and smooth muscle, heart, adrenal gland and kidney w11,24x. NPR-C knockout mice are characterized by a prolonged halflife of exogenous ANP, mild reductions in blood pressure, increased basal bone turnover and bone deformities w33x. The relative importance of these two mechanisms in the clearance is controversial. Although data from a number of studies in normal animals have demonstrated that NPR-C blockade has a greater effect on ANP clearance than do NEP inhibitors, others have demonstrated that the enzymatic and receptor clearance pathways equally contribute to the degradation of ANP and BNP at physiological plasma concentrations. In addition, it has been demonstrated that in states of chronically elevated endogenous natriuretic peptides, such as occurs in chronic heart failure, the clearance receptor may play a lesser role than NEP in the metabolism of the peptides because of higher receptor occupancy and species dependent ANP-mediated down-regulation of the NPR- C w36x. 5. Regulation and induction of ANP and BNP At the cellular level, stretch is the predominant stimulus controlling the release of BNP from the atria and the ventricles. The increased wall stretch acts directly or via local paracrine factors such as endothelin-1 w37x, nitric oxide w17x, and angiotensin II w38x. Apart from myocyte stretch other stimuli such as tachycardia w39x and glucocorticoids w40x contribute to the induction of cardiac BNP mrna in overt heart failure w17x.
6 266 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) ANP is primarily released by increased atrial transmural pressure. The release of BNP is modulated by both pressure and volume overload as evidenced by the correlation between left-ventricular chamber size w41x, left ventricular enddiastolic pressure w42xand plasma BNP concentration. Note, in vivo data demonstrated a slow ANP gene induction within days after the initiation of increased cardiac overload. In contrast there is a rapid within hours activation of the BNP gene, whenever wall stretch increases w43x. The slow induction of ANP allows storage of ANP in granules and periodical release from ANP out of these granules w44x. Because of the high turnover of the BNP messenger RNA, BNP cannot be stored but is released in bursts w45x. Experimental data suggest that upregulation of cardiac ANP is less dependent on the severity of heart failure; Indeed ANP mrna is already induced in compensated heart failure when hypertrophy is present but LVEDP is still normal. In contrast BNP mrna is only induced in heart failure when LVEDP is elevated w46x. Taken together these data not only give rise to the concept of BNP as an emergency hormone but also point toward the role of BNP as a marker for diagnosing the transition from compensated to decompensated heart failure w47x. 6. Actions of the natriuretic peptides 6.1. Renal effects At the level of the kidney, natriuretic peptides have multiple actions including stimulating natriuresis and diuresis. Atrial as well as brain natriuretic peptide exert their effects on the kidney primarily at the level of the glomerulus and collecting duct. In the glomerulus, it causes afferent arteriolar dilation together with efferent arteriolar vasoconstriction, thereby increasing the glomerular filtration rate w48x. In the collecting duct, it decreases sodium reabsorption, thereby increasing sodium excretion w49x. Both also inhibit the secretion of renin, angiotensin II and aldosterone w50x. Finally, mice over-expressing the BNP gene have a lower degree of glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion with intraglomerular cells than wild mice in response to renal ablation w51x Cardiovascular effects Transgenic mice that overexpress BNP have a lower blood pressure and a lower peripheral vascular resistance than wild types w51x. This is chiefly caused by a primary shift of intravascular fluid into the extravascular compartment and an increase in venous capacitance with subsequent rise in natriuresis, resulting in a reduction of preload w20x. However, mice with targeted disruption of BNP develop multifocal fibrotic lesions in the cardiac ventricle in the absence of systemic hypertension or ventricular hypertrophy w52x. These observations together with the lusitropic effects of BNP infusion suggest BNP acts as a cardiomyocyte-derived antifibrotic factor in vivo that may function as a local regulator of ventricular remodeling w24x. Atrial as well as brain natriuretic peptides also have important central and peripheral sympathoinhibitory effects w7x. Damping of the baroreceptors, suppressed release of catecholamines from autonomic nerve findings and especially suppression of sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system all have been reported w17x. Finally, the activation threshold of vagal afferents is lowered thereby suppressing the reflex tachycardia and vasoconstriction that accompanies the reduction in preload w53x. 7. Conclusion The natriuretic peptide family plays a distinct physiological and pathophysiological role in cardiovascular control. It consists of at least four ligands, ANP, BNP, CNP DNP and three types of receptors expressed in target tissues with tissue specificity. By binding to all three classes of receptors the natriuretic peptides act in concert to regulate cardiovascular function. Because of its fast induction and specific expression in overt heart failure, BNP seems the most promising natriuretic peptide as a marker of LV dysfunction and makes it an important component of future cardiac care. References w1x de Bold AJ, Borenstein HB, Veress AT, Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci 1981;28: w2x Sudoh T, Minamino N, Kangawa K, Matsuo H. Brain natriuretic peptide-32: N-terminal six amino acid extended form of brain natriuretic peptide identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1988;155: w3x Dao Q, Krishnaswamy P, Kazanegra R, et al. Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in an urgent-care setting. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37: w4x McCullough PA, Nowak RM, McCord J, et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and clinical judgment in emergency diagnosis of heart failure: analysis from breathing not properly (BNP) multinational study. Circulation 2002;106: w5x Cheng V, Kazanagra R, Garcia A, et al. A rapid bedside test for B-type peptide predicts treatment outcomes in patients admitted for decompensated heart failure: a pilot study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37: w6x Nakao K, Ogawa Y, Suga S, Imura H. Molecular biology and biochemistry of the natriuretic peptide system. II: Natriuretic peptide receptors. J Hypertens 1992;10: w7x Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK. Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med 1998;339: w8x Valli N, Gobinet A, Bordenave L. Review of 10 years of the clinical use of brain natriuretic peptide in cardiology. J Lab Clin Med 1999;134: w9x Tamura N, Ogawa Y, Yasoda A, Itoh H, Saito Y, Nakao K. Two cardiac natriuretic peptide genes (atrial natriuretic peptide
7 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) and brain natriuretic peptide) are organized in tandem in the mouse and human genomes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1996;28: w10x Richards AM, Lainchbury JG, Nicholls MG, Cameron AV, Yandle TG. Dendroaspis natriuretic peptide: endogenous or dubious? Lancet 2002;359:5 6. w11x Espiner EA, Richards AM, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG. Natriuretic hormones. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1995;24: w12x Vesely DL, Douglass MA, Dietz JR, et al. Three peptides from the atrial natriuretic factor prohormone amino terminus lower blood pressure and produce diuresis, natriuresis, andyor kaliuresis in humans. Circulation 1994;90: w13x Schulz-Knappe P, Forssmann K, Herbst F, Hock D, Pipkorn R, Forssmann WG. Isolation and structural analysis of urodilatin, a new peptide of the cardiodilatin-(anp)-family, extracted from human urine. Klin Wochenschr 1988;66: w14x Ritter D, Chao J, Needleman P, Tetens E, Greenwald JE. Localization, synthetic regulation, and biology of renal atriopeptin-like prohormone. Am J Physiol 1992;263:F503 F509. w15x Onuoha GN, Nicholls DP, Patterson A, Beringer T. Neuropeptide secretion in exercise. Neuropeptides 1998;32: w16x Yasue H, Yoshimura M, Sumida H, et al. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation 1994;90: w17x de Lemos JA, McGuire DK, Drazner MH. B-type natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2003;362: w18x McCullough PA, Omland T, Maisel AS. B-type natriuretic peptides: a diagnostic breakthrough for clinicians. Rev Cardiovasc Med 2003;4: w19x Hunt PJ, Richards AM, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Doughty RN, Espiner EA. Immunoreactive amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-PROBNP): a new marker of cardiac impairment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1997;47: w20x Vesely DL. Natriuretic peptides and acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2003;285:F167 F177. w21x McCullough PA, Sandberg KR. B-type natriuretic peptide and renal disease. Heart Fail Rev 2003;8: w22x Sudoh T, Minamino N, Kangawa K, Matsuo H. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP): a new member of natriuretic peptide family identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990;168: w23x Tawaragi Y, Fuchimura K, Tanaka S, Minamino N, Kangawa K, Matsuo H. Gene and precursor structures of human C-type natriuretic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991;175: w24x Kone BC. Molecular biology of natriuretic peptides and nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res 2001;51: w25x Barr CS, Rhodes P, Struthers AD. C-type natriuretic peptide. Peptides 1996;17: w26x Goy MF, Oliver PM, Purdy KE, et al. Evidence for a novel natriuretic peptide receptor that prefers brain natriuretic peptide over atrial natriuretic peptide. Biochem J 2001;358: w27x Schweitz H, Vigne P, Moinier D, Frelin C, Lazdunski M. A new member of the natriuretic peptide family is present in the venom of the green mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps). J Biol Chem 1992;267: w28x Porter JG, Arfsten A, Fuller F, Miller JA, Gregory LC, Lewicki JA. Isolation and functional expression of the human atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor cdna. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990;171: w29x Koller KJ, Goeddel DV. Molecular biology of the natriuretic peptides and their receptors. Circulation 1992;86: w30x Pandey KN, Oliver PM, Maeda N, Smithies O. Hypertension associated with decreased testosterone levels in natriuretic peptide receptor-a gene-knockout and gene-duplicated mutant mouse models. Endocrinology 1999;140: w31x Schulz S, Singh S, Bellet RA, et al. The primary structure of a plasma membrane guanylate cyclase demonstrates diversity within this new receptor family. Cell 1989;58: w32x Maack T, Suzuki M, Almeida FA, et al. Physiological role of silent receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Science 1987;238: w33x Matsukawa N, Grzesik WJ, Takahashi N, et al. The natriuretic peptide clearance receptor locally modulates the physiological effects of the natriuretic peptide system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999;96: w34x Suga S, Nakao K, Hosoda K, et al. Receptor selectivity of natriuretic peptide family, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, and C-type natriuretic peptide. Endocrinology 1992;130: w35x Rademaker MT, Charles CJ, Kosoglou T, et al. Clearance receptors and endopeptidase: equal role in natriuretic peptide metabolism in heart failure. Am J Physiol 1997;273:H2372 H2379. w36x Kishimoto I, Nakao K, Suga S, et al. Downregulation of C- receptor by natriuretic peptides via ANP-B receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 1993;265:H1373 H1379. w37x Bruneau BG, Piazza LA, de Bold AJ. BNP gene expression is specifically modulated by stretch and ET-1 in a new model of isolated rat atria. Am J Physiol 1997;273:H2678 H2686. w38x Wiese S, Breyer T, Dragu A, et al. Gene expression of brain natriuretic peptide in isolated atrial and ventricular human myocardium: influence of angiotensin II and diastolic fiber length. Circulation 2000;102: w39x Riddervold F, Smiseth OA, Hall C, Groves G, Risoe C. Rateinduced increase in plasma atrial natriuretic factor can occur independently of changes in atrial wall stretch. Am J Physiol 1991;260:H1953 H1958. w40x Nishimori T, Tsujino M, Sato K, Imai T, Marumo F, Hirata Y. Dexamethasone-induced up-regulation of adrenomedullin and atrial natriuretic peptide genes in cultured rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1997;29: w41x Qi W, Mathisen P, Kjekshus J, et al. Natriuretic peptides in patients with aortic stenosis. Am Heart J 2001;142: w42x Haug C, Metzele A, Kochs M, Hombach V, Grunert A. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide and atrial natriuretic peptide concentrations correlate with left ventricular end-diastolic pressure. Clin Cardiol 1993;16: w43x Hama N, Itoh H, Shirakami G, et al. Rapid ventricular induction of brain natriuretic peptide gene expression in experimental acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1995;92: w44x Sumida H, Yasue H, Yoshimura M, et al. Comparison of secretion pattern between A-type and B-type natriuretic peptides in patients with old myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25: w45x Yasue H, Yoshimura M, Sumida H, et al. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation 1994;90: w46x Langenickel T, Pagel I, Hohnel K, Dietz R, Willenbrock R. Differential regulation of cardiac ANP and BNP mrna in different stages of experimental heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2000;278:H1500 H1506. w47x Yoshimura M, Yasue H, Okumura K, et al. Different secretion patterns of atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide
8 268 M. Vanderheyden et al. / The European Journal of Heart Failure 6 (2004) in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1993;87: w48x Weidmann P, Hasler L, Gnadinger MP, et al. Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man. J Clin Invest 1986;77: w49x Zeidel ML, Kikeri D, Silva P, Burrowes M, Brenner BM. Atrial natriuretic peptides inhibit conductive sodium uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest 1988;82: w50x Richards AM, McDonald D, Fitzpatrick MA, et al. Atrial natriuretic hormone has biological effects in man at physiological plasma concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1988;67: w51x Kasahara M, Mukoyama M, Sugawara A, et al. Ameliorated glomerular injury in mice overexpressing brain natriuretic peptide with renal ablation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000;11: w52x Tamura N, Ogawa Y, Chusho H, et al. Cardiac fibrosis in mice lacking brain natriuretic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97: w53x Schultz HD, Gardner DG, Deschepper CF, Coleridge HM, Coleridge JC. Vagal C-fiber blockade abolishes sympathetic inhibition by atrial natriuretic factor. Am J Physiol 1988;255:R6 R13.
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Brain natriuretic peptide: its relevance to the cardiologist. Journal of Hong Kong College of Cardiology, 1995, v. 3 n. 2, p.
 Title Brain natriuretic peptide: its relevance to the cardiologist Author(s) Cheung, BMY Citation Journal of Hong Kong College of Cardiology, 1995, v. 3 n. 2, p. 112-117 Issued Date 1995 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/223767
Title Brain natriuretic peptide: its relevance to the cardiologist Author(s) Cheung, BMY Citation Journal of Hong Kong College of Cardiology, 1995, v. 3 n. 2, p. 112-117 Issued Date 1995 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/223767
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
During exercise the heart rate is 190 bpm and the stroke volume is 115 ml/beat. What is the cardiac output?
 The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido Boerrigter, Horng C Chen, Fernando L Martin, and John C Burnett Jr
 Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Blood Pressure Regulation. Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure
 Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
Sheet physiology(18) Sunday 24-November Blood Pressure Regulation Slides 9-12 Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) = 1/3 systolic pressure + 2/3 diastolic pressure MAP= Diastolic Pressure+1/3 Pulse Pressure CO=MAP/TPR
NATRIURETIC PEPTIDES IN CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received: 18 January 2007 Volume 13 (2008) pp 155-181 Revised form accepted: 08 May 2007 DOI: 10.2478/s11658-007-0046-6 Published online: 29
CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received: 18 January 2007 Volume 13 (2008) pp 155-181 Revised form accepted: 08 May 2007 DOI: 10.2478/s11658-007-0046-6 Published online: 29
Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic Peptides and Adrenomedullin
 REVIEW Korean Circ J 2008;38:507-513 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2008 The Korean Society of Cardiology Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic
REVIEW Korean Circ J 2008;38:507-513 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2008 The Korean Society of Cardiology Bio-Molecular Markers for Cardiovascular Disease: Significance of Natriuretic
NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure
 Reference Section NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure a report by Drs Rahul Sakhuja and James L Januzzi Cardiology Division and Department of Medicine,
Reference Section NT-proBNP A New Test for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Congestive Heart Failure a report by Drs Rahul Sakhuja and James L Januzzi Cardiology Division and Department of Medicine,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure: Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure 5/1/12
 Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
CASE 13. What neural and humoral pathways regulate arterial pressure? What are two effects of angiotensin II?
 CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
CASE 13 A 57-year-old man with long-standing diabetes mellitus and newly diagnosed hypertension presents to his primary care physician for follow-up. The patient has been trying to alter his dietary habits
As the prevalence of congestive heart failure (CHF) has
 Therapeutic Actions of a New Synthetic Vasoactive and Natriuretic Peptide, Dendroaspis Natriuretic Peptide, in Experimental Severe Congestive Heart Failure Ondrej Lisy, John G. Lainchbury, Hanna Leskinen,
Therapeutic Actions of a New Synthetic Vasoactive and Natriuretic Peptide, Dendroaspis Natriuretic Peptide, in Experimental Severe Congestive Heart Failure Ondrej Lisy, John G. Lainchbury, Hanna Leskinen,
 http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au This is the author version of the paper published as: Author: T.-W. Sun, S.-Y. Zhang and L. Wang Author Address: lwang@csu.edu.au Title: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide
http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au This is the author version of the paper published as: Author: T.-W. Sun, S.-Y. Zhang and L. Wang Author Address: lwang@csu.edu.au Title: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
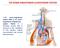 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Mineralocorticoids. Introduction
 Mineralocorticoids Introduction concepts to remember: a) water, glucose, mineral metabolism; b) adrenal in stress and blood pressure 15 Renin - angiotensin (RAS) and kallikrein kinin (KKS) systems: synthesis,
Mineralocorticoids Introduction concepts to remember: a) water, glucose, mineral metabolism; b) adrenal in stress and blood pressure 15 Renin - angiotensin (RAS) and kallikrein kinin (KKS) systems: synthesis,
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology
 Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
Cardiorenal Syndrome Prof. Dr. Bülent ALTUN Hacettepe University Faculty of Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Division of Nephrology Heart and Kidney The kidney yin dominates water, The heart yang
ARG-13 OF B-TYPE NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE RECIPROCALLY MODULATES BINDING TO GUANYLYL CYCLASE BUT NOT CLEARANCE RECEPTORS #
 Molecular Pharmacology This article has not Fast been Forward. copyedited and Published formatted. The on final June version 8, 2010 may differ as doi:10.1124/mol.110.066084 from this version. MOL #66084
Molecular Pharmacology This article has not Fast been Forward. copyedited and Published formatted. The on final June version 8, 2010 may differ as doi:10.1124/mol.110.066084 from this version. MOL #66084
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Physiology of osmo- and volume regulation, LOs #78 & #79
 Physiology of osmo- and volume regulation, LOs #78 & #79 Gyöngyi Karcsúné Kis, MSc, PhD 2 nd March 2018 Characteristic Osmoregulation Volume regulation What is being sensed Plasma osmolality Effective
Physiology of osmo- and volume regulation, LOs #78 & #79 Gyöngyi Karcsúné Kis, MSc, PhD 2 nd March 2018 Characteristic Osmoregulation Volume regulation What is being sensed Plasma osmolality Effective
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
Mechanism: 1- waterretention from the last part of the nephron which increases blood volume, venous return EDV, stroke volume and cardiac output.
 Blood pressure regulators: 1- Short term regulation:nervous system Occurs Within secondsof the change in BP (they are short term because after a while (2-3 days) they adapt/reset the new blood pressure
Blood pressure regulators: 1- Short term regulation:nervous system Occurs Within secondsof the change in BP (they are short term because after a while (2-3 days) they adapt/reset the new blood pressure
Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome
 RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2
 Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Cardiovascular System B L O O D V E S S E L S 2 Blood Pressure Main factors influencing blood pressure: Cardiac output (CO) Peripheral resistance (PR) Blood volume Peripheral resistance is a major factor
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine
 Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
Medical Management of Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure William T. Abraham, MD Director, Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Orlando, Florida October 7-9, 2011 Goals of Acute Heart Failure Therapy Alleviate
DOWNLOAD PDF ABC OF HEART FAILURE
 Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Chapter 1 : The ABCs of managing systolic heart failure: Past, present, and future Heart failure is a multisystem disorder which is characterised by abnormalities of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and renal
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Rapid Publication. Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure. Abstract. Methods. Introduction
 Rapid Publication Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure Michihisa Jougasaki, Richard J. Rodeheffer, Margaret M. Redfield, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Chi-Ming Wei, Linda J. McKinley, and John
Rapid Publication Cardiac Secretion of Adrenomedullin in Human Heart Failure Michihisa Jougasaki, Richard J. Rodeheffer, Margaret M. Redfield, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Chi-Ming Wei, Linda J. McKinley, and John
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
BODY FLUID. Outline. Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid. Regulation of fluid homeostasis
 BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
Close to site of release (at synapse); binds to receptors in
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
The ability of the kidneys to regulate extracellular fluid volume by altering sodium
 REGULATION OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID VOLUME BY INTEGRATED CONTROL OF SODIUM EXCRETION Joey P. Granger Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
REGULATION OF EXTRACELLULAR FLUID VOLUME BY INTEGRATED CONTROL OF SODIUM EXCRETION Joey P. Granger Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation
 BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
BNP. Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York
 Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York October 10, 2005 1 Outline The Biochemistry of Natriuretic Peptides
Daniel J. Fink, MD, MPH Director, Core Laboratory New York Presbyterian Hospital Columbia University Medical Center New York, New York October 10, 2005 1 Outline The Biochemistry of Natriuretic Peptides
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
The functional genomics of guanylyl cyclase natriuretic peptide receptor-a: Perspectives and paradigms
 MINIREVIEW The functional genomics of guanylyl cyclase natriuretic peptide receptor-a: Perspectives and paradigms Kailash N. Pandey Department of Physiology, Tulane University Health Sciences Center School
MINIREVIEW The functional genomics of guanylyl cyclase natriuretic peptide receptor-a: Perspectives and paradigms Kailash N. Pandey Department of Physiology, Tulane University Health Sciences Center School
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Original Article. Β-Natriuretic Peptide Level as a Predictor for the Severity of LV Dysfunction. Summary:
 BNatriuretic ΒNatriuretic (M.B.Ch.B, M.Sc.)* Hedef Dhafir ElYassin (Ph.D. Post Doctoral) ** Sabbah Yakoob ( M.B.Ch.B, M.R.C.P.) ** Summary: Fac Med Baghdad 2007; Vol.49, No.4 Received July 2006 Accepted
BNatriuretic ΒNatriuretic (M.B.Ch.B, M.Sc.)* Hedef Dhafir ElYassin (Ph.D. Post Doctoral) ** Sabbah Yakoob ( M.B.Ch.B, M.R.C.P.) ** Summary: Fac Med Baghdad 2007; Vol.49, No.4 Received July 2006 Accepted
Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in. Healthy Individuals
 1 Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in Healthy Individuals Jan Krupicka, MD, Tomas Janota, MD, Zdislava Kasalova, MD, Jaromir Hradec, MD 3rd Department of Internal Medicine, 1st
1 Effect of Short-term Maximal Exercise on BNP Plasma Levels in Healthy Individuals Jan Krupicka, MD, Tomas Janota, MD, Zdislava Kasalova, MD, Jaromir Hradec, MD 3rd Department of Internal Medicine, 1st
Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Vert Phys PCB3743 Blood Pressure Fox Chapter 14 part 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. 1 Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure How to Measure Blood Pressure Contribution of vascular resistance to blood pressure Cardiovascular
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System
 Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease. Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018
 Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
Biomarkers in cardiovascular disease Felix J. Rogers, DO, FACOI April 29, 2018 Biomarkers NIH: A biomarker is a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological
A-type (atrial) and B-type (brain) natriuretic peptides (ANP and
 Secretion of A-type and B-type natriuretic peptides into the bloodstream and pericardial space in children with congenital heart disease Yoshio Ootaki, MD, PhD Masahiro Yamaguchi, MD, PhD Naoki Yoshimura,
Secretion of A-type and B-type natriuretic peptides into the bloodstream and pericardial space in children with congenital heart disease Yoshio Ootaki, MD, PhD Masahiro Yamaguchi, MD, PhD Naoki Yoshimura,
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis
 Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion
 Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
Influence of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation Attack on Brain Natriuretic Peptide Secretion Keizo Kazuhiko TSUCHIDA,MD TANABE, MD Abstract Objectives. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide BNP concentration is
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Arg13 of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Reciprocally Modulates Binding to Guanylyl Cyclase but Not Clearance Receptors
 0026-895X/10/7803-431 435$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 78, No. 3 Copyright 2010 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 66084/3615388 Mol Pharmacol 78:431 435, 2010 Printed
0026-895X/10/7803-431 435$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 78, No. 3 Copyright 2010 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 66084/3615388 Mol Pharmacol 78:431 435, 2010 Printed
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
Blood pressure control Contin. Reflex Mechanisms Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 17-12-2018 A. Baroreceptor reflexes Baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the walls of several large systemic arteries( specially
Hormone of the heart & adipose tissues
 Hormone of the heart & adipose tissues Natriuretic hormones The muscle cells in the atria and, to a much lesser extent in the ventricles, contains secretory granules. The granules increase in number when
Hormone of the heart & adipose tissues Natriuretic hormones The muscle cells in the atria and, to a much lesser extent in the ventricles, contains secretory granules. The granules increase in number when
Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are
 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΤΑΓΩΝΙΣΤΕΣ ΑΛΔΟΣΤΕΡΟΝΗΣ ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ MD, FESC. E.Α Κ/Δ Γ.Ν.ΚΑΤΕΡΙΝΗΣ
 ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΤΑΓΩΝΙΣΤΕΣ ΑΛΔΟΣΤΕΡΟΝΗΣ ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ MD, FESC. E.Α Κ/Δ Γ.Ν.ΚΑΤΕΡΙΝΗΣ Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone synthesized by the adrenal glands that has several regulatory
ΚΑΡΔΙΑΚΗ ΑΝΕΠΑΡΚΕΙΑ ΚΑΙ ΑΝΤΑΓΩΝΙΣΤΕΣ ΑΛΔΟΣΤΕΡΟΝΗΣ ΣΠΥΡΟΜΗΤΡΟΣ ΓΕΩΡΓΙΟΣ MD, FESC. E.Α Κ/Δ Γ.Ν.ΚΑΤΕΡΙΝΗΣ Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone synthesized by the adrenal glands that has several regulatory
Brain natriuretic peptide and optimal management of heart failure
 Li et al. / J Zhejiang Univ SCI 2005 6B(9):877-884 877 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 1009-3095 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Brain natriuretic peptide and optimal management
Li et al. / J Zhejiang Univ SCI 2005 6B(9):877-884 877 Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE ISSN 1009-3095 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Brain natriuretic peptide and optimal management
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 9(36) December 2015, Pages: ISSN: Journal home page:
 ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Role of Biochemical Tests Artery Disease (ANP, BNP) in the Evaluation of Patients with Coronary 1 Saad
ISSN:1991-8178 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Role of Biochemical Tests Artery Disease (ANP, BNP) in the Evaluation of Patients with Coronary 1 Saad
Nesiritide: new hope for acute heart failure syndromes?
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement B), B25 B30 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui010 Nesiritide: new hope for acute heart failure syndromes? John C. Burnett* Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement B), B25 B30 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui010 Nesiritide: new hope for acute heart failure syndromes? John C. Burnett* Department of Medicine, Mayo Clinic
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure
 June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
June 28, 2016 Overview & Update on the Utilization of the Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure Linda C. Rogers, PhD, DABCC, FACB. Agenda Overview of the Natriuretic Peptides and Efficacy studies Similarities
BBSG 503, 2009 Section 11: Systems Biology
 BBSG 503, 2009 Section 11: Systems Biology Section Director: W.K. Samson, Ph.D. Classes: April 6-May 1 Study Day: April 30 Progress Exam: May 1 Faculty: W.K. Samson, Ph.D. C-207A 977-8677 samsonwk@slu.edu
BBSG 503, 2009 Section 11: Systems Biology Section Director: W.K. Samson, Ph.D. Classes: April 6-May 1 Study Day: April 30 Progress Exam: May 1 Faculty: W.K. Samson, Ph.D. C-207A 977-8677 samsonwk@slu.edu
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Role of Minerals in Hypertension
 Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
Since atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) was first
 758 Natriuretic Peptides in the Human Kidney Kazuhito Totsune, Kazuhiro Takahashi, Osamu Murakami, Fumitoshi Satoh, Masahiko Sone, Takao Saito, Hironobu Sasano, Toraichi Mouri, Keishi Abe Abstract We studied
758 Natriuretic Peptides in the Human Kidney Kazuhito Totsune, Kazuhiro Takahashi, Osamu Murakami, Fumitoshi Satoh, Masahiko Sone, Takao Saito, Hironobu Sasano, Toraichi Mouri, Keishi Abe Abstract We studied
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance
 Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
A rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay accurately diagnoses left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure: A multicenter evaluation
 Congestive Heart Failure A rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay accurately diagnoses left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure: A multicenter evaluation Stacey J. Wieczorek, PhD, a Alan H. B. Wu,
Congestive Heart Failure A rapid B-type natriuretic peptide assay accurately diagnoses left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure: A multicenter evaluation Stacey J. Wieczorek, PhD, a Alan H. B. Wu,
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure
 Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Blood Pressure Regulation -1
 CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
CVS Physiology Lecture 18 Blood Pressure Regulation -1 Please study the previous sheet before studying this one, even if the first part in this sheet is revision. In the previous lecture we were talking
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management
 Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
Pearls in Acute Heart Failure Management Best Practices Juan M. Aranda Jr., M.D. Professor of Medicine Medical Director of Heart Failure/ Transplant Program University of Florida College of Medicine Disclosures:
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Jonas Addae Medical Sciences, UWI REGULATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Intrinsic Coupling of cardiac and vascular functions - Autoregulation of vessel diameter Extrinsic
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
: ANP mrna. ANP, BNP mrna DEX
 291 Vol. 32, pp. 291300, 2004 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 : 16 8 20 DEX ANP BNP 17 Wistar 19, 20 Wistar DEX 1 mgkg day 2 s.c. 19 21 1 3 5 ANP mrna BNP mrna ANP mrna 1 DEX ANP mrna BNP mrna DEX ANP, BNP mrna DEX ANP
291 Vol. 32, pp. 291300, 2004 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 1 : 16 8 20 DEX ANP BNP 17 Wistar 19, 20 Wistar DEX 1 mgkg day 2 s.c. 19 21 1 3 5 ANP mrna BNP mrna ANP mrna 1 DEX ANP mrna BNP mrna DEX ANP, BNP mrna DEX ANP
Copyright 2011, 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Normal Cardiac Anatomy
 Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Mosby,, an affiliate of Elsevier Normal Cardiac Anatomy Impaired cardiac pumping Results in vasoconstriction & fluid retention Characterized by ventricular dysfunction, reduced exercise tolerance, diminished
Pathophysiology and Clinical Spectrum of Acute Congestive Heart Failure
 SUCCESS WITH HEART FAILURE Pathophysiology and Clinical Spectrum of Acute Congestive Heart Failure Mona Shah, MD,* Vaqar Ali, MD, Sumant Lamba, MD, William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC *Department of Internal
SUCCESS WITH HEART FAILURE Pathophysiology and Clinical Spectrum of Acute Congestive Heart Failure Mona Shah, MD,* Vaqar Ali, MD, Sumant Lamba, MD, William T. Abraham, MD, FACP, FACC *Department of Internal
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
CKD Satellite Symposium
 CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
CKD Satellite Symposium Recommended Therapy by Heart Failure Stage AHA/ACC Task Force on Practice Guideline 2001 Natural History of Heart Failure Patients surviving % Mechanism of death Sudden death 40%
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
