CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
|
|
|
- Louisa Holt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow into the ventricle from the aorta and not be able to move forward 6 toward 11 The chambers of the heart function to pump blood either to other chambers of the heart or to vessels leaving 16 The left ventricle is the most muscular. It needs to be very muscular because of the four chambers. It is the one that needs to pump to the farthest reaches of the body (the systemic system). 2 This condition is called hemophilia. This condition prevents proper blood clotting so easy bruising and prolonged bleeding is one of the consequences. 7 a) descending/abdominal aorta the ascending aorta and going toward the lower body. 12 If the valves of the heart malfunction, the blood would pool in the chambers and not be able to move forward through 17 The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the systemic system while the right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary system. 3 A person with the AB blood type is the universal recipient. They can receive all types of blood because they do not have any antibodies against the A antigen or the B antigen so they won t be able to attack any of the red blood cells that are donated to them. 8 The function of the valves of the heart is to prevent the backflow of blood through the heart and to help move the blood forward. 13 Similarity: They are smaller versions of their larger forms veins and arteries. Difference: Arterioles are carrying blood toward capillaries and venules are carrying blood away from capillaries. 18 Difference 1: The atria are smaller/less muscular than the ventricles. Difference 2: The atria receive blood from the body and pump it to the ventricles while the ventricles receive blood from atria and pump it to the body. Difference 3: The atria are located on the top of the heart and the ventricles are located on the bottom. Difference 4: The atria pump blood through the atrioventricular valves and the ventricles pump blood through semilunar valves. 4 a) left atrioventricular valve / mitral or bicuspid valve b) This valve prevents blood from backflowing from the left ventricle back to the left atrium and thus it keeps the blood moving forward through 9 right atrium 14 Red blood cells function to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. 19 septum 5 The cardiac cycle refers to one complete heartbeat which involves one cycle of relaxation and filling of the heart followed by the contraction and emptying of 10 a) inferior vena cava the lower body and it is being carried to the right 15 You might have leukemia. 20 a) superior vena cava the upper body and it is being carried to the right
2 21 Purkinje fibers are located in walls of the ventricles. They function to carry the electrical signal to the muscles of the ventricles to cause them to contract. 26 leukocyte 22 erythrocyte 27 serum 23 a) right ventricle the right atrium and it is being carried to the pulmonary trunk. 28 a) left pulmonary veins the left lung and it is being carried to the left 24 Vasodilation is the widening of the blood vessels and vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels. 29 thrombocyte 25 a) chordae tendineae b) They function to prevent the flaps of the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral/bicuspid valve) from going into the atria when the ventricles are contracting. They ensure the flaps stay in place in the ventricles. 30 capillaries 31 Arteries contain high blood pressure and they combat this by having muscular walls to resist this high pressure. 36 left atrium 32 a) left atrium the left and right pulmonary veins and it is being carried to the left ventricle. 37 aorta 33 away 38 Capillaries must contain low blood pressure so that the flow of blood is slow enough to allow sufficient time for gas exchange to occur between the blood and the body tissues / alveoli of the lungs. 34 The valves in the veins help blood move back towards the heart, against gravity, by preventing the backflow of blood. 39 a) left ventricle the left atrium and it is being carried to the ascending aorta. 35 a) ascending aorta the left ventricle and it is being carried to the arteries of the upper body and to the descending aorta. 40 pulmonary
3 41 bone marrow 46 A person with type O blood is a universal donor because their red blood cells do not contain any A or B antigens, so the cells won t be attacked by the antibodies of the recipient. 51 plasma 56 You have arteriosclerosis which can be caused by an unhealthy life style that includes a lack of exercise, smoking and a diet high in fatty and processed foods. 42 a) right semilunar valve / pulmonary valve b) This valve prevents blood from backflowing from the pulmonary trunk back into the right ventricle and thus keeps the blood moving forward through 47 Systole is the phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart contracts and empties and diastole is the phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart relaxes and fills. 52 electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG) 57 a) right atrioventricular valve / tricuspid valve b) Failure of this valve will cause the backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right This will impair the forward movement of blood through 43 Hypertension occurs when you have chronic high blood pressure and hypotension occurs when you have chronic low blood pressure. 48 a) pulmonary trunk the right ventricle and it is being carried to the left and right pulmonary arteries. 53 a) arteries to the head, neck and arms the ascending aorta. 58 The pain is called angina and it occurs when a part of the heart is not receiving enough oxygen. This is usually due to the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries delivering oxygenated blood to 44 You have a condition called anemia caused by low hemoglobin levels or low red blood cell levels. Both are often caused by a deficiency of iron. 49 The pericardium is a double membrane system with a fluid between the two membranes. This structure covers the heart and functions to anchor it within the chest cavity, protect it from infection and protect it against the friction that occurs during beating. 54 The AV node slows down the conduction of the nerve impulse from the sinoatrial node (so that the atria can complete their contractions) before sending the signal down the Bundle of His in the septum to be propagated to the ventricles. 59 During angioplasty, a narrowed or obstructed artery is widened by inserting and inflating a balloon into the area and forcing the vessel open. A stent can then be inserted to keep the vessel open. 45 a) papillary muscles b) If these muscles fail, then the atrioventricular valves may be pushed into the atria when the ventricles contract. This will cause a backflow of blood in the heart and impair the blood s forward movement. 50 a) left pulmonary arteries the pulmonary trunk and it is being carried to the left lung. 55 a) right pulmonary arteries the pulmonary trunk and it is being carried to the right lung. 60 Platelets are responsible for initiating blood clotting.
4 61 a) septum b) The oxygenated blood in the left ventricle and the deoxygenated blood in the right ventricle would mix. This would cause the heart to pump blood that is not fully oxygenated to the tissues of the body. 66 White blood cells function to seek and destroy invading pathogens and precancerous cells. They also produce antibodies to help defend you against future infections. 62 The coronary blood vessels carry oxygenated blood to the heart tissue and carry deoxygenated blood from the heart tissue to be reoxygenated. 67 The pacemaker cells of the heart are found in a cluster of cells called the sinoatrial node. This node generates electrical impulses to set the rate of contraction for 63 hemoglobin 68 spleen 64 a) right atrium the inferior and superior vena cavas and it is being carried to the right ventricle. 69 During cardiac bypass surgery, a healthy artery from another part of your body is used to connect the parts of a coronary artery above and below the obstructed area of the artery. This helps divert the blood flow around the blockage and this helps restore blood flow to 65 myocardial infarction 70 Unlike other muscle types, myogenic muscle does not depend on nerve impulses from the nervous system. This muscle can contract due to signals sent from other areas of the heart and hence the heart is not dependent on nervous control to function. 71 a) right pulmonary veins the right lung and going toward the left 72 You have developed varicose veins. Prolonged standing causes blood to pool in the legs and without much muscular activity; the veins cannot move the blood upwards. The pooling of blood damages the valves of the veins and thus makes it more likely that more blood will pool /80 74 Bundle of His 75 myocardium 76 sickle cell anemia 77 endocardium 78 sphygmomanometer 79 A, N, U, K, E 80 During the first pregnancy with an Rh positive baby, the baby s Rh positive blood mixed with the mother s Rh negative blood during birth. After birth, this caused the mother to produce antibodies against the Rh factor which she didn t previously have. With her second Rh positive baby, her newly acquired Rh antibodies will attack the second baby s Rh positive red blood cells causing the baby to become seriously ill.
5 Created by Anh-Thi Tang Tangstar Science Copyright November 2014 Anh-Thi Tang (a.k.a. Tangstar Science) All rights reserved by author. This document is for your personal classroom use only. This entire document, or any parts within, may not be electronically distributed or posted to any website including teacher or classroom blogs and websites.
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
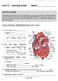 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms?
 Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Main Menu. Circulatory System. click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System
 Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
Name: Period: Unit 8: Blood / Lymph / Cardiovascular System Test Review 1. Identify the general formed elements of the blood and their general functions. a. Erythrocytes: b. Leukocytes: c. Thrombocytes:
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz
 Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
Quiz Description Clinical Cardiovascular System Quiz Q.1) Q.2) Q.3) Q.4) Q.5) Q.6) Q.7) Q.8) The prefix angio refers to. artery blood heart cavity ves sel The prefix cardio refers to. veins heart blood
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton. Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node.
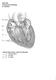 BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
The Circulatory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction The cardiovascular system
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
: thick middle layer; cardiac muscles : thin inner layer; endothelial lining
 1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation. Biology 2201
 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
