Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition
|
|
|
- Jonathan Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M Ganesh Kumar et al REVIEW RTICLE /jp-journals Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition 1 M Ganesh Kumar, 2 Rajarajan Ganesan, 3 Goverdhan D Puri STRCT Dextrocardia (DC) is a rare cardiac anomaly that can be associated with other congenital abnormalities. Transesophageal echocardiographic imaging for evaluating these patients requires modification of the omniplane angle from the standard angles used. We describe the imaging technique in this condition when it is associated with situs solitus (SS) and situs inversus. Keywords: Dextrocardia, Echocardiography, Situs inversus, Transesophageal. How to cite this article: Kumar MG, Ganesan R, Puri GD. Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition. J Perioper Echocardiogr 2017;5(2): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None INTRODUCTION Dextrocardia is one of the rare cardiac anomalies with an incidence rate of <1 per 10,000 pregnancies/live birth. 1,2 It is defined as a position of the major portion of the heart in the right hemithorax with the base to apex directed to the right and caudal. It is a congenital anomaly that has to be differentiated from a similar condition called dextroposition of the heart in which the major portion of the heart is situated in the right hemithorax with base to apex directed to the left. The latter condition is mostly due to associated lung or diaphragm pathology (Fig. 1). 3 With improvements in surgical techniques, 85% of children born with congenital heart disease reach their adulthood. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) is one of the definitive modalities to image the associated cardiac anomalies in DC. When these children/adults are planned for surgery, a systematic approach should be followed to delineate the anatomy and associated 1,2 Senior Resident, 3 Professor and Head 1-3 Department of nesthesia and Intensive Care, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India Corresponding uthor: Rajarajan Ganesan, Senior Resident Department of nesthesia and Intensive Care, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India Phone: , raja2n@gmail.com abnormalities. The omniplane angles need to be modified while performing TEE in these patients. PTHOGENESIS ND ITS CLINICL IMPORTNCE Van Praagh 4 in his study described a segmental approach in the evaluation of a child with congenital heart disease, in which the heart is divided into three segments visceroatrial situs, ventricular loop, and position of the great vessels. The term situs refers to the organ configuration within the body, mainly abdomen and thorax, based on which an individual can have any one of the configurations SS, situs inversus (SI; mirror image of SS), or situs ambiguous. The position of the heart is evaluated following situs evaluation. With levocardia (LC) being the normal position of the heart (Fig. 1), malposition can be either mesocardia or DC. The presence of DC in a patient should raise the suspicion of associated cardiac and noncardiac anomalies. Dextrocardia can be associated with any situs (Figs 1C and D) and the incidence of cardiac malformation associated with it varies with the situs, ranging from 3 to 5% (SI, DC) to 95% (SS, DC). 5 Situs solitus with DC is associated with other lesions like anomalous pulmonary venous connections, patent ductus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation of aorta, transposition of the great arteries (TG) corrected/ uncorrected, and septal defects. 6-8 Situs inversus with DC has a lower incidence of associated cardiac anomalies, which can be TG corrected/uncorrected, ventricular septal defect, or double outlet right ventricle. 9 Patients with DC and situs ambiguous always have associated cardiac anomalies, which may be classified based on the type of atrial isomerism. 2 Patients with left atrial isomerism typically have pulmonary venous confluence returning close to the midline of an often-common atrium, atrioventricular (V) valve with V canal type defects, left-sided obstructive lesions like aortic stenosis and coarctation, and interrupted inferior vena cava (IVC). Patients with right atrial isomerism have bilateral SVCs, total anomalous pulmonary venous return, common V valves with V canal type defects, and right-sided obstructive lesions like pulmonary atresia. oth types have risk of arrhythmia and conduction abnormalities, with left atrial isomeric patients having greater risk of sinus node dysfunction. 64
2 Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition Figs 1 to D: () Normal subject (SS, LC); () dextroposition. Note the position of the major portion of the heart in the right hemithorax. The position of the abdominal viscera and base to apex direction of the heart are still maintained (noncardiac pathology); (C) situs inversus, DC which is the mirror image of normal; and (D) SS, DC. Note the normal position of the abdominal organs. lso note the left to right base to apex orientation of the heart. R: Right side; : ase of the heart; : pex of the heart; L: Liver; S: Stomach C D Figs 2 to C: () Probe in the lower esophageal position showing the junction of IVC and the right atrium. lso note the broad-based appendage of the right atrium; () TEE schematic of broad-based right atrial appendage; (C) TEE schematic of narrow finger-like left atrial appendage. R: Right atrium; TV: Tricuspid valve C ROLE OF TEE IN PPROCH Physical examination like palpation, auscultation of the cardiothoracic system, and electrocardiography will give clues regarding the cardiac position. The common finding in SI, DC is marked right-axis deviation of the P wave (negative in avl and lead I) and of the QRS complex, and low voltage in the precordial leads, V4 through V6. The trace of lead avr in SI, DC is similar to lead avl of SS, LC. 10 Echocardiography finds its role in confirming the diagnosis and evaluating the other associated cardiac anomalies in these patients. Situs determination is fundamental in patients with congenital heart disease. 11,12 ecause of the uncertain nature of the systemic and pulmonary venous drainage and subtle anatomical characteristics of the crista terminalis and V valves in congenital heart disease patients, situs should be determined solely based on the atrial appendage. The atrial appendage maintains its characteristics even in cases of atrial enlargement due to shunt lesions. 13 Transthoracic echocardiography can be used to image the atrial morphology and the situs in children, whereas it is often difficult to do the same in adults. 14 The TEE, because of its close proximity to the atria, provides clear details of both the appendages and helps in determining situs. The right atrial appendage (R) is short with blunt end and smooth inner surface. The left atrial appendage (L) is long and narrow with crenelated cavity (Figs 2 and C). With the probe in the lower esophageal position, rotating the probe to the right brings the liver and short axis of the IVC into view in SS. Slight withdrawal, anteflexion, and increasing the omniplane angle to around 90 help visualize the entry of IVC into the right atrium (Fig. 2). This view can also be obtained by advancing the probe from the bicaval position. The right atrial appendage can also be visualized in this view. part from determining the situs, TEE helps in finding the associated anomalies. However, use of standard multiplane angles for TEE recommended in SS, LC patients will not image the desired views in cardiac malposition. The midesophageal four-chamber view of SI, DC is a mirror image of the view conventionally obtained in a normally positioned heart, with the right atrium on the right side of the screen (Fig. 3 and Video 1). Journal of Perioperative Echocardiography, July-December 2017;5(2):
3 M Ganesh Kumar et al Figs 3 and : () Midesophageal four-chamber view of SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot (postrepair) subject, which is a mirror image of that obtained in a normal subject. () Midesophageal fourchamber view of a normal subject. L: Left atrium; R: Right atrium; MV: Mitral valve; TV: Tricuspid valve; LV: Left ventricle; RV: Right ventricle Figs 4 to C: () Midesophageal view of a patient with SS, DC, tricuspid atresia. Note that the right atrium is on the left side of the screen as in a normal subject. Right ventricle is hypoplastic; () TEE schematic of four-chamber view in SS, DC. Note the base to apex direction. The ventricles may be concordant or discordant; (C) TEE schematic of a midesophageal four-chamber view in a normal subject. R: Right atrium; L: Left atrium; MV: Mitral valve; LV: Left ventricle; RV: Right ventricle C Figs 5 and : () Midesophageal aortic valve short-axis view of SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot (postrepair) subject obtained at an omniplane angle between 135 and 155. Image is similar to that obtained in a normal subject; and () midesophageal aortic valve short axis view of normal subject note the difference in omniplane angle. ov: ortic valve However, in SS, DC, it is only the base to apex direction that is changed and the right atrium is visualized on the left side of the screen (Fig. 4 and Video 2). Other midesophageal views in SI, DC yield similar images to those obtained in normal cardiac position when the omniplane angles are at 180 minus the 66 prescribed angle for the standard view (Figs 5 to 7 and Videos 3 to 5). This may not be possible in SS, DC because the axes of the TEE planes and the axis of the heart are no longer parallel to each other, as depicted in Figure 4. Hence, the other standard midesophageal views cannot be obtained.
4 Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition Figs 6 and : () Midesophageal right ventricle inflow outflow view in SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot (postrepair) subject obtained at an omniplane angle between 110 and 130. Image is similar to that obtained in a normal subject; and () midesophageal right ventricle inflow outflow view of normal subject note the difference in omiplane angle. R: Right atrium; TV: Tricuspid valve; RVOT: Right ventricle outflow tract Figs 7 and : () Midesophageal long-axis view of a SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot subject obtained at an omniplane angle between 40 and 60. Image is similar to that of a normal subject; and () Midesophageal long-axis view in a normal subject note the difference in omiplane angle. L: Left atrium; MV: Mitral valve; ov: ortic valve; LV: Left ventricle; IVS: Interventricular septum Figs 8 and : () Transgastric midpapillary short-axis view of a SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot patient, which is a mirror image of that obtained in a normal subject; and () Transgastric midpapillary short-axis view in a normal subject. LV: Left ventricle; PM: Posteromedial papillary muscle; L: nterolateral papillary muscle; RV: Right ventricle Similar principles apply to imaging in the transgastric view in a SI, DC patient, with mirror image of the normal obtained at 0 (Fig. 8 and Video 6) and other standard images at 180 minus the standard angle (Figs 9 and 10, Videos 7 and 8). The presence of stomach and heart on opposite sides of the midline precludes much of the transgastric imaging in SS, DC. In SI, DC, threedimensional image can also be obtained from the twodimensional image, the only difference being that the left right orientation on the screen will be reversed. Journal of Perioperative Echocardiography, July-December 2017;5(2):
5 M Ganesh Kumar et al Figs 9 and : () Transgastric long-axis view of a SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot (postrepair) patient obtained at an angle between 40 and 60. Image is similar to that obtained in a normal subject; and () Transgastric long-axis view in a normal subject note the difference in angle. LV: Left ventricle; LVOT: Left ventricle outflow tract Figs 10 and : () Transgastric two-chamber view of a SI, DC, tetralogy of Fallot (postrepair) patient. Note that the image and angle are similar to that of a normal subject.() Transgastric twochamber view in a normal subject. L: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; MV: Mitral valve CONCLUSION Dextrocardia is a rare cardiac anomaly that can be associated with other cardiac and noncardiac abnormalities. It is pertinent upon the perioperative echocardiographer to be aware of the anomalies associated with DC, the maneuvers by which the views are obtained, and the situations when the images cannot be obtained. CKNOWLEDGMENT uthors would like to thank Dr Subhrashis Guha Niyogi for the illustrations. REFERENCES 1. Kidd S, Lancaster P, McCredie RM. The incidence of congenital heart disease in the first year of life. J Paediatr Child Health 1993 Oct;29(5): ohun CM, Potts JE, Casey M, Sandor GG. populationbased study of cardiac malformations and outcomes associated with dextrocardia. m J Cardiol 2007 Jul;100(2): harati S, Lev M. Positional variations of the heart and its component chambers. Circulation 1979 May;59(5): Van Praagh R. The importance of segmental situs in the diagnosis of congenital heart disease. Semin Roentgenol 1985 Jul;30(3): Tonkin, IL. The definition of cardiac malpositions with echocardiography and computed tomography. In: Friedman WF, Higgins C, editors. Pediatric cardiac imaging. Philadelphia (P): Saunders; uxton E, Morganroth J, Josephson ME, Perloff JK, Shelburne JC. Isolated dextroversion of the heart with asymmetric septal hypertrophy. m Heart J 1976 Dec;92(6): Calcaterra G, nderson RH, Lau KC, Shinebourne E. Dextrocardia value of segmental analysis in its categorisation. Heart 1979 Nov;42(5): Stanger P, Rudolph M, Edwards JE. Cardiac malpositions. n overview based on study of sixty-five necropsy specimens. Circulation 1977 ug;56(2): Oppido G, Pace Napoleone C, Martano S, Gargiulo G. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome in situs inversus totalis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2004 Nov;26(5): l-khadra S. Mirror-image dextrocardia with situs inversus. Circulation 1995 Mar;91(5):
6 Transesophageal Echocardiographic Diagnosis and Imaging of Cardiac Situs and Malposition 11. Van Praagh R. Terminology of congenital heart disease. Glossary and comments. Circulation 1977 ug;56(2): Tynan MJ, ecker E, Macartney FJ, Jimenez MQ, Shinebourne E, nderson RH. Nomenclature and classification of congenital heart disease. Heart 1979 May;41(5): Sharma S, Devine W, nderson RH, Zuberbuhler JR. The determination of atrial arrangement by examination of appendage morphology in 1842 heart specimens. Heart 1988 Sep;60(3): Marelli J, Child JS, Perloff JK. Transesophageal echocardiography in congenital heart disease in the adult. Cardiol Clin 1993 ug;11(3): Journal of Perioperative Echocardiography, July-December 2017;5(2):
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography -
 Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography - Jan Marek Great Ormond Street Hospital & Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, University College London No disclosures
Segmental approach to normal and abnormal situs arrangement - Echocardiography - Jan Marek Great Ormond Street Hospital & Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, University College London No disclosures
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Segmental Analysis. Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis
 Segmental Analysis Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis Segmental Analysis Segmental Analysis: From Veins to Ventricles Segmental Approach to Evaluation of Congenital
Segmental Analysis Gautam K. Singh, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine St. Louis Segmental Analysis Segmental Analysis: From Veins to Ventricles Segmental Approach to Evaluation of Congenital
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Congenital Heart Disease Systematic Interpretation of CT Suhny Abbara, MD
 Congenital Heart Disease Systematic Interpretation of CT Suhny Abbara, MD Chief, Cardiothoracic Imaging Division Professor of Radiology UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX Suhny.Abbara@UTSouthwestern.edu
Congenital Heart Disease Systematic Interpretation of CT Suhny Abbara, MD Chief, Cardiothoracic Imaging Division Professor of Radiology UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX Suhny.Abbara@UTSouthwestern.edu
Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:205-211 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.205 Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice Tse Hang
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:205-211 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.205 Congenital Heart Disease: a Pictorial Illustration of Putting Segmental Approach into Practice Tse Hang
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram
 JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival:
 Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Common Defects With Expected Adult Survival: Bicuspid aortic valve :Acyanotic Mitral valve prolapse Coarctation of aorta Pulmonary valve stenosis Atrial septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus (V.S.D.)
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD)
 Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Surgical challenges in atrio-ventricular septal defect in grown-up congenital heart disease Anatomy of Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD) S. Yen Ho Professor of Cardiac Morphology Royal Brompton and
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery
 The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Disclosures. Outline. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Introduction. Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart
 Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
F etal dextrocardia is a condition in which the major axis
 1590 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Fetal dextrocardia: diagnosis and outcome in two tertiary centres A Bernasconi, A Azancot, J M Simpson, A Jones, G K Sharland... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1590 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Fetal dextrocardia: diagnosis and outcome in two tertiary centres A Bernasconi, A Azancot, J M Simpson, A Jones, G K Sharland... See end of article for authors affiliations...
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis
 JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
J Somerville and V Grech. The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 12(1): 1 8.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
was judged subjectively. The left ventricle was considered to be slightly hypoplastic when the cardiac
 British Heart J7ournal, 1976, 38, 1124-1132. Double outlet right ventricle Study of 27 cases A. H. Cameron, F. Acerete, M. Quero, and M. C. Castro From the Department of Patlology, Children's Hospital,
British Heart J7ournal, 1976, 38, 1124-1132. Double outlet right ventricle Study of 27 cases A. H. Cameron, F. Acerete, M. Quero, and M. C. Castro From the Department of Patlology, Children's Hospital,
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALCAPA. See Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery. Angiosarcoma computed tomographic assessment of, 809 811 Anomalous
All You Need to Know About Situs and Looping Disorders: Embryology, Anatomy, and Echocardiography
 All You Need to Know About Situs and Looping Disorders: Embryology, Anatomy, and Echocardiography Helena Gardiner Co-Director of Fetal Cardiology, The Fetal Center, University of Texas at Houston Situs
All You Need to Know About Situs and Looping Disorders: Embryology, Anatomy, and Echocardiography Helena Gardiner Co-Director of Fetal Cardiology, The Fetal Center, University of Texas at Houston Situs
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography
 485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
485 JACC Vol. 5, No. I Assessing Cardiac Anatomy With Digital Subtraction Angiography DOUGLAS S., MD, FACC Cleveland, Ohio The use of intravenous digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of patients
Comprehensive Transoesophageal Echocardiography Examination
 IJUTPC PICTORIAL REVIEW Comprehensive Transoesophageal Echocardiography Examination Comprehensive Transoesophageal Echocardiography Examination 1 Ravi Hebballi, 2 Ann Ngui 1 Consultant in Cardiothoracic
IJUTPC PICTORIAL REVIEW Comprehensive Transoesophageal Echocardiography Examination Comprehensive Transoesophageal Echocardiography Examination 1 Ravi Hebballi, 2 Ann Ngui 1 Consultant in Cardiothoracic
Comprehensive evaluation of complex congenital heart disease using the Van Praagh notation: step by step in MDCT
 Comprehensive evaluation of complex congenital heart disease using the Van Praagh notation: step by step in MDCT Poster No.: C-2050 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y.-P. Chang, Y.-T.
Comprehensive evaluation of complex congenital heart disease using the Van Praagh notation: step by step in MDCT Poster No.: C-2050 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y.-P. Chang, Y.-T.
Dextrocardia in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart, Lung and Circulation (2016) 25, 352 357 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2015.09.003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dextrocardia in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease Sophie Offen, MBBS a,b,
Heart, Lung and Circulation (2016) 25, 352 357 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2015.09.003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dextrocardia in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease Sophie Offen, MBBS a,b,
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Data Collected: June 17, Reported: June 30, Survey Dates 05/24/ /07/2010
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
 Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Preoperative Echocardiographic Assessment of Uni-ventricular Repair
 Preoperative Echocardiographic Assessment of Uni-ventricular Repair Salem Deraz, MD Pediatric Cardiologist, Aswan Heart Centre Magdi Yacoub Heart Foundation Uni-ventricular repair A single or series of
Preoperative Echocardiographic Assessment of Uni-ventricular Repair Salem Deraz, MD Pediatric Cardiologist, Aswan Heart Centre Magdi Yacoub Heart Foundation Uni-ventricular repair A single or series of
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
This is the left, right?
 This is the left, right? Poster No.: C-1214 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L.-L. Huang, L. Mitchell, S. Andronikou, F. Suleman, Z. I. Lockhat; Pretoria/ZA Keywords: Congenital, Diagnostic
This is the left, right? Poster No.: C-1214 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L.-L. Huang, L. Mitchell, S. Andronikou, F. Suleman, Z. I. Lockhat; Pretoria/ZA Keywords: Congenital, Diagnostic
Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography
 Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography Timothy M. Cordes, MD, Patrick W. O'Leary, MD, James B. Seward, MD, and Donald J. Hagler, MD, Rochester, Minnesota Improved
Distinguishing Right From Left: A Standardized Technique for Fetal Echocardiography Timothy M. Cordes, MD, Patrick W. O'Leary, MD, James B. Seward, MD, and Donald J. Hagler, MD, Rochester, Minnesota Improved
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions
 Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
Appendix A.1: Tier 1 Surgical Procedure Terms and Definitions Tier 1 surgeries AV Canal Atrioventricular Septal Repair, Complete Repair of complete AV canal (AVSD) using one- or two-patch or other technique,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
NASCI 2012 Segmental Analysis
 NASCI 2012 Segmental Analysis Frandics Chan, M.D., Ph.D. Stanford University Medical Center Lucile Packard Department Children s of Radiology Hospital Menagerie of Congenital Cardiac Lesions 1. Absent
NASCI 2012 Segmental Analysis Frandics Chan, M.D., Ph.D. Stanford University Medical Center Lucile Packard Department Children s of Radiology Hospital Menagerie of Congenital Cardiac Lesions 1. Absent
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract'
 Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Anatomy of left ventricular outflow tract' ROBERT WALMSLEY British Heart Journal, 1979, 41, 263-267 From the Department of Anatomy and Experimental Pathology, The University, St Andrews, Scotland SUMMARY
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1
 Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease
 Chapter 44 Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease John L. Cotton and G. William Henry Multiple-plane cardiac imaging by echocardiography can noninvasively define the anatomy of the heart and the
Chapter 44 Echocardiography in Congenital Heart Disease John L. Cotton and G. William Henry Multiple-plane cardiac imaging by echocardiography can noninvasively define the anatomy of the heart and the
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital
 Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Giovanni Di Salvo MD, PhD, FESC Second University of Naples Monaldi Hospital VSD is one of the most common congenital cardiac abnormalities in the newborn. It can occur as an isolated finding or in combination
Revealing new insights. irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging. Ultrasound cardiology. irotate and xplane
 Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus*
 Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT WITH CAVEATS 1. In one study of 50 CHARGE patients with CHD, 75% required surgery. 2. Children with CHARGE may be resistant to chlo
 CARDIOLOGY IN CHARGE SYNDROME: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Angela E. Lin, M.D. Teratology Program/Active Malformation Surveillance, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Old PBBH-B501, 75 Francis St., Boston, MA 02115 alin@partners.org
CARDIOLOGY IN CHARGE SYNDROME: FOR THE PHYSICIAN Angela E. Lin, M.D. Teratology Program/Active Malformation Surveillance, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Old PBBH-B501, 75 Francis St., Boston, MA 02115 alin@partners.org
List of Videos. Video 1.1
 Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Video 1.1 Video 1.2 Video 1.3 Video 1.4 Video 1.5 Video 1.6 Video 1.7 Video 1.8 The parasternal long-axis view of the left ventricle shows the left ventricular inflow and outflow tract. The left atrium
Since the introduction of transesophageal echocardiography
 ASE/SCA Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Intraoperative Multiplane Transesophageal Echocardiography Examination: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council for Intraoperative
ASE/SCA Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Intraoperative Multiplane Transesophageal Echocardiography Examination: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council for Intraoperative
FUNCTIONALLY SINGLE VENTRICLE
 MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
MORPHOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS VI TRAN EuroEcho, Budapest, 7 th December 2011 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST: I have nothing to declare What is the functionally single ventricle? The heart that is incapable
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Cardiac Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus*
 Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
The Triply Twisted Heart: Cyanosis in an Adult With Situs Inversus, Levocardia, Double Outlet Right Ventricle, and Malposition of the Great Arteries
 Elmer ress Case Report Cardiol Res. 2015;6(6):362-366 The Triply Twisted Heart: Cyanosis in an Adult With Situs Inversus, Levocardia, Double Outlet Right Ventricle, and Malposition of the Great Arteries
Elmer ress Case Report Cardiol Res. 2015;6(6):362-366 The Triply Twisted Heart: Cyanosis in an Adult With Situs Inversus, Levocardia, Double Outlet Right Ventricle, and Malposition of the Great Arteries
3/14/2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS CARDIAC INTENSIVE CARE CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 WITH HEART DEFECTS
 CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
CONFERENCE FOR HEALTH PROFESSIONALS IRVINE, CA. MARCH 7, 2011 MANAGEMENT OF NEWBORNS WITH HEART DEFECTS A NTHONY C. CHANG, MD, MBA, MPH M E D I C AL D I RE C T OR, HEART I N S T I T U T E C H I LDRE N
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view.
 An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
Approach to Dextrocardia in Adults: Review
 AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Approach to Dextrocardia in Adults: Review Pierre D. Maldjian 1 and Muhamed Saric 2 OBJECTIVE The educational objectives of this article are to describe
AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Approach to Dextrocardia in Adults: Review Pierre D. Maldjian 1 and Muhamed Saric 2 OBJECTIVE The educational objectives of this article are to describe
Situs inversus. Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate
 Situs inversus Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate Definiton History Types Cause Clinical features Diagnosis Treatment Definition The term situs inversus is a short form of the latin phrase
Situs inversus Dr praveena pulmonology- final year post graduate Definiton History Types Cause Clinical features Diagnosis Treatment Definition The term situs inversus is a short form of the latin phrase
Among the congenital defects of the heart diagnosed
 Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation
 Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard. Frank Hanley
 The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard Frank Hanley No relationships to disclose CCTGA Interesting Points for Discussion What to do when. associated defects must be addressed surgically:
The Double Switch Using Bidirectional Glenn and Hemi-Mustard Frank Hanley No relationships to disclose CCTGA Interesting Points for Discussion What to do when. associated defects must be addressed surgically:
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease
 CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
CMR for Congenital Heart Disease * Second-line tool after TTE * Strengths of CMR : tissue characterisation, comprehensive access and coverage, relatively accurate measurements of biventricular function/
Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle
 Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
Communication of Mitral Valve with Both Ventricles Associated with Double Outlet Right Ventricle By RAJENTDRA TANDON, M.D., JAMES H. MOLLR, MD, AND JESSE E. EDWARDS, M.D. SUMMARY A rare case of an infant
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY. Abstract. Case
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232604 Isolated subpulmonary membrane causing critical neonatal pulmonary stenosis with concordant atrioventricular and ventriculoarterial connections
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images PMCID: PMC3232604 Isolated subpulmonary membrane causing critical neonatal pulmonary stenosis with concordant atrioventricular and ventriculoarterial connections
Epidemiology and classification according to sequential
 Br Heart J 1987;58:653-8 Congenital heart malformations in Jutland, Denmark: a three year necropsy study in children aged 0-14 years Epidemiology and classification according to sequential segmental analysis
Br Heart J 1987;58:653-8 Congenital heart malformations in Jutland, Denmark: a three year necropsy study in children aged 0-14 years Epidemiology and classification according to sequential segmental analysis
MEDICAL SCIENCES Vol.I -Adult Congenital Heart Disease: A Challenging Population - Khalid Aly Sorour
 ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: A CHALLENGING POPULATION Khalid Aly Sorour Cairo University, Kasr elaini Hospital, Egypt Keywords: Congenital heart disease, adult survival, specialized care centers. Contents
Ventricular inversion without transposition of the great vessels in situs inversus
 British HeartJournal, I970, 32, 292-303. Ventricular inversion without transposition of the great vessels in situs inversus Jorge Espino-Vela, Maria V. de la Cruz, Luis Muioz-Castellanos, Leandro Plaza,
British HeartJournal, I970, 32, 292-303. Ventricular inversion without transposition of the great vessels in situs inversus Jorge Espino-Vela, Maria V. de la Cruz, Luis Muioz-Castellanos, Leandro Plaza,
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Univentricular Heart with two separate Atrioventricular Valves: Diagnosed clinically and by Trans Thoracic Two - Dimensional Echocardiography.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 85-90 Univentricular Heart with two separate Atrioventricular Valves:
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 1 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 85-90 Univentricular Heart with two separate Atrioventricular Valves:
Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass grafting surgery
 Kusaka et al. JA Clinical Reports (2015) 1:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-015-0004-7 CASE REPORT Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass
Kusaka et al. JA Clinical Reports (2015) 1:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-015-0004-7 CASE REPORT Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
The Hemodynamics of Common
 The Hemodynamics of Common (or Single) Ventricle By SHAHBUDIN H. RAHIMTOOLA, M.B., PATRICK A. ONGLEY, M.B., CH.B,. AND H. J. C. SWAN, M.B., PH.D. THE anatomy of common ventricle has been the subject of
The Hemodynamics of Common (or Single) Ventricle By SHAHBUDIN H. RAHIMTOOLA, M.B., PATRICK A. ONGLEY, M.B., CH.B,. AND H. J. C. SWAN, M.B., PH.D. THE anatomy of common ventricle has been the subject of
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart. Axial Anatomy of Heart
 CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
CARDIAC AND CORONARY ARTERY ANATOMY NO DISCLOSURES NASCI MEETING, ORLANDO FLORIDA 2009 KOSTAKI G. BIS, MD, FACR DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL Royal Oak, Michigan OBJECTIVES CARDIAC
CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION
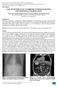 CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION *Sagar H S, Basanta Manjari Swain, Jayashree Mohanty and Sasmita Parida Department of Radio diagnosis, S.C.B. Medical College, Cuttack
CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION *Sagar H S, Basanta Manjari Swain, Jayashree Mohanty and Sasmita Parida Department of Radio diagnosis, S.C.B. Medical College, Cuttack
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Advanced Congenital Cardiac Morphology. Sunday, Oct. 22, to Thursday, Oct. 26, Learn more: chop.cloud-cme.com
 Advanced Congenital Cardiac Morphology Sunday, Oct. 22, to Thursday, Oct. 26, 2017 Ruth and Tristram Colket, Jr. Translational Research Building Learn more: chop.cloud-cme.com 1 Course Information Course
Advanced Congenital Cardiac Morphology Sunday, Oct. 22, to Thursday, Oct. 26, 2017 Ruth and Tristram Colket, Jr. Translational Research Building Learn more: chop.cloud-cme.com 1 Course Information Course
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Fetal Cardiac Anomaly
 89 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 12 : 10 1 2 : 30 Fetal Cardiac Anomaly 1. One third of all congenital anomalies 2. 6 10/1,000 live births 3. Related with more than 50% of childhood deaths and 20-30% of
89 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 12 : 10 1 2 : 30 Fetal Cardiac Anomaly 1. One third of all congenital anomalies 2. 6 10/1,000 live births 3. Related with more than 50% of childhood deaths and 20-30% of
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns
 Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz
Normal TTE Examination, Doppler Echocardiography and Normal Antegrade Flow Patterns Pravin Patil, MD FACC FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Cardiovascular Disease Training Program Lewis Katz
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies
 Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies Michael D. Pettersen, MD Director, Echocardiography Rocky Mountain Hospital for Children Denver, CO None Disclosures 1 ASCeXAM Contains
Congenital Heart Disease An Approach for Simple and Complex Anomalies Michael D. Pettersen, MD Director, Echocardiography Rocky Mountain Hospital for Children Denver, CO None Disclosures 1 ASCeXAM Contains
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
