BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p. 1
|
|
|
- Barry Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p. 1 READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page, in both packets of stapled-together pages. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. Do NOT write on the BACK of any page unless you get a TA s permission FIRST. 3. About writing answers: All questions can be answered briefly. For full credit, discuss mechanisms. In problems asking for an answer and a reason, more credit is given for a correct reason. 4. Use a pen or pencil to write your answers, but do NOT use RED INK and DO NOT USE WHITE-OUT of any kind. However, if you use pencil, you cannot request a regrade. 5. All answers should be on pages in this packet. (Anything written on pages in the packet of multiple-choice questions will not be graded.) 6. Before you leave the testing room, turn in both packets of stapled-together pages. POTENTIALLY USEFUL EQUATIONS: Ix = Gx (Vm-Ex) V = Q/A P = QR Ix = Gx (Vm-Ex) A = πr 2 WAIVER: By signing this waiver I give permission that this exam can be left for me to pick up in the hall outside the elevators on the third floor of Pacific Hall. I realize that this procedure may expose my grade to public scrutiny and my exam to theft. If I do not sign this waiver, I understand I will be able to get my graded exam back only as described on the course Web site. Signature Date
2 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name PID p. 2 Multiple choice answers: I. Material from MT1 I-1. [B,C] I-2. [A,C] I-3. [A] I-4. [B,C] I-5. [A,B,D] I-6. [B,C] I-7. [D] I-8. [B,C] I-9. [A,C,D] I-10. [A,C,D] I-11. [C] I-12. [A,D] I-13. [A,B,C] I-14. [None] I-15. [A,D] II. Material from MT2 II-1. [B,C,D] II-2. [C,D] II-3. [C,D] II-4. [B] II-5. [A,C,D] II-6. [C,D] II-7. [B,C,D] II-8. [A, D] II-9. [A,C] II-10. [A, B, D] II-11. [A,B,D] II-12. [none] II-13. [B, D] II-14. [A,B,D] II-15. [B] III. New material III-1. [A,C,D] III-2. [C,D] III-3. [A,B,C,D] III-4. [A, D] III-5. [C,D] III-6. [A,B,D] III-7. [A,C] III-8. [A,D] Scores and grade: Final: MT1 Final: MT2 Final: New Final: Total Midterm 1 Midterm 2 Grand Total Course Grade
3 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p (20 points total) Edema is swelling of the body often the arms or legs caused by increased levels of interstitial fluid. Edema is a condition, not a disease state: it can have many different causes. For each of the causes of edema listed below, briefly explain the major physiological mechanism that causes it. A. (5 points) Eating too much salt. The ingested salt is taken up through the intestines into the plasma, making the plasma hyperosmotic compared to normal. The plasma and interstitial fluid mix, as the plasma filters across the capillary walls in the near half of the capillaries, then returns in the far half. This mixing dilutes the plasma somewhat, but it remains hyper-osmotic, as does the interstitial fluid. The hyper-osmotic interstitial fluid draws fluid out of the cells into the extracellular fluid (water is in higher concentration inside the cells), which increases the volume of both the plasma and the interstitial fluid. The increased volume of the interstitial fluid is the edema. B. (5 points) Sunburn (which damages the capillary wall cells, allowing leakage of large molecules). Normally, the hydrostatic pressure driving fluid out of the capillaries along the capillary bed is just balanced by the oncotic pressure pulling fluid back into the capillaries. Normally, the oncotic pressure is high because there are proteins in the plasma but none in the interstitial fluid. When the capillary walls are damaged in sunburn, proteins leak into the interstitial fluid, lowering the oncotic pressure difference. (In the extreme, the plasma proteins equilibrate between the plasma and interstitial fluid; in this case, the oncotic pressure is zero.) Lowering the oncotic pressure tips the balance in favor of fluid leaving the capillaries into the interstitial fluid, so the volume of the interstitial increases; this is edema. C. (5 points) Failure of the valves in the veins of the legs. The muscle pump in the legs helps to move blood along the veins back to the heart. Contractions of leg muscles squeeze the leg veins. Normally, this pushes blood toward the heart because the valves close in the veins on the side of the side of the contraction away from the heart, which prevents backward flow of the blood. If the valves do not close (this is what is meant by failure ), the blood is forced backward into the veins. This builds up the hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries, so that more fluid comes out of the capillaries. Because there is no change in the oncotic pressure, excess fluid comes out of the capillaries in the legs; this is edema. D. (5 points) Right heart failure. When the muscles in the right ventricle weaken (this is what is meant by right heart failure), the right heart cannot pump all of the blood volume returning to it from the systemic system, so the blood backs up in the systemic vessels. This increases the pressure in the systemic veins, which builds up the hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries, so that more fluid comes out of the capillaries. Because there is no change in the oncotic pressure, excess fluid comes out of the capillaries into the interstitial fluid in the whole systemic system; this is edema.
4 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p (20 points total) Hyperosmotic laxatives cause diarrhea by drawing water from the bloodstream into the colon, which is then expelled from the body through the anus. The loss of water from the bloodstream increases the osmolarity of the plasma. A. (8 points) Describe what happens to the volume and osmolarity of the other two body fluid compartments as a result of this hyperosmotic diarrhea, before there is any compensation by kidney mechanisms. The loss of water from the plasma increases its osmolarity and decreases its volume. This hyper-osmotic fluid mixes with the interstitial fluid, across the capillary walls, so the interstitial fluid also loses some volume to the plasma and becomes more concentrated. The hyper-osmotic interstitial fluid causes water to move out of cells (rather than ions moving into the cells, because water moves across membranes faster than ions). At equilibrium, all three body fluid compartments would have a lower volume and a higher osmolarity. [ NOTE: In all compartments, the volume would be decreased by the same percentage, and the osmolarity would be equal.] B. (4 points) Is the release of ADH triggered by hyperosmotic diarrhea? Briefly explain. Yes. The osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus would be activated by the increased osmolarity of the plasma, which triggers ADH release. [If the decrease in blood volume is sufficiently great, the blood pressure could decrease enough to slow the activity of the baroreceptors, which would also signal the release of ADH.] C. (4 points) Would ADH help to reverse the changes in the body fluid volumes caused by hyperosmotic diarrhea? Explain your answer. The ADH would minimize the loss of water through the kidney by increasing the permeability of the collecting ducts to water, so that as much water as possible would move out of the nephrons and, ultimately, back into the plasma. By forming a highly concentrated urine, excess salt would be lost, which would bring the osmolarity back toward normal levels. This mechanism does not, however, replace the water lost in the diarrhea; it can only minimize the loss of any additional water in the urine. Therefore, all three body fluid volumes would remain lower than normal. D. (4 points) Describe one other important mechanism triggered by the changes in the fluid compartments that would help to compensate for the effects of this laxative. The major physiological mechanism is that thirst is also triggered strongly by the increased activity of the osmoreceptors. After hyperosmotic diarrhea, you would become very thirsty. Drinking water would replace the water that was lost. As the water is absorbed in the intestine, all the steps in part A above would be reversed and all the volumes and osmolarities in the three fluid compartments would return to normal. [A second mechanism, of lesser importance, is that the lowered blood pressure could trigger the release of aldosterone, which would cause the distal tubules and collecting ducts to retain more NaCl, which would help to build up the blood volume. This retential of salt would, however, keep the osmolarity higher and would still depend upon drinking water to bring the osmolarity back to normal. In addition, the aldosterone mechanism is very slow, much slower than the ADH and thirst mechanisms.]
5 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p (10 points total) An increase in venous return to the right atrium (caused by either increased blood volume, increased blood pressure, or both) causes the release of a hormone called Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) from cells in the atrium. This hormone is part of a homeostatic system that involves both the cardiovascular system and the kidneys. A. (5 points) ANP has a direct effect on the muscles of the veins and arterioles. Predict whether ANP would cause vasodilation or vasoconstriction, and explain your prediction. To be homeostatic, the ANP must cause vasodilation, which would produce negative feedback: an increase in blood pressure would relax the muscles of the arteries and veins, lowering the blood pressure. [In fact, this is exactly what happens: ANP relaxes smooth muscle cells in most blood vessels.] [An alternative answer: if ANP caused vasoconstriction, an increase in blood pressure would result in a further increase in blood pressure, which is a positive feedback.] B. (5 points) ANP also has an effect on the kidneys, acting primarily through aldosterone. Predict whether ANP would increase or decrease the amount of aldosterone in the blood, and explain your prediction. Again, to be homeostatic, ANP must decrease the release of aldosterone. The trigger for ANP release is increased blood volume and blood pressure. The effect of aldosterone on the kidney is to retain NaCl, which would increase blood volume and blood pressure. Therefore, to be a negative feedback system, aldosteone must be inhibited. [In fact, aldosterone is inhibited by ANP both directly (by acting on the cells in the adrenal cortex that release aldosterone) and indirectly (by decreasing the production of other hormones that relese aldosterone).]
6 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name Answer Key PID p (18 points total) People with a disease called Fanconi s Syndrome (FS) have malfunctions in the reabsorbtion of molecules in the proximal tubule of their nephrons. In the most extreme form, the proximal tubule cannot reabsorb glucose, amino acids, or Na +. The major symptoms of FS are polyuria (the production of huge amounts of urine) and polydipsia (extreme thirst). A. (5 points) Explain the polyurea: how do the kidneys of a person with FS produce an abnormally high quantity of urine? Because the proximal tubule cannot reabsorb the major components in the plasma (glucose, amino acids, or Na + ), they pass through the nephon in large quantities. In addition, because the proximal tubule allows water to pass freely through its walls, the fluid in the proximal tubule is isosmotic to the plasma, which means that a huge amount of water that normally is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule flows into the Loop of Henle in a person with FS. The remainder of the nephron cannot reabsorb the excess of substances, including the water, so large quantities of fluid are lost as urine. [This is a condition known as osmotic diuresis.] B. (5 points) Explain the polydipsia: why (i.e., by what mechanism) is a person constantly thirsty? The huge water loss from the polyurea lowers the volume of blood, which activates the thirst center to produce drinking. C. (4 points) Would the glomerular flow filtration rate (GFR) in an FS patient be higher, lower, or the same as the GFR of a normal person? Briefly explain why. It would be the same. The amount of fluid that passes through the nephron would be much greater, but the amount that is filtered at the capsule would not change. [An alternative explanation: the inulin clearance which measure GRF would be the same because the quantity of inulin that is filtered would not change. The concentration of inulin in the urine would be very low, but the volume of urine would be much greater because the quantity of inulin in the urine (which is concentration of inulin in the urine times the volume/minute of urine produced) would be the same.] D. (4 points) How would the clearance of amino acids in an FS patient compare to a normal patient? State whether it would be higher, lower, or the same as the amino acid clearance in a normal person, and briefly explain why. The clearance of amino acids would be much higher in an FS patient. Normally, no amino acids are in the urine, so their clearance = 0. In FS, all of the amino acids that are filtered make it past the proximal tubule. Because amino acids are neither reabsorbed nor secreted throughout the rest of the nephron, amino acids are handled exactly the same way as inulin in FS patients, so that: clearance of amino acids = clearance of inulin = GFR
BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name PID p. 1
 BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name PID p. 1 READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page, in both packets of stapled-together pages. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.)
BIPN100 F12 FINAL EXAM ANSWERS Name PID p. 1 READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page, in both packets of stapled-together pages. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.)
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1
 BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are
 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance Body Water Content Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60%
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1
 BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
Physiology of Circulation
 Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
Physiology of Circulation Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Blood vessels Arteries: Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to the lungs and tissues. Arterioles are small arteries that deliver blood to the
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
Blood Pressure Regulation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction There are two basic mechanisms for regulating
UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life
 Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
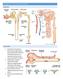 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions
 Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) During exercise, plasma levels of Renin increase moderately. Why should Renin levels be elevated during
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) During exercise, plasma levels of Renin increase moderately. Why should Renin levels be elevated during
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
BIOL 221 Chapter 26 Fluids & Electrolytes. 35 slides
 BIOL 221 Chapter 26 Fluids & Electrolytes 35 slides 1 Body Water Content Total Body Water is the percentage of a person s weight that is water. TBW can easily vary due to: gender males have higher TBW
BIOL 221 Chapter 26 Fluids & Electrolytes 35 slides 1 Body Water Content Total Body Water is the percentage of a person s weight that is water. TBW can easily vary due to: gender males have higher TBW
Body Water Content Total Body Water is the percentage of a person s weight that is water. TBW can easily vary due to: gender
 BIOL 221 Chapter 26 Fluids & Electrolytes 35 slides 1 Body Water Content Total Body Water is the percentage of a person s weight that is water. TBW can easily vary due to: gender males have higher TBW
BIOL 221 Chapter 26 Fluids & Electrolytes 35 slides 1 Body Water Content Total Body Water is the percentage of a person s weight that is water. TBW can easily vary due to: gender males have higher TBW
Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140
 هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
WJEC. BY4 Kidney Questions
 NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
8. URINE CONCENTRATION
 8. URINE CONCENTRATION The final concentration of the urine is very dependent on the amount of liquid ingested, the losses through respiration, faeces and skin, including sweating. When the intake far
8. URINE CONCENTRATION The final concentration of the urine is very dependent on the amount of liquid ingested, the losses through respiration, faeces and skin, including sweating. When the intake far
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
BIPN100B FIRST MIDTERM Fall 2010 Name PID
 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name and PID on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit, write your answers LEGIBLY in the
General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name and PID on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit, write your answers LEGIBLY in the
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم ** Note: the curve discussed in this page [TF]/[P] curve is found in the slides, so please refer to them.**
![بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم ** Note: the curve discussed in this page [TF]/[P] curve is found in the slides, so please refer to them.** بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم ** Note: the curve discussed in this page [TF]/[P] curve is found in the slides, so please refer to them.**](/thumbs/87/96174275.jpg) بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم ** Note: the curve discussed in this page [TF]/[P] curve is found in the slides, so please refer to them.** INULIN characteristics : 1 filtered 100 %. 2-Not secreted. 3-Not reabsorbed
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم ** Note: the curve discussed in this page [TF]/[P] curve is found in the slides, so please refer to them.** INULIN characteristics : 1 filtered 100 %. 2-Not secreted. 3-Not reabsorbed
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44828 1 Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of
OpenStax-CNX module: m44828 1 Hormonal Control of Osmoregulatory Functions * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Lecture 16: The Nephron
 Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME
 ᄋセM@セ @ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Biomedical Sciences QUALIFICATION CODE: 50BBMS
ᄋセM@セ @ POLYTECHNIC OF NAMIBIA SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES PROGRAMME QUALIFICATION(S): Bachelor of Biomedical Sciences QUALIFICATION CODE: 50BBMS
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
41B. Metabolism produces wastes that must be eliminated from the body. This. Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation
 41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi
 Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Hill et al. 2004, Fig. 27.6
 Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
