Physiology and Bio Medical Instrumentation 1
|
|
|
- Claire Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Western Technical College Physiology and Bio Medical Instrumentation 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 Total Hours This course is the first of a two-part series introducing the student to human physiology and anatomy, as well as the acquisition of biophysical measurements made in the clinical environment. The primary focus is in the areas of an overview of body systems in general and the cardiovascular system in specific. The course includes weekly 2-hour laboratory sessions at the main campus. Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics Associate Degree Courses Types of Instruction Instruction Type Lecture Lab Credits/Hours 2 CR / 36 HR 1 CR / 36 HR Course History Last Approval Date 5/6/2016 Purpose/Goals Understand basic human physiological systems. Explain the human/machine interface including the limitations and inherent need for safety requirements. Use medical terminology to be able to communicate with medical professionals regarding medical equipment. This course focuses on topics related to details of the cardiovascular system, details of the circulatory system, basics of the digestive system, and basics of the muscular system, and the related medical equipment. Target Population Associate Degree Biomedical Electronics Program Students. Course Outcome Summary - Page 1 of 10
2 Pre/Corequisites Pre/Corequis ite Textbooks Intro to Bio Medical Technology Human Body in Health and Disease. 6th Edition. Copyright Ptton, Kevin T. and Gary A. Thibodeau. Publisher: Elsevier Science. ISBN-13: Required. Biomedical Instrumentation Systems. Copyright Chatterjee, Shakti and Leo Chartrand. Publisher: Cengage Learning. ISBN-13: Required. Biomedical Device Technology Principles and Design. Copyright Chan, Anthony Y. K. Publisher: Charles C Thomas. ISBN-13: Required Physiology and Biomedical Inst. Handouts. Western. Publisher: Western. Required. Bibliography Introduction to Biomedical Equipment Technology, 3rd or 4th ed., by Carr, Joseph J. and Brown, John M. ISBN , copyright 1999, published by Prentice Hill, Inc. Learner Supplies Two, 2-3 three-ring binders. Vendor: Campus Shop. Required. Core Abilities 1. Apply mathematical concepts Make decisions that incorporate the importance of sustainability Use technology effectively. Program Outcomes 1. Manage medical equipment and systems Type TSA Summative 1.1. Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET) practice exam 1.1. You install and assemble medical equipment Course Outcome Summary - Page 2 of 10
3 1.2. You operate basic medical equipment 1.3. You maintain medical equipment 1.4. You repair/troubleshoot medical equipment 1.5. You calibrate equipment 1.6. You verify medical equipment is working correctly 1.7. You assist users with medical equipment 1.8. You document activities 1.9. You use hand tools You use medical test equipment You adhere to industry codes and standards 2. Problem-solve electronic circuits and systems Type TSA Summative 2.1. Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET) practice exam 2.1. You interpret basic schematic circuitry 2.2. You use various electronic testing devices 2.3. You troubleshoot electronic circuits 2.4. You repair electronic circuits 2.5. You perform basic soldering skills 3. Apply principles of anatomy, physiology, and medical terminology Summative 3.1. Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET) practice exam 3.1. You communicate with clinical staff 3.2. You use appropriate medical terminology related to medical equipment supported 3.3. You recognize the interaction of medical equipment with the human body 4. Demonstrate safety precautions and practices with medical equipment Type TSA Summative 4.1. Certified Biomedical Equipment Technician (CBET) practice exam 4.1. You follow SDS guidelines 4.2. You follow classroom/clinical site safety guidelines 4.3. You comply with clinical site mandatory education regarding health risks and safety practices 4.4. You dispose/recycle of equipment and batteries in an environmentally safe manner 5. Demonstrate professionalism Type Local Summative 5.1. Internship Evaluation 5.1. You arrive for work on time 5.2. You manage time effectively 5.3. You dress professionally 5.4. You act ethically 5.5. You act as a member of the team 5.6. You are tactful and understanding when working with diverse groups of people 5.7. You demonstrate attention to detail and follow direction with a willingness to implement solutions for the best possible outcomes Course Outcome Summary - Page 3 of 10
4 5.8. You provide customer service with confidence; recognize limitations and ask for assistance 5.9. You adhere to HIPAA requirements Course Competencies 1. Utilize medical terminology in communications. Domain Cognitive Level Applying 1.1. Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 1.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests You identify the following component parts: prefix, suffix, combining vowel, combining form, and root You define common prefixes, suffixes, combining vowels, combining forms, and roots You combine component parts to determine complete term meaning. 1.a. Break terms into component parts. 1.b. Define common medical terminology component parts. 1.c. Define complete medical terms. 2. Describe basic human physiology. Domain Cognitive Level Applying 2.1. Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 2.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your basic definitions include: anatomy, physiology, disease, pathology, homeostasis, feedback, and levels of organization You relate body position to make sense of directional terms You define locations using anatomical directions, planes/body sections, depth, body cavities, and body regions Your chemistry explanations include chemistry building blocks, bonding, organic/inorganic, water chemistry, ph, and major types of organic molecules Your explanation of cells and tissues includes major cell components, organelles, active/passive transport, DNA/RNA, cell reproduction, and structure/function of cells to tissues You use appropriate human physiology terminology on all assigned activities. 2.a. Define terms related to human physiology. 2.b. Define terms related to body positions. 2.c. Define terms related to locations in the body. 2.d. Explain basic chemistry of the cell and organism. Course Outcome Summary - Page 4 of 10
5 2.e. Explain the structures and functions of a cell and tissues. 3. Explain the major human body systems. Domain Cognitive Level Applying 3.1. Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 3.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your explanation includes the major functions of each system Your explanation includes the major anatomy and organs of each system Your explanation lists medical equipment used with each system including the name and purpose of that equipment You use appropriate body system terminology on all assigned activities. 3.a. Explain major body systems including: cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine, integumentary, lymphatic/immune, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, skeletal, and urinary. 3.b. Describe medical equipment used with each body system. 4. Explain the major structures of the human cardiovascular system. Domain Cognitive Level Analyzing 4.1. Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 4.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests You identify anatomy including the heart location/orientation in body, heart chambers, heart sides, heart valves, sounds from anatomy, major arteries/veins, blood flow path, EKG relationship to anatomy, and common anatomy disorders You include the function of each part of anatomy including the heart location/orientation in body, heart chambers, heart sides, heart valves, major arteries/veins, and blood flow path Your explanation of the electrical conduction system includes the anatomical components, their function, and relationship to the PQRST signal and heart actions You include the following parts of the electrical conduction system: SA node, intermodal pathway, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches, purkinje fibers, electrical path, timing of electrical signal, and disorders You use appropriate cardiovascular system terminology on all assigned activities. 4.a. Explain anatomy of the cardiovascular system. 4.b. Explain the electrical conduction system of the heart. 5. Explain the cardiac operation of the human cardiovascular system. Course Outcome Summary - Page 5 of 10
6 Domain Cognitive Level Analyzing Apply mathematical concepts Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 5.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your explanation of the action potential includes ionic vs electronic current, polarization, depolarization, cardiac muscle contraction, timing, and variation between action potentials of muscles/heart/nerves You explain the cardiac cycle including the relationships between the anatomy, electrical conduction, blood flow, EKG wave, heart sounds, pressures, valve actions, systole, diastole, and graphs of all parameters Your explanation of cardiac cycle includes average values and definitions of cardiac cycle, stroke volume, cardiac output, and heart rate Your explanation of cardiac output includes formula relating cardiac output/heart rate/stroke volume, typical values, and measurement methods You use appropriate cardiovascular system terminology on all assigned activities. 5.a. Explain the action potential and how it relates to an EKG and heart actions. 5.b. Explain the cardiac cycle. 5.c. Explain cardiac output. 6. Explain cardiovascular disorders and the related medical equipment. Domain Cognitive Level Analyzing Apply mathematical concepts Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 6.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your explanation of medical equipment used on the cardiovascular system includes its name, and purpose Your explanation distinguishes between the types of information that can be obtained with 3, 5, 6, and 12 lead EKG including distinguishing what portions of the heart are focused on and the difference between monitoring EKG and diagnostic EKG Your explanation of EKG includes Einthoven s triangle, electrode labels, relationship between electrodes/wires/leads, limb leads, augmented leads, and chest leads Your explanation of the parts of an EKG signal includes identifying and listing timing of segments, waves, and intervals of the PQRST wave and stating how monitors use this timing information to provide an analysis of the EKG to assist in diagnosis or patient care Your explanation of the lead equations includes stating the equations You include the following common cardiovascular disorders, myocardial infarction, valve problems, Course Outcome Summary - Page 6 of 10
7 anatomic abnormalities, atherosclerosis, angina pectoris, thrombus, common dysrhythmias, and heart failure You use appropriate cardiovascular system terminology on all assigned activities. 6.a. Describe medical equipment used with the cardiovascular system. 6.b. Describe electrocardiography. 6.c. Explain the parts of an EKG electrical signal. 6.d. Explain the lead equations used to obtain an EKG. 6.e. Explain common cardiovascular disorders. 7. Maintain medical equipment related to the human cardiovascular system. Domain Psychomotor Level Practicing Apply mathematical concepts. Make decisions that incorporate the importance of sustainability. Use technology effectively Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 7.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests You relate resistance, voltage values, and current values to acquiring an EKG with electrodes including the requirements for skin prep to reduce resistance and the requirement for high input impedance to avoid losing the signal Your explanation of EKG equipment includes relationship between electrodes/wires/leads, noise reduction, circuit isolation, and circuitry required to obtain lead signals Your lab report adheres to format presented in class including cover page, purpose, equipment, procedure, data, analysis, and conclusion Your lab report requires specific concrete statements of clear information using correct grammar and must answer specific lab questions You use a multi-parameter simulator and safety analyzer to test an EKG monitor You operate an EKG monitor to obtain an actual EKG signal, analyze the signal, and simulate faults with signal acquisition You include an explanation of the circuit blocks of an EKG monitor including circuit isolation, amplifiers, and filters You analyze EKG tracings to determine the equipment fault focusing on electrode problems and filter problems You operate equipment to obtain heart rates researching the theory of operation of each piece of equipment, comparing heart rates obtained, comparing the capabilities of each piece of equipment, and determining appropriate procedures to test the equipment You use appropriate cardiovascular system terminology and electronics terminology on all assigned activities You adhere to lab safety precautions while working on medical equipment related to the cardiovascular system. 7.a. Apply basic electronic knowledge to the acquisition an ECG signal. 7.b. Explain 3, 6, and 12 lead EKG equipment. 7.c. Use a lab report to present results of cardiovascular system medical equipment labs when assigned. 7.d. Test an EKG monitor. 7.e. Operate medical equipment capable of being used to obtain a heart rate. 8. Explain the human circulatory system. Course Outcome Summary - Page 7 of 10
8 Domain Cognitive Level Analyzing 8.1. Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 8.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your explanation of blood vessels includes the structure and functions of arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, and capillaries Your explanation of circulation of blood includes the systemic, pulmonary, hepatic portal, and fetal circulation Your explanation of control of localized blood flow includes concepts of capillary bed control, osmosis, hydrostatic pressures, osmotic pressures, autoregulation, chemical controls, ph, CO2/O2 concentration gradients, nutrient gradients, body temperature, capillary anatomy, and diffusion Your explanation includes the following disorders of the circulatory system: arteriosclerosis, varicose veins, thrombus, pulmonary embolism, aneurysm, cerebrovascular accident/stroke, hypertension, and hypotension You use appropriate circulatory system terminology on all assigned activities. 8.a. Describe blood vessels. 8.b. Describe the circulation of blood. 8.c. Describe control of localized blood flow. 8.d. Describe disorders of the circulatory system. 9. Explain blood pressure. Domain Cognitive Level Analyzing Apply mathematical concepts Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to 9.2. Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your explanation of blood pressure includes its definition and the values in different parts of the circulatory system You explain the role of the artery elasticity in arterial circulation, and the muscular pump and respiratory pump in venous circulation Your explanation of blood pressure includes a definition and a graph of pressure in time of the following: systolic, diastolic, dicrotic notch, pulse pressure, mean arterial pressure You include the mathematical relationships of pulse pressure/systolic pressure/diastolic pressure and mean arterial pressure/diastolic pressure/pulse pressure You explain the oscillometric and asculcatory methods of acquiring blood pressure including the blocks of equipment required to make those measurements You explain factors influencing blood pressure including the roles of and descriptions of peripheral Course Outcome Summary - Page 8 of 10
9 resistance, cardiac output, blood volume, and vessel elasticity You include an explanation of determining blood pressure with a stethoscope and cuff by listening to the sounds of the blood in the artery You include an explanation of obtaining blood pressure non-invasivly (NIBP) and invasively Your explanation of blood pressure regulation includes short term mechanisms (vessel diameter, heart rate, contractility) and long term mechanisms (blood volume) You use appropriate circulatory system terminology on all assigned activities. 9.a. Explain the acquisition of blood pressures. 9.b. Explain factors influencing blood pressure. 9.c. Describe how the blood pressure is regulated by the body. 10. Maintain medical equipment related to the human circulatory system. Domain Psychomotor Level Practicing Apply mathematical concepts. Make decisions that incorporate the importance of sustainability. Use technology effectively Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests You test a NIBP monitor using documentation, a simulator, and a subject to determine accuracy, function, and safety characteristics You include the identification and function of the major blocks of a NIBP monitor including possible failures You use appropriate circulatory system terminology and electronics terminology on all assigned activities You adhere to lab safety precautions while working on medical equipment related to the circulatory system. 10.a. Maintain NIBP monitors. 11. Explain the basics of the human digestive system. Domain Cognitive Level Applying Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your functional explanation includes gastrointestinal, chemical and mechanical breakdown of foods, Course Outcome Summary - Page 9 of 10
10 enzyme actions, and absorption You identify and list the function of the following anatomy of the digestive system: mouth, uvula, palate, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, appendix, large intestine, colon, rectum, sphincters, wall structure, salivary glands, liver, and pancreas Your explanation of medical equipment related to the digestive system includes listing the names and function of different types of scopes used in endoscopy, feeding pumps, suction units, surgical equipment, and imaging equipment Your list of major disorders includes: cancer, reflux, gallstones, ulcers, cleft lip/palate, ulcers, appendicitis, inflammation, celiac, diverticulosis, and polyps You use appropriate digestive system terminology on all assigned activities. 11.a. Explain the function of the digestive system. 11.b. Describe the major anatomy of the digestive system. 11.c. Explain the use of medical equipment on the human digestive system. 11.d. List major disorders of the digestive system. 12. Explain the basics of the human muscular system. Domain Cognitive Level Applying Participation in assigned activities including classroom discussions, observation of and responses to Skill demonstration in simulated or actual situations Objective tests Your comparison of muscle types includes: cell shapes, nuclei, striations, voluntary/involuntary control, locations in the body, and functions Your explanation of skeletal muscles includes: muscle fibers, tendons, bursae, posture, fatigue, types of movements produced, and temperature control Your explanation of medical equipment related to the muscular system includes the name and function of the following: EMG, imaging equipment, scopes, and physical therapy equipment You use appropriate muscular system terminology on all assigned activities. 12.a. Compare the characteristics of the different types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiovascular. 12.b. Describe the basics of the skeletal muscle system. 12.c. Explain the use of medical equipment on the muscular system. Course Outcome Summary - Page 10 of 10
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number:
 Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number: 25.44000 Course Description: Anatomy and Physiology is a vital part of most healthcare post-secondary education programs. The Essentials
Health Science Career Cluster Essentials of Healthcare Course Number: 25.44000 Course Description: Anatomy and Physiology is a vital part of most healthcare post-secondary education programs. The Essentials
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Essentials of Healthcare
 Essentials of Healthcare Georgia 25.44000-2013 This document provides the correlation between interactive e-learning curriculum, and the Essentials of Healthcare standards, published by the state of Georgia.
Essentials of Healthcare Georgia 25.44000-2013 This document provides the correlation between interactive e-learning curriculum, and the Essentials of Healthcare standards, published by the state of Georgia.
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21)
 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb,
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Six main classes of blood vessels (on handout) Wall structure of arteries and veins (on handout) Comparison: Arteries vs. Veins (on handout)
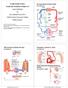 Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Circulation (Chapter 21) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Six main classes of blood vessels Primary Sources
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
CORE MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Outline. Electrical Activity of the Human Heart. What is the Heart? The Heart as a Pump. Anatomy of the Heart. The Hard Work
 Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
MURRAY STATE UNIVERSITY COURSE SYLLABUS. DEPARTMENT: Wellness and Therapeutic Sciences CREDIT HOURS: 3.0 COURSE NUMBER: EXS 250 Spring 2002
 MURRAY STATE UNIVERSITY COURSE SYLLABUS DEPARTMENT: Wellness and Therapeutic Sciences CREDIT HOURS: 3.0 COURSE NUMBER: EXS 250 Spring 2002 I. TITLE: Fundamentals of Exercise Physiology II. III. IV. CATALOG
MURRAY STATE UNIVERSITY COURSE SYLLABUS DEPARTMENT: Wellness and Therapeutic Sciences CREDIT HOURS: 3.0 COURSE NUMBER: EXS 250 Spring 2002 I. TITLE: Fundamentals of Exercise Physiology II. III. IV. CATALOG
Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb 2016
 A Correlation of Marieb 2016 To the for Science A Correlation of, Science, HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes 1. Develop and use models and appropriate SE:
A Correlation of Marieb 2016 To the for Science A Correlation of, Science, HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes 1. Develop and use models and appropriate SE:
b) List the steps that may occur in hemostasis with a brief explanation of what happens in those steps.
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Physical Therapist Assistant Therapeutic Modalities
 Western Technical College 10524143 Physical Therapist Assistant Therapeutic Modalities Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total
Western Technical College 10524143 Physical Therapist Assistant Therapeutic Modalities Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total
Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / /
 Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB
 BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) PRESENTED AND APPROVED: JANUARY 12, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FA 2012-13 Prefix & Number BIO 202 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
BIO 202 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II with LAB (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) PRESENTED AND APPROVED: JANUARY 12, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FA 2012-13 Prefix & Number BIO 202 Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology I Purpose
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Syllabus. BIO 110 Fundamentals of Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Syllabus BIO 110 Fundamentals of Human Anatomy and Physiology General Information Date May 23rd, 2018 Author Christy Parker Department Science and Technology Course Prefix BIO Course Number 110 Course
Syllabus BIO 110 Fundamentals of Human Anatomy and Physiology General Information Date May 23rd, 2018 Author Christy Parker Department Science and Technology Course Prefix BIO Course Number 110 Course
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science
 Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
Geneva CUSD 304 Content-Area Curriculum Frameworks Grades 6-12 Science Mission Statement The Mission of Science Education Is: 1) To nurture an active interest in science that continues throughout life.
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes. Pulmonary Circulation H E A R T. Systemic Circulation
 The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
The Cardiovascular System: Vessels and Routes 1. Overview of Blood Circulation A. Pulmonary Circulation Lung Arterioles Pulmonary Artery Capillaries Pulmonary Circulation Venules Pulmonary Veins H E A
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Heart. Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat
 Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Lassen Community College Course Outline. I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body.
 Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
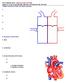 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Circulatory System. Functions and Components of the Circulatory System. Chapter 13 Outline. Chapter 13
 Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
TEST 5. Module 9 & 10
 TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Circulatory System. - Consists of a pumping heart and blood vessels. Two types of circulatory fluids: Blood OR Hemolymph
 Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
General Anatomy & Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Circulatory System Function Move circulatory fluid (blood) around body Gas Transport Nutrient Transport Excretory Product Transport
 Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION
 66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
66 EI2311 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION 1. What is meant by cell? UNIT I PHYSIOLOGY AND TRANSDUCERS The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
