Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for oral contrast**
|
|
|
- Lewis Jacobs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MRB AB01AMR 01aAbdomen (with dynamics) + Pelvis (pre/post) A74183 A72197 Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for oral contrast** **oral contrast-water 450 ml 60 min, 40 min, 20 min prior to scan and 400 ml on the table (if hx of small bowel or mesenteric tumor) Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients with a history of gynecologic malignancy to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Coronal SSFSE through abdomen and pelvis Axial SSFSE through abdomen Axial SSFSE through pelvis Sagittal T2 TSE with breath hold through pelvis Sagittal T2 TSE without breath hold through pelvis Oblique axial T2 TSE, 6mm pelvis Axial dual echo through abd Axial dual echo through pelvis DWI through abdomen DWI through pelvis Pre LAVA (3D) fat sat through abd, 4 mm Pre LAVA (3D) fat sat through pelvis, 4 mm Dynamic LAVA (3D) fat sat through abdomen, 4 mm Coronal LAVA 2D, 6 mm through abdomen Axial post contrast LAVA (3D) fat sat delayed through pelvis Sagittal post contrast T1 (2D) fat sat through abdomen and pelvis Coronal post contrast T1 (2D) fat sat through abdomen and pelvis
2 MRB AB01BMR 01bPelvis (with dynamics) + Abdomen (pre/post) A72197 A74183 Indications: General follow up for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for oral contrast** **oral contrast-water 450 ml 60 min, 40 min, 20 min prior to scan and 400 ml on the table). If there is history of female pelvic malignancy, give vaginal surgilube. Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients with a history of gynecologic malignancy to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Coronal SSFSE through pelvis Coronal SSFSE through abdomen Axial SSFSE through abdomen Axial SSFSE through pelvis Sagittal T2 TSE with breath hold through pelvis Sagittal T2 TSE without breath hold through pelvis Oblique axial T2 TSE Axial dual echo through abd Axial dual echo through pelvis DWI through abdomen DWI through pelvis Pre LAVA (3D) fat sat through abd Pre LAVA (3D) fat sat through pelvis Axial dynamic LAVA (3D) fat sat through pelvis Coronal post contrast LAVA (2D) fat sat delayed through abdomen Coronal post contrast LAVA (2D) fat sat delayed through pelvis
3 Axial 3D LAVA post contrast through abd, 4mm Axial 3D LAVA post contrat through pelvis, 4mm Oblique axial post contrast T1 (2D) fat sat through pelvis, 6mm Sagittal post contrast T1 (2D) fat sat through abdomen and pelvis, 6mm Liver Hemangioma Gadavist Indication: Possible hepatic hemangioma. (Note, for other hepatic lesions, use Eovist protocol) Use in cirrhosis/hcc if bilirubin >3. (If Gadavist not available, may substitute Multihance) Gadavist 10 ml/sec If GFR < 30 and stable, Gadavist 0.05 mmol/kg If GFR <15 or < 30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Gadavist with 40 ml ml/sec Sequences (all single breath hold): Cover top of the liver to the bottom of the kidneys Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Ax DE Ax DWI Ax LAVA pre Ax LAVA Dynamic Cor LAVA Ax Lipoquant Ax LAVA Delayed MRB AB01MR 01Routine Abdomen A74183 Indication: General eval of abdomen, mass, metastatic disease.
4 Sequences (all single breath hold): Cover top of the liver to the bottom of the kidneys Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Ax DE Ax DWI Ax LAVA pre Ax LAVA Dynamic Cor LAVA Ax Lipoquant Ax LAVA Delayed ADC:make sure ADC is calculated FF and R2* maps created and sent to PACS MRB AB02MR 02Liver Eovist 1.5 T A74183 Indications: Cirrhosis, hepatitis, risk for HCC (PBC, hemochromatosis) Primary liver lesions (HCC, FNH, adenoma) Cholangiocarcinoma Metastasis Contraindications: Bili > 3, did not work last time, severe iron overload, work up for hemangioma, major reason for exam is evaluation of portal or hepatic veins Eovist If GFR >60, Eovist 10 ml (Eovist mmol/kg) at 1 ml/sec If GFR and stable, Eovist mmol/kg If GFR <30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Eovist with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec Coronal SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Axial pre LAVA (3D) with fat sat
5 Axial dynamic post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Coronal delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial SSFSE/HASTE Axial T2 FSE FS, BH Axial DWI Lipoquant Axial delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat* *repeat LAVA every 5 min until: (1) bile ducts are bright AND blood vessels in liver are dark OR (2) 30 minutes have elapsed since Eovist injection, whichever comes first ADC Make sure ADC is calculated. Make sure FF and R2* maps are made and sent to PACS. MRB AB03MR 03Liver Eovist 3T A74183 Indications: Cirrhosis, hepatitis, risk for HCC (PBC, hemochromatosis) Primary liver lesions (HCC, FNH, adenoma) Metastasis Contraindications: Bili > 3, did not work last time, severe iron overload, work up for hemangioma, major reason for exam is evaluation of portal or hepatic veins Eovist If GFR >60, Eovist 10 ml (Eovist mmol/kg) at 1 ml/sec If GFR and stable, Eovist mmol/kg If GFR <30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Eovist with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec Coronal SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Axial pre LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial dynamic post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Coronal delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial SSFSE/HASTE Axial DWI Axial T2 FSE FS, BH
6 Lipoquant Axial delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat* *repeat LAVA every 5 min until: (1) bile ducts are bright AND blood vessels in liver are dark OR (2) 30 minutes have elapsed since Eovist injection, whichever comes first ADC Make sure ADC is calculated. Make sure FF and R2* maps are made and sent to PACS. MRB AB03MRB 03b Liver Eovist 3T Bydder B_74183 Indications: Cirrhosis, hepatitis, risk for HCC (PBC, hemochromatosis) Primary liver lesions (HCC, FNH, adenoma) Metastasis Contraindications: Bili > 3, did not work last time, severe iron overload, work up for hemangioma, major reason for exam is evaluation of portal or hepatic veins Eovist If GFR >60, Eovist 10 ml (Eovist mmol/kg) at 1 ml/sec If GFR and stable, Eovist mmol/kg If GFR <30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Eovist with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec Coronal SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Axial pre LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial dynamic post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Coronal delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial SSFSE/HASTE Axial DWI Axial T2 FSE FS, BH Lipoquant Axial delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat* *repeat LAVA every 5 min until (1) bile ducts are bright AND blood vessels in liver are dark
7 first ADC OR (2) 30 minutes have elapsed since Eovist injection, whichever comes Liver Ablavar Indications: 1. ATYPICAL hemangiomas of liver, spleen 2. MR venography of portal vein or hepatic veins or IVC Ablavar 0.12 ml/kg (0.03 mmol/kg) over a period of time of up to 30 seconds Follow with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec Coronal SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Axial pre LAVA (3D) with fat sat Axial dynamic post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Coronal delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat Sagittal LAVA with fat sat Axial SSFSE/HASTE Axial DWI Axial T2 FSE FS, BH Lipoquant Coronal delayed LAVA with fat sat Sagittal delayed LAVA with fat sat ADC Make sure ADC is calculated. Make sure FF and R2* maps are made and sent to PACS. MRB AB04MR 04MRCP non contrast A74181 Indications: Evaluate biliary stones or post-op obstruction NO concern for cancer NONE
8 (expiration preferred) Coronal SSFSE/HASTE Axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section 3D dual echo Oblique coronal SSFSE/HASTE thin section-parallel to posterior right hepatic duct, cover main ducts Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to proximal/superior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to distal/inferior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct and duodenum Oblique coronal 3D MRCP fat sat thin section Optional rotating thick slabs, 2D functional MRCP in free breathing MRCP with Eovist Indications: Bile leak, assess biliary function, detailed eval of biliary strictures Only if total bili <2 Eovist If GFR >60, Eovist 10 ml (Eovist mmol/kg) at 1 ml/sec If GFR and stable, Eovist mmol/kg If GFR <30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Eovist with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec (expiration preferred) Coronal SSFSE/HASTE Axial SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Oblique coronal SSFSE/HASTE thin section-parallel to posterior right hepatic duct, cover main ducts Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to proximal/superior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to distal/inferior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct and duodenum Oblique coronal 3D MRCP fat sat Optional rotating thick slabs, 2D functional MRCP in free breathing Axial LAVA pre Axial LAVA dynamic post Coronal LAVA post ADC map Axial delayed post LAVA (3D) with fat sat* *repeat LAVA every 5 min until (1) bile ducts are bright AND blood vessels in liver are dark
9 OR (2) 30 minutes have elapsed since Eovist injection, whichever comes first Then call MD to check images: Additional images at 2 hours for bile leak, may need additional up to 8 hours MRCP with Gadavist Indications: Cholangiocarcinoma Gadavist 10 ml/sec If GFR < 30 and stable, Gadavist 0.05 mmol/kg If GFR <15 or < 30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Gadavist with 40 ml ml/sec (expiration preferred) Coronal SSFSE/HASTE Axial SSFSE/HASTE 3D dual echo Oblique coronal SSFSE/HASTE thin section-parallel to posterior right hepatic duct, cover main ducts Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to proximal/superior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct Oblique axial SSFSE/HASTE thin section-perpendicular to distal/inferior extrahepatic duct, cover entire extrahepatic duct and duodenum Oblique coronal 3D MRCP fat sat Optional rotating thick slabs, 2D functional MRCP in free breathing Axial LAVA pre Axial LAVA dynamic post Coronal LAVA post ADC map MRB ab07mr 07Adrenals Non Contrast A74181 Indications: adrenal lesion Determine prior to exam if contrast is to be given, requires separate protocol none Coronal SSFE: 8 mm
10 Axial SSFSE: 8 mm, top of liver to bottom of kidneys Axial SSFSE: 4 mm, through adrenals 3D axial dual echo: 4 mm, through adrenals Axial lipoquant: 4 mm, through adrenals MRB AB08MR 08Adrenals With Contrast A74183 Indications: adrenal lesion MultiHance at 2 ml/sec as follows: Coronal SSFSE 8 mm Axial SSFSE 8 mm, top of liver to bottom of kidneys Axial SSFSE 4 mm through adrenals 3D axial DE through adrenals, 4mm Axial LAVA (3D) pre fat sat, 4 mm through adrenals Axial LAVA (3D) dynamic post fat sat, 4 mm through adrenals Coronal LAVA (3D) delayed fat sat, 4mm through adrenals MRB AB09MR 09MRA Renal Artery A MRA Indications: Renal artery stenosis Renovascular hypertension MultiHance MultiHance at 2 ml/sec as follows:
11 Cor SSFSE Ax DE Ax SSFSE Inhance (3D uses resp trigger) Coronal Pre contrast 3D MRA fat sat Coronal 3D MRA with contrast, dynamic 3 runs Subtraction x3 Coronal 3D T1 GRE fat sat delayed- ureteral enhancement and excretion Coronal MIP fat sat for each side Coronal MIP for each side MRB AB10AMR 10Pancreas A74183 Indications: Pancreatic mass, pancreatic cancer, mets from pancreatic cancer Give water 400 ml on the table Coronal HASTE/SSFSE Axial HASTE/SSFSE through liver and pancreas Oblique axial HASTE/SSFSE, 4 mm, parallel to main pancreatic duct Oblique coronal HASTE/SSFSE, 4 mm, through CBD and distal pancreatic duct (same plane as in MRCP) Oblique coronal 3D MRCP fat sat, Perpendicular to proximal (superior) extrahepatic duct, cover the central intrahepatic and the extrahepatic bile ducts (i.e. the left duct and bifurcation of left duct, right duct and bifurcation of right duct) 3D dual echo through liver and pancreas
12 DWI through liver and pancreas Axial pre LAVA (3D) fat sat 3mm Axial dynamic post LAVA (3D) fat sat, 3 mm Coronal delayed post LAVA (3D) fat sat, 4 mm Axial delayed post LAVA (3D) fat sat, 3 mm Secretin Patient Preparation: Drink 300 ml of blueberry or pineapple juice 30 minutes before Drink 300 ml of blueberry or pineapple juice immediately before Place IV Gadavist 10 ml/sec If GFR < 30 and stable, Gadavist 0.05 mmol/kg If GFR <15 or < 30 and decreasing, consult faculty Follow Gadavist with 40 ml ml/sec Localizaers ASSET calibration Coronal SSFSE 6mm Axial SSFSE 6mm Axial dual echo Thick coronal oblique 6-cm slab T2w, parallel to pancreatic duct --- make sure entire pancreas and duodenum are covered. Call MD to check Give IV test dose of secretin 0.2 micrograms Infuse secretin 0.2 micrograms/kg over 1 minute Repeat thick coronal oblique 6-cm slab T2w, parallel to pancreatic duct every 30 seconds for 10 minutes Repeat coronal SSFSE 6mm ONCE Repeat axial SSFSE 6mm ONCE 3D MRCP free breathing 3D MRCP BH Then proceed images covering top of the liver to bottom of kidneys, including entire pancreas and duodenum
13 Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Ax DE Ax DWI Ax LAVA pre Ax LAVA Dynamic Cor LAVA Ax Lipoquant Ax LAVA Delayed MRB AB11MR 11Renal Mass A74183 Indications: Evaluate for renal mass; hematuria Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Ax DE Ax DWI Ax LAVA pre Ax LAVA Dynamic Cor LAVA Ax LAVA Delayed Subtractions Urogram Prior to imaging, pt must drink 300 cc of water Prior to imaging, administer 100 cc normal saline IV
14 Localizer x2 1 st diaphragm to iliac; 2 nd kidneys to pelvis, 3plane GRE Cor SSFSE abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation Axial SSFSE FS abdomen, BH Axial SSFSE FS pelvis, BH Axial Dual echo abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation Sagittal FIESTA for localization of ureters (no BH)-2 nd loc Axial LAVA pre abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-1 st loc Coronal Pre mask, BH, from above kidneys to iliac bifurcation-2 nd loc Contrast Axial LAVA post x3 abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-1 st loc Coronal T1 GRE FS post abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-1 st loc Axial T1 GRE FS post, BH, thin slices (3mm)/cover kidneys-1 st loc Coronal 3D post 5 min delay abd, BH, above kidneys to iliac bifurcation-2 nd loc Coronal SSFSE abdomen, BH, thin slices (3mm), cover kidneys-1 st loc Axial SSFSE abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-1 st loc Coronal FIESTA abdomen, BH, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-1 st loc-1 st loc Axial 3D LAVA post abd, BH, thin-2.5mm, diaphragm to iliac bifurcation-2 nd loc Coronal 3D post 10 min delay, BH, thin-1.25 mm, above kidneys to iliac bifurcation-2 nd loc Coronal 3D LAVA post, BH, thin-2.5 mm, above kidneys to iliac bifurcation Axial 3D LAVA post pelvis, BH, thin-2.5mm MRB ab18mr 18Pregnant Female with Appendicitis A74181 Indications: evaluate for appendicitis None Cor SSFSE
15 Ax SSFSE Cor FIESTA Ax FIESTA Ax SSFSE FS Ax DE Ax DWI MRB MRB LEG RUN OFF STUDY A73725-BILAT 1) Axial 2D TOF renal to feet (use superior sat for venous or inferior sat for arterial) 2) 3D contrast-enhanced MRA renal to feet Aorta Ablavar 0.12 ml/kg (0.03 mmol/kg) over a period of time of up to 30 seconds Follow with 40 ml saline at 1 ml/sec Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Inhance (3D uses resp trigger) Axial non gated fiesta Coronal nongated feista Gated ax fiesta Gated candy cane fiesta
16 3D gated fiesta Gated Fast CINE Post contrast TRICKS MRA MRB PL06AMR 06aMR Enterography with Detailed Perianal A EO-PA Additional contrast: Oral Volumen 450 ml 60 min, 40 min, 20 min prior 400 ml water on the table Glucagon: 0.6 mg subcutaneous injection immediately prior to the study 0.4 mg IV before contrast Consider vaginal surgilube Cor SSFSE Ax DE Cor FIESTA Ax SSFSE Cor SSFSE FS Ax SSFSE FS Ax FIESTA Ax T2 non BH (Radiologist to determine slice location) Perianal: Sag SSFSE Optional - Perianal: Sag SSFSE FS Perianal: Sag T2 non BH Perianal small FOV 4mm Ax T2 non BH Perianal small FOV Cor T1 non BH Perianal small FOV 4mm Ax T2 FS non BH Perianal small FOV Cor T2 non BH Perianal small FOV 4mm Oblique T2 non BH (short axis to rectum/anus) Optional - Oblique STIR Optional - whole abdomen pelvis Sag SSFSE
17 Cor LAVA pre Cor LAVA dynamic (Radiologist to review before contrast coverage is whole abdomen pelvis) Ax T1 FS post whole abdomen pelvis Cor T1 FS post BH (perianal) Ax T1 FS post BH (perianal) Sag T1 FS post BH (perianal) MRB PL06BMR 06bPerianal Fistula/Abscess A72197 Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Sag SSFSE Sag SSFSE FS Sag T2 non BH Ax T2 non BH Cor T1 non BH Ax DE Ax T2 FS non BH Cor T2 non BH Oblique T2 non BH (short axis to rectum/anus) Optional - Oblique STIR LAVA pre LAVA dynamic (Radiologist to review before contrast) Cor T1 FS post BH Ax T1 FS post BH Sag T1 FS post BH Non BH sequences should be small FOV
18 MRB PL06CMR 06cRectal Mass A72197 *Radiologist review before contrast Ax SSFSE Sag SSFSE Sag T2 non BH Ax T2 non BH Ax T1 non BH Ax DE Cor T2 non BH Oblique T2 non BH (short axis to rectum/anus) Ax diffusion B-1000 optional - oblique coronal T2 LAVA pre - check whether need straight axial or oblique axial LAVA Dynamic Cor T1 FS post BH Ax T1 FS post BH Sag T1 FS post BH Non BH sequences should be small FOV MRB PL06MR 06MR ENTEROGRAPHY A74183 ENTER Indication: Inflammatory bowel disease
19 Additional contrast: Oral Volumen 450 ml 60 min, 40 min, 20 min prior 400 ml water on the table Glucagon: 0.6 mg subcutaneous injection immediately prior to the study 0.4 mg IV before contrast Cor SSFSE Ax DE Cor FIESTA Ax SSFSE Cor SSFSE FS Ax SSFSE FS Ax FIESTA Ax T2 non BH (Radiologist to determine slice location) Optional - Sag SSFSE Cor LAVA pre Cor LAVA Dynamic (Radiologist to review before contrast) Ax T1 FS post MRB PL14MR 14Routine female pelvis with contrast A72197 Indications: Eval mass Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is
20 administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Coronal HASTE/SSFSE Axial HASTE/SSFSE Angled Sagittal to uterus T2 FSE BH Angled Sagittal T2 FSE non-bh Angled Axial T2 FSE non-bh Angled axial dual echo T1 GE (BH) Angled axial FS T1 GE (BH) Axial DWI through pelvis B1000 Pre LAVa fat sat --plane per MD protocol or MD on service Dynamic post LAVA/VIBE fat sat --plane as above Axial delayed T1 post with fat sat Coronal delayed T1 post with fat sat Sagittal delayed T1 post with fat sat MRB PL15MR 15Female Pelvis non con A72195 Indications: uterine anomaly no IVC Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Coronal HASTE/SSFSE Axial HASTE/SSFSE Sagittal T2 with breath hold Oblique axial dual echo Oblique axial T2 Axial DWI through pelvis at B=0, 500, and 1000 Axial T1 fat sat
21 MRB PL16MR 16Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) A72197 Indications: fibroids pre UAE for Dr. Roberts Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Angled Sag to uterus T2 FSE BH Angled Ax T2 FSE BH Angled Ax DE Oblq to uterus (BH) Ax DWI 1000 Cor MRA pre+post x3 Post gad 3-plane FS T1 GE MRB PL17MR 7Urethral Diverticulum A72195 Indications: urethral diverticulum noncon, with possible Multihance, to be determined if necessary after noncon Vaginal contrast should be administered to patients to enable better evaluation of the vagina, cervix, vaginal cuff and parametrial tissues. Vaginal contrast is administered via a catheter while the patient is on the scanning table. 60 ml of
22 surgilube or equivalent aqueous gel should be administered in the presence of a female technologist, LIP, or chaperone. STOP if patient has significant discomfort. Cor SSFSE Sag T2 Cor T1 Cor T2 Ax T2 Ax T1 After obtaining the non-contrast images, call the radiologist to see if IV gadolinium is necessary. If deemed so, then obtain T1 post-contrast images through the urethra with a small field of view in the axial, coronal and sagittal planes. IF NEEDED - IV- MultiHance hand inject I f GFR 30-60, give MultiHance 0.1 mmol/kg MRB PL19MR 19Pregnant Female Evaluate Placenta A72197 Indications: Placental invasion, placenta position Noncon first. If necessary per MD monitoring the case, Radiologist MUST be present during this exam Cor SSFSE Ax SSFSE Sag SSFSE
23 Ax 2D FIESTA Sag 2D FIESTA Oblq DE Oblq T1 LAVA pre LAVA dynamic Ax T1 FS post MRB PL20MR 20Male Pelvis: Scrotum contrast A72197 Indication: Evaluate scrotal pathology, scrotal infection suspected Cor T1 Cor T2 Ax T1 Ax T2 Cor T1 FS post Ax T1 FS post Sag T1 FS post MRB PL21MR 21Male Pelvis: Cancer not prostate or scrotum A72197 Indications: Evaluate cancer not from prostate or scrotum I
24 f GFR 30-60, give MultiHance 0.1 mmol/kg See Protocol Book MRB PL22MR 22PROSTATE WITH ENDORECTAL COIL W/WO CONTRAST A72197 LOC AXIAL SSFSE SAG T1 Right sidewall SAG T1 Left sidewall SAG T2 (HR) COR OBL T2 (HR) COR OBL T1 (HR) AX OBL T2 (HR) AX OBL T1 (HR) TRICKS pre no injection TRICKS-post gd **DEFLATE COIL AND REMOVE** loc Asset Cal DWI B=1000 NEX=12 DWI B=1000 NEX=12 (3mm below first DWI) Multishell diffusion (B500, 1500 and 4000 with directions of 6, 6 and 15 respectively) +C COR FGRE FS +C SAG FGRE FS
25 +C AX T2 (HR) MRB PL23MR 23PROSTATE WITHOUT ENDORECTAL COIL W/WO CONTRAST A72197 LOC SAG T2 (HR) COR OBL T1 (HR) SAG T1 RIGHT SIDEWALL SAG T1 LEFT SIDEWALL COR OBL T2 (HR) AX OBL T2 (HR) AX OBL T1 (HR) DWI B=1000 NEX=12 Multishell diffusion (B500, 1500 and 4000 with directions of 6, 6 and 15 respectively) TRICKS-INJECT AFTER 21 SEC +C COR FGRE FS +C SAG FGRE FS +C AX T2 (HR) MRB PL24MR 24PROSTATECTOMY NO ENDORECTAL COIL A72197
26 LOC COR FSEXL (BC) SAG FSEXL (BC) SAG T2 (HR) COR T1 (HR) COR T2 (HR) SAG T1 (HR) SIDE WALL RIGHT SAG T1 (HR) SIDE WALL LEFT AX T2 (HR) AX T1 (HR) TRICKS INJECT AFTER 21 SEC MRB PL25MR 25PROSTATE FOR RADIATION SEEDS C_72195-PROST Indication: verify radiation seed placement CPT is for 1 hour. Exam only at CMR Sag T2 high res Cor Oblq T1/T2 high res Sag T1 Rt & Lt sidewall Ax Oblq T1/T2 high res Axial with various flip angles Axial DWI Axial T2
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T
 BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
Revised June Body MR Protocols
 Body MR Protocols Abdomen focus protocols A 1: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI A 1L: Abdomen MRI without contrast A 1P: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI (pancreas protocol) A 1R: Pre- and post-contrast
Body MR Protocols Abdomen focus protocols A 1: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI A 1L: Abdomen MRI without contrast A 1P: Pre- and post-contrast abdomen MRI (pancreas protocol) A 1R: Pre- and post-contrast
1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018)
 General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018)
 General Guidelines 3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE HASTE TR 1600, no
General Guidelines 3T BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated July 15, 2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE HASTE TR 1600, no
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
Body MRI General Comments
 Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology
 Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations
 Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations V1.3 - April 2009 CanSCMR CMR Protocol and SOP Recommendation 2009 (15 minutes) 2 Planning of LV fct. real time multiple axes Realtime 3 cine long axis 6 long axes
Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations V1.3 - April 2009 CanSCMR CMR Protocol and SOP Recommendation 2009 (15 minutes) 2 Planning of LV fct. real time multiple axes Realtime 3 cine long axis 6 long axes
Liver MRI in 30 minutes
 X Liver MRI in 30 minutes SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 18, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
X Liver MRI in 30 minutes SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 18, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
MRI of the Hepatobiliary System
 BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis
 ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis Sequence Coverage Slice/Gap Notes COR T2 ssfse 32-40 6/-1 Coverage from all sequences is above the liver dome, through the kidneys.
ROUTINE MRI PROTOCOLS: I. Abdomen Plus Post Gadolinium Screening Pelvis Sequence Coverage Slice/Gap Notes COR T2 ssfse 32-40 6/-1 Coverage from all sequences is above the liver dome, through the kidneys.
CT: Common Protocols. Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology
 CT: Common Protocols BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Heart & Vascular Center Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology msteigner@bwh.harvard.edu
CT: Common Protocols BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Heart & Vascular Center Harvard Medical School Teaching Hospital Michael Steigner, M.D. Director, Vascular CT/MR Assistant Professor of Radiology msteigner@bwh.harvard.edu
W/ (2) (3) (4) (5) (5) (6) (6) CTA
 Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous)
 CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
CTA Chest Pulmonary Embolism & Routine CT Abdomen + Pelvis W CTA Chest W (arterial) & CT Abdomen + Pelvis W (venous) Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact:
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº70, pág. 41-50, Abr.-Jun., 2006 CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº70, pág. 41-50, Abr.-Jun., 2006 CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Crohn s Disease. bowel. Two picks of diagnosis - 2nd and 6th decades of life. Multifactorial - Genetic and Environmental.
 Crohn s Disease Chronic and Inflammatory disease of the small and or large bowel. Two picks of diagnosis - 2nd and 6th decades of life. Multifactorial - Genetic and Environmental. In Israel: 40,000 patients.
Crohn s Disease Chronic and Inflammatory disease of the small and or large bowel. Two picks of diagnosis - 2nd and 6th decades of life. Multifactorial - Genetic and Environmental. In Israel: 40,000 patients.
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D
 Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Liver 4 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V.D Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA
 Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest
 (Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
(Non-EKG Gated) CTA Thoracic Aorta = CTA Chest Reviewed By: Dan Verdini, MD, Rachael Edwards, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial)
 CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CTA Pulmonary Embolism CTA Chest W (arterial) Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
Non-Contrast MRA. How and When 1996! Why Non-Contrast MRA? Angiography: What are our goals? Inflow Techniques Differences in excitation hx
 A major teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Angiography: What are our goals? Non-Contrast MRA: How and When Neil M. Rofsky, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of MRI &
A major teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Angiography: What are our goals? Non-Contrast MRA: How and When Neil M. Rofsky, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of MRI &
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital
 Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu 1991 1997 Whole body MRI: multistation approach x z Isocenter: Table Move: Multiple Steps Whole body
Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu 1991 1997 Whole body MRI: multistation approach x z Isocenter: Table Move: Multiple Steps Whole body
ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR
 ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR Frank Miller, M.D. FACR Professor of Radiology Chief, Body Imaging Section Medical Director, MR Imaging Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine fmiller@northwestern.edu
ABDOMINAL DIFFUSION WEIGHTED MR Frank Miller, M.D. FACR Professor of Radiology Chief, Body Imaging Section Medical Director, MR Imaging Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine fmiller@northwestern.edu
Objectives 8/17/2011. Challenges in Cardiac Imaging. Challenges in Cardiac Imaging. Basic Cardiac MRI Sequences
 8/17/2011 Traditional Protocol Model for Tomographic Imaging Cardiac MRI Sequences and Protocols Frandics Chan, M.D., Ph.D. Stanford University Medical Center Interpretation Lucile Packard Children s Hospital
8/17/2011 Traditional Protocol Model for Tomographic Imaging Cardiac MRI Sequences and Protocols Frandics Chan, M.D., Ph.D. Stanford University Medical Center Interpretation Lucile Packard Children s Hospital
Abdominal Ultrasonography
 Abdominal Ultrasonography David A. Masneri, DO, FACEP, FAAEM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Director, Emergency Medicine Residency Medical Director, Operational Medicine Division Center
Abdominal Ultrasonography David A. Masneri, DO, FACEP, FAAEM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Director, Emergency Medicine Residency Medical Director, Operational Medicine Division Center
UPPER EXTREMITY
 UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V
 CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
CT Pancreas 3 Phase CT Abdomen WO W - NC.A.V Reviewed By: Rachael Edwards, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: January 2019 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Renal and adrenal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Renal cell carcinoma 3 Clinical
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Renal and adrenal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Renal cell carcinoma 3 Clinical
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Body CT Protocols General tips:
 Body CT Protocols General tips: -Check the list of protocol types on Intrad -Look at prior studies for help -Look up clinical info in Epic or Powerchart -Call ordering clinician if you have unanswered
Body CT Protocols General tips: -Check the list of protocol types on Intrad -Look at prior studies for help -Look up clinical info in Epic or Powerchart -Call ordering clinician if you have unanswered
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
MRI OF FOCAL LESIONS IN
 Introduction MRI OF FOCAL LESIONS IN THE NON-CIRRHOTIC LIVER Ivan Pedrosa M.D. Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Advanced Imaging Research Center University of Texas Southwestern. Dallas, TX Incidental
Introduction MRI OF FOCAL LESIONS IN THE NON-CIRRHOTIC LIVER Ivan Pedrosa M.D. Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiology and Advanced Imaging Research Center University of Texas Southwestern. Dallas, TX Incidental
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds
 Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015
 Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
Colorectal Pathway Board (Clinical Subgroup): Imaging Guidelines September 2015 1 Contents Page No. 1. Objective 3 2. Imaging Techniques 3 3. Staging of Colorectal Cancer 5 4. Radiological Reporting 6
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS
 BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
03/01/17. Table of Contents GENERAL CT GUIDELINES... 3 ORAL CONTRAST... 3 RECTAL CONTRAST... 5 VAGINAL CONTRAST... 5
 03/01/17 Table of Contents GENERAL CT GUIDELINES... 3 ORAL CONTRAST... 3 RECTAL CONTRAST... 5 VAGINAL CONTRAST... 5 ROUTINE ABDOMEN/PELVIS... 6 ABDOMEN/PELVIS with DELAY... 7 NON CONTRAST ABDOMEN/PELVIS...
03/01/17 Table of Contents GENERAL CT GUIDELINES... 3 ORAL CONTRAST... 3 RECTAL CONTRAST... 5 VAGINAL CONTRAST... 5 ROUTINE ABDOMEN/PELVIS... 6 ABDOMEN/PELVIS with DELAY... 7 NON CONTRAST ABDOMEN/PELVIS...
CARDIAC MRI. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Overview
 CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CT abdomen and pelvis
 CT abdomen and pelvis General indications: Assessment of vague abdominal symptoms (pain, colics,distenstion,...) Varifecation of a lesion discovered by other diagnostic modalities as US, barium,ivp, Staging
CT abdomen and pelvis General indications: Assessment of vague abdominal symptoms (pain, colics,distenstion,...) Varifecation of a lesion discovered by other diagnostic modalities as US, barium,ivp, Staging
Pancreas Case Scenario #1
 Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review
 How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
How do the Parameters affect Image Quality and Dose for Abdominal CT? Image Review Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD, DNB Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Financial Disclosure This presentation
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System
 Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System January 2007 Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Understand
Guide to Small Animal Vascular Imaging using the Vevo 770 Micro-Ultrasound System January 2007 Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Understand
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment
 State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER
 IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
Fulfilling the Promise
 Fulfilling the Promise of Cardiac MR Non-contrast, free-breathing technique generates comprehensive evaluation of the coronary arteries By Maggie Fung, MR Cardiovascular Clinical Development Manager; Wei
Fulfilling the Promise of Cardiac MR Non-contrast, free-breathing technique generates comprehensive evaluation of the coronary arteries By Maggie Fung, MR Cardiovascular Clinical Development Manager; Wei
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE)
 Clinical How-I-do-it Cardiovascular How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE) Manuela Rick, Nina Kaarmann, Peter Weale, Peter Schmitt Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany Introduction
Clinical How-I-do-it Cardiovascular How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE) Manuela Rick, Nina Kaarmann, Peter Weale, Peter Schmitt Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany Introduction
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI
 ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI GENERAL INFORMATION: Pregnant Patients May undergo an MRI exam at any stage of pregnancy if the risk-benefit ratio to the patient warrants the study be performed. Present data
ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI GENERAL INFORMATION: Pregnant Patients May undergo an MRI exam at any stage of pregnancy if the risk-benefit ratio to the patient warrants the study be performed. Present data
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
CT angiography techniques. Boot camp
 CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
CT angiography techniques Boot camp Overview Basic concepts Contrast administration arterial opacification Time scan acquisition during the arterial phase Protocol examples Helical non-gated CTA Pulmonary
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad
 CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
11/1/2014. Radiologic incidentalomas Ordering pitfalls Newer technology and applications
 Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
Bilal Tahir, MD Gitasree Borthakur, MD Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology & Imaging Sciences October 31, 2014 ACP 2014 Dr. V. Aaron Nuclear (vaaron@iupui.edu) Dr. S. Westphal
FieldStrength. Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging. SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology. Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
To describe normal anatomy and common variants in biliary tree anatomy including the prevalence of these.
 Up for debate: Should 3.0T magnetic resonance pancreatography (MRCP) become a routine part of preoperative planning for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Poster No.: C-0196 Congress: ECR
Up for debate: Should 3.0T magnetic resonance pancreatography (MRCP) become a routine part of preoperative planning for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Poster No.: C-0196 Congress: ECR
Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis
 GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay
 rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
rown et al. MRI of the Female Pelvis Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.41 on 12/17/17 from IP address 37.44.202.41. Copyright RRS. For personal use only;
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol
 Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
Abdominal Ultrasound
 Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
Diagnostic Imaging
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V
 CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
CT Renal 3 Phase + Pelvis CT Abdomen Pelvis WO W - NC.A.V, Pelvis during V Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
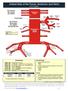 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer
 Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer Thoughts on the use of MRI in the treatment of prostate cancer
Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer Thoughts on the use of MRI in the treatment of prostate cancer
Pelvic Ultrasound.
 Pelvic Ultrasound Before Your Exam: Drink 32 oz. of water one hour before your examination time. Try to drink all the liquid within 30 minutes. Do not urinate before the exam. Arrive for your exam with
Pelvic Ultrasound Before Your Exam: Drink 32 oz. of water one hour before your examination time. Try to drink all the liquid within 30 minutes. Do not urinate before the exam. Arrive for your exam with
Abdominal Ultrasound. Diane Hallinen, MD. Bloodroot
 Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Parnassus Abdominal Imaging: CT protocol tips (Updated 2015)
 Parnassus Abdominal Imaging: CT protocol tips (Updated 2015) --- "To read CT scans is human, but to protocol is divine!" -- Herodotos, ancient Greek radiologist, 453 BC Here's a 6 pager with tips on CT
Parnassus Abdominal Imaging: CT protocol tips (Updated 2015) --- "To read CT scans is human, but to protocol is divine!" -- Herodotos, ancient Greek radiologist, 453 BC Here's a 6 pager with tips on CT
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO
 Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
Routine CT Chest + Abdomen WO Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD; Brett Mollard, MD Last Reviewed: August 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 In accordance with the ALARA principle, TRA policies and protocols
CASE 1 11/1/2016 HEPATOBILIARY IMAGING CASE PRESENTATIONS DECLARATION. Dr. Chirag Patel ORGAN IMAGING yr old lady
 HEPATOBILIARY IMAGING CASE PRESENTATIONS DECLARATION No financial disclosures or affiliations with commercial organisations No discussion of investigational or off-label use of medical devices, products
HEPATOBILIARY IMAGING CASE PRESENTATIONS DECLARATION No financial disclosures or affiliations with commercial organisations No discussion of investigational or off-label use of medical devices, products
Acknowledgements. Update of Focal Liver Lesions Goals. Focal Liver Lesions. Imaging Choices For Liver Lesions. Focal Liver Lesions
 Acknowledgements Update of Focal Liver Lesions 2012 Giles Boland Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures Dushyant Sahani Mukesh Harisinghani Goals Focal liver lesions Imaging
Acknowledgements Update of Focal Liver Lesions 2012 Giles Boland Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures Dushyant Sahani Mukesh Harisinghani Goals Focal liver lesions Imaging
