HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Lloyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LECTURE #5 1
2 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The Nervous System The Endocrine Glands The Hemopoietic System The Circulatory System The Respiratory Tract The Digestive Tract The Urinary Tract The Reproductory System The Locomotor System The Skin E. MORAN
3 THE BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS (THE HEMOPOIETIC SYSTEM) 3
4 Blood E. MORAN
5 BLOOD COMPONENTS Plasma Cells: Red blood cells (RBC or erythrocytes) White blood cells (WBC): Granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils Lymphocytes: T- and B-lymphocytes Monocytes - macrphages Platelets E. MORAN
6 CELLULAR BLOOD COMPONENTS RBC - carry Oxygen and CO 2 WBC Various functions Neutrophils Fight infections Lymphocytes Active in immune responses Monocytes Promote neutrophils Eosinophils Active in allergy Platelets - essential in initiating blood clotting E. MORAN
7 Blood film (smear) to show: Red blood cells, white blood cells (neutrophils), and a platelet E. MORAN
8 DEVELOPMENT OF THE GRANULOCYTES E. MORAN
9 LIFETIME OF BLOOD CELLS RBC 120 days WBC days Platelets ~ one week E. MORAN
10 LACK OF RED BLOOD CELLS (ANEMIA) Bone marrow failure: Leukemia, lymphoma Nutritional deficiencies: Iron, Folate, Vitamin B 12 Destruction of RBC s: Inherited abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobinopathy) (Sickle cell anemia) Auto-immune hemolytic anemia E. MORAN
11
12 SICKLE CELLS E. MORAN
13 SICKLE CELLS PLUGGING BLOOD VESSEL E. MORAN
14 BLOOD CLOTTING 14
15 15
16 THE COAGULATION CASCADE 16
17 BLOOD COAGULATION (CLOTTING) Blood changing from liquid to a gel state in 7-8 min. The gel is the clot (thrombus) and the liquid is called serum. 1. Damaged endothelial surface of vessels or slow blood movement (stasis) activation, adhesion, and aggregation of platelets (platelet plug) 2. Prothrombin in plasma changes to thrombin 3. Thrombin changes fibrinogen (soluble in blood) into fibrin 4. Fibrin + RBC s form a clot (thrombus) 5. Thrombus will be digested by fibrinolysis. E. MORAN
18 ANTICOAGULATION Anti-platelets medications: aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix) interfere with platelets function and impede their agglutination Anticoagulants: Warfarin, coumadin affect the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X) Heparin action of antithrombin and factor Xa. Newer drugs interfere with the enzymatic action of coagulation factors E. MORAN
19 BLOOD GROUPS AND TRANSFUSION 19
20 BLOOD TYPES (GROUPS) Classification of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of RBC s. Contributions from both parents Some of these antigens may be present on the surface of other cells. >600 Ag s in 33 blood groups. Some types are related to resistance to diseases (absence of Duffy Ag. resistance to malaria) E. MORAN
21 BLOOD TYPES ABO System (C. Landsteiner, 1901) A Anti-B antibody. B Anti-A antibody. AB No antibody. Universal recipient. O Anti-A and Anti-B antibody. Universal donor Rh System (A. Wiener, 1937) Positive (+) Anti Rh factor antibody present Negative (-) Anti-Rh factor antibody absent E. MORAN
22 RED BLOOD CELL COMPATIBILITY 22
23 BLOOD TRANSFUSION Blood banks Blood products: Packed RBC s Plasma Platelets Cryoprecipitate Fresh frozen plasma (factors V and VIII) Cross matching for compatible RBC s E. MORAN
24 BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS Cross-matching No agglutination of RBC s Transfusion of incompatible blood causes destruction of the recipient s RBC, (hemolysis), renal failure, shock, and possible death If an Rh (-) woman receives Rh (+) blood she gets sensitized to the Rh factor (develops anti-rh antibodies). If later she is pregnant with an Rh (+) baby, she may risk to cause massive destruction of baby s RBC (hemolytic disease of the newborn) E. MORAN
25 ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION Definition: Moving tissues/organs from one site of a person to another person (allografts) or tissues/organs from one body to another site of the same (autografts). Autografts: Blood, vessels, skin Isografts: Identical twins - Genetically identical, cannot trigger an immune response Allografts: Between two non-identical persons Xenografts: Porcine heart valve E. MORAN
26 ALLOGRAFTS - SOURCES Living persons: Single kidney, partial liver, lung lobe, intestine Brain death or circulatory death: Kidney, liver, heart, lungs, intestine, thymus. Cornea, bone marrow, bones, tendons Recovery of tissues/organs up to 24 hrs. after last heart beat Best outcomes when using brain death sources Tissues may be banked for up to 5 years Bioethical issues: Definition of death, Consent, Pay Organ sales are illegal E. MORAN
27 ALLOGRAFTS (CONT D) Dr. P. Medawar: Tissue rejection, Graft vs. Host reaction. Immunosuppressive therapy Non-identical require ABO and tissue antigens compatibility Cyclosporine treatment USA, United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) - Identification and allocation of organs from deceased persons E. MORAN
28 PATHOLOGY OF BLOOD CELLS Decreased production: Diseases of the bone marrow Increased destruction: Usually in the blood. Congenital or acquired E. MORAN
29 CHANGES IN THE NUMBER OF BLOOD CELLS Decreased number of cells: Red cells Anemia White cells Infections Platelets Bleeding Increased number of cells: Red cells Erythrocytosis Polycythemia White cells Leukocytosis in infections Leukemia Platelets Thrombocytosis - Thrombocythemia E. MORAN
30 LACK OF RED BLOOD CELLS (ANEMIA) Bone marrow failure: Leukemia, lymphoma Nutritional deficiencies: Iron, Folate, Vitamin B 12 Destruction of RBC s: Inherited abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobinopathy) (Sickle cell anemia) Auto-immune hemolytic anemia Symptoms: Weakness, dizziness E. MORAN
31 BLOOD CLOTTING 31
32 32
33 THE COAGULATION CASCADE 33
34 BLOOD COAGULATION (CLOTTING) Blood changing from liquid to a gel state in 7-8 min. The gel is the clot (thrombus) and the liquid is called serum. 1. Damaged endothelial surface of vessels or slow blood movement (stasis) activation, adhesion, and aggregation of platelets (platelet plug) 2. Prothrombin in plasma changes to thrombin 3. Thrombin changes fibrinogen (soluble in blood) into fibrin 4. Fibrin + RBC s form a clot (thrombus) 5. Thrombus will be digested by fibrinolysis. E. MORAN
35 ANTICOAGULATION Anti-platelets medications: aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix) interfere with platelets function and impede their agglutination Anticoagulants: Warfarin, coumadin affect the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X) Heparin action of antithrombin and factor Xa. Newer drugs interfere with the enzymatic action of coagulation factors E. MORAN
36 INTERMISSION 36
37 Infectious Mononucleosis 37
38 38
39 Infectious Mononucleosis 39
40 Clinically: ACUTE VS. CHRONIC LEUKEMIA Acute leukemia: Acute course, with bleeding, infections Chronic leukemia: Course is chronic - years Microscopically: Acute: Primitive bone marrow cells with poor differentiation in the bone marrow and in the blood Chronic: Relatively differentiated bone marrow cells in the blood E. MORAN
41 ACUTE LEUKEMIA 41
42 42
43 HOMEOSTASIS OF THE BLOOD 43
44 Genetic factors Viral infection ACUTE LEUKEMIA ETIOLOGY Radiation exposure Chemicals exposure E. MORAN
45 ACUTE LEUKEMIA ETIOLOGY GENETIC FACTORS Chromosome imbalance: Down s syndrome Other aneuploidies Chromosome breakage: Bloom s syndrome Fanconi s syndrome Ataxia telangiectasia Genetic susceptibility : Familial (?) Coexistent neoplasm (?) E. MORAN
46 ACUTE LEUKEMIA ETIOLOGY VIRAL LEUKEMOGENESIS In animals: Experimental evidence In humans: Viruses and virus-like particles in leukemic cells and plasma of patients Are viruses bystanders? Are viruses co-carcinogens? Koch s postulate not fulfilled E. MORAN
47 ACUTE LEUKEMIA ETIOLOGY RADIATION EXPOSURE In the general population: Survivors of the atomic bomb explosions (Japan, 1945) Radiologists exposed to ionizing radiation In patients treated for other diseases: Ankylosing spondylitis Thymus radiation in childhood Diagnostic tests: Unknown dose threshold E. MORAN
48 LEUKEMIA BURDEN OF SUFFERING US 2015 Est. new cases 54,270 Acute lymphocytic leukemia 6,250 Chronic lymphocytic leukemia 14,620 Acute myeloid leukemia 20,830 Chronic myeloid leukemia 6,660 Other leukemias 5,910 E. MORAN
49 LEUKEMIA - SYMPTOMS Weakness, fatigue Recurrent infections Bleeding, gum bleeding Bone pain Anorexia E. MORAN
50 A child with bleeding in the mouth mucosa had low platelets E. MORAN
51 E. MORAN
52 BLEEDING INTO THE BRAIN IN LEUKEMIA B/O LOW PLATELETS E. MORAN
53 CHRONIC LEUKEMIAS Polycythemia rubra vera (P. vera) Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML or CGL) Chronic lymphatic leukemia E. MORAN
54 E. MORAN
55 CLOTTED BLOOD THE WHITE CELL COUNT WAS 1,000,000/CCM E. MORAN
56 TREATMENT OF LEUKEMIA Acute leukemia (lymphatic and myeloid): Chemotherapy Bone marrow transplantation Chronic lymphatic leukemia: Chemotherapy Chronic myeloid leukemia: Chemotherapy BMT (?) Polycythemia rubra vera: Phlebotomies Chemotherapy E. MORAN
57 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 57
58 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Intercellular spaces Lymphatic capillaries Lymphatic vessels (afferent and efferent) Lymph nodes, spleen (see the Immune System) Thoracic duct Blood Spleen Thymus E. MORAN
59 E. MORAN
60 LYMPH NODE STRUCTURE - SCHEMA E. MORAN
61 The Spleen E. MORAN
62 mmm muscles The Female Breast E. MORAN
63 DISEASES OF THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Obstruction to the lymph flow Edema Draining infected areas Lymphadenitis Cancer: Lymphomas, Hodgkin s disease, Leukemia E. MORAN
64 ENLARGED GLANDS (LYMPHADENOPATHY) Subjective: tender or painless Objective: Acute or chronic Local or general Isolated or matted glands Differential diagnosis: Chronic infections Cancer Diagnosis: Biopsy and pathologic examination No needle biopsy E. MORAN
65 Left cervical lymphadenopathy (Enlarged lymph nodes) 65
66 Hodgkin s disease of the mediastinum with metastases to the right cervical area 66
67 CONSTITUTIONAL SYMPTOMS Weakness, fatigue Unexplained fever Night sweats Lack of appetite, weight loss Alcohol-induced pain at the site of the cancer E. MORAN
68 E. MORAN
69 EVALUATION OF HODGKIN S DISEASE AND LYMPHOMA Physical examination Laboratory profile CT or PET CT scan Other tests as indicated by the presentation E. MORAN
70 E. MORAN
71 E. MORAN
72 E. MORAN
73 LYMPHOMAS OTHER THAN HODGKIN S DISEASE Classified by their rate of proliferation: Low-grade Intermediate grade Hi-grade E. MORAN
74 ABDOMINAL CT SCAN IN A PATIENT WITH LYMPHOMA E. MORAN
75 LARGE CELL LYMPHOMA E. MORAN
76 High-grade lymphoma involving the floor of the mouth 76
77 HIGH-GRADE LYMPHOMA OF THE LT. TONSIL 77
78 TREATMENT OF LYMPHOMAS Low-grade (Indolent) lymphomas: Observation Chemotherapy at time of progression +/- Radiation High-grade (aggressive) lymphomas: Chemotherapy Bone marrow transplantation Multiple myeloma: Chemotherapy + BMT E. MORAN
79 BURKITT s LYMPHOMA 79
80 MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES PLAQUE and TUMOR STAGE 80
81 MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES TUMOR STAGE E. MORAN
82 MULTIPLE MYELOMA C = Serum calcium elevated R = Renal (kidney) failure A = Anemia B = Bone lesions E. MORAN
83 KAPOSI s SARCOMA (KS) 83
84 E. MORAN
85 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The Nervous System The Endocrine Glands The Hemopoietic System The Circulatory System The Respiratory Tract The Digestive Tract The Urinary Tract The Reproductory System The Locomotor System The Skin E. MORAN
86 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Heart 2. Arteries 3. Capillaries 4. Veins E. MORAN
87 87
88 The Coronary Arteries Lt. coronary artery Lt. circumflex art. Lt. anterior descending Rt. coronary artery 88
89 The Heart Chambers - schema 89
90 Heart autonomous conduction system 90
91 Heart s conduction system 91
92 THE HEART CHAMBERS, VALVES, AND CIRCULATION 92
93 Blood Circulation 93
94 RESPIRATION BLOOD-GAS EXCHANGES Heart Lung Heart Rt. Atrium Rt. Ventricle Pulmonary artery Release oxygen Get carbon dioxide Lt. atrium Lt. ventricle Systemic circulation E. MORAN
95 Schema of an artery wall Endothelium Tunica media Tunica externa Tunica intima 95
96 Artery and Vein structures 96
97 Schema of an artery and vein wall 97
98 ATHEROSCLEOSIS 98
99 ATHEROMA PLAQUE 99
100 ATHEROMA AND THROMBUS 100
101 VASCULAR ISCHEMIC EVENTS (I) Acute - d/t closure of blood supply by a blood clot (thrombus) or by a circulating clot, tumor, gas, fat (embolus) Chronic - d/t narrowing of arteries by: Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries Atheroma plaque E. MORAN
102 VASCULAR ISCHEMIC EVENTS (II) Brain Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or Cerebral vascular accident (CVA, Stroke) Heart Angina, or Heart attack (Myocardial infarct or MI) Limbs Claudication, Peripheral vascular insufficiency (PVI) Lung Pulmonary infarct Kidney, Spleen - Infarcts E. MORAN
103 Tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) Angioplasty Intracoronary stent placement Antiplatelets: aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix) Physical exercise Lifestyle Diet Weight reduction CORONARY THROMBOSIS TREATMENT E. MORAN
104 Stent with balloon angioplasty 104
105 Tissue plasminogen activator (tpa) Angioplasty Intracoronary stent placement Antiplatelets: aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix) Physical exercise Lifestyle Diet Weight reduction CORONARY THROMBOSIS TREATMENT E. MORAN
106 AORTIC STENOSIS 106
107 AORTIC STENOSIS 107
108 AORTIC STENOSIS SYMPTOMS Usually present in the advanced stage: 1. Syncope (loss of consciousness) 2. Anginal chest pain 3. Shortness of breath with effort Later, dyspnea at rest (PND, edema) E. MORAN
109 MITRAL VALVE MECHANISMS 109
110 MITRAL VALVE DISEASES 110
111 MITRAL VALVE STENOSIS (NARROWING) 111
112 Shortness of breath (dyspnea) Fast breathing (tachypnea) Sleeping with more than one pillow (orthopnea) Weakness or dizziness Panic attack Swelling of ankles and feet (edema) Rapid weight gain Rapid pulse VALVULAR HEART DISEASE SYMPTOMS Cough of frothy sputum E. MORAN
113 CARDIAC MEDICATIONS Water pills (diuretics) remove fluid accumulated in tissues Beta-blockers Slow the heart rate - Lower the blood pressure ACE inhibitors Treat hypertension Vasodilators Reduce the heart work Anti-arrhythmic medications Blood thinners Anticoagulants Digitalis Oldest heart medication E. MORAN
114 Vein thrombus and embolus 114
115 Vein blood clot (thrombus) 115
116 DVT PREVENTION 1. Active lifestyle 2. Manage your weight 3. No smoking 4. Check BP 5. (?) Family hx. of blood clotting 6. Alternatives to birth control pills 7. Walk/leg stretches on long airplane trips E. MORAN
117 END OF LECTURE #5 117
CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 LECTURE #4 1 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 2 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY T-lymphocytes (activated in the thymus) identify aggressors and try to destroy them through the production of lymphokines (synthesized proteins) Killer
LECTURE #4 1 LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 2 CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY T-lymphocytes (activated in the thymus) identify aggressors and try to destroy them through the production of lymphokines (synthesized proteins) Killer
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Blood. Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11
 Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood. Functions:
 Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Functions: Transports nutrients, oxygen, cellular waste products, and hormones Aids in distribution of heat Regulates acid-base balance Helps protect against infection
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD. MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 14: BLOOD MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. BLOOD A connective tissue Average volume of 5 liters (70 kg male) 45% solid cells or formed elements (hematocrit [HCT] quantitation)
Chapter 11. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 11 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Blood Clotting Functions of Blood Transportation
 1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
1 CH 11 Blood OUTLINE: Functions of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Cell Disorders Blood Types Functions of Blood Transportation Protection Regulation ph Temperature Composition of Blood Plasma: liquid
Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System
 Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood. Multiple Choice
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice 1) The matrix of blood is called: A) buffy coat B) plasma C) erythrocytes D) lymphocytes E) formed elements Diff: 1 Page
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice 1) The matrix of blood is called: A) buffy coat B) plasma C) erythrocytes D) lymphocytes E) formed elements Diff: 1 Page
4/5/17. Blood. Blood. Outline. Blood: An Overview. Functions of Blood
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Branch of medicine that deals with blood, its formation and disorders is called. Three main functions of cardiovascular system are,, and.
 Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
Chapter 19 The Blood Human body must maintain a balance called. Body fluid inside the cells is called fluid; that outside is called or fluid. Two major fluid networks that help in connecting cells are
Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012
 Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012 1. Leukocytes are attracted to a site of injury or disease by: a. diapedesis b. chemotaxis c. leukocytosis d. heparin e. leukomotosis 2. Leukocytes leave
Blood Lecture Test Questions Set 2 Summer 2012 1. Leukocytes are attracted to a site of injury or disease by: a. diapedesis b. chemotaxis c. leukocytosis d. heparin e. leukomotosis 2. Leukocytes leave
Hematology. The Study of blood
 Hematology The Study of blood Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Composition: PLASMA liquid portion of blood without cellular components Serum plasma after a blood clot is formed Cellular elements are
Hematology The Study of blood Average adult = 8-10 pints of blood Composition: PLASMA liquid portion of blood without cellular components Serum plasma after a blood clot is formed Cellular elements are
Blood. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 11 Blood Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu Community
Chapter 13 The Blood
 Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Chapter 13 The Blood Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms agglutination erythrocyte lymphocyte albumin fibrin megakaryocyte anemia hematocrit monocyte antigen
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.1 Blood
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.1 Blood Blood Function Function Nutritive Respiratory Excretory Regulatory Protective Effects on Body Transporting nutrient molecules (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Blood. The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue. Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma
 Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Blood Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body Classified as a connective tissue Living cells = formed elements Non-living matrix = plasma Blood Physical Characteristics of Blood Color range Oxygen-rich
Functions of Blood. Transport. Transport. Defense. Regulation. Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Unit 6 Cardiovascular System: Blood Functions of Blood With each beat of the heart, approximately 75 ml of blood is pumped On average, the heart beats 70 times per minute Every minute, the heart pumps
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. 2012 Pearson Permission Education,
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Chapter 46. Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder
 Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 06 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood Multiple Choice Part I Questions
 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e (Marieb) Chapter 10 Blood 10.1 Multiple Choice Part I Questions Using Figure 10.1, identify the following: 1) The neutrophil is indicated by. A) Label A
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved
 Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Bio 100 Guide 21 Blood consists of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma Blood is about 55% plasma and 45% cellular elements Plasma 90% water 10% dissolved inorganic ions, proteins, nutrients,
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Unit 10 - Blood The only fluid tissue in the human body. c) Plasma rises to the top (55% of blood)
 Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Unit 10 - Blood 1 I. Unit 10: Blood A. Blood 1. The only fluid tissue in the human body 2. Classified as a connective tissue 3. Components of blood a) Living cells (1) Formed elements b) Non-living matrix
Unit 10: Blood. 2. Buffy coat contains leukocytes and platelets (less than 1% of blood)
 Unit 10: Blood I. Blood A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells a. Formed elements 2. Non-living matrix a. Plasma D. If blood
Unit 10: Blood I. Blood A. The only fluid tissue in the human body B. Classified as a connective tissue C. Components of blood 1. Living cells a. Formed elements 2. Non-living matrix a. Plasma D. If blood
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Blood. Plasma. The liquid part of blood is called plasma. 1. Pale yellow fluid; forms more than half the blood volume.
 11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
11 Blood FOCUS: Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The plasma is 91% water with dissolved or suspended molecules, including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. The formed elements include erythrocytes,
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC. A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters
 A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
A. Blood is considered connective tissue. RBC A. Blood volume and composition 1. Volume varies - average adult has 5 liters 2. 45% cells by volume called hematocrit (HCT) a. red blood cells (RBC) mostly
Composition and Functions of Blood. Text p WB 193
 Chapter 10 Blood Composition and Functions of Blood Text p. 337-339 WB 193 Blood Transports everything that must be carried from one place to another. Nutrients, ions, gases, hormones, proteins Urea, waste
Chapter 10 Blood Composition and Functions of Blood Text p. 337-339 WB 193 Blood Transports everything that must be carried from one place to another. Nutrients, ions, gases, hormones, proteins Urea, waste
Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS. Pages Pages Pages
 Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS Pages 635-657 Pages 661-688 Pages 696-701 Homeostatic Imbalances of Erythrocytes H. I. Description Anemia blood with low O2 carrying capacity; symptomatic
Ch. 17: BLOOD Ch. 18: HEART Ch. 19: BLOOD VESSELS Pages 635-657 Pages 661-688 Pages 696-701 Homeostatic Imbalances of Erythrocytes H. I. Description Anemia blood with low O2 carrying capacity; symptomatic
Composition of Blood
 Blood Blood Blood serves as a vehicle for distributing body heat and for transporting nutrients, respiratory gases, and other substances throughout the body. Composition of Blood Blood is the only fluid
Blood Blood Blood serves as a vehicle for distributing body heat and for transporting nutrients, respiratory gases, and other substances throughout the body. Composition of Blood Blood is the only fluid
Chapter 14. Blood. Blood Volume. Blood Composition. Blood
 Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood connective tissue transports vital substances maintains stability of interstitial fluid distributes heat Chapter 14 Blood Blood Cells form mostly in red bone marrow red blood cells white blood cells
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Chapter 19 Blood Lecture Outline
 Chapter 19 Blood Lecture Outline Cardiovascular system Circulatory system Blood 1. distribution 2. regulation 3. protection Characteristics: ph 7.4 38 C 4-6 L Composition: Plasma Formed elements Erythrocytes
Chapter 19 Blood Lecture Outline Cardiovascular system Circulatory system Blood 1. distribution 2. regulation 3. protection Characteristics: ph 7.4 38 C 4-6 L Composition: Plasma Formed elements Erythrocytes
Which blood type is the universal donor? Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease:
 Scrub In: Which blood type is the universal donor? a. A b. B c. AB d. O Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease: a. Plasma b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes
Scrub In: Which blood type is the universal donor? a. A b. B c. AB d. O Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease: a. Plasma b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes
Composition of Blood
 Composition of Blood Erythrocytes Disorders of Erythrocytes Hematocrit Leukocytes Disorders of Leukocytes Platelets Hemostasis Disorders of Clotting Blood Types Blood Transfusion Unit 7 Blood Composition
Composition of Blood Erythrocytes Disorders of Erythrocytes Hematocrit Leukocytes Disorders of Leukocytes Platelets Hemostasis Disorders of Clotting Blood Types Blood Transfusion Unit 7 Blood Composition
Functions of Blood. 1. Transportation 2. Protection against invasion 3. Blood clotting 4. Regulation. Blood: Functions Blood clotting
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Lecture Packet 13 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII.
Outline Blood Biol 105 Lecture Packet 13 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood I. Functions of Blood A. List and describe the seven major homeostatic functions of blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. II. Plasma A. Composition 1. It is a fluid consisting
Chapter 19: Cardiovascular System: Blood I. Functions of Blood A. List and describe the seven major homeostatic functions of blood: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. II. Plasma A. Composition 1. It is a fluid consisting
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC
 RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
RENAL & HEMATOLOGY EMERGENCIES JEFF SIMONS B.S. F-PC GOALS Overview of renal system anatomy / physiology Discuss common medical / trauma renal issues Identify associated assessment keys GOALS Introduction
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System
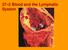 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System 1 Blood Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs,
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood
 BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Blood and the Lymphatic System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Blood and the Lymphatic System
 Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
Lesson Overview 33.2 Blood and the Lymphatic System THINK ABOUT IT When you think about body tissues, you probably picture something with a definite shape, like muscle or skin. But blood is a tissue too
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 !!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
HEART HEALTH WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT. A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Fatty deposits can narrow and harden the artery
 WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
WEEK 2 SUPPLEMENT HEART HEALTH A Beginner s Guide to Cardiovascular Disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS FIGURE 1 Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory process where cholesterol is deposited in the wall of arteries and
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1
 Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1 Major Functions of Blood The body contains 4 to 6 liters of blood with an average ph of 7.35 to 7.45. Functions include: Transport Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones,
Bio& 242 Unit 3 / Lecture 1 Major Functions of Blood The body contains 4 to 6 liters of blood with an average ph of 7.35 to 7.45. Functions include: Transport Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones,
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Circulatory System. Functions and Components of the Circulatory System. Chapter 13 Outline. Chapter 13
 Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and
 Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and nutrients, transport of metabolic wastes for elimination,
Blood Outline 17.1 The functions of blood are transport, regulation, and protection (p. 636) A. Transport functions include delivery of oxygen and nutrients, transport of metabolic wastes for elimination,
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions. Plasma
 Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: TRANSPORT AND SUPPLY
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: TRANSPORT AND SUPPLY Chapter 13 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Identify structures and functions of the cardiovascular system Trace the blood flow through the vessels and chambers of the
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: TRANSPORT AND SUPPLY Chapter 13 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Identify structures and functions of the cardiovascular system Trace the blood flow through the vessels and chambers of the
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. Chapter 11
 BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder. ph Volume pints. Red blood cells (RBC) White blood cells (WBC)
 Slide 1 Chapter 7 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Characteristics of blood Consistency (viscous) 45% blood cells RBC WBC Platelets 55%
Slide 1 Chapter 7 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Characteristics of blood Consistency (viscous) 45% blood cells RBC WBC Platelets 55%
C18 The Circulatory System / MC3. What is the difference between the cardiovascular. What are the formed elements? Include subcategories:
 C18 The Circulatory System / MC3 What is the difference between the cardiovascular and circulatory system? What are the formed elements? Include subcategories: What are the three primary functions of the
C18 The Circulatory System / MC3 What is the difference between the cardiovascular and circulatory system? What are the formed elements? Include subcategories: What are the three primary functions of the
Blood and Defense. Chapter 11
 Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
Blood and Defense Chapter 11 Functions of Blood 1. Carry nutrients from the small intestine and oxygen from the lung to tissues in the body 2. Transport wastes from tissues to the kidneys and carbon dioxide
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
12 Dynamic Interactions between Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells and the Bone Marrow: Current Biology of Stem Cell Homing and Mobilization
 Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
What is the composition of blood, including blood cells? What organs and structures control the flow of blood throughout the body?
 3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
3 Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic System In this chapter, you will learn about the structure and function of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. What is the composition of blood,
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Class X Chapter 7 The Circulatory System Biology REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
The Circulatory System. The Circulatory System. The circulatory system distributes materials such as oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
 The Circulatory System Melissa Zelaya Spring 2010 Senior Seminar The circulatory system distributes materials such as oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. The Circulatory System The heart muscular
The Circulatory System Melissa Zelaya Spring 2010 Senior Seminar The circulatory system distributes materials such as oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. The Circulatory System The heart muscular
b) List the steps that may occur in hemostasis with a brief explanation of what happens in those steps.
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood (use anatomy vocabulary)? b) List
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS
 CHILDREN S HOSPITALS AND CLINICS OF MINNESOTA Introduction: GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS These guidelines have been developed in conjunction with the hospital Transfusion Committee.
CHILDREN S HOSPITALS AND CLINICS OF MINNESOTA Introduction: GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS These guidelines have been developed in conjunction with the hospital Transfusion Committee.
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1
 Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 3, D CODES DISEASES OF THE BLOOD AND BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS AND CERTAIN DISORDERS INVOLVING THE IMMUNE MECHANISM Preferred Clinical Services for Leading
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 3, D CODES DISEASES OF THE BLOOD AND BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS AND CERTAIN DISORDERS INVOLVING THE IMMUNE MECHANISM Preferred Clinical Services for Leading
What is a hematological malignancy? Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies. Etiology of hematological malignancies. Leukemias
 Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
BLOOD. Dr. Vedat Evren
 BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
BLOOD Dr. Vedat Evren Blood Liquid suspension of formed elements Blood = Blood cells + plasma Plasma = Coagulation factors + serum Cells = Erythrocytes + Leukocytes + Thrombocytes 8 % of the total body
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
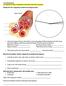 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a
 S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a diagnosis categorization scheme based on the ICD-9-CM that aggregates all diagnosis codes into 262 mutually exclusive, clinically homogeneous
S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a diagnosis categorization scheme based on the ICD-9-CM that aggregates all diagnosis codes into 262 mutually exclusive, clinically homogeneous
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: HEMATOLOGY Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: HEMATOLOGY Revised: 11/2013 What type of tissue is blood? Blood is considered liquid connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: HEMATOLOGY Revised: 11/2013 What type of tissue is blood? Blood is considered liquid connective
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Medical Surgical Review Handout- Hematology/Oncology 2016
 Medical Surgical Review Handout- Hematology/Oncology 2016 Overview Blood circulates in the cardiovascular system o Carries oxygen to the cells o Carries waste away from the cells Functions of blood o Transportation:
Medical Surgical Review Handout- Hematology/Oncology 2016 Overview Blood circulates in the cardiovascular system o Carries oxygen to the cells o Carries waste away from the cells Functions of blood o Transportation:
