General Surgery Anatomy Course
|
|
|
- Laurence Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Surgery Anatomy Course May 2018 Course will meet on Wednesdays during May in Fee Hall in East Lansing from 12:00 5:00 May 2 12:00 1:00 Abdomen Lecture 1:15 5:00 dissection Dr. Mary Bee May 9 12:00 1:00 Chest Lecture 1:15 5:00 dissection J. Christopher Reed, PhD May 16 12:00 1:00 Vascular Lecture 1:15 5:00 dissection Kerent Pihl, DO May 23 12:00 1:00 Surgical Considerations 1:15 5:00 dissection Karlin Sevensma, DO Course Textbooks: Grant s Dissector Netter Atlas of Human Anatomy Goals: Following this course, the learner should be able to: 1) Describe the listed anatomical structures relating to the practice of general surgery procedures, including vascular access (see lab list) 2) Describe the relationships of anatomical structures within the abdomen and chest as they are pertinent to surgical dissection and procedures Relationships Pleura around the hilum, attachments of the lung within the chest Contents of the mediastinum Attachments of the liver to the diaphragm Diaphragmatic crura and penetrating structures Vena cava to the liver and diaphragm Clavicle, first rib, muscles and vasculature Levels of axillary lymph nodes and the critical structures to identify during axillary dissection Greater and lesser sac Foramen of Winslow to surrounding structures Ligament of Treitz to surrounding structures Celiac plexus, SMA and IMA and their courses Review Pringle maneuver, Kocher maneuver Relationships of structures within the inguinal and femoral canals Access to pancreas and the structures which surround the pancreas, spleen 1 P age
2 Retroperitoneal dissection 3) Describe the anatomical structures of the retroperitoneum and their relationships to intraperitoneal structures 4) Describe the embryological development of the alimentary tract and name common malformations 5) Draw out the vascular supply and drainage of the abdominal viscera 2 P age
3 Lab List Abdomen Abdominal Wall Rectus abdominis External abdominal oblique Internal abdominal oblique Transversus abdominis Parietal peritoneum Transversalis fascia Rectus sheath Linea alba Arcuate line Diaphragm Left and right crura Median arcuate ligament Medial arcuate ligaments Central tendon Esophageal hiatus Caval foramen Aortic hiatus Right and left inferior phrenic arteries Phrenic nerves Thoracic splanchnic nerves Gastrointestinal tract: Stomach Cardia Fundus Body Pylorus Lesser Sac Greater Sac 3 P age
4 Duodenum Superior (1 st portion) Descending (2 nd portion) Inferior/Horizontal (3 rd portion) Ascending (4 th portion) Major duodenal papilla Suspensory muscle (ligament of Treitz) Jejunum Ileum (vascular arcades) Dorsal fat pad (of Treves) Appendix Mesoappendix Appendiceal artery Colon Cecum, right, transverse, descending, sigmoid, rectum Haustra Taenia coli Epiploic appendages Vessels to colon Ileocolic artery Right colic artery Middle colic artery Left colic artery Sigmoidal artery Marginal artery (of Drummond) and variant Spleen Hilum Short gastric arteries Splenic artery Peritoneal attachments 4 P age
5 Pancreas Tail Body Head Uncinate process Major and minor ducts Superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries Kidney Renal capsule Renal cortex Pelvis Ureter Renal arteries Renal veins Gonadal vessels Liver Right lobe anatomical & functional Left lobe anatomical & functional Quadrate lobe Caudate lobe Liver segments Porta hepatis Hepatic veins Falciform ligament Round ligament (ligamentum teres hepatica) Coronary ligament of liver Right and left triangular ligaments Bare area Common bile duct Common hepatic duct Right and left hepatic ducts Cystic duct 5 P age
6 Arteries Abdominal aorta Celiac trunk Splenic Left gastric Left gastroepiploic Common hepatic Right gastric Gastroduodenal Right gastroepiploic Proper hepatic Right hepatic Left hepatic Cystic Superior mesenteric Arcades Vasa recta (straight aa) Ileocolic Right colic Middle colic Inferior mesenteric Left colic Sigmoidal Superior rectal Renal Suprarenal Lumbar aa Common iliac arteries Internal iliac arteries External iliac arteries Deep cicumflex iliac artery 6 P age
7 Veins Hepatic portal Splenic Superior mesenteric Inferior mesenteric Renal Left gonadal (drains into left renal) Suprarenal Inferior vena cava Right gonadal (drains into right renal) Common iliac External iliac Internal iliac Peritoneal Structures: Greater omentum Lesser omentum Hepatogastric ligament Hepatoduodenal ligament Epiploic foramen Transverse mesocolon Mesojejunum Mesoileum Sigmoid mesocolon Paracolic gutters (R & L) Infracolic spaces (R & L) Hepatorenal recess of subhepatic space Pelvis Muscles Iliacus Psoas major Obturator internus Piriformis Greater sciatic foramen Lesser sciatic foramen 7 P age
8 Obturator foramen Inguinal ligament Lateral crus Medial crus Superficial inguinal ring Deep inguinal ring Spermatic cord/round ligament Cremaster muscle Conjoined tendon (falx inguinalis) Pelvic diaphragm: levator ani, coccygeus External and internal anal sphincters Bladder Trigone Detrusor muscle Internal urethral orifice Internal urethral sphincter Ureters Retropubic space Rectum Nerves Obturator Femoral Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh Genitofemoral Genital branch Femoral branch Pudendal Sacral ventral rami Lumbosacral trunk Arteries/Veins: Common iliac External iliac Deep circumflex iliac 8 P age
9 Internal iliac Lateral sacral Iliolumbar Superior gluteal Inferior gluteal Umbilical Superior vesical Obturator Internal pudendal Arteries/Veins Femoral Profunda femoris Perforating arteries Medial circumflex femoral Lateral circumflex femoral Popliteal Genicular arteries (any) Anterior tibial Dorsalis pedis Posterior tibial Lateral plantar Medial plantar Fibular Femoral sheath Femoral canal Great saphenous vein Small saphenous vein Chest Vessels: Aorta ascending, descending; aortic arch Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries and veins Internal thoracic artery Superior epigastric artery Inferior epigastric artery 9 P age
10 Brachiocephalic trunk Right common carotid artery Right subclavian artery Left common carotid artery Left subclavian artery Pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries and veins Brachiocephalic veins Vena cava superior and inferior Nerves (trace the course) Phrenic nerves Vagus nerve (anterior and posterior) Recurrent laryngeal nerve Thoracic sympathetic trunk Intercostal nerves Mediastinum Trachea Carina Bronchi Thoracic duct Esophagus, arterial supply and venous drainage Paratracheal posterior parietal and tracheobronchial nodes Pleura Parietal and visceral Pulmonary ligament Lungs Base Apex Hilum Root Heart Pericardium 10 P age
11 Axilla Subclavian artery Axillary vein Thoracodorsal neurovascular bundle Long thoracic nerve Pectoralis major Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior NECK Platysma Thyrohyoid Sternothyroid Sternohyoid Omohyoid Digastric Sternocleidomastoid Scalenes Trachea Epiglottis Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Cricothyroid ligament Hyoid bone Vagus nerve Recurrent laryngeal nerve Superior laryngeal nerve Common carotid artery Superior thyroid artery Inferior thyroid artery Superior, middle and inferior thyroid veins Internal, external and anterior jugular veins Thyroid gland Ligaments of Berry 11 P age
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures would have been cut EXCEPT the:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES. Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga
 ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space
 Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Posterior Abdominal wall-
 Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
NBME Anatomy Review. Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015
 NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
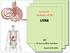 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
-the stones will obstruct the common bile duct and it might also be precancerous. -so the best treatment is chlolycyctoctomy.
 At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Academic Year 2017/2018. FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm
 CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
CURRICULUM FOR HUMAN ANATOMY COURSE LAB SESSIONS Academic Year 2017/2018 FALL SEMESTER DDS Program Monday: 5:45pm 7:15pm Thursday: 5:30pm- 7:00pm Category 1: Bones name, type, structure Joints: type, articular
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, 1996. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT: A. The fibrous
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, 1996. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT: A. The fibrous
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
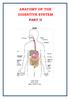 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment. Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD
 Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. External oblique muscle Origin: outer surface of the
Abdominal muscles. Subinguinal hiatus and ingiunal canal. Femoral and adductor canals. Neurovascular system of the lower limb. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. External oblique muscle Origin: outer surface of the
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
ANATOMY - II. FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX
 ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
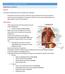 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics.
 NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of the renal system. Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi
 Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Anatomy of thoracic wall
 Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
Anatomy of thoracic wall Topographic Anatomy of the Thorax 1 Bones of Thoracic wall ribs 1-7"true" ribs -those which attach directly to the sternum true ribs actually attach to the sternum by means of
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
ABDOMEN. 2. The highest branch of the abdominal aorta is: (a) R suprarenal a (b) Coeliac trunk (c) L renal a (d) L gonadal a (e) SMA
 ABDOMEN 1. The duodenum: (a) is a retroperitoneal structure (b) is 25cm long (c) lies between the levels of L2-L4 (d) in its fourth part lies to the R of the aorta (e) all of the above 2. The highest branch
ABDOMEN 1. The duodenum: (a) is a retroperitoneal structure (b) is 25cm long (c) lies between the levels of L2-L4 (d) in its fourth part lies to the R of the aorta (e) all of the above 2. The highest branch
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. September 13, 2012 B C
 STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
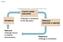 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
thoracic cage inlet and outlet landmarks of the anterior chest wall muscles of the thoracic wall sternum joints ribs intercostal spaces diaphragm
 Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib
 8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
8 Omar Sami --- Muhammad Al-Muhatasib This sheet is a remake from 2015 s sheet for the same lecture; I have checked the record, added, omitted, edited & illustrated all what the Professor mentioned in
CT Basics: Cross-sectional Anatomy of the Chest, Abdomen and Pelvis Module 9
 Module 9 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
Module 9 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES
 THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES THE ABDOMINAL AORTA The abdominal aorta begins at the aor9c hiatus in the diaphragm at the level of the T12 vertebra and ends at the
THE PELVIS VASCULAR AND NERVOUS SYSTEM SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVES THE ABDOMINAL AORTA The abdominal aorta begins at the aor9c hiatus in the diaphragm at the level of the T12 vertebra and ends at the
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
Al-Mohtaseb. Saba Alfayoumi. Mo Alfarra
 8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Femoral Artery. Its entrance to the thigh Position Midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
 Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
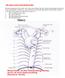 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall
 Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
