A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.
|
|
|
- August Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5 Published by Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd. Penthouse Level, Suntec Tower 3 8 Temasek Boulevard Singapore editorial@panstanford.com Web: British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library. Handbook of Dynein Copyright 2012 Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved. This book, or parts thereof, may not be reproduced in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording or any information storage and retrieval system now known or to be invented, without written permission from the publisher. For photocopying of material in this volume, please pay a copying fee through the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc., 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923, USA. In this case permission to photocopy is not required from the publisher. ISBN (Hardcover) ISBN (ebook) Printed in the USA
6 Contents 1. Dyneins: Ancient Protein Complexes Gradually Reveal their Secrets 1 Linda A. Amos and Keiko Hirose 1.1 Introduction Dynein Molecular Structure Coming into View Axonemal Arms Dynein Molecules Lighter Components of the Complexes Effect on the Heavy Chain of Vanadate and UV Motility of Dynein Evolution Where did Dyneins Come From? AAA+ Proteins Ancestors and Relatives of the Dynein Heavy Chain CD-2 Is Probably Similar to the Common Ancestor Almost All Eukaryotic Organisms Express Dynein Summary Two Decades of Cytoplasmic Dynein: From Fast to Forceful 27 Richard J. McKenney and Richard B. Vallee 2.1 Introduction Cytoplasmic Dynein Functions Compositional and Regulatory Diversity Cytoplasmic Dynein Isoforms Accessory Complexes Dynactin LIS1 and NudE/NudEL Effects of LIS1 and NudE on Dynein Activity in vitro LIS1/NudE Enhancement of Multiple Motor Transport Cytoplasmic Dynein Regulation by Dynactin vs. NudE-LIS Functional Analysis of the Dynein Motor Domain 43 Tomohiro Shima, Kazuo Sutoh, and Takahide Kon 3.1 Introduction The Dynein Motor Domain ATPase Cycles in the Head Domain Movement of the Linker 49
7 vi Contents 3.5 Microtubule Binding at the Stalk Perspectives Structural Studies on the Dynein Heavy Chain 63 Anthony J. Roberts and Stan A. Burgess 4.1 Introduction The Form and Function of the Heavy Chain The Tail Domain The Stalk Domain The Head Domain The AAA+ ring The C-terminal sequence The linker domain Conformational Changes Conclusions and Outlook Structural Analysis of Dynein Bound to Microtubules 81 Keiko Hirose 5.1 Introduction Formation of a Dynein-Microtubule Complex MT-Binding of Outer-Arm Dynein Purified from Chlamydomonas Axoneme MT-Binding of Outer-Arm Dynein Purified from Tetrahymena Axoneme MT-Binding of Outer-Arm Dynein Purified from Sea Urchin Axonemes MT-Binding of Cytoplasmic Dynein MT-Binding of Recombinant Dynein Motor Domains Analysis of the Dynein-Microtubule Complex D Structural Analysis of the Dynein-MT Complex D structural analysis of recombinant dynein stalk regions bound to MTs D structural analysis of recombinant dynein bound to MTs D structural analysis of axonemal dynein cross-bridging MTs Angles of Dynein Stalks Bound to MTs Movement of the Heads in MT-Bound Axonemal Dynein Motile Mechanism of Dynein Future Outlook 94
8 Contents vii 6. The Dynein Stalk: Atomic Structure and Roles in the Mechanism of the Dynein Motor 99 Andrew P. Carter 6.1 Introduction Structural Features of the Dynein Stalk Historical Background Microtubule-Binding Domain Stalk Coiled Coil Junction of Stalk and AAA Ring Communication Along the Dynein Stalk Models for Communication Large scale conformational changes Communication via changes in stalk binding angle Relative sliding of helices in the coiled coil Structural Changes During Communication Half-heptad movement Smaller shifts in the coiled coil Conformational changes around the kink in the stalk Role of the Stalk in the Dynein Powerstroke Models of Stalk Involvement in the Powerstroke Stalk acts as a paddle Structural change near MTBD rotates stalk (stalk lever arm model) Stalk is rigid and holds AAA ring so that conformational change is directed Stalk acts as a tether, preferentially binding toward the MT minus end The Stalk and Directionality Conclusion Motile and Enzymatic Properties of Native Dynein Molecules 123 Yoko Y. Toyoshima and Hideo Higuchi 7.1 Introduction Preparations of Native Dynein Molecules for Functional Assays Cytoplasmic Dynein from Mammalian Brain Axonemal Dyneins from Tetrahymena Cilia 126
9 viii Contents 7.3 Measurement of Dynein ATPase Activity Method for Steady-State ATPase Assaying of Dyneins ATPase Activity Properties of Native Dyneins In vitro Motility of Native Dynein Molecules In vitro Motility Assay for Dynein Motile Properties of Native Dynein Molecules In vitro Motility of Single Native Dynein Molecules Processivity of Single Dynein Molecules Processivity and Step Size as Determined with FIONA Method Step Size and Force Measurement of Single Dynein Molecules by Optical Trapping Model of Dynein Walking Vesicles Transport Driven by Dynein in Cells Step Size of Dynein During Vesicle Transport in Cells Force Generation by Dynein in Cells In vivo Mechanical Measurement of Dynein Summary Motile Properties of Cytoplasmic Dynein 145 Samara L. Reck-Peterson, Ronald D. Vale, and Arne Gennerich 8.1 Introduction Sources of Cytoplasmic Dynein Native Dynein Recombinant Dynein Cytoplasmic Dynein Motility in the Absence of Load Cytoplasmic Dynein is a Processive Motor Stepping Behavior of Cytoplasmic Dynein Under Unloaded Conditions Directionality of Cytoplasmic Dynein Response of Cytoplasmic Dynein to Load Regulation of Cytoplasmic Dynein Motility AAA+ Domains AAA AAA2, AAA AAA Dynein Cofactors Dynactin LIS1 and NudE 163
10 Contents ix 8.6 In vivo Studies of Dynein Motility Conclusions and Future Directions Motility of Inner-Arm Dyneins 173 Yuji Shitaka, Hiroaki Kojima, and Kazuhiro Oiwa 9.1 Introduction Description of Inner Arms In vitro Motility Assays Single-Molecule Measurements Solutions Protein Preparations Inner-Arm Dynein Subspecies Preparation of Microtubules and their Fluorescent Labeling In vitro Motility Assays Overview Preparation of dynein-coated beads for optical trap nanometry Preparation of a flow cell Preparation of patterned surface for bio-nano device development In vitro motility assay of inner-arm dyneins Evaluation of the processivity Optical trap nanometry Results In vitro Motility Assays Optical-Trap Nanometry Studies on Dynein Motility The Directional Control of MT Movement on Dynein-Coated Surfaces Summary and Outlook Levels of Coordination that Need to be Studied Dynein Motility in Cilia and Flagella 203 Avanti Gokhale, Maureen Wirschell, Winfield S. Sale, and David R. Mitchell 10.1 Introduction Axoneme Structural Organization and Dynein Subforms Basic Axonemal Structure, Axis of Bending and the 96 nm Repeat 205
11 x Contents Definition of the Dyneins and their Functions The outer dynein arms, beat frequency, and force The inner dynein arms and control of ciliary waveform Axonemal Structures that Regulate Dynein The Central Pair Radial Spoke Network The DRC The Dynein Arm Linkers Sliding Microtubule/Direction Switching Model The Sliding Microtubule Model A Switching Model for Forward and Reverse Bending Inherent Regulation of Microtubule Sliding Mechanical Feedback and Calcium Regulation Mechanical Feedback Mechanisms Central pair orientation Radial spoke tilting Central pair asymmetry Signaling Mechanisms in Bend Propagation Central pair as control center Control via bend-plane doublets Calcium Sensors and Control of Dynein Asymmetry in metazoan spermatozoa Waveform control in algal flagella Arm-associated calcium-binding proteins Regulation of Motility by Phosphorylation Regulation of Outer Arms by Calcium and Phosphorylation Control of beat frequency Activation of motility Regulation of Inner Dynein Arms by Phosphorylation Protein kinase inhibition IC138 mutants Inhibition of CK Role of IC Future Challenges and Opportunities 231
12 Contents xi 11. 3D Structures of Axonemes 245 Takashi Ishikawa 11.1 Introduction Single-Particle Analysis and Electron Tomography Specimen Preparation for Electron Tomography/ Microscopy Ice-embedding by plunge freezing (cryo) Freeze-fracture deep-etch replica and rotary shadowing Negative staining, cryo-negative, and positive staining Plastic embedded sections Data Acquisition and Reconstruction in Electron Tomography D Averaging from Tomogram, Classification, and Modeling In situ Structure of Dynein Arms Revealed by Electron Tomography D Structure of Outer Dynein Arms D Structure of Inner Dynein Arms Asymmetric Dynein Arrangement in Chlamydomonas Flagella Nucleotide-Induced Structural Change of Flagellar Dynein Arms Structures of Other Components in Flagella Nexin and Other Interdoublet Linkers IFT Radial Spokes and Central Pairs Future Outlook Functional Diversity of Axonemal Dyneins 267 Ritsu Kamiya 12.1 Introduction Biochemical Analyses Separation of Individual Dyneins Subunit Composition Total gene assignment of axonemal dynein heavy chains Phylogeny of axonemal dyneins 272
13 xii Contents 12.3 Functional Diversity Assessed by the Mutant Motility Available Mutants Mutant Phenotypes Mutants lacking any single type of dynein can swim slowly Outer- and inner-arm dynein Specific functions of certain types of dyneins Function of individual heavy chains In Vitro Motility Assays General Features ADP Sensitivity Functional Interactions Between Outer-Arm Heavy Chains Novel Phenomena in Inner-Arm Dyneins Microtubule bending Ratchet-like properties Conclusions and Outlook Assembly and Regulation of Dynein Light Chains 285 Afua Nyarko and Elisar Barbar 13.1 Introduction The Regulatory Subunits: Structure, Functions, and Association States Interactions Between the Intermediate and Light Chain Subunits Mapping Interactions Identifying Conformational Changes High-Resolution Complex Structures Regulation by Disorder-to-Order Transitions Disorder-to-Order Transition at the Sites of Binding Disorder-to-Order Transition Distant from Binding Regulation by Subunit Phosphorylation Poly-Bivalency in Assembled IC The Light Chains Intermediate Chain Assembled Subcomplex Regulatory Subunits of Axonemal Dynein 303 Kazuo Inaba 14.1 Introduction Chlamydomonas Outer-Arm Dynein 304
14 Contents xiii Heavy Chains Intermediate Chains Light Chains LC1: leucine-rich repeat light chain LC2: Tctex2-related light chain LC3 and LC5: thioredoxin homolog associated with dynein HCs LC4: Ca 2+ -binding light chain LC7a and LC7b: Drosophila roadblock homologs LC8, LC6, and LC10: highly conserved protein LC8 and its homologs Dynein Docking Complex Proteins Associated with Outer-Arm Dynein Outer-Arm Dynein from Sperm Flagella Heavy Chains Intermediate Chains Light Chains Proteins Associated with Outer-Arm Dynein Chlamydomonas Inner-Arm Dynein Subunits of Dynein-f/I Subunits of Other Inner-Arm Dyneins Inner-Arm Dynein from Sperm Flagella Regulatory Functions of Dynein Subunits in Ciliary and Flagellar Motility Protein Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation Ca 2+ -Dependent Regulation Redox Poise Nucleotide Metabolism Comparison and Evolutionary Aspects of Axonemal Dynein Components The Role of Dynein in Yeast Nuclear Segregation 325 Melissa D. Stuchell-Brereton, Jeffery K. Moore, and John A. Cooper 15.1 Introduction Mechanisms that Position Nucleus and Spindle The Kar9 Pathway The Dynein Pathway 327
15 xiv Contents Discovery of dynein in yeast Dynein localizes to MT plus ends and the cell cortex in S. cerevisiae Dynein generates force at interface between cmts and the cortex Components of the Yeast Dynein Complex and Conservation Across Species Heavy Chain/DYN Intermediate Chain/PAC Light Intermediate Chain/DYN Light Chain/DYN Regulatory Components Contributing to Dynein Function Dynactin Nip100/p150 Glued Jnm1/dynamitin Yll049w/Ldb18/p Arp Arp10/Arp Bik1/CLIP-170 and the Kinesin Kip Pac1/LIS1 and Ndl1/NudE(L) Num Cell Polarity and Cell Cycle Regulators Offloading Model Methods for Studying Dynein Function in Yeast Assaying the Position of the Nucleus and Spindle as a Measure of Dynein Activity Examining nuclear segregation by DAPI-stain Examining the position of the mitotic spindle using GFP-labeled MTs 349 Index 363
3-2 Mechanisms of Dynein Functions as Information Processing Devices
 3-2 Mechanisms of Dynein Functions as Information Processing Devices SAKAKIBARA Hitoshi We study mechanisms of motor-protein functions to find sources of new technology of information processing devices.
3-2 Mechanisms of Dynein Functions as Information Processing Devices SAKAKIBARA Hitoshi We study mechanisms of motor-protein functions to find sources of new technology of information processing devices.
Motile Properties of Cytoplasmic Dynein
 Chapter 8 Motile Properties of Cytoplasmic Dynein Samara L. Reck-Peterson, a Ronald D. Vale, b and Arne Gennerich c a Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA b Department of
Chapter 8 Motile Properties of Cytoplasmic Dynein Samara L. Reck-Peterson, a Ronald D. Vale, b and Arne Gennerich c a Department of Cell Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA b Department of
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep
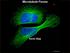 Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
Fifty years of microtubule sliding in cilia
 Fifty years of microtubule sliding in cilia Stephen M. King, University of Connecticut Winfield S Sale, Emory University Journal Title: Molecular Biology of the Cell Volume: Volume 29, Number 6 Publisher:
Fifty years of microtubule sliding in cilia Stephen M. King, University of Connecticut Winfield S Sale, Emory University Journal Title: Molecular Biology of the Cell Volume: Volume 29, Number 6 Publisher:
Cryo-electron tomography of motile cilia and flagella. Ishikawa. Ishikawa Cilia (2015) 4:3 DOI /s
 Cryo-electron tomography of motile cilia and flagella Ishikawa Ishikawa Cilia (2015) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s13630-014-0012-7 Ishikawa Cilia (2015) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s13630-014-0012-7 REVIEW Cryo-electron tomography
Cryo-electron tomography of motile cilia and flagella Ishikawa Ishikawa Cilia (2015) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s13630-014-0012-7 Ishikawa Cilia (2015) 4:3 DOI 10.1186/s13630-014-0012-7 REVIEW Cryo-electron tomography
Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro
 4014 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 May 2008 4014 4019 Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro Kenji Kikushima* and Ritsu Kamiya* y *Department of Biological Sciences,
4014 Biophysical Journal Volume 94 May 2008 4014 4019 Clockwise Translocation of Microtubules by Flagellar Inner-Arm Dyneins In Vitro Kenji Kikushima* and Ritsu Kamiya* y *Department of Biological Sciences,
RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM
 J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
J. exp. Biol. 192, 73 81 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 73 RECONSTITUTION OF METACHRONAL WAVES IN CILIATED CORTICAL SHEETS OF PARAMECIUM II. ASYMMETRY OF THE CILIARY
One of the Nine Doublet Microtubules of Eukaryotic Flagella Exhibits Unique and Partially Conserved Structures
 One of the Nine Doublet Microtubules of Eukaryotic Flagella Exhibits Unique and Partially Conserved Structures Jianfeng Lin, Thomas Heuser, Kangkang Song, Xiaofeng Fu, Daniela Nicastro* Biology Department,
One of the Nine Doublet Microtubules of Eukaryotic Flagella Exhibits Unique and Partially Conserved Structures Jianfeng Lin, Thomas Heuser, Kangkang Song, Xiaofeng Fu, Daniela Nicastro* Biology Department,
Functional Diversity of Axonemal Dyneins as Assessed by in Vitro and in Vivo Motility Assays of Chlamydomonas Mutants
 Functional Diversity of Axonemal Dyneins as Assessed by in Vitro and in Vivo Motility Assays of Chlamydomonas Mutants Author(s): Ritsu Kamiya and Toshiki Yagi Source: Zoological Science, 31(10):633-644.
Functional Diversity of Axonemal Dyneins as Assessed by in Vitro and in Vivo Motility Assays of Chlamydomonas Mutants Author(s): Ritsu Kamiya and Toshiki Yagi Source: Zoological Science, 31(10):633-644.
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Dynein is a motor protein that utilizes ATP as its energy
 Three-dimensional structure of cytoplasmic dynein bound to microtubules Naoko Mizuno*, Akihiro Narita, Takahide Kon, Kazuo Sutoh, and Masahide Kikkawa*, ** *Department of Cell Biology, University of Texas
Three-dimensional structure of cytoplasmic dynein bound to microtubules Naoko Mizuno*, Akihiro Narita, Takahide Kon, Kazuo Sutoh, and Masahide Kikkawa*, ** *Department of Cell Biology, University of Texas
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments Copyright 2013
Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments Copyright 2013
Mechanism of Muscular Contraction
 ~ Sorin2:er Jack A. Rail Mechanism of Muscular Contraction Contents 1 Setting the Stage: Myosin, Actin, Actomyosin and ATP... 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Muscle Structure as Observed by Nineteenth Century
~ Sorin2:er Jack A. Rail Mechanism of Muscular Contraction Contents 1 Setting the Stage: Myosin, Actin, Actomyosin and ATP... 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Muscle Structure as Observed by Nineteenth Century
Single-Molecule Analysis of Dynein Processivity and Stepping Behavior
 Single-Molecule Analysis of Dynein Processivity and Stepping Behavior Samara L. Reck-Peterson, 2 Ahmet Yildiz, 2,3 Andrew P. Carter, 2,3 Arne Gennerich, 2 Nan Zhang, 1,2 and Ronald D. Vale 1,2, * 1 Howard
Single-Molecule Analysis of Dynein Processivity and Stepping Behavior Samara L. Reck-Peterson, 2 Ahmet Yildiz, 2,3 Andrew P. Carter, 2,3 Arne Gennerich, 2 Nan Zhang, 1,2 and Ronald D. Vale 1,2, * 1 Howard
EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA URCHIN SPERM FLAGELLA UNDER IMPOSED HEAD VIBRATION
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 98, 645 65 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 645 EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA
The Journal of Experimental Biology 98, 645 65 (995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 995 645 EFFECT OF BEAT FREQUENCY ON THE VELOCITY OF MICROTUBULE SLIDING IN REACTIVATED SEA
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Yamamoto et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201211048/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. The FAP100 and FAP73 antibodies are specific for the
Supplemental material Yamamoto et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201211048/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. The FAP100 and FAP73 antibodies are specific for the
NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP. Neurology for MRCP Downloaded from The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES
 NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES This page intentionally left blank MRCP NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2
NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2 and PACES This page intentionally left blank MRCP NEUROLOGY FOR MRCP The Essential Guide to Neurology for MRCP Part 1, Part 2
The Geometric Clutch as a Working Hypothesis for Future Research on Cilia and Flagella
 The Geometric Clutch as a Working Hypothesis for Future Research on Cilia and Flagella CHARLES B. LINDEMANN Department of Biological Sciences, Oakland University, Rochester, Michigan, USA ABSTRACT: The
The Geometric Clutch as a Working Hypothesis for Future Research on Cilia and Flagella CHARLES B. LINDEMANN Department of Biological Sciences, Oakland University, Rochester, Michigan, USA ABSTRACT: The
Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa.
 Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa. Correspondence sranjanivenkadesan@gmail.com Disciplines Medical Sciences Keywords Spermatozoa, Motility Humans
Spermatozoa motility in reverse gear? An observation of backward-moving human spermatozoa. Correspondence sranjanivenkadesan@gmail.com Disciplines Medical Sciences Keywords Spermatozoa, Motility Humans
Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella
 Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella Matthew J. Wargo and Elizabeth F. Smith* Department of Biological Sciences, Dartmouth College,
Asymmetry of the central apparatus defines the location of active microtubule sliding in Chlamydomonas flagella Matthew J. Wargo and Elizabeth F. Smith* Department of Biological Sciences, Dartmouth College,
Polarity of Dynein-Microtubule Interactions in Vitro : Cross-bridging between Parallel and Antiparallel Microtubules
 Polarity of Dynein-Microtubule Interactions in Vitro : Cross-bridging between Parallel and Antiparallel Microtubules F. D. WARNER and D. R. MITCHELL Department of Biology, Biological Research Laboratories,
Polarity of Dynein-Microtubule Interactions in Vitro : Cross-bridging between Parallel and Antiparallel Microtubules F. D. WARNER and D. R. MITCHELL Department of Biology, Biological Research Laboratories,
Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy
 Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-based Approach This page intentionally left blank Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-based Approach Editors Heleen van Aswegen Department
Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-based Approach This page intentionally left blank Cardiopulmonary Physiotherapy in Trauma An Evidence-based Approach Editors Heleen van Aswegen Department
Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of ATP to an elastase-treated flagellar axoneme
 Journal of Cell Science 108, 1359-1369 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1359 Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of
Journal of Cell Science 108, 1359-1369 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 1359 Cyclical bending movements induced locally by successive iontophoretic application of
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Dynein is a molecular motor that moves along microtubules
 Overlapping hand-over-hand mechanism of single molecular motility of cytoplasmic dynein Shiori Toba*, Tomonobu M. Watanabe, Lisa Yamaguchi-Okimoto*, Yoko Yano Toyoshima*, and Hideo Higuchi *Department
Overlapping hand-over-hand mechanism of single molecular motility of cytoplasmic dynein Shiori Toba*, Tomonobu M. Watanabe, Lisa Yamaguchi-Okimoto*, Yoko Yano Toyoshima*, and Hideo Higuchi *Department
Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued
 Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Cell structure of Eukaryotic cells Lecture 6 9/17 Dr. Hirsh Organization of Cells, continued Lots of double-membraned organelles Existence of an Endo-membrane system separation of areas of cell, transport
Docking Complex-independent alignment of outer dynein arms with 24-nm periodicity in vitro
 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd. Docking Complex-independent alignment of outer dynein arms with 24-nm periodicity in vitro Toshiyuki Oda 1,2 *, Tatsuki Abe 1, Haruaki Yanagisawa 1, and
2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd. Docking Complex-independent alignment of outer dynein arms with 24-nm periodicity in vitro Toshiyuki Oda 1,2 *, Tatsuki Abe 1, Haruaki Yanagisawa 1, and
Fungal cell walls are rigid with less flexibility due to a combination of more sugar (more chitin) and protein flexibility.
 Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Fertilization: Beginning a New New Organism Or
 Fertilization: Beginning a New Organism 1. Contact and recognition between sperm and egg. In most cases, this ensures that the sperm and egg are of the same species. 2. Regulation of sperm entry into the
Fertilization: Beginning a New Organism 1. Contact and recognition between sperm and egg. In most cases, this ensures that the sperm and egg are of the same species. 2. Regulation of sperm entry into the
CMB621: Cytoskeleton. Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved
 CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 4. Most cells are microscopic. Cells vary in size and shape
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Mechanical Properties of Inner-Arm Dynein-F (Dynein I1) Studied With In Vitro Motility Assays
 886 Biophysical Journal Volume 93 August 2007 886 894 Mechanical Properties of Inner-Arm Dynein-F (Dynein I1) Studied With In Vitro Motility Assays Norito Kotani,* Hitoshi Sakakibara, y Stan A. Burgess,
886 Biophysical Journal Volume 93 August 2007 886 894 Mechanical Properties of Inner-Arm Dynein-F (Dynein I1) Studied With In Vitro Motility Assays Norito Kotani,* Hitoshi Sakakibara, y Stan A. Burgess,
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Cell Biology Monographs
 Cell Biology Monographs Edited by M. Alfert, Berkeley, Calif. w. Beermann, Tilbingen L. Goldstein, Lexington, Ky. K. R. Porter, Boulder, Colo. Advisory Board J. Brachet, Bruxelles D. Branton, Cambridge,
Cell Biology Monographs Edited by M. Alfert, Berkeley, Calif. w. Beermann, Tilbingen L. Goldstein, Lexington, Ky. K. R. Porter, Boulder, Colo. Advisory Board J. Brachet, Bruxelles D. Branton, Cambridge,
Identification of predicted human outer dynein arm genes- candidates for primary ciliary dyskinesia genes
 JMG Online First, published on June 3, 2005 as 10.1136/jmg.2005.033001 Identification of predicted human outer dynein arm genes- candidates for primary ciliary dyskinesia genes Gregory J. Pazour 1, Nathan
JMG Online First, published on June 3, 2005 as 10.1136/jmg.2005.033001 Identification of predicted human outer dynein arm genes- candidates for primary ciliary dyskinesia genes Gregory J. Pazour 1, Nathan
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
FUTURE DIRECTIONS FOR STUDIES OF MECHANISMS FOR GENERATING FLAGELLAR BENDING WAVES
 y. Cell Sci. Suppl. 4, 103-113 (1986) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 103 FUTURE DIRECTIONS FOR STUDIES OF MECHANISMS FOR GENERATING FLAGELLAR BENDING WAVES C H A R L ES
y. Cell Sci. Suppl. 4, 103-113 (1986) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 103 FUTURE DIRECTIONS FOR STUDIES OF MECHANISMS FOR GENERATING FLAGELLAR BENDING WAVES C H A R L ES
Lis1 Acts as a Clutch between the ATPase and Microtubule-Binding Domains of the Dynein Motor
 Acts as a Clutch between the ATPase and Microtubule-Binding Domains of the Dynein Motor Julie Huang, 1,4 Anthony J. Roberts, 1,2,4 Andres E. Leschziner, 3 and Samara L. Reck-Peterson 1, * 1 Department
Acts as a Clutch between the ATPase and Microtubule-Binding Domains of the Dynein Motor Julie Huang, 1,4 Anthony J. Roberts, 1,2,4 Andres E. Leschziner, 3 and Samara L. Reck-Peterson 1, * 1 Department
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Identification of dynein as the outer arms of sea urchin
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol 74, No. 11, pp. 5006-5010, November 1977 Cell Biology Identification of dynein as the outer arms of sea urchin sperm axonemes (flagella/adenosinetriphosphatase/motility/immunoelectron
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol 74, No. 11, pp. 5006-5010, November 1977 Cell Biology Identification of dynein as the outer arms of sea urchin sperm axonemes (flagella/adenosinetriphosphatase/motility/immunoelectron
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography
 Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography A Color Atlas This page intentionally left blank Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography A Color Atlas Kelvin Y.C. Teo Wong Chee Wai Andrew S.H. Tsai Daniel
Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography A Color Atlas This page intentionally left blank Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography A Color Atlas Kelvin Y.C. Teo Wong Chee Wai Andrew S.H. Tsai Daniel
ATPases; P-type, V-type & F-type, how does H + power V & F-type 2015
 ATPases; P-type, V-type & F-type, how does H + power V & F-type 2015 1 /2 O 2 +NADH 2 H 2 O + NAD + ΔE O =0.82-(-0.32)= 1.14V ΔG O = -218KJ/mol The oxidation of 1mol of NADH is associated with the release
ATPases; P-type, V-type & F-type, how does H + power V & F-type 2015 1 /2 O 2 +NADH 2 H 2 O + NAD + ΔE O =0.82-(-0.32)= 1.14V ΔG O = -218KJ/mol The oxidation of 1mol of NADH is associated with the release
IC97 Is a Novel Intermediate Chain of I1 Dynein That Interacts with Tubulin and Regulates Interdoublet Sliding
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biological Sciences Faculty Research and Publications Biological Sciences, Department of 7-1-2009 IC97 Is a Novel Intermediate Chain of I1 Dynein That Interacts
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biological Sciences Faculty Research and Publications Biological Sciences, Department of 7-1-2009 IC97 Is a Novel Intermediate Chain of I1 Dynein That Interacts
Epithelium-1. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Epithelium-1 Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD General features Epithelium is an avascular tissue composed of cells that cover the exterior body surfaces and line internal closed cavities and tubes. It also forms
Epithelium-1 Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD General features Epithelium is an avascular tissue composed of cells that cover the exterior body surfaces and line internal closed cavities and tubes. It also forms
Emerging mechanisms of dynein transport in the cytoplasm versus the cilium
 Review Article Emerging mechanisms of dynein transport in the cytoplasm versus the cilium Anthony J. Roberts Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, Birkbeck, University of London, Malet Street,
Review Article Emerging mechanisms of dynein transport in the cytoplasm versus the cilium Anthony J. Roberts Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology, Birkbeck, University of London, Malet Street,
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center. The Golgi apparatus. Functions of the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
 The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
CHAPTER 6: A TOUR OF THE CELL AP BIOLOGY 2011
 CHAPTER 6: A TOUR OF THE CELL AP BIOLOGY 2011 1 IMPORTANCE OF CELLS ALL ORGANISMS ARE MADE OF CELLS CELLS ARE THE SMALLEST LIVING UNIT STRUCTURE IS CORRELATED TO FUNCTION ALL CELLS ARE RELATED BY THEIR
CHAPTER 6: A TOUR OF THE CELL AP BIOLOGY 2011 1 IMPORTANCE OF CELLS ALL ORGANISMS ARE MADE OF CELLS CELLS ARE THE SMALLEST LIVING UNIT STRUCTURE IS CORRELATED TO FUNCTION ALL CELLS ARE RELATED BY THEIR
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
The dynein cortical anchor Num1 activates dynein motility by relieving Pac1/LIS1-mediated inhibition
 JCB: Article The dynein cortical anchor Num1 activates dynein motility by relieving Pac1/LIS1-mediated inhibition Lindsay G. Lammers and Steven M. Markus Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
JCB: Article The dynein cortical anchor Num1 activates dynein motility by relieving Pac1/LIS1-mediated inhibition Lindsay G. Lammers and Steven M. Markus Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,
M ICROTUBULES are involved in a variety of motile
 Published Online: 1 October, 1987 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.105.4.1781 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 22, 2019 Direction of Force Generated by the Inner Row of Dynein Arms on Flagellar
Published Online: 1 October, 1987 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.105.4.1781 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 22, 2019 Direction of Force Generated by the Inner Row of Dynein Arms on Flagellar
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza
 Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
The N-DRC forms a conserved biochemical complex that maintains outer doublet alignment and limits microtubule sliding in motile axonemes
 The N-DRC forms a conserved biochemical complex that maintains outer doublet alignment and limits microtubule sliding in motile axonemes Raqual Bower, University of Minnesota Douglas Tritschler, University
The N-DRC forms a conserved biochemical complex that maintains outer doublet alignment and limits microtubule sliding in motile axonemes Raqual Bower, University of Minnesota Douglas Tritschler, University
Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine
 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine World Century Compendium to TCM Volume 1 Volume 2 Volume 3 Volume 4 Volume 5 Volume 6 Volume 7 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Hong-zhou Wu,
Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine World Century Compendium to TCM Volume 1 Volume 2 Volume 3 Volume 4 Volume 5 Volume 6 Volume 7 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Hong-zhou Wu,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!!
 Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme
 Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme CHIKAKO SHINGY0J1*, JUN KATADA, KEHCHI TAKAHASHI Zoological Institute,
Rotating the plane of imposed vibration can rotate the plane of flagellar beating in sea-urchin sperm without twisting the axoneme CHIKAKO SHINGY0J1*, JUN KATADA, KEHCHI TAKAHASHI Zoological Institute,
mechanisms and significance of IFT in the ciliate, Tetrahymena thermophila. In the first
 JASON MITCHELL BROWN Studies on the Mechanisms and Significance of Ciliary Biogenesis in Tetrahymena thermophila (Under the Direction of JACEK GAERTIG) Cilia are microtubule-based organelles adapted to
JASON MITCHELL BROWN Studies on the Mechanisms and Significance of Ciliary Biogenesis in Tetrahymena thermophila (Under the Direction of JACEK GAERTIG) Cilia are microtubule-based organelles adapted to
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment DR CLAIRE HOGG DEPT. RESPIRATORY PAEDIATRICS ROYAL BROMPTON HOSPITAL LONDON.
 Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment DR CLAIRE HOGG DEPT. RESPIRATORY PAEDIATRICS ROYAL BROMPTON HOSPITAL LONDON. Pathogenesis of PCD Autosomal recessive Heterogeneous Defect
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment DR CLAIRE HOGG DEPT. RESPIRATORY PAEDIATRICS ROYAL BROMPTON HOSPITAL LONDON. Pathogenesis of PCD Autosomal recessive Heterogeneous Defect
Is the Curvature of the Flagellum Involved in the Apparent Cooperativity of the Dynein Arms along the "9+2" Axoneme?
 Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University From the SelectedWorks of Andrei Ludu July, 2010 Is the Curvature of the Flagellum Involved in the Apparent Cooperativity of the Dynein Arms along the "9+2" Axoneme?
Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University From the SelectedWorks of Andrei Ludu July, 2010 Is the Curvature of the Flagellum Involved in the Apparent Cooperativity of the Dynein Arms along the "9+2" Axoneme?
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Translocation of microtubules caused by the αβ, β and γ outer arm dynein subparticles of Chlamydomonas
 Journal of Cell Science, - (998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 998 JCS7 Translocation of microtubules caused by the αβ, β and γ outer arm dynein subparticles of Chlamydomonas
Journal of Cell Science, - (998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 998 JCS7 Translocation of microtubules caused by the αβ, β and γ outer arm dynein subparticles of Chlamydomonas
Functional recombination of outer dynein arms with outer arm-missing flagellar axonemes of a Chlamydomonas mutant
 Functional recombination of outer dynein arms with outer arm-missing flagellar axonemes of a Chlamydomonas mutant HITOSHI SAKAKIBARA and RITSU KAMIYA Department of Molecular Biology, Faculty of Science,
Functional recombination of outer dynein arms with outer arm-missing flagellar axonemes of a Chlamydomonas mutant HITOSHI SAKAKIBARA and RITSU KAMIYA Department of Molecular Biology, Faculty of Science,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Cell Theory. Chapter 6. cell. fundamental unit of structure and function for all living organisms. arise only from previously existing cell
 Chapter 6 cell Cell Theory fundamental unit of structure and function for all living organisms arise only from previously existing cell Figure 5.4 The size range of cells WHY are your brain cells the same
Chapter 6 cell Cell Theory fundamental unit of structure and function for all living organisms arise only from previously existing cell Figure 5.4 The size range of cells WHY are your brain cells the same
A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE. Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life
 4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s
 Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
ATTACHMENT OF THE CAP TO THE CENTRAL MICROTUBULES OF TETRAHYMENA CILIA
 J. Cell Sci. 66, 167-173 (1984) 167 Printed in Great Britain 'Hie Company of Biologists Limited 1984 ATTACHMENT OF THE CAP TO THE CENTRAL MICROTUBULES OF TETRAHYMENA CILIA WILLIAM L. DENTLER Department
J. Cell Sci. 66, 167-173 (1984) 167 Printed in Great Britain 'Hie Company of Biologists Limited 1984 ATTACHMENT OF THE CAP TO THE CENTRAL MICROTUBULES OF TETRAHYMENA CILIA WILLIAM L. DENTLER Department
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
Nanometer Scale Vibration in Mutant Axonemes of Chlamydomonas
 Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 29:177-185 (1994) Nanometer Scale Vibration in Mutant Axonemes of Chlamydomonas Toshiki Yagi, Shinji Kamimura, and Ritsu Kamiya Department of Molecular Biology, School
Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 29:177-185 (1994) Nanometer Scale Vibration in Mutant Axonemes of Chlamydomonas Toshiki Yagi, Shinji Kamimura, and Ritsu Kamiya Department of Molecular Biology, School
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
Ciliobrevin is a specific and membrane-permeable inhibitor
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Cytoskeleton, April 2015 72:182 192 (doi: 10.1002/cm.21218) VC 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Effects of the Dynein Inhibitor Ciliobrevin on the Flagellar Motility of Sea Urchin Spermatozoa
RESEARCH ARTICLE Cytoskeleton, April 2015 72:182 192 (doi: 10.1002/cm.21218) VC 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Effects of the Dynein Inhibitor Ciliobrevin on the Flagellar Motility of Sea Urchin Spermatozoa
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell. 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells Concepts of Microscopy MAGNIFICATION factor by which the image
1. Studying Cells. Concepts of Microscopy 11/7/2016. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
Electron microscope Light microscope Unaided eye 11/7/2016 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Studying Cells 2. Intracellular Structures 3. The Cytoskeleton 4. Extracellular Structures 1. Studying Cells
3D reconstruction of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer dynein arm in the presence of nucleotides
 Research Collection Doctoral Thesis 3D reconstruction of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer dynein arm in the presence of nucleotides Author(s): Movassagh, Tandis Publication Date: 2010 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-006186348
Research Collection Doctoral Thesis 3D reconstruction of Chlamydomonas flagellar outer dynein arm in the presence of nucleotides Author(s): Movassagh, Tandis Publication Date: 2010 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-006186348
