Butorphanol attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mice
|
|
|
- Myra Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: Butorphanol attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mice L.-H. HUANG 1, J. LI 2, J.-P. GU 3, M.-X. QU 3, J. YU 3, Z.-Y. WANG 3 1 Heart Function Examination Room, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China 2 Department of Cardiology, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai, China 3 Department of Critical Care Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China Lihong Huang and Jun Li contributed equally to this work Abstract. OBJECTIVE: To investigate the role of the opioid receptors agonist butorphanol on mice myocardial ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The left anterior descending of coronary artery was ligatured for 30 min and then reperfusion for 6 h was performed to mimic the mouse myocardial I/R injury. All mice were randomly divided into three groups: sham group, I/R group and I/R + butorphanol group. Blood samples were collected for the measurement of cardiac troponin I (CTnI) and creatine kinase MB (CK-MB) levels. The infarct size was stained by triphenyltetrazolium chloride. The mitochondria morphology was observed by electron microscopy. The expressions of cleaved caspase-9 and -3, p38, ERK and JNK were detected by Western blot. RESULTS: The myocardial infarct size, serum CK-MB and CTn I levels, expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3, phosphorylation of p38 and JNK were all increased in the I/R group compared with the sham group (all p < 0.01). Butorphanol reduced the myocardial infarct size, serum CTn I and CK-MB levels, expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3, and phosphorylation levels of p38 and JNK (all p < 0.01). The number of mitochondria and the individual mitochondrial cross-sectional areas were decreased in the I/R mice compared with the sham-operated mice (all p < 0.01). Butorphanol reversed these changes in mitochondrial morphology (all p < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Butorphanol attenuates myocardial I/R injury through reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway, and blockage of p38 and JNK phosphorylation. Key Words: Butorphanol, Ischemia reperfusion injury, Apoptosis, Mitochondria, Mitogen-activated protein kinase. Introduction Ischemic heart diseases, such as coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome, have been the leading cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Cardiac myocyte apoptosis plays a key role in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury 1. In contrast, inhibition of apoptosis has a powerful effect on cardioprotective. Activation of opioid receptor has been reported to be significantly associated with myocardial protection 2. The opioid receptor family consists of three members: κ, δ, and μ 3. Many studies 4,5 have revealed that κ- and δ-, but not μ-receptors, are expressed in cardiomyocytes, and the activation of κ- and δ-receptors can attenuate myocardial I/R injury. Butorphanol is a novel opioid receptor agonist, which possesses a high affinity for κ-receptor and partially activation on δ-receptor. Pharmacological researches 6,7 demonstrated that the administration of butorphanol has the effect of analgesia and relaxation. However, to date, there are few reports focused on butorphanol-induced cardioprotective in myocardial I/R injury. Recently, Wu et al 8 reported that butorphanol post-conditioning could attenuate myocardial I/R injury through activating κ-receptor in rats. However, the molecular mechanism involved in butorphanol-induced cardioprotective in myocardial I/R injury has not yet been fully elucidated. Corresponding Author: Jian Yu, MD; yujian862@sina.com; Zhiyu Wang, MM. dlwangzhiyu@sina.com 1819
2 L.-H. Huang, J. Li, J.-P. Gu, M.-X. Qu, J. Yu, Z.-Y. Wang Thus, we created a myocardial I/R mouse model to investigate the role and molecular mechanism of butorphanol in myocardial protection. Materials and Methods Reagents Butorphanol injection was obtained from Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd., (Lianyungang, China). Serum cardiac troponin I (CTnI) and creatine kinase MB (CK-MB) detection kits were obtained from Jiancheng Bioengineering Research (Nanjing, China). All antibodies were provided by Cell Signaling Technology (CST, Danvers, MA, USA). Total protein extraction kits were provided by KeyGen Biotechnology (Nanjing, China). Ethics Statements 8-10 weeks old and g body weight male C57BL/6 mice were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Jiangsu Province (Nanjing, China). Animal experiments followed the Guide for Laboratory Animals published by the NIH. Mice were fed with standard mouse food and water, and were kept under 12:12 hour light/dark cycles with 22 C. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Dalian Medical University Animal Center. Mice Model of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury The mice were anesthetized by pentobarbital (50 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection), intubated and ventilated. A left horizontal incision was made at the third intercostal space. To achieve I/R injury, a 8-0 silk suture was tied around both the left anterior descending (LAD) and a silicon tube. Myocardial ischemia was measured by the electrocardiograph performance (ST elevated). The sham-operated mice underwent an identical surgical procedure without ligature. After ischemia for 30 min, the silicon tube was removed to achieve reperfusion for 6 h. There were three groups: (1) sham group; (2) I/R group, sodium chloride was injected intramuscularly at the start of reperfusion; (3) I/R + butorphanol (B) group, butorphanol (50 μg/kg) was injected intramuscularly at the start of reperfusion. n = 15 in each group. After reperfusion, the heart samples were harvested and then stored at -70 C. Assessment of Myocardial Infarct Size Evans blue dye was perfused into the aorta to demarcate the ischemic area-at-risk. Hearts were excised and sliced. The heart sections were stained with 1% triphenyltetrazolium chloride at 37 C for 20 min and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 8 h. Infracted myocardium was carefully separated from the non-infarcted myocardium and weighed. The infarct size is presented as a percentage of the ischemic area-at-risk. Measurement of Serum Myocardial Enzymes The enzyme-labeled immunosorbent assay was used to measure the serum CK-MB and CTn I levels. After 6 h of reperfusion, blood samples were collected and centrifuged, then transferred to Eppendorf (EP) tubes. The following steps were performed according to the instructions of detection kits. Electron Microscopy Analysis The performance of electron microscopy analysis was described as previously 9. Electron microscopy images of mitochondria were collected for analysis. PhotoshopCS5.0 software was used to analysis the electron microscopy images and to measure both the number and the size of the myocardial mitochondria. Western Blotting Western blot analysis was used to determinate the expression of protein extracted from the I/R myocardium. Briefly, gel electrophoresis was performed to separate the different molecular weight proteins and then transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. These membranes were incubated with anti-cleaved caspase9, anti-cleaved caspase3, anti-p-p38, anti-p38, anti-p-erk1/2, anti-erk1/2, anti-p- JNK and anti-jnk for overnight at 4 C. After incubating with these primary antibodies, the membranes were washed in Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20 (TBST-20). After that, they were incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody at room temperature for another 2 h. Western blot detection kit and ImageJ software (NIH) were used to measure the blot signal and density. Statistical Analysis SPSS 19.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for statistical analysis. All results were presented as means ± standard deviations (SD). Differences among different groups were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. Differ- 1820
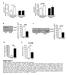
3 Butorphanol attenuates myocardial I/R injury Figure 1. Effect of butorphanol on infarct size and myocardial enzymes. CTnI: cardiac troponin I; CK-MB: creatine kinase MB; I/R: ischemia/reperfusion; B: butorphanol. **p < 0.01 and ***p < vs. sham; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 and ### p < vs. I/R. ences between two groups were analyzed by Student s t-test. A value of p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results Butorphanol Reduced Myocardial I/R-induced Increase in Infarct Size and Myocardial Enzymes As shown in Figure 1, compared with the sham group, the myocardial infarct size and serum CTn I and CK-MB levels were significantly increased in I/R group (p < 0.001; p < 0.001; p < 0.001, respectively). Butorphanol significantly reduced the myocardial infarct size and serum CTn I and CK-MB levels in contrast to the I/R group (p < 0.001; p < 0.001; p < 0.001, respectively). Butorphanol Inhibited Myocardial I /R-induced Mitochondrial Apoptosis Myocardial mitochondrial morphology was observed via electron microscopy (Figure 2). Compared with sham group, the mitochondria in the I/R group were smaller and more disor- Figure 2. Effect of butorphanol on mitochondrial morphology in I/R myocardium. I/R: ischemia/reperfusion (magnification of 10,000 ) (B indicates butorphanol). **p < 0.01 and ***p < vs. sham; ## p < 0.01 vs. I/R. 1821
4 L.-H. Huang, J. Li, J.-P. Gu, M.-X. Qu, J. Yu, Z.-Y. Wang Figure 3. Effect of butorphanol on the expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3 in the I/R myocardium. I/R: ischemia/ reperfusion; B: butorphanol. **p < 0.01 and ***p < vs. sham; ## p < 0.01 and ### p < vs. I/R. ganized. Both the number and size of mitochondria per area were significantly decreased in the I/R group (p < 0.01; p < 0.001, respectively). Butorphanol administration substantially reversed these changes in mitochondrial morphology (p < 0.01; p < 0.01, respectively). The expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3 was markedly increased in the I/R mice compared with the sham mice (p < 0.001; p < 0.01, respectively). Butorphanol administration significantly decreased the expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3 in the I/R mice (p < 0.001; p < 0.01, respectively) (Figure 3). Butorphanol Inhibited Myocardial I/R-induced p38 and JNK Phosphorylation Compared with the sham group, the phosphorylation levels of p38 and JNK were both significantly increased in the I/R group (p < 0.001; p < 0.001, respectively). However, myocardial I/R did not induce the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (Figure 4). Butorphanol administration prevented the increases in p38 and JNK phosphorylation induced by I/R injury (p < 0.01; p < 0.01, respectively). Discussion We focused on the cardioprotective effect of butorphanol in a mouse myocardial I/R injury model. Our results shown that butorphanol administration markedly attenuated I/R injury, as confirmed by decrease in infarct size and myocardial enzymes levels. This protective effect was associated with the reduction in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis and the inhibition of p38 and JNK phosphorylation. It is now known that activation of κ- and δ-receptors are significantly associated with the cardioprotection 2. Butorphanol is a novel opioid receptor agonist, which possesses a high affinity for κ-receptor and partially activation on δ-receptor. Wu et al 8 reported that butorphanol post-conditioning could attenuate myocardial I/R Figure 4. Effect of butorphanol on the phosphorylation of p38, ERK and JNK in the I/R myocardium. I/R: ischemia/ reperfusion; B: butorphanol. ***p < vs. sham; ## p < 0.01 vs. I/R. 1822
5 Butorphanol attenuates myocardial I/R injury injury, and this protective effect could be abolished by κ-receptor antagonist nor-binaltorphimine. Down-stream signal targets that involved in opioid-induced cardioprotection include mitochondria and MAPK pathway 10,11. Mitochondria have been considered as the central organelles of cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and the change of mitochondrial morphology reflects the state of cardiomyocytes 9. Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis has been reported as an important mechanism involved in myocardial I/R injury 12. The mitochondria injury can promote cytochrome c to diffuse from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm, thereby activating caspase-9, which ultimately cleaves and activates the key executioner caspase-3, resulting in apoptosis 13,14. Consistent with these studies, we demonstrated that the mitochondria became smaller and more disorganized, and the expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3 was significantly increased in the I/R myocardium. Butorphanol administration reserved mitochondrial morphology and inhibited the mitochondria-dependent apoptosis by reducing the expression of cleaved caspase-9 and -3. p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) are the three components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway 15. p38 and JNK have been viewed as two major effectors that involved in mitochondria-dependent apoptosis 16. The activated JNK and p38 can inhibit the anti-apoptotic role of Bcl-2 via phosphorylating Bcl-2 17,18. Moreover, Kim et al 19 reported that the activation of p38 could facilitate apoptosis by increasing the expression of the pro-apoptotic factor Bax. Donovan et al 20 observed that phosphorylated JNK could facilitate the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by activating the pro-apoptotic factors Bad and Bid. Conversely, the cardiomyocyte apoptosis was significantly inhibited by the specific inhibitors of JNK and p38 (SP and SB203580) in response to numerous stimuli in vitro 16. We found that the phosphorylation levels of p38 and JNK were significantly increased in the I/R myocardium. Butorphanol suppressed the phosphorylation of p38 and JNK induced by myocardial I/R injury. Fryer et al 21 reported that ERK phosphorylation was involved in opioid-induced delayed myocardial protection. However, we showed that ERK was not activated in I/R myocardium and ERK phosphorylation was not involved in butorphanol-induced myocardial protection. It may be due to the butorphanol was administrated at the onset of reperfusion. Conclusions We showed the protective effect of butorphanol on myocardial I/R injury. Overall, butorphanol attenuates myocardial I/R injury through reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, and blockage of p38 and JNK phosphorylation. The limitation of the current work is the lack of research on the cellular mechanism. Thus, future research is needed to investigate the potential therapeutic target of butorphanol in cardiomyocytes in vitro. Conflict of Interest The Authors declare that they have no conflict of interests. References 1) Liu YF, Chu YY, Zhang XZ, Zhang M, Xie FG, Zhou M, Wen HH, Shu AH. TGFβ1 protects myocardium from apoptosis and oxidative damage after ischemia reperfusion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2017; 21: ) Tanaka K, Kersten JR, Riess ML. Opioid-induced cardioprotection. Curr Pharm Des 2014; 20: ) Minami M, Satoh M. Molecular biology of the opioid receptors: structures, functions and distributions. Neurosci Res 1995; 23: ) Wittert G, Hope P, Pyle D. Tissue distribution of opioid receptor gene expression in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 218: ) Peart JN, Gross ER, Reichelt ME, Hsu A, Headrick JP, Gross GJ. Activation of kappa-opioid receptors at reperfusion affords cardioprotection in both rat and mouse hearts. Basic Res Cardiol 2008; 103: ) Gupta A, Kaur S, Attri JP, Saini N. Comparative evaluation of ketamine-propofol, fentanyl-propofol and butorphanol-propofol on haemodynamics and laryngeal mask airway insertion conditions. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2011; 27: ) Du BX, Song ZM, Wang K, Zhang H, Xu FY, Zou Z, Shi XY. Butorphanol prevents morphine-induced pruritus without increasing pain and other side effects: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Can J Anaesth 2013; 60: ) Wu Y, Wan J, Zhen WZ, Chen LF, Zhan J, Ke JJ, Zhang ZZ, Wang YL. The effect of butorphanol postconditioning on myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in rats. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2014; 18: ) Chen L, Gong Q, Stice JP, Knowlton AA. Mitochondrial OPA1, apoptosis, and heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 2009; 84:
6 L.-H. Huang, J. Li, J.-P. Gu, M.-X. Qu, J. Yu, Z.-Y. Wang 10) Patel HH, Hsu A, Moore J, Gross GJ. BW373U86, a delta opioid agonist, partially mediates delayed cardioprotection via a free radical mechanism that is independent of opioid receptor stimulation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2001; 33: ) Fryer RM, Hsu AK, Gross GJ. ERK and p38 MAP kinase activation are components of opioid-induced delayed cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol 2001; 96: ) Fliss H, Gattinger D. Apoptosis in ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res 1996; 79: ) Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ, Kitsis RN. The mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ Res 2004; 95: ) Dorn GN. Apoptotic and non-apoptotic programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 2009; 81: ) Wang Y. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in heart development and diseases. Circulation 2007; 116: ) Baines CP, Molkentin JD. STRESS signaling pathways that modulate cardiac myocyte apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2005; 38: ) Fan M, Goodwin M, Vu T, Brantley-Finley C, Gaarde WA, Chambers TC. Vinblastine-induced phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL is mediated by JNK and occurs in parallel with inactivation of the Raf- 1/MEK/ERK cascade. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: ) Torcia M, De Chiara G, Nencioni L, Ammendola S, Labardi D, Lucibello M, Rosini P, Marlier LN, Bonini P, Dello SP, Palamara AT, Zambrano N, Russo T, Garaci E, Cozzolino F. Nerve growth factor inhibits apoptosis in memory B lymphocytes via inactivation of p38 MAPK, prevention of Bcl-2 phosphorylation, and cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: ) Kim SJ, Hwang SG, Shin DY, Kang SS, Chun JS. P38 kinase regulates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of articular chondrocytes by accumulating p53 via NFkappa B-dependent transcription and stabilization by serine 15 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: ) Donovan N, Becker EB, Konishi Y, Bonni A. JNK phosphorylation and activation of BAD couples the stress-activated signaling pathway to the cell death machinery. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: ) Fryer RM, Hsu AK, Gross GJ. ERK and p38 MAP kinase activation are components of opioid-induced delayed cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol 2001; 96:
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
 Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
Ginkgo biloba extract postconditioning reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury K. Ran 1, D.-L. Yang 1, Y.-T. Chang 1, K.-M. Duan 2, Y.-W. Ou 2, H.-P. Wang 3 and Z.-J. Li 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology,
The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7720-7724 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene. Zhenjun Liu *, Guangming He, Lili Zhao Intensive Care
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7720-7724 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The alleviation of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by lycopene. Zhenjun Liu *, Guangming He, Lili Zhao Intensive Care
Nabeel R. Obeid Mentors: Erin A. Booth and Dr. Benedict R. Lucchesi
 Cardioprotective Action of Selective Estrogen-receptor Agonists against Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Nabeel R. Obeid Mentors: Erin A. Booth and Dr. Benedict R. Lucchesi Abstract Cell death
Cardioprotective Action of Selective Estrogen-receptor Agonists against Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Nabeel R. Obeid Mentors: Erin A. Booth and Dr. Benedict R. Lucchesi Abstract Cell death
Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 protein expression
 original article Cardiology Journal 213, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 6 64 DOI: 1.563/CJ.213.159 Copyright 213 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting
original article Cardiology Journal 213, Vol. 2, No. 6, pp. 6 64 DOI: 1.563/CJ.213.159 Copyright 213 Via Medica ISSN 1897 5593 Exendin-4 attenuates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB
 Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning
 Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Correlations among copeptin, ischemia-modified albumin, and the extent of myocardial injury in patients with acute carbon monoxide poisoning J. Li, J.S. Wang, Z.X. Xie, W.Z. Wang, L. Wang, G.Y. Ma, Y.Q.
Introduction. Animals
 Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(4):242-247 Protective Effects of Phosphocreatine Administered Post- Treatment Combined With Ischemic Post-Conditioning on Rat Hearts With Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion
Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2015;7(4):242-247 Protective Effects of Phosphocreatine Administered Post- Treatment Combined With Ischemic Post-Conditioning on Rat Hearts With Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It?
 MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
MI/CAD: Practical Question in Management of AMI Patients Reperfusion Injury: How Can We Reduce It? Hyun-Jai Cho, M.D., Ph.D Cardiovascular Center & Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National University
Ameliorating Reperfusion Injury During Resuscitation from Cardiac Arrest
 Ameliorating Reperfusion Injury During Resuscitation from Cardiac Arrest Scott T. Youngquist, MD, MSc Associate Professor, Emergency Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, Salt
Ameliorating Reperfusion Injury During Resuscitation from Cardiac Arrest Scott T. Youngquist, MD, MSc Associate Professor, Emergency Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, Salt
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Induction of myocardial infarction Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (7 mg/kg). In the supine position, endotracheal intubation was performed.
Supplementary Material Induction of myocardial infarction Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (7 mg/kg). In the supine position, endotracheal intubation was performed.
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: , 2014
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 973-977, 2014 Pharmacological postconditioning with tanshinone IIA attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats by activating the phosphatidylinositol
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 973-977, 2014 Pharmacological postconditioning with tanshinone IIA attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats by activating the phosphatidylinositol
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury
 Tan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:198 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0436-4 RESEARCH Open Access Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury Jian Tan, Jianpeng Hu,
Tan et al. Diagnostic Pathology (2015) 10:198 DOI 10.1186/s13000-015-0436-4 RESEARCH Open Access Protective role of silymarin in a mouse model of renal Ischemia Reperfusion injury Jian Tan, Jianpeng Hu,
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
EETs mediate cardioprotection of salvianolic acids through MAPK signaling pathway
 Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2013;3(1):25 31 Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Chinese Pharmaceutical Association Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B www.elsevier.com/locate/apsb
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2013;3(1):25 31 Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Chinese Pharmaceutical Association Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B www.elsevier.com/locate/apsb
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: , 2015
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 527-532, 2015 Oxysophoridine attenuates the injury caused by acute myocardial infarction in rats through anti oxidative, anti inflammatory and anti apoptotic pathways CONG
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 527-532, 2015 Oxysophoridine attenuates the injury caused by acute myocardial infarction in rats through anti oxidative, anti inflammatory and anti apoptotic pathways CONG
Role of high mobility group box 1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and the effect of ethyl pyruvate
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 1537-1541, 2015 Role of high mobility group box 1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and the effect of ethyl pyruvate YUNLING LIN, LIANGLONG CHEN, WEIWEI
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 1537-1541, 2015 Role of high mobility group box 1 in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and the effect of ethyl pyruvate YUNLING LIN, LIANGLONG CHEN, WEIWEI
European Society of Cardiology Congress DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS
 European Society of Cardiology Congress 28 Aug - 01 Sep 2009, Stockholm - Sweden DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS Massimiliano
European Society of Cardiology Congress 28 Aug - 01 Sep 2009, Stockholm - Sweden DONOR AGE NEGATIVELY INFLUENCES THE CYTOPROTECTIVE PARACRINE EFFECTS EXERTED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS Massimiliano
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6135-6139 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. Ying Han 1*, Wen-Yan Xie 2*, Chang-Sheng Xu 1, Hua-Jun
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6135-6139 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effect of microrna-21 on PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a signal transduction pathway. Ying Han 1*, Wen-Yan Xie 2*, Chang-Sheng Xu 1, Hua-Jun
Remifentanil Protects Myocardium through Activation of Anti- Apoptotic Pathways of Survival in Ischemia-Reperfused Rat Heart
 Physiol. Res. 59: 347-356, 2010 Remifentanil Protects Myocardium through Activation of Anti- Apoptotic Pathways of Survival in Ischemia-Reperfused Rat Heart H. S. KIM 1,2, J. E. CHO 3, S. W. HONG 4, S.
Physiol. Res. 59: 347-356, 2010 Remifentanil Protects Myocardium through Activation of Anti- Apoptotic Pathways of Survival in Ischemia-Reperfused Rat Heart H. S. KIM 1,2, J. E. CHO 3, S. W. HONG 4, S.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2017, 9(3):214-218 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Extraction Optimization and Antioxidant Activity
Protein kinase A mediated stimulation of activating transcription factor 3 by hypertrophic stimuli in cardiomyocytes
 Protein kinase A mediated stimulation of activating transcription factor 3 by hypertrophic stimuli in cardiomyocytes Elina Koivisto, MD, PhD Institute of Biomedicine, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology
Protein kinase A mediated stimulation of activating transcription factor 3 by hypertrophic stimuli in cardiomyocytes Elina Koivisto, MD, PhD Institute of Biomedicine, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats
 Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Effects and mechanisms of Fenofibrate on the secretion of vascular endothelial contraction factors in hypertensive rats Y. Zhu 1, H.-S. Wang 1, X.-M. Li 1 and C. Qu 2 1 Department of Cardiac Surgery, General
Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning
 Original Cardiovascular 229 Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning Xujin Xiang 1 Haixia Lin 2 Jin Liu 1 Zeyan Duan 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital,
Original Cardiovascular 229 Equivalent Cardioprotection Induced by Ischemic and Hypoxic Preconditioning Xujin Xiang 1 Haixia Lin 2 Jin Liu 1 Zeyan Duan 1 1 Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital,
CURRICULUM VITAE Shanshan Zhou. Shanshan Zhou. Department of Cardiology. Tel: Feb 25, 1982, China. Chinese.
 CURRICULUM VITAE Shanshan Zhou PERSONAL DETAILS Name: Work address: Shanshan Zhou Department of Cardiology The General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army 28 Fuxing Road, Haidian District, Beijing,
CURRICULUM VITAE Shanshan Zhou PERSONAL DETAILS Name: Work address: Shanshan Zhou Department of Cardiology The General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army 28 Fuxing Road, Haidian District, Beijing,
The effect of elemene reversing the multidurg resistance of A549/DDP lung cancer cells
 213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic
 Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Product Information. Instruction for Use. Troponin I ELISA kit Catalog Number: EA Storage Temperature: 2 8 C
 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: www.origene.com Product Information Troponin I ELISA kit Catalog Number:
9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: www.origene.com Product Information Troponin I ELISA kit Catalog Number:
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury)
 Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
Special Issue on Pain and Itch
 Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
InteractionofInflammatoryResponseandSympatheticNervousSystemintheCentralRegulationofChronicHeartFailureinRats
 : I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
: I Surgeries and Cardiovascular System Volume 16 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Original Article mir-210 inhibits oxidative stress damage in myocardial cell injury model
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3077-3084 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0042144 Original Article mir-210 inhibits oxidative stress damage in myocardial cell injury model Yu Pan, Xianqing Shi, Songsong
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3077-3084 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0042144 Original Article mir-210 inhibits oxidative stress damage in myocardial cell injury model Yu Pan, Xianqing Shi, Songsong
cardiac pre and post conditioning
 cardiac pre and post conditioning i Stefan De Hert Department of Anesthesiology University Hospital Ghent University of Ghent 2010 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Belgium = limited exposition to a small potential
cardiac pre and post conditioning i Stefan De Hert Department of Anesthesiology University Hospital Ghent University of Ghent 2010 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent Belgium = limited exposition to a small potential
Prediction of Life-Threatening Arrhythmia in Patients after Myocardial Infarction by Late Potentials, Ejection Fraction and Holter Monitoring
 Prediction of Life-Threatening Arrhythmia in Patients after Myocardial Infarction by Late Potentials, Ejection Fraction and Holter Monitoring Yu-Zhen ZHANG, M.D.,* Shi-Wen WANG, M.D.,* Da-Yi Hu, M.D.,**
Prediction of Life-Threatening Arrhythmia in Patients after Myocardial Infarction by Late Potentials, Ejection Fraction and Holter Monitoring Yu-Zhen ZHANG, M.D.,* Shi-Wen WANG, M.D.,* Da-Yi Hu, M.D.,**
Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Acute lung injury in children : from viral infection and mechanical ventilation to inflammation and apoptosis Bern, R.A. Link to publication Citation for published
E. Cervio, P. Danieli, C. Ciuffreda, F. Pisano, M. Roccio, M. Gnecchi. The authors have no financial disclosures to declare
 16 th ISCT Annual Meeting SOLUBLE FACTORS RELEASED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS OF FETAL ORIGIN LEAD TO CARDIOMYOCYTE PROTECTION THROUGH THE INHIBITION OF PRO-APOPTOTIC SIGNALING E. Cervio, P. Danieli,
16 th ISCT Annual Meeting SOLUBLE FACTORS RELEASED BY HUMAN MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS OF FETAL ORIGIN LEAD TO CARDIOMYOCYTE PROTECTION THROUGH THE INHIBITION OF PRO-APOPTOTIC SIGNALING E. Cervio, P. Danieli,
Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury
 Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury P. Zhu 1 *, M.Y. Zhao 1,2 *, X.H. Li 1 *, Q. Fu 1, Z.F. Zhou 1, C.F. Huang 1, X.S. Zhang 1, H.L.
Effect of low temperatures on BAX and BCL2 proteins in rats with spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury P. Zhu 1 *, M.Y. Zhao 1,2 *, X.H. Li 1 *, Q. Fu 1, Z.F. Zhou 1, C.F. Huang 1, X.S. Zhang 1, H.L.
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury
 Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Achyranthes bidentata Polypeptides Reduces Oxidative Stress and Exerts Protective Effects against Myocardial Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury in Rats
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 213, 14, 19792-1984; doi:1.339/ijms14119792 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Achyranthes bidentata Polypeptides Reduces
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 213, 14, 19792-1984; doi:1.339/ijms14119792 Article OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Achyranthes bidentata Polypeptides Reduces
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Concurrent Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report
 Concurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage and AMI 155 Concurrent Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report Chen-Chuan Cheng 1, Wen-Shiann Wu 1, Chun-Yen Chiang 1, Tsuei-Yuang Huang
Concurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage and AMI 155 Concurrent Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report Chen-Chuan Cheng 1, Wen-Shiann Wu 1, Chun-Yen Chiang 1, Tsuei-Yuang Huang
Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells.
 Chem Biol Interact. 2010 May 14;185(3):174-81. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells. Zhang Y, Zhou L, Bao YL, Wu
Chem Biol Interact. 2010 May 14;185(3):174-81. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Butyrate induces cell apoptosis through activation of JNK MAP kinase pathway in human colon cancer RKO cells. Zhang Y, Zhou L, Bao YL, Wu
MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012)
![MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012) MCD-microRNA. WU Hong-quan, LIU Di-chuan *, TONG Xin, CAI Min, HUANG Jing. (LVIDd) A [ ] (2012)](/thumbs/81/83672149.jpg) MCD-microRNA [ ] A (MCD)-microRNA MCD MCD 4 MCD-microRNA HEK293 PCR MCD mrna 28 + 3 ( + + + + + + ) 7 7 ( + ) MCD-microRNA 4 4d 1 28d (LVEF) (FS) (LVIDd)A PCR 1 MCD mrna82% + + + LVEF FS (P 0.05) (P 0.05)
MCD-microRNA [ ] A (MCD)-microRNA MCD MCD 4 MCD-microRNA HEK293 PCR MCD mrna 28 + 3 ( + + + + + + ) 7 7 ( + ) MCD-microRNA 4 4d 1 28d (LVEF) (FS) (LVIDd)A PCR 1 MCD mrna82% + + + LVEF FS (P 0.05) (P 0.05)
Effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on myocardial apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats
 Effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on myocardial apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats M.X. Zhou 1 *, J.H. Fu 2 *, Q. Zhang 2 and J.Q. Wang 3 1 Beijing Hospital of TCM Affiliated with Capital
Effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on myocardial apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats M.X. Zhou 1 *, J.H. Fu 2 *, Q. Zhang 2 and J.Q. Wang 3 1 Beijing Hospital of TCM Affiliated with Capital
Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion injury
 Bei et al. BMC Medicine (2019) 17:42 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-019-1268-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion
Bei et al. BMC Medicine (2019) 17:42 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-019-1268-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide protects against myocardial ischemia/ reperfusion
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Efficacy of Coenzyme Q10 Administra Aortic Stenosis and Pacemaker Induc Igarashi, Katsuro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1984, 29 Issue Date 1984-10-25
Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Master Eudipharm 2012 Introductory Module, Principles of Discovery of Medicine and Development Planning. Nathan Mewton, MD, PhD. September 26 th 2012
 Master Eudipharm 2012 Introductory Module, Principles of Discovery of Medicine and Development Planning * Nathan Mewton, MD, PhD. September 26 th 2012 *A little bit of History *Rabies a viral disease that
Master Eudipharm 2012 Introductory Module, Principles of Discovery of Medicine and Development Planning * Nathan Mewton, MD, PhD. September 26 th 2012 *A little bit of History *Rabies a viral disease that
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Cardiac macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits JNK pathway activation and injury during ischemia/reperfusion
 Research article Cardiac macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits JNK pathway activation and injury during ischemia/reperfusion Dake Qi, 1 Xiaoyue Hu, 1 Xiaohong Wu, 1 Melanie Merk, 2 Lin Leng,
Research article Cardiac macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits JNK pathway activation and injury during ischemia/reperfusion Dake Qi, 1 Xiaoyue Hu, 1 Xiaohong Wu, 1 Melanie Merk, 2 Lin Leng,
Original Article Protective effects of quercetin against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(4):6176-6183 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0045887 Original Article Protective effects of quercetin against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats Hai-Zhu Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(4):6176-6183 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0045887 Original Article Protective effects of quercetin against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats Hai-Zhu Zhang
Sean Davidson. The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK
 Key pathways to ischemia-reperfusion injury Sean Davidson The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK Outline What is ischaemia-reperfusion injury? What causes ischaemia-reperfusion
Key pathways to ischemia-reperfusion injury Sean Davidson The Hatter Cardiovascular Institute University College London, UK Outline What is ischaemia-reperfusion injury? What causes ischaemia-reperfusion
Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4685-4689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017991 Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia Chen Lv, Hui Zheng, Mingyang Wei,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4685-4689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017991 Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia Chen Lv, Hui Zheng, Mingyang Wei,
Sodium selenite induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells via Bax-dependent mitochondrial pathway
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Sodium selenite induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells via Bax-dependent mitochondrial pathway Z. LI 1,2, J. MENG 3, T.-J. XU 4, X.-Y. QIN 5, X.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Sodium selenite induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells via Bax-dependent mitochondrial pathway Z. LI 1,2, J. MENG 3, T.-J. XU 4, X.-Y. QIN 5, X.-D.
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Honokiol protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 5: 315-319, 2013 Honokiol protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation YUN WANG, ZHONG ZE ZHANG,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 5: 315-319, 2013 Honokiol protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation YUN WANG, ZHONG ZE ZHANG,
Running head: REMIFENTANIL AND DESFLURANE PROTECTIVE FOR DONOR HEART 1
 Running head: REMIFENTANIL AND DESFLURANE PROTECTIVE FOR DONOR HEART 1 Remifentanil and Desflurane as a Myocardial Protective Regimen for Donor Hearts in the Perioperative Procurement Phase of the Brain-dead
Running head: REMIFENTANIL AND DESFLURANE PROTECTIVE FOR DONOR HEART 1 Remifentanil and Desflurane as a Myocardial Protective Regimen for Donor Hearts in the Perioperative Procurement Phase of the Brain-dead
Effects of Heat Shock Proteins on Protein Aggregation Induced by Transient Myocardial Ischemia
 CN 4321262/ R 2003 11 5 391 [ ] 100723949 (2003) 1120420391206,,,,, (, 410078) [ ] ; ; ; ; ; B2 ; [ ] 70 B2 Wistar 70 B2 : 15 min 30 min 4 h,24 h,72 h, 15 min 4 h 24 h, 24 h 70 70, 15 min 4 h 70, B2 15
CN 4321262/ R 2003 11 5 391 [ ] 100723949 (2003) 1120420391206,,,,, (, 410078) [ ] ; ; ; ; ; B2 ; [ ] 70 B2 Wistar 70 B2 : 15 min 30 min 4 h,24 h,72 h, 15 min 4 h 24 h, 24 h 70 70, 15 min 4 h 70, B2 15
Ischemic Postconditioning During Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Mechanisms and Clinical Application Jian Liu, MD FACC FESC FSCAI Chief Phy
 Ischemic Postconditioning During Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Mechanisms and Clinical Application Jian Liu, MD FACC FESC FSCAI Chief Physician, Professor of Medicine Department of Cardiology,
Ischemic Postconditioning During Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Mechanisms and Clinical Application Jian Liu, MD FACC FESC FSCAI Chief Physician, Professor of Medicine Department of Cardiology,
Myocardial cell death caused by necrosis and apoptosis is
 Role of Akt Signaling in Mitochondrial Survival Pathway Triggered by Hypoxic Preconditioning Takamichi Uchiyama, MD; Richard M. Engelman, MD; Nilanjana Maulik, PhD; Dipak K. Das, PhD Background The signaling
Role of Akt Signaling in Mitochondrial Survival Pathway Triggered by Hypoxic Preconditioning Takamichi Uchiyama, MD; Richard M. Engelman, MD; Nilanjana Maulik, PhD; Dipak K. Das, PhD Background The signaling
The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats
 Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
Adenosine stimulates the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells to the ischemic heart
 Adenosine stimulates the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells to the ischemic heart Involvement of the microrna-150-cxcr4-sdf-1α pathway Emeline Goretti, MSc No conflict of interest Endothelial
Adenosine stimulates the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells to the ischemic heart Involvement of the microrna-150-cxcr4-sdf-1α pathway Emeline Goretti, MSc No conflict of interest Endothelial
Relative SOD1 activity. Relative SOD2 activity. Relative SOD activity (Infected:Mock) + CP + DDC
 Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Oxidative Stress in PGE2 Treated H9c2 Cardiomyocytes. Rose Picklo
 Oxidative Stress in PGE2 Treated H9c2 Cardiomyocytes Rose Picklo Abstract Heart disease is the leading cause of adult death in the United States. Chronic ischemia resulting from obstruction of coronary
Oxidative Stress in PGE2 Treated H9c2 Cardiomyocytes Rose Picklo Abstract Heart disease is the leading cause of adult death in the United States. Chronic ischemia resulting from obstruction of coronary
Original Article Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):4100-4106 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0037711 Original Article Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats Ge Jin,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):4100-4106 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0037711 Original Article Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats Ge Jin,
Endotoxin Induces Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Vascular Cells: A Novel Mechanism Involved in Vascular Inflammation
 Endotoxin Induces Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Vascular Cells: A Novel Mechanism Involved in Vascular Inflammation Introduction Feng-Yen Lin, Ph.D. 1, and Shing-Jong Lin, M.D., PhD. 2, 1 Department
Endotoxin Induces Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Vascular Cells: A Novel Mechanism Involved in Vascular Inflammation Introduction Feng-Yen Lin, Ph.D. 1, and Shing-Jong Lin, M.D., PhD. 2, 1 Department
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
perk/erk STAT5B
 pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
pakt/akt relative to saline (fold).5.5.5 control perk/erk relative to saline (fold).6.4..8.6.4. p=.6 control db/+ Hsp6 VDAC Hsp6/VDAC (relative to db/+) 8 6 4 db/+ C db/+ Hsp6 Hsp6/actin (relative to db/+)
Original Article Protective effects of LM22A-4 on injured spinal cord nerves
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):6526-6532 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008748 Original Article Protective effects of LM22A-4 on injured spinal cord nerves Guangzhe Yu 1, Wenbo Wang 2 Departments
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):6526-6532 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008748 Original Article Protective effects of LM22A-4 on injured spinal cord nerves Guangzhe Yu 1, Wenbo Wang 2 Departments
Original Article Reduction of apoptosis as a target of dexmedetomidine effects on ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic myocardium
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):2606-2612 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0042011 Original Article Reduction of apoptosis as a target of dexmedetomidine effects on ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(2):2606-2612 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0042011 Original Article Reduction of apoptosis as a target of dexmedetomidine effects on ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic
Challenging Issues in Cardiac Biomarker interpretation. F. Nikaeen. MD interventional Cardiologist
 Challenging Issues in Cardiac Biomarker interpretation F. Nikaeen. MD interventional Cardiologist Biomarkers Types of Troponin Troponin C Binds calcium Troponin I Binds actin Troponin T Binds tropomyosin
Challenging Issues in Cardiac Biomarker interpretation F. Nikaeen. MD interventional Cardiologist Biomarkers Types of Troponin Troponin C Binds calcium Troponin I Binds actin Troponin T Binds tropomyosin
ab Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions.
 ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Microstructural Basis of Conduction II Introduction to Experimental Studies
 Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Microstructural Basis of Conduction II Introduction to Experimental Studies Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Microstructural Basis of Conduction
Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Microstructural Basis of Conduction II Introduction to Experimental Studies Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu Overview Microstructural Basis of Conduction
6. Lochner, A., Tromp, E., Mouton, R. Signal transduction in myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion. Mol Cell Biochem., 160/161: , 1996.
 PUBLICATIONS IN PEER-REVIEWED JOURNALS: 1. Moolman, J.A., Genade, S., Tromp, E., Lochner, A. Ischaemic preconditioning: interaction with antiadrenergic interventions. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27(6): A161, June
PUBLICATIONS IN PEER-REVIEWED JOURNALS: 1. Moolman, J.A., Genade, S., Tromp, E., Lochner, A. Ischaemic preconditioning: interaction with antiadrenergic interventions. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27(6): A161, June
The Effects of Fasudil at Different Doses on Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:524 530 Basic Science The Effects of Fasudil at Different Doses on Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats Lijuan Tan, Nana Pan, Lingfan Yu, Renchao Yu and Bin Yang
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:524 530 Basic Science The Effects of Fasudil at Different Doses on Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats Lijuan Tan, Nana Pan, Lingfan Yu, Renchao Yu and Bin Yang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):11847-11853 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012859 Review Article Microenviromental change after synthetic E-selectins interfere in ischemia-reperfusion in rats and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(9):11847-11853 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012859 Review Article Microenviromental change after synthetic E-selectins interfere in ischemia-reperfusion in rats and
Human Troponin I ELISA Kit
 Human Troponin I ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA2358 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This kit is intended for the quantitative determination of cardiac troponin I in human serum. Measurement of troponin I values are
Human Troponin I ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA2358 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use This kit is intended for the quantitative determination of cardiac troponin I in human serum. Measurement of troponin I values are
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis
 Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
Silibinin i activates p53-caspase-2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of Cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma RT4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between
Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 against MPTP-induced apoptosis in mouse substantia nigra neurons 1
 Chen XC et al / Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002 Sep; 23 (9): 829-834 829 2002, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN 1671-4083 Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com
Chen XC et al / Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002 Sep; 23 (9): 829-834 829 2002, Acta Pharmacologica Sinica ISSN 1671-4083 Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Sciences http://www.chinaphar.com
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
S everal studies of apoptosis in the heart have been
 362 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tempero spatial dissociation between the expression of Fas and apoptosis after coronary occlusion Q Z Feng, T D Li, L X Wei, X Qiao, J Yi, L Wang, T S Yang... See end of article for
362 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tempero spatial dissociation between the expression of Fas and apoptosis after coronary occlusion Q Z Feng, T D Li, L X Wei, X Qiao, J Yi, L Wang, T S Yang... See end of article for
Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 739702, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/739702 Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia Kiyotake Ishikawa, Dennis Ladage, Kleopatra Rapti,
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 739702, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/739702 Case Report Multimodality Imaging of Chronic Ischemia Kiyotake Ishikawa, Dennis Ladage, Kleopatra Rapti,
Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction. Rita Alonaizan
 Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction Rita Alonaizan Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics St Catherine s College Supervisor:
Cell therapy: enhancing the therapeutic potential of cardiac progenitors for delivery post myocardial infarction Rita Alonaizan Department of Physiology, Anatomy & Genetics St Catherine s College Supervisor:
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Cardiac Protective Effects of Resveratrol Glucoside in Rat Models with Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion
 Cardiac Protective Effects of Resveratrol Glucoside in Rat Models with Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Jihong Li 1, Haiyan Yu 2, Jingya Yang 3 1.Zhang Zhongjing School of Chinese Medicine, Nangyang Institute
Cardiac Protective Effects of Resveratrol Glucoside in Rat Models with Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Jihong Li 1, Haiyan Yu 2, Jingya Yang 3 1.Zhang Zhongjing School of Chinese Medicine, Nangyang Institute
Mingjin Jiang 1, Jing Li 1, Qiuxian Peng 1,2, Yi Liu 1, Wei Liu 1, Chaohua Luo 1, Ju Peng 1, Junkui Li 1, Ken Kin Lam Yung 2* and Zhixian Mo 1*
 Jiang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2014, 11:167 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated
Jiang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2014, 11:167 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated
Effect of Taurine on Acinar Cell Apoptosis and Pancreatic Fibrosis in Dibutyltin Dichloride-induced Chronic Pancreatitis
 212 66 4 329334 Effect of Taurine on Acinar Cell Apoptosis and Pancreatic Fibrosis in Dibutyltin Dichloride-induced Chronic Pancreatitis a,c a* b b a a b a a b c 33 66 4 ʼ 6 6 6 28 6 5 5 5 28 45 ʼ ʼ ʼ
212 66 4 329334 Effect of Taurine on Acinar Cell Apoptosis and Pancreatic Fibrosis in Dibutyltin Dichloride-induced Chronic Pancreatitis a,c a* b b a a b a a b c 33 66 4 ʼ 6 6 6 28 6 5 5 5 28 45 ʼ ʼ ʼ
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
Title: Bradykinin and adenosine receptors mediate desflurane induced postconditioning in human myocardium: role of reactive oxygen species
 Author's response to reviews Title: Bradykinin and adenosine receptors mediate desflurane induced postconditioning in human myocardium: role of reactive oxygen species Authors: Sandrine Lemoine (sand.lemoine2@wanadoo.fr)
Author's response to reviews Title: Bradykinin and adenosine receptors mediate desflurane induced postconditioning in human myocardium: role of reactive oxygen species Authors: Sandrine Lemoine (sand.lemoine2@wanadoo.fr)
