Cardiomyocyte precursors and telocytes in epicardial stem cell niche: electron microscope images
|
|
|
- Myra Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JCMM Express J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 4, 2010 pp Cardiomyocyte precursors and telocytes in epicardial stem cell niche: electron microscope images Mihaela Gherghiceanu a, L. M. Popescu a, b, * a Victor Babes National Institute of Pathology, Bucharest, Romania b Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Received: February 4, 2010; Accepted: February 28, 2010 Abstract A highly heterogeneous population of stem and progenitor cells has been described by light immunohistochemistry in the mammalian adult heart, but the ultrastructural identity of cardiac stem cells remains unknown. Using electron microscopy, we demonstrate the presence of cells with stem features in the adult mouse heart. These putative cardiac stem cells are small (6 10 m), round cells, with an irregular shaped nucleus, large nucleolus, few endoplasmic reticulum cisternae and mitochondria, but numerous ribosomes. Stem cells located in the epicardial stem cell niche undergo mitosis and apoptosis. Cells with intermediate features between stem cells and cardiomyocyte progenitors have also been seen. Moreover, electron microscopy showed that cardiomyocyte progenitors were added to the peripheral working cardiomyocytes. Telocytes make a supportive interstitial network for stem cells and progenitors in the stem cell niche. This study enhances the hypothesis of a unique type of cardiac stem cell and progenitors in different stages of differentiation. In our opinion, stem cells, cardiomyocyte progenitors and telocytes sustain a continuous cardiac renewal process in the adult mammalian heart. Keywords: cardiac stem cells cardiomyocytes progenitors telocytes cardiac stem cell niche cardiac renewal regenerative medicine epicardium Introduction A highly heterogeneous population of stem and progenitor cells [1 11] has been described by light immunohistochemistry in the mammalian adult heart, but the ultrastructural identity of cardiac stem cells (CSC) remains unknown. All these resident stem cells seem to have regenerative potential and to be the most appropriate source for cardiac cellular therapy [8]. However, it is still not clear that the different putative adult cardiac stem and progenitor cells represent different developmental and/or physiological stages of a unique type of resident stem cell [3, 11]. In this paper, we try to identify by electron microscopy (EM) CSC in a cardiac stem cell niche (CSCN) which contains cardiomyocyte progenitors (CMP) already described in the peri-coronary epicardial space [12]. The identity of putative CSC is still indefinite and their ultrastructural phenotype(s) should be of particular interest for their precise location in the myocardial complex architecture in order to understand the regenerative physiology of the *Correspondence to: L. M. POPESCU, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, P.O. Box 35 29, Bucharest 35, Romania. LMP@jcmm.org heart. We show here the ability of putative CSC to continuously self-renew and produce differentiated CMP. Materials and methods Small fragments from mouse atrioventricular myocardium with epicardium were processed for transmission electron microscopy (EM) according to routine procedures, as we previously described [12]. Hearts from six 4-, 6- and 12-month-old C57BL/6 mice have been examined after the institutional ethical committee approval. Results We have previously reported the existence of CMP, cells with immature features, in the adult mouse heart [12], exclusively located in the subepicardium surrounding coronary artery (Fig. 1). EM showed that in CSCN the connective tissue is loose and particularly rich in capillaries and interstitial cells: mast cells, doi: /j x
2 Fig. 1 High resolution light microscopy on toluidine blue stained semithin section (~1 m thick ultramicrotome section) of Epon-embedded mouse heart (6 month old) shows the limited space where cardiomyocyte progenitors have been found by electron microscopy. Cardiac stem cell niche is located in the subepicardial area surrounding coronary artery next to the emergence from aorta (rectangle red mark). adipocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, nerves, telocytes [13], CMP and mononuclear cells (Fig. 2). Using EM and exclusion criteria we found that some mononuclear cells (Fig. 2A) present ultrastructural features of stem cells (Fig. 3). These putative CSC have been found in the loose connective tissue surrounding the epicardial coronary artery (Fig. 1). CSC are small, round-oval cells (6 10 m), with large, irregular nuclei, scattered chromatin and large nucleolus, few mitochondria, few long endoplasmic reticulum cisternae and a large amount of free ribosomes (Fig. 3A and B). Another type of mononuclear cell in CSCN is a cell which is slightly larger (10 15 m) than CSC. These cells have large and indented nuclei with less scattered chromatin and prominent nucleoli, more numerous endoplasmic reticulum cisternae, few mitochondria, clusters of small and clear vacuoles generating a multilocular appearance, few dense granules and lysosomes and well-developed Golgi apparatus (Fig. 3C). These cells could be considered an early committed cell, an intermediate stage between CSC and CMP, because some of their ultrastructural features Fig. 2 (A) Electron microscopy of the niche depicted in Fig. 1 shows the presence of putative cardiac stem cells (CSC), isolated or in small groups, cardiomyocyte progenitors (CMP) and cells with intermediate features (CSC-CMP). All these cells are placed in a loose extracellular matrix. (B) Details at higher magnification from area marked in (A) with a dotted square. The CMP have characteristic leptofibrils (arrow) and is closely assisted by telocytes processes (TCp) which contain few dense granules (asterisk) suggesting paracrine signalling. CM cardiomyocyte; macro macrophage; coll collagen fibres. 872
3 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 4, 2010 Fig. 3 Electron microscopy images show putative cardiac stem cells (CSC) in mouse cardiac stem cell niche. (A, B) CSC are small, round cells, with discrete irregular shaped nucleus, large nucleolus (nu), few endoplasmic reticulum cisternae (ER) and mitochondria (m), dense granules (arrows) and numerous ribosomes. Telocyte processes (TCp) are in close proximity or applied on the plasma membrane of CSC (small arrows in Inset). n nerve fibres. (C) Committed cell with more abundant ER and numerous long mitochondria (m), well-developed Golgi apparatus (G), clusters of vesicles (v) but few filaments (f) and no basal lamina. (e.g. clusters of cytoplasmic vesicles, well-developed Golgi apparatus) are still visible in the early differentiated CMP (Fig. 4). Unlike CSC, the CMP [12] are recognizable without difficulty (Figs 2 and 4). These cells display typical ultrastructural features of immature cardiomyocytes including: high nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio, unorganized bundles of filaments, lipid droplets, intracytoplasmatic dense bodies (similar to primordial Z-lines), intracytoplasmatic desmosome-like structures (primordial intercalated discs) and cortical leptofibrils. Moreover, these cells have large mitochondria, numerous caveolae and a continuous basal lamina. A central 873
4 Fig. 4 Electron microscopy images from epicardial stem cell niche show more differentiated CMP with characteristic leptofibrils (lf). (A) Telocyte (TC) chaperone a low differentiated CMP with distinctive leptofibrils (lf), unorganized myofibrils (f), Golgi apparatus and clusters of mitochondria (m). (B) Higher magnification of CMP from A on a successive ultrathin section demonstrates the presence of well-developed Golgi apparatus (G), cytoplasmic vesicles (v), mitochondria (m), myofibrils (f) and incomplete basal lamina (arrows). (C) Low differentiated CMP with leptofibrils (lf), mitochondria (m), numerous free ribosomes, myofilaments (f) and a continuous basal lamina (arrows). TCp telocyte processes; A adipocytes. 874
5 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 4, 2010 Fig. 5 Cardiac stem cells in epicardial stem cell niche maintain their dynamic equilibrium through mitosis (A, B) and apoptosis (C, D). (A, B) CSC in prophase of mitosis: condensed chromatin (chr), nuclear envelope breaks (small arrows). Detached nuclear envelope fragments make parallel pairs with ER cisternae in the cytoplasm (arrowhead). Nucleolus (nu) is still visible in (B). (C, D) Apoptosis of stem cells: hypercondensation of chromatin and nuclear fragmentation (nc1 3). Plasma membrane scission (arrows) generates apoptotic bodies containing nuclear fragments. Note the chromatin clumping in a nuclear fragment (nc2 in D) and preserved nuclear envelope. CM cardiomyocyte; TCp telocyte processes. 875
6 Fig. 6 Cardiomyocyte progenitors (CMP) merge with adult mouse cardiomyocytes (CM). Rectangular marked areas in A, C, E are enlarged in B, D and F, respectively. (A, B) Direct cellular contact (arrows) between a committed cell and a cardiomyocyte shows none distinctive junctional structure. Basal lamina of cardiomyocytes encloses the CMP cellular projection (asterisks in B). (C, D) Finger-like cellular projections (dashed arrow) of CMP interacts with neighbouring cardiomyocytes to form adhesive contacts. Asymmetric reinforced contacts (immature desmosomes arrows) and electron-dense lamellar material (asterisks) in between adjoining cells. (E, F) Completely differentiated desmosomes (arrows) and reduced electron-dense material (asterisk) in gap between contacting membranes of CMP and cardiomyocytes. 876
7 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 4, 2010 element of the niche is represented by telocytes, stromal supporting cells. EM showed that telocytes (Figs 2B, 3 and 4A) are real candidates for this role, offering physical and informational support for CMP [12]. The mononuclear cells presented in this paper as putative stem cells have been found to undergo mitosis (Fig. 5A and B) and apoptosis (Fig. 5C and D) in the CSCN. Because we have found mitosis and apoptosis in cells with stemness features with EM, sometimes in the same section, we appreciate that this behaviour is quite common. The integration of newly formed cardiomyocytes into the cardiac muscle is of particular interest. In Fig. 6, we illustrate a possible integration mechanism: committed cells connect with adult cardiomyocytes in the presence of telocytes (Fig. 6A), gradually differentiate into cardiomyocytes and develop their particular junctional complexes at the same time (Fig. 6B and C). Discussion This EM study supports the idea of a unique type of cardiac stem cell in different stages of differentiation and maturation [11] and demonstrates the ability of putative CSC to continuously self-renew and produce differentiated cardiomyocyte progenitors. The mitotic and apoptotic CSC (Fig. 5), the presence of CMP in different stages of development (Figs 4 and 6) and the integration of newly formed cardiomyocytes suggest that there is a dynamic pool of stem cells in a continuous process of commitment and differentiation. In our opinion, stem cells, progenitors and telocytes sustain a continuous cardiac renewal process in the adult mammalian heart [12]. The next step would be to identify surface molecules (markers) which accurately differentiate stem cells from progenitors. Another important aspect to be clarified is telocyte involvement (Figs 1 6) [12 24] in stem cell homeostasis and cardiac renewal. References 1. Urbanek K, Cesselli D, Rota M, et al. Stem cell niches in the adult mouse heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006; 103: Bearzi C, Rota M, Hosoda T, et al. Human cardiac stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007; 104: Torella D, Ellison GM, Karakikes I, et al. Resident cardiac stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007; 64: Barile L, Messina E, Giacomello A, et al. Endogenous cardiac stem cells. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;50: Zhou B, Pu WT. More than a cover: epicardium as a novel source of cardiac progenitor cells. Regen Med. 2008; 3: Wu SM, Chien KR, Mummery C. Origins and fates of cardiovascular progenitor cells. Cell. 2008; 132: Roccio M, Goumans MJ, Sluijter JP, et al. Stem cell sources for cardiac regeneration. Panminerva Med. 2008; 50: Winter EM, van Oorschot AA, Hogers B, et al. A new direction for cardiac regeneration therapy: application of synergistically acting epicardium-derived cells and cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Circ Heart Fail. 2009; 2: Stamm C, Choi YH, Nasseri B, et al. A heart full of stem cells: the spectrum of myocardial progenitor cells in the postnatal heart. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2009; 3: Bergmann O, Bhardwaj RD, Bernard S, et al. Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science. 2009; 324: Ellison GM, Galuppo V, Vicinanza C, et al. Cardiac stem and progenitor cell identification: different markers for the same cell? Front Biosci. 2010; 2: Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Manole CG, et al. Cardiac renewing: interstitial Cajal-like cells nurse cardiomyocyte progenitors in epicardial stem cell niches. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13: Popescu LM, Faussone-Pellegrini MS. Telocytes A case of serendipity: the winding way from interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), via interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) to telocytes. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; doi: /j x 14. Hinescu ME, Popescu LM. Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in human atrial myocardium. J Cell Mol Med. 2005; 9: Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Cretoiu D, et al. The connective connection: interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) and ICC-like cells establish synapses with immunoreactive cells. Electron microscope study in situ. J Cell Mol Med. 2005; 9: Hinescu ME, Gherghiceanu M, Mandache E, et al. Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in atrial myocardium: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical characterization. J Cell Mol Med. 2006; 10: Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Hinescu ME, et al. Insights into the interstitium of ventricular myocardium: interstitial Cajallike cells (ICLC). J Cell Mol Med. 2006; 10: Mandache E, Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M. Myocardial interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) and their nanostructural relationships with intercalated discs: shed vesicles as intermediates. J Cell Mol Med. 2007; 11: Gherghiceanu M, Hinescu ME, Andrei F, et al. Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in myocardial sleeves of human pulmonary veins. J Cell Mol Med. 2008; 12: Morel E, Meyronet D, Thivolet-Bejuy F, et al. Identification and distribution of interstitial Cajal cells in human pulmonary veins. Heart Rhythm. 2008; 5: Suciu L, Popescu LM, Regalia T, et al. Epicardium: interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) highlighted by immunofluorescence. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13: Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M, Manole CG, et al. Cardiac renewing: interstitial Cajal-like cells nurse cardiomyocyte progenitors in epicardial stem cell niches. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13: Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM. Human epicardium: ultrastructural ancestry of mesothelium and mesenchymal cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13: Kostin S, Popescu LM. A distinct type of cell in myocardium: interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLCs). J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13:
Cardiac telocytes: serial dynamic images in cell culture
 Images in cellular, molecular medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 11, 2010 pp. 2687-2692 Cardiac telocytes: serial dynamic images in cell culture L. Suciu a, b, M. I. Nicolescu a, b, L. M. Popescu a,
Images in cellular, molecular medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 14, No 11, 2010 pp. 2687-2692 Cardiac telocytes: serial dynamic images in cell culture L. Suciu a, b, M. I. Nicolescu a, b, L. M. Popescu a,
Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in myocardial sleeves of human pulmonary veins
 Images in Cellular/Molecular Medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 12, No 5A, 2008 pp. 1777-1781 Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in myocardial sleeves of human pulmonary veins Mihaela Gherghiceanu a, M.
Images in Cellular/Molecular Medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 12, No 5A, 2008 pp. 1777-1781 Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) in myocardial sleeves of human pulmonary veins Mihaela Gherghiceanu a, M.
The Tandem: Telocytes - Stem Cells
 The Tandem: Telocytes - Stem Cells Lawrence M. Popescu Abstract - We have recently described a novel type of interstitial (stromal) cells Telocytes () in several cavitary and non-cavitary organs from humans
The Tandem: Telocytes - Stem Cells Lawrence M. Popescu Abstract - We have recently described a novel type of interstitial (stromal) cells Telocytes () in several cavitary and non-cavitary organs from humans
Transmission electron microscope evidence of telocytes in canine dura mater
 Images in Cellular and Molecular Medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 20, No 1, 2016 pp. 188-192 Transmission electron microscope evidence of telocytes in canine dura mater Ting Xu a, Shanshan Lu a, Hongqi
Images in Cellular and Molecular Medicine J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 20, No 1, 2016 pp. 188-192 Transmission electron microscope evidence of telocytes in canine dura mater Ting Xu a, Shanshan Lu a, Hongqi
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Integrated Muscle. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ultrastructural identification of telocytes in the muscularis of chicken ileum
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 10: 2325-2330, 2015 Ultrastructural identification of telocytes in the muscularis of chicken ileum PING YANG, YA'AN LIU, NISAR AHMED, SHAKEEB ULLAH, YI LIU and QIUSHENG
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 10: 2325-2330, 2015 Ultrastructural identification of telocytes in the muscularis of chicken ileum PING YANG, YA'AN LIU, NISAR AHMED, SHAKEEB ULLAH, YI LIU and QIUSHENG
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei Department of Histology & Embryology
 The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
The Cytoplasm Li Shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology Cell components Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Organelles Cytoplasmic deposits Cytoskeleton Cytosol ( Matrix ) Nucleus Plasma membrane
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
The Animal Cell. English. Introduction
 R04 (1000523) English The Animal Cell Introduction Cells in animal multicellular organisms principally only occur in groups of similar cells or together with other differentiated cells, or embedded in
R04 (1000523) English The Animal Cell Introduction Cells in animal multicellular organisms principally only occur in groups of similar cells or together with other differentiated cells, or embedded in
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Structure of a Generalized Cell
 A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
A Quick Tour Through A Cell BIO130 Lab 2 Exercise 4 The Cell: Anatomy Structure of a Generalized Cell -plasma membrane -cytoplasm: cytosol organelles -nucleus Play TourOfAnimalCell.mpg Plasma membrane
ENDOGENOUS CARDIAC STEM CELLS IN THE REGENERATION OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC ISCHEMIC MYOCARDIUM
 ENDOGENOUS CARDIAC STEM CELLS IN THE REGENERATION OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC ISCHEMIC MYOCARDIUM Bernardo Nadal-Ginard, M.D., Ph.D. New York Medical College Angioplasty Summit 2004, Seoul 04/29/04 MYOCARDIAL
ENDOGENOUS CARDIAC STEM CELLS IN THE REGENERATION OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC ISCHEMIC MYOCARDIUM Bernardo Nadal-Ginard, M.D., Ph.D. New York Medical College Angioplasty Summit 2004, Seoul 04/29/04 MYOCARDIAL
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Basophilic. Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue
 Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
Cell Overview Basophilic Basophilic structures are stained by basic dyes: Basic dyes are positive Basophilic structures are negative (ex. DNA, RNA, ribosomes, RER) Mnemonic: Basophilic = Blue Acidophilic
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Name 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of
 Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
*Need a summary just not covered yet!
 *Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
*Need a summary just not covered yet! Organelle Pupil Organelle Pupil Nucleus KO N Microtubules + centrioles LF Endoplasmic reticulum ED Plant cell wall OC Ribosomes KL Chloroplasts RK Golgi apparatus
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
PARTS OF A CELL. The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus.
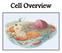 Cell Overview PARTS OF A CELL The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus. Cell Overview (Light Microscope) The initial information in histology was gained by
Cell Overview PARTS OF A CELL The cell is divided into three main parts: 1. Plasma membrane. 2. Cytoplasm. 3. Nucleus. Cell Overview (Light Microscope) The initial information in histology was gained by
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4
 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 18, No 12, 2014 pp. 2417-2424 Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4 Liu Rui #, Nie Yu #, Lian Hong, He Feng, Han Chunyong, Meng Jian, Zheng
J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 18, No 12, 2014 pp. 2417-2424 Extending the time window of mammalian heart regeneration by thymosin beta 4 Liu Rui #, Nie Yu #, Lian Hong, He Feng, Han Chunyong, Meng Jian, Zheng
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
The Cell. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
The Cell Cell Theory The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life The organism activity depends on individual and collective activity of cells Biochemical activities of cells are dictated
Chapter 6 Review Page 1
 hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
hapter 6 Review Page 1 1 Which of the following statements about prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is FLS? They both contain ribosomes. They both contain mitochondria. They are both bounded by a plasma
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them
 Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
Resident cardiac stem cells: how to find and use them G. Hasenfuß Cardiology and Pneumology Heart Research Center Göttingen Georg-August-University Göttingen Definition: Stem cell Selfrenewal Stem cell
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell. 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
1. Studying Cells. Concepts of Microscopy 11/7/2016. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14
 Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook
 Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Mansoura university Faculty of medicine Histology and cell Biology Department Curriculum Content And Logbook For the 1 st year Medical Student s In Histology and cell Biology Mansoura university Faculty
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
4. TEXTBOOK: ABUL K. ABBAS. ANDREW H. LICHTMAN. CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY. 5 TH EDITION. Chapter 2. pg
 LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
LECTURE: 03 Title: CELLS INVOLVED IN THE IMMUNE RESPONSE LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Identify the organs where the process of the blood formation occurs. Identify the main cell
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Identification of telocytes in the upper lamina propria of the human urinary tract
 J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 16, No 9, 2012 pp. 2085-2093 Identification of telocytes in the upper lamina propria of the human urinary tract Thomas Gevaert a, b, c, *, Rita De Vos b, Frank Van Der Aa a, Steven
J. Cell. Mol. Med. Vol 16, No 9, 2012 pp. 2085-2093 Identification of telocytes in the upper lamina propria of the human urinary tract Thomas Gevaert a, b, c, *, Rita De Vos b, Frank Van Der Aa a, Steven
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Heyam Awad
 number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
number 4 Done by Waseem Abu Obeida Corrected by Saad Al-Hayek Doctor Heyam Awad Cell injury -in the previous lectures we talked about the causes (etiology) and the mechanism (pathogenesis) of cell injury.
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Electron Microscopy Studies on the Ultrastructure of the Myocardium in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (1-2) Sofia 2018 Electron Microscopy Studies on the Ultrastructure
Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 25 (1-2) Sofia 2018 Electron Microscopy Studies on the Ultrastructure
Model of answer. 1) Give short notes about the following: (6 marks; 2 for each)
 Histology and Cell Biology Department, course code: MED 0702 First year Final Exam. (2 nd term) Date: 21/ 6 /2012 Allocated time: 1 1 / 2 hour Total allocated marks: 37.5 Number of papers: 3 papers Number
Histology and Cell Biology Department, course code: MED 0702 First year Final Exam. (2 nd term) Date: 21/ 6 /2012 Allocated time: 1 1 / 2 hour Total allocated marks: 37.5 Number of papers: 3 papers Number
8.2. Types of Neurons
 Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Yara shwabkeh. Osama Alkhader. Heba Kalbouneh
 2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
Sheet #7. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
Sheet #7 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Connective tissue The differences between epithelial and connective tissue - Epithelial cells are tightly packed (no or minimal spaces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL
 CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL Microscopes Con. 4.1 magnification: size resolution: clarity contrast: differences in parts Light Microscopy Techniques (p.68) a. Brightfield unstained b. Brightfield stained
CHAPTER 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL Microscopes Con. 4.1 magnification: size resolution: clarity contrast: differences in parts Light Microscopy Techniques (p.68) a. Brightfield unstained b. Brightfield stained
