Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University
|
|
|
- Stephany Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University
2 Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Understand the components and functions of the digestive system 2. Understand the anatomical features of each part of GIT. 3. Apply the normal topographical anatomy of the digestive system on the live animal. 4. Understand the clinical correlation of anatomy to some affections of the GIT.
3 Prehension Mastication Chemical digestion Absorption Elimination of wastes Functions
4 Key terms Digestive tube Digestive tract Gastrointestinal tract (GI) Gastroenteric tract Alimentary canal Gut Entery ---- intestine Entritis
5 Abdominal Regions 9 regions Imaginary planes: 2 transverse planes (cr, middle, ca abdominal) 2 sagittal planes
6 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Abdominal Regions
7
8 Body cavities and serous membranes Thoracic Abdominal Pelvic
9
10
11 The Peritoneum Largest serous membrane in the body Closed sac in male 2 openings in female (uterine tube) Peritoneal cavity (between 2 contain serous fluid) Parietal and visceral
12
13 Def. 3 sections Rosette-like in C.S Esophagus
14 The Stomach
15
16 Stomach of the horse Type Description: Shape and Size Position
17 Equine stomach
18 Parts Stomach Cardia Fundus (saccus cecus) Body Pyloric Prof. Fawzy Elnady
19 Orifices Sphicters Surfaces Extremities Curvatures Regions
20 Prof. Fawzy Elnady
21 Equine stomach
22 Fixation of the stomach Non peritoneal Peritoneal Vessels: Arteries Celiac a Veins Gastric veins --- into portal vein Lymph gastric l. nodes Nerves: Vagus and sympathetic
23 Renosplenic lig spleen Left lobe of pancreas Gastrosplenic lig. Lesser curvature Visceral surface Greater curvature Greater omentum Rt. lobe of pancreas pancreatic ring body of pancreas epiploic foramen
24
25 Clinical Ext. clinical examination of the stomach in horse is inaccessible Why? Gastric distension in horse (if left). Rupture Why? Horse can t vomit. Why? ----V3S
26 Length of the mesentries Herniation and retraction of the gut tube. Fixed viscera: stomach and duodenum (cranially) Ileum, cecum and colon (caudally) Mobile viscera: Jejunum
27 Small intestine Duodenum jejunum ileum
28 Prof. Fawzy Elnady
29 Duodenum Stomach and duodenum dorsal aspect
30 Starts caudal to pylorus --- ends at duodenojejunal flexure Length 1m Shape: horse shoe like 4 Parts: 1. Cranial part: a. S shaped loop (duodenal bulb or duodenal ampula) b. Cr. duodenal flexure c. Major and minor duodenal papilla 2. Descending (ca duodenal flexure) 3. Transverse 4. Ascending (duodenojejunal flexure) Blood Supply Duodenum
31
32 Longest: about 22 m Jejunum Begins at DJ flexure & ends at JI junction. Long meso-jejunum (originate at T18 L1&2) Found anywhere in abdomen, but mainly in Left dorsal part. (vlovulus- intussusception incarceration of jejunal loops in the epiploic foramen or tunica vaginalis jejunal Aa. (arcades)
33 Ileum Shortest ½ m Opens at ileocecal opening 2 curvatures: Greater. Ileocecal fold Lesser mesoileum (short) Thick wall (ileal sphincter) At L3-4 it passes from ileocecal opening: into lesser curvature of base of cecum. Ileal papilla: (site of intussusception)
34 Cecum Large intestine Colon Rectum Anal canal
35 Cecum Def. Shape & Length curvatures Parts Teniae ceci (bands) Orifices Blood and Nerve supply
36 Auscultation
37 Trocharization of cecum
38
39 Colon Ascending Transverse Descending
40 Prof. Fawzy Elnady
41 Prof. Fawzy Elnady
42 Arrangement of Asc. Colon Part # of taeniae Sacculation Diameter Bl. supply RVC 4 SF 4 LVC 4 4 rows Wide Colic A. PF 1 anastomosis LDC 1 No smallest DF 3 wide RDC 3 Weak Largest (ampulla coli) Rt. Colic A.
43 Right side
44
45
46
47 Continuation of desc. Colon through pelvic cavity, to terminate as the anal canal. Parts Relations Female Male Muscles: Rectococcygeus Rectum Prof. Fawzy Elnady
48 Anal Canal Terminal part of digestive tract. Muscles 1- internal anal sphincter 2- external anal sphinter 3- Levator ani 4- Suspensory lig. of anus (ventral rectal loop) Origin: 1 st. cd vertebra Insertion: I. in male. Continues as retractor penis m. II. In female.. Continues as retractor clitoridis & blends with constrictor vulvae M. Action as accessory anal sphincter.
49 Liver = hepar Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
50
51 Basic lobation of liver
52
53 Weight Position & direction Surfaces Borders Lobes Gall bladder Porta hepatis Renal impression Prof. Fawzy Elnady
54 Liver of a horse (visceral view)
55 Liver of a horse (visceral view)
56 Liver of a horse (visceral view)
57 Peritoneal fixation Coronary lig. Rt. & Lt. triangular ligg. Falciform lig. (ventral part of ventral mesogastrium) Round lig Lesser omentum (dorsal part of ventral mesogastrium) Hepaticgastric Hepatoduodenal Hepato renal lig. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
58
59 Portal vein Hepatic artery Hepatic vein Blood Supply Prof. Fawzy Elnady
60
61
62
63
64
65 Pancreas Prof. Fawzy Elnady
66 Shape triangular Position --- sublumbar, cd to stomach and liver Description 2 surfaces 3 borders Pancreas 3 parts (body and Rt, left lobes) The body is perforated by portal ring for portal V. Secretory ducts (pancreatic duct and accessory pancreatic duct.)
67 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady
68 Quiz Prof. Fawzy Elnady
69 What problems can you see associated with the large colon? Its poorly attached to the body wall. Secured only at the cecal base and transverse colon. The rest is freely moveable and susceptible to volvulus Prof. Fawzy Elnady
70 Why do you sometimes see blockage in the transverse colon? Funnel shaped and short. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
71 Which site is the most dangerous Pelvic flexure in terms of blockage? Prof. Fawzy Elnady
72 Why do you sometimes see impaction at the ceco-colic opening? What do you do to fix? Enlarged cranial part of base falls over cranioventrally and blocks the ceco-colic orifice. Trocarization needs to be done. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
73 Why do you sometimes see impaction (or peristasis) at the ileo-cecal opening? How would you fix this? The ileum telescopes into the cecum (intussusception). Surgical remedy. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
74 Why do you sometimes see impaction at the ileum? Thick walled. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
75 Potential areas of intestinal Ileum Ileo-cecal opening Ceco-colic opening Pelvic flexure Transverse colon obstruction. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
76 Name features of the transverse Funnel shaped (risk of impaction) Attached to roof of body cavity. 2 taeniae. colon. Present cranial to the cranial mesenatric artery Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
77 Name features of the right dorsal colon, including location, size and taeniae number. Mostly within the thoracic cage. Shortest but widest. At base of cecum it turns left close to the stomach and liver and becomes the transverse. 3 taeniae Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
78 Which parts of the colon can be Left ventral colon Left dorsal colon palpated per rectum? Prof. Fawzy Elnady
79 How many taeniae are at the pelvic flexure? 1 Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
80 What is the flexure where the left dorsal colon turns right? Diaphragmatic flexure Prof. Fawzy Elnady
81 What flexure does the left ventral colon flex upon itself sharply and the diameter narrows. Pelvic flexure Prof. Fawzy Elnady
82 What is the flexure where the right ventral colon turns on itself to become left ventral colon. Sternal flexure Prof. Fawzy Elnady
83 Where does the right ventral colon begin? At the caeco-colic junction at base cecum at the level of last rib, running ventrally and cranially on right body wall and abdominal floor to the xiphoid area. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
84 How can the base of the cecum be palpated? Located dorsally and can be palpated per rectum. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
85 What attaches the body of the cecum to the right ventral colon? Cecocolic fold Prof. Fawzy Elnady
86 Where does the cecum extend and how many taeniae ceci does it have? Pelvic inlet to diaphragmatic area. 4 Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
87 What are unique features of the large intestine that differentiate the horse from a dog or ox? Longitudinal bands (taeniae coli) which are responsible for sacculations (haustra). Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
88 What can get strangulated at the Loops of jejunum epiploic foramen? Prof. Fawzy Elnady
89 Describe the location of the epiploic foramen. Between the right lobe of liver and descending duodenum, and between caudal vena cava and portal vein. Prof. Fawzy Elnady
90 Characteristics of internal surface of stomach Margo plicatus Cardiac sphincter thick, enters oblique Two pyloric sphincters (cranial/caudal) Prof. Fawzy Elnady
91 The peritoneal fold that attaches the intestine to the posterior abdominal wall is the 1. Mesentery 2. Lesser curvature 3. omentum Prof. Fawzy Elnady
92 Vermiform is a name given to the 1. cecum 2. appendix 3. rectum Prof. Fawzy Elnady profelnady@cu.edu.eg
93 Another name for the gallbladder is 1. choledochus 2. Ductus choledochus 3. cholecyst Prof. Fawzy Elnady
94 The fluid secreted by the liver and poured into the intestines is called 1. chyle 2. bile 3. chyme Prof. Fawzy Elnady
95 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady 4 How mane taeniae are at the pelvic flexure? How can the base of the cecum be palpated? Where does the right ventral colon begin? How many taeniae does the left ventral colon have?
96 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Vermiform is a name given to the 1. cecum 2. appendix 3. rectum
97 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What problems can you see associated with the large colon? Its poorly attached to the body wall. Secured only at the cecal base and transverse colon. The rest is freely moveable and susceptible to volvulus
98 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Why do you sometimes see blockage in the transverse colon? Funnel shaped and short.
99 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Which site is the most dangerous Pelvic flexure in terms of blockage?
100 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Why do you sometimes see impaction at the ceco-colic opening? What do you do to fix? Enlarged cranial part of base falls over cranioventrally and blocks the ceco-colic orface. Trocarization needs to be done.
101 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Why do you sometimes see impaction (or peristasis) at the ileo-cecal opening? How would you fix this? The ileum telescopes into the cecum (intussusception). Surgical remedy.
102 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Why do you sometimes see impaction at the ileum? Thick walled.
103 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady When would a duodeno-cecostomy need to be performed? Gastro-duodeno-jejunitis (side to side anastomoses of descending duodenum to base of the cecum)
104 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Potential areas of intestinal Duodenocecostomy Long great mesentery Ileum Ileo-cecal opening Ceco-colic opening Pelvic flexure Transverse colon obstruction.
105 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Name features of the transverse colon. Funnel shaped (risk of impaction) Attached to roof of body cavity. 2 taeniae.
106 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Name features of the right dorsal colon, including location, size and taeniae number. Mostly within the thoracic cage. Shortest but widest. At base of cecum it turns left close to the stomach and liver and becomes the transverse. 3 taeniae
107 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Which parts of the colon can be Left ventral colon Left dorsal colon palpated per rectum?
108 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady How many taeniae are at the pelvic flexure? 1
109 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What is the flexure where the left dorsal colon turns right? Diaphragmatic flexure
110 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What flexure does the left ventral colon flex upon itself sharply and the diameter narrows. Pelvic flexure
111 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What is the flexure where the right ventral colon turns on itself to become left ventral colon. Sternal flexure
112 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Where does the right ventral colon begin? At the caeco-colic junction at base cecum at the level of last rib, running ventrally and cranially on right body wall and abdominal floor to the xiphoid area.
113 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady How can the base of the cecum be palpated? Located dorsally and can be palpated per rectum.
114 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What attaches the body of the cecum to the right ventral colon? Cecocolic fold
115 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Where does the cecum extend and how many taeniae ceci does it have? Pelvic inlet to diaphragmatic area. 4
116 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What are unique features of the large intestine that differentiate the horse from a dog or ox? Longitudinal bands (taeniae coli) which are responsible for sacculations (haustra).
117 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What can get strangulated at the Loops of jejunum epiploic foramen?
118 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Describe the location of the epiploic foramen. Between the right lobe of liver and descending duodenum, and between caudal vena cava and portal vein.
119 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Where is the jejunoileum? Mostly on left dorsal part of abdomen. (loose coils mixed with coils of small colon)
120 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady What are three ligaments of the greater omentum? Gastrophrenic ligament Gastrosplenic ligament Ienorenal (renosplenic) ligament
121 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Characteristics of internal surface of stomach Margo plicatus Cardiac sphincter thick, enters oblique Two pyloric sphincters (cranial/caudal)
122 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady The ileum telescopes into the cecum (intussusception). Surgical remedy. Why do you sometimes see impaction (or peristasis) at the ileo-cecal opening? How would you fix this? Do you ever see impaction in the cecum? Why do you sometimes see blockage in the transverse colon? Why do you sometimes see impaction at the ileum?
123 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Stomach capacity is: a ml depending on the animal s size. b.. ml depending on the animal s size. c.... ml depending on the animal s size.
124 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady The falciform ligament attaches 1. Diaphragm 2. Stomach 3. Spleen 4. Duodenum. the liver to the:
125 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady The peritoneal fold that attaches the intestine to the posterior abdominal wall is the 1. Mesentery 2. Lesser curvature 3. omentum
126 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Vermiform is a name given to the 1. cecum 2. appendix 3. rectum
127 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady Another name for the gallbladder is 1. choledochus 2. Ductus choledochus 3. cholecyst
128 Prof. Dr. Fawzy Elnady The fluid secreted by the liver and poured into the intestines is called 1. chyle 2. bile 3. chyme
129 Activities Prof. Fawzy Elnady
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
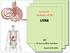 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES. Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga
 ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut
 Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
Embryology of the Midgut and Hind gut Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Abdominal organs www.google.co.uk/search? Development of Duodenum The
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM I. Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen A. Surface landmarks 1. Xiphoid process 2. Costal margin 3. Iliac crest 4. ASIS 5. Pubic symphysis 6. Inguinal groove B. Anterior abdominal
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine
 Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
Fareed Khdair, MD Assistant Professor Chief, Section of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition University of Jordan School of Medicine Outline Lecture one : Gut formation Foregut: esophagus,
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
Lab 8: Digestive System
 BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
BIOL 221 A&P II Lab 8: Digestive System Become familiar with the gross anatomy of the digestive system (Exercise 38) using the models, Fig. 38.1 (Activity 1), and the rat. Recognize and know the functions
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM consists of: Muscular, hollow tube (= digestive tract ) + Various accessory organs FUNCTION Individual parts function in: ingestion mechanical digestion chemical and enzymatic digestion
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology
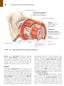 458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
458 Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses: Myenteric nerve plexus Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa: Surface epithelium Lamina propria Muscle
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13
 Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment. Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD
 Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Chapter 25
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Chapter 25 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Digestive Tract Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Anus Accessory Organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gallbladder
Nutrition and the Digestive System
 C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestive System. Digestive Processes. The Digestive System. Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells
 The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
CEA (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
 (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
(CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
-the stones will obstruct the common bile duct and it might also be precancerous. -so the best treatment is chlolycyctoctomy.
 At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
Gastrointestinal System!
 Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
Gastrointestinal System! Assoc. Prof. Prasit Suwannalert, Ph.D. (Email: prasit.suw@mahidol.ac.th)! Objectives: After learning, student should be able to describe and discuss in topics of! 1. Anatomical
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Lecture 1. Introduction to splanhnology. Digestive system
 Lecture 1 Introduction to splanhnology. Digestive system SPLANCHNOLOGY (THE SCIENCE OF THE VISCERA) SOMATOLOGY SPLANCHNOLOGY The general cover body (skin) The skeletal system The connection system The
Lecture 1 Introduction to splanhnology. Digestive system SPLANCHNOLOGY (THE SCIENCE OF THE VISCERA) SOMATOLOGY SPLANCHNOLOGY The general cover body (skin) The skeletal system The connection system The
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Done by: nisreen obeidat
 Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
The Digestive System 1
 The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
The Digestive System 1 Digestion Processing of food Types Mechanical (physical) Chew Tear Grind Mash Mix Chemical Catabolic reactions Enzymatic hydrolysis Carbohydrate Protein Lipid 2 Digestion Phases
Digestive System. 13. In the normal adult, the esophagus is located to the trachea. A. Posterior C. Medial B. Anterior D. Lateral
 Digestive System 1. The process by which food particles are mechanically reduced into smaller particles in the mouth is termed: A. Absorption C. Mastication B. Peristalsis D. Deglutition 2. Projecting
Digestive System 1. The process by which food particles are mechanically reduced into smaller particles in the mouth is termed: A. Absorption C. Mastication B. Peristalsis D. Deglutition 2. Projecting
Lungs a. d. b. c. e.
 Lungs d. e. Lungs Right superior lobe Right middle lobe Right inferior lobe d. Left superior lobe e. Left inferior lobe Sinuses d. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. g. i. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. h. d. f. e.
Lungs d. e. Lungs Right superior lobe Right middle lobe Right inferior lobe d. Left superior lobe e. Left inferior lobe Sinuses d. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. g. i. Nasal Cavity & Sinuses g. h. d. f. e.
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Al-Mohtaseb. Saba Alfayoumi. Mo Alfarra
 8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures would have been cut EXCEPT the:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
2. A digestive organ that is not part of the alimentary canal is the: a. stomach b. liver c. small intestine d. large intestine e.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
