REVISION CARDS Biology B2
|
|
|
- Clarissa Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVISION CARDS Biology Modified 15/02/2015 (PB)
2 Index Topic 1 2 Microscopes 3 Plant cells 4 Animal cells 5 Bacteria cells 6 Double Helix 7 DNA 8 Genetic engineering 9 Mitosis 10 Meiosis 11 Cloning 12 Protein synthesis 13 Enzymes 14 Lock and Key Topic 2 15 Aerobic respiration 16 Heart rate and Breathing 17 Anaerobic respiration 18 Plant leaves 19 Photosynthesis 20 Roots 21 Ecosystems Topic 3 22 Fossil records 23 Growth 24 Blood 25 Cells, Tissues, Organs 26 Heart 27 Circulatory system 28 Digestive system 29 Digestive enzymes 30 Functional foods
3 Topic 1 Microscopes Changes in microscope technology, improved lighting, better lenses, digital cameras etc. enable cells to be seen with more clarity and detail than before. Light microscopes allow objects to be magnified up to at least 2,000 times. Eyepiece Objective Total Magnification 10 x 4 x 40 x 10 x 10 x 100 x 10 x 40 x 400 x 10 x 100 x 1000 x The magnification of the eyepiece multiplied by the objective gives the total magnification
4 Topic 1 Plant cell 1.2 Mitochondria: Converts the energy stored in glucose for use in the cell Large Vacuole: Water filled space that stores chemicals that exerts pressure against the walls. Cell wall: Composed of cellulose this provides both protection and structure Nucleus: Controls many functions of the cell and contains the DNA Cytoplasm: Stores chemical and maintains the shape of the cell. Cell membrane: A thin semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm Chloroplast: Where photosynthesis takes place. Contains chlorophyll. 4
5 Topic 1 Animal cell Cytoplasm: Stores chemical and maintains the shape of the cell
6 Topic 1 Bacteria cell Chromosomal DNA: carries genes that specify the proteins that make up the organism. Flagella: allow the cell to move Cell wall Plasmid DNA: Non-essential small circles of DNA containing between 5 and 100 genes. DNA can be extracted from many types of cells: Grind a piece of tissue (onion) to break it open. Add salt solution (NaCl) and detergent - these solutions break down and emulsify the fat & proteins that make up a cell membrane. Add alcohol. Because DNA is soluble in water, the alcohol causes DNA to precipitate out of the solution, leaving behind all the cellular components that aren't soluble in alcohol. DNA can then be wound on a stirring rod and pulled from the solution. 6
7 Topic 1 Double Helix DeoxyriboNucleicAcid and the linking between Adenine and Thymine (A=T), Cytosine and Guanine (C=G) were know to exist years before the discovery by James Watson and Francis Crick. They, based in Cambridge, were in competition with others in America and around the World to determine the 3D structure of the molecule. Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin in London were using X-ray crystallography to try to determine the shape and structure of DNA. Wilkins shared Franklin s research with Watson and Crick, helping them to make the vital breakthrough (H) The Human Genome Project: An international research project set up at the Sanger Institute to determine the sequence of chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. 7
8 Topic 1 DNA The DNA molecule consists of two strands coiled to form a double helix. These strands are linked by a series of complementary base pairs joined together by weak hydrogen bonds: i adenine (A) with thymine (T) ii cytosine (C) with guanine (G) A gene is a section of a molecule of DNA that codes for a specific protein 8
9 Topic 1 Genetic Engineering Genetic engineering involves the removal of a gene from the DNA of one organism and the insertion of that gene into the DNA of another. For example, special bacteria can have a human gene inserted allowing them to manufacture insulin that can be used by Diabetes sufferers. Herbicide resistant crops allow non-specific sprays to be used to control weeds. However, there are concerns that sprays will be used more often, that the weeds too will become resistant and that there will be negative impacts on wild plants and biodiversity of farming. Easy to grow, genetically modified Golden Rice contains beta carotene which helps to reduce vitamin A deficiency and to prevent blindness in children in areas of Asia and Africa. There is though a risk that high dependency on one crop will reduce biodiversity in these areas and some widely respected organisations, such as Greenpeace, are strongly opposed to the introduction of any GM organisms
10 Topic 1 Mitosis Mitosis: results in two daughter cells, each with identical sets of chromosomes in the nucleus to the parent cell. This results in the formation of two genetically identical diploid body cells. Mitosis occurs during growth, repair and asexual reproduction Cloning is an example of asexual reproduction that produces genetically identical copies 10
11 Topic 1 Meiosis Meiosis: The production of four daughter cells (genetically different haploid gametes), each with half the number chromosomes At fertilisation, haploid gametes combine to form a diploid zygote
12 Topic 1 Cloning 1.18(H) Remove a diploid nucleus Egg removal Egg Cell Enucleation of egg cell Implant into surrogate Stem cells in the embryo can differentiate into all other types of cells but lose this ability as the animal matures. Electrical stimulation Normal mitosis Stem cells removed Cloning is notoriously difficult and risky, this will improve with time. Advantages: Offspring will all have the same (modified) genetic characteristics. Risks: Increased chance of genes behaving abnormally, increased risk of infection and cancer. Disadvantages: Cloned animals often have enlarged organs. Stem cell research has similar problems and also raises a lot of ethical concerns 12
13 B1 Topic 1 Protein synthesis Transcription: mrna is produced in the nucleus, it carries complimentary genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome. The mrna carries specific triplets of bases (codons) that code for specific amino acids. Translation: trna carries these amino acids to the ribosome where the amino acids link to form polypeptides in an order decided by the mrna (or ultimately the base order of the DNA). The order of bases in a section of DNA therefore decides the order of amino acids in the protein. Each protein has its own specific number and sequence of amino acids, resulting ultimately in different-shaped molecules that have different functions, including enzymes. trna (H) Gene mutations change the DNA base sequence, these mutations can be harmful, beneficial or neither. 13
14 Topic 1 Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyse chemical reactions occurring inside and outside living cells: In protein synthesis, enzymes catalyse the production of amino acids, the joining of amino acids to form peptides and finally proteins. In DNA replication, enzymes are involved in the unwinding of the DNA, the breaking up of the strands, replication of new strands and the joining together / rewinding of the new DNA Pepsin catalyses the break down of food proteins in the stomach and has to operate in an acid environment (ph 2) whilst Trypsin, which also catalyses the break down of proteins, works in the alkalinity of the intestine (ph8). 14
15 Topic 1 Lock and key Enzymes are highly specific for a particular substrate molecule. The lock and key hypothesis is a good analogy for the way that the active site on the enzyme molecule works. The enzyme can be denatured, this results in a change of shape of the active site, meaning that it no longer works effectively. Changes can be caused by low substrate concentrations, high (or low) temperature and changes in ph
16 Topic 2 Aerobic Respiration The human circulatory system facilitates respiration: glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries into respiring cells carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells into capillaries Respiration: A process used by all living organisms that releases the energy in organic molecules. Can be represented by the following word equation: Osmosis: The movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration of water to an area of lower concentration of water through a partially permeable membrane
17 Topic 2 Heart rate & Breathing Exercise increases both breathing rate and heart rate. The volume of blood pumped per minute (cardiac output of the heart) is calculated from the stroke volume (output of the left ventricle) x heart rate (pulse) Exercise increases the need for energy / additional glucose and oxygen in the body. Breathing increases to rid the body of the carbon dioxide produced by respiration and to provide more oxygen. Heart rate will increase to provide the extra food and oxygen needed Recovery time is also known as the amount of time it takes the human body to repay an oxygen debt. A person in poor physical shape will require much more recovery time to keep exercising. 17
18 Topic 2 Anaerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration releases energy from glucose: During vigorous exercise, muscle cells may not receive sufficient oxygen for their energy requirements and so start to respire anaerobically. Lactic acid builds up Aerobic respiration releases approximately 16 x more energy than anaerobic respiration A build-up of lactic acid requires extra oxygen to break it down. This is called excess post-exercise oxygen consumption or EPOC (formerly known as oxygen debt) 18
19 Topic 2 Plant leaves Leaves are adapted for photosynthesis: They have a large surface area to capture light. Chlorophyll in chloroplasts absorb sunlight. Stomata in the underside of the leaf allow gas exchange (carbon dioxide, oxygen and water vapour) Photosynthesis uses light energy to produce glucose: (You only need to know the word equation) 19
20 Topic 2 Photosynthesis There are various limiting factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis: Light Carbon Dioxide Temperature The loss of water vapour from leaves drives transpiration Xylem vessels transport water and minerals in one direction from the roots to the rest of the plant. Movement is facilitated by the negative pressure created by the replacement of water lost through transpiration. Phloem translocates sugars from photosynthesis to storage organs due to hydrostatic / diffusion pressure created in cells. Minerals are taken up in the roots by active transport 20
21 Topic 2 Roots Water passes from an area of high concentration to the next cell (low water concentration) by osmosis. In this way water continues to move along the cells of the root up the xylem to the leaf. All the time water is moving to areas of lower water concentration Osmosis can be investigated using various sugar solutions and discs or chips of potato Root hairs have a large surface area. The cell membrane acts as a partially permeable membrane (the cell wall is fully permeable) and, because the cell sap inside the vacuole is a concentrated solution, water passes from the soil into the root hair cell by osmosis. 21
22 Topic 2 Ecosystems Pooters: Using the tube, airborne insects are drawn into the container. Thermometer: Measures temperature. Pond nets: Used to dip for insects in ponds 2.23 Sweep nets: Waved through shrubs, these will collect larger insects Pitfall traps: Used to collect insects and small animals. All can be used to investigate the relationship between organisms and their environment. Light meter: Used to measure the intensity of light incident on surfaces. Quadrats: Sample a select area randomly in a larger area ph meter: To measure acidity / alkalinity of water and soil. 22
23 Topic 3 Fossil record Fossils that can be dated show clear evidence of evolution. There is still much to be found and some things, like soft tissue are rarely found, hence there are gaps in the fossil record: The pentadactyl limb, with 5 fingers, is common to most four limbed creatures - humans, mammals, birds, dinosaurs, other reptiles and amphibians. It is seen as evidence of a common ancestry. Darwin noted this in his Origin of Species (H) 23
24 Topic 3 Growth Growth is an increase in size, length and mass of an organism Plants grow mainly by cell enlargement / elongation and can often grow continuously. Many plant cells are able differentiate. Growth data is often expressed in terms of percentile charts: As animals grow, the number of cells tend to increase, cells divide and change from embryonic stem cells to become more specialised cell types which then loose the ability to differentiate. Animals tend to grow to a maximum size. 24
25 Topic 3 Blood Red blood cells: Have a unique shape for their function which is carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide around the body, White blood cells: Also called leucocytes, these play an important role in the immune system and help protect against disease 3.8 Platelets: Contain proteins on their surface that allow them to stick together and fill breaks in a blood vessel. Plasma: A watery liquid that suspends red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Also transports dissolved gases, proteins, nutrients and waste products. 25
26 Topic 3 Cells, tissues, organs Organs: Heart, lungs, liver etc. 3.9 A group of cells working together is defined as a tissue and several tissues working together comprise an organ. An organ system would be a group of organs working together such as the cardiovascular or digestive systems. Tissue: For example muscle cells 26
27 Topic 3 Heart Valves in the heart help ensure that the blood only flows in one direction. The right atrium and ventricle pump deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary artery to the lungs where oxygenated blood returns through the pulmonary vein (veins take blood to the heart) 3.10 The left atrium and ventricle (which has a thicker muscular wall than the right) pump oxygenated blood out through the aorta around the body. Deoxygenated blood returns through the inferior and superior vena cava 27
28 Topic 3 Circulatory system The circulatory system transports substances around the body: Arteries transport blood away from the heart Veins transport blood to the heart Capillaries exchange materials with tissues
29 Topic 3 Digestive system The mouth breaks up food and starts the digestive process. The oesophagus transports food and fluid, after being swallowed, from the mouth to the stomach which churns the food and releases acids and enzymes to break it down. Most digestion and absorption occurs in the small intestine and finally food passes via peristalsis into the large intestine where the faeces are formed. Peristalsis: The muscular wall behind a bolus of food in the alimentary canal contracts and in front it relaxes. The resulting wave forces food down the oesophagus (H) Mouth Liver Gall bladder Large Intestine (Colon) The pancreas aids digestion and regulates blood sugar. The liver produces bile which is held in the gallbladder. When released into the small intestine, bile neutralises stomach acid and emulsifies /helps to breakdown fats. Oesophagus Stomach Pancreas Small intestine 29
30 Topic 3 Digestive enzymes Villi in the small intestine, with their large surface area, single layer of cells and capillary network, allow efficient absorption of the soluble products of digestion. Enzymes play an important role in digestion: Lipase digests fats to fatty acids and glycerol Proteases, including pepsin, digest proteins to amino acids Carbohydrases, including amylase, which digest starch to simple sugars (H) 3.17 Rates of reaction can be investigated by changing the concentrations of digestive enzymes, using models such as visking tubing. 30
31 Topic 3 Functional foods Probiotics contain Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus (lactic acid bacteria), such as Activia and Yakult, are live bacteria and yeasts, usually described as friendly bacteria. Whilst these have some resistance to stomach acid and anti-bacterial properties, there is limited evidence to support the claims made by these foods they are not medicines. Prebiotic oligosaccharides are simple sugars found in plants like beans and vegetables. They are reported to stimulate the growth of bacteria that are beneficial to the well-being of the body. Plant stanol esters, found naturally in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, cereals, and vegetable oils are known to help block the absorption of cholesterol in the blood
32
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
What is the function of ribosomes? Draw and label a Bacteria cell.
 Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Q1 Q2 Q3 What does the mitochondria do? What is the function of ribosomes? What is the function of the cell wall? Q4 Q5 Q6 What is the function of cell membranes? What is diffusion? What is found in plant
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
B2 PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
 B2 PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS The structure of cells can be studied using a light microscope. Image is magnified by lens (made bigger) and the different parts of a cell can be seen. Plant and animal cells
B2 PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS The structure of cells can be studied using a light microscope. Image is magnified by lens (made bigger) and the different parts of a cell can be seen. Plant and animal cells
Biology/Additional Science
 Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Candidate Number Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Monday 10 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour You must have:
Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Candidate Number Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Monday 10 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour You must have:
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
B2 - Revision! Topic 3- Common Systems! Name:!
 B2 - Revision Topic 3- Common Systems Name: Lesson Topic B2.25 Fossils and Evolution B2.26 Growth B2.27 Blood B2.28 The Heart B2.29 The Circulatory System B2.30 The Digestive System B2.31 Breaking Down
B2 - Revision Topic 3- Common Systems Name: Lesson Topic B2.25 Fossils and Evolution B2.26 Growth B2.27 Blood B2.28 The Heart B2.29 The Circulatory System B2.30 The Digestive System B2.31 Breaking Down
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Mark Scheme (Results) March GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01
 Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Mark Scheme (Results) March 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H/01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range of
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Where in the cell are proteins made? Which part of a cell controls its activities? ribosomes. nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur?
 Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
Which part of a cell controls its activities? nucleus Where in the cell do chemical reactions occur? cytoplasm Which part of a cell controls what goes in and out? membrane Where in the cell is energy released
B2 Cells and simple transport
 B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
B2 Cells and simple transport What are the parts of most human and animal cells? Nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes What is yeast? A single celled organism made of cytoplasm, nucleus,
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Animal cells: label the main parts. Plant and algal cells: label the parts Cell wall. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm. nucleus. mitochondrion.
 B2 Cells and simple transport: Part 1: cell, ribosomes, respiration, chemical reactions, protein, nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplasts, cell wall, mitochondrion, vacuole, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, sap,
B2 Cells and simple transport: Part 1: cell, ribosomes, respiration, chemical reactions, protein, nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplasts, cell wall, mitochondrion, vacuole, photosynthesis, chlorophyll, sap,
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
OCR (A) Biology GCSE. Topic 1: Cell Level Systems
 OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
OCR (A) Biology GCSE Topic 1: Cell Level Systems Notes (Content in bold is for higher tier only) Cell structures Microscopes (1.1a and c) Light (optical) microscopes The specimen is placed onto a slide,
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Year 10A2 10A7. Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59%
 Year 10A2 10A7 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
Year 10A2 10A7 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance
 Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Tuesday 15 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Tuesday 15 May 2012 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY
 Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells Elements= Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler form Made up of only one kind of atom Found in the body Carbon
Chapter 3 CELL PROCESSES AND ENERGY Section 1: Chemical Compounds in Cells Elements= Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler form Made up of only one kind of atom Found in the body Carbon
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
B2 Revision Pack Please keep this pack with you
 Name: B2 Revision Pack Please keep this pack with you Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths questions (10%+ of the exam is maths!) Maths and Science Skills Questions Foundation Questions
Name: B2 Revision Pack Please keep this pack with you Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths questions (10%+ of the exam is maths!) Maths and Science Skills Questions Foundation Questions
Mark Scheme (Results)
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2H) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
GraspIT AQA GCSE Organisation Questions
 A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
A. Principles of organisation 1. Describe the levels of organisation in the human circulatory system in size order from the smallest part. Muscle Cell can contract and respiration occurs here Muscle (cardiac)
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
17. What are lipids made from? Fatty acids and glycerol 18. What are proteins used in the body for? (What is their function?) Growth and repair 19.
 100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
100 Facts Biology 1. What is a eukaryote? A plant or animal cell that have a membrane and a nucleus 2. What five things do most animal cells contain? Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosomes, mitochondria
Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE
 Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Monday 10 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
Paper Reference(s) 5BI2H/01 Edexcel GCSE Biology/Additional Science Unit B2: The Components of Life Higher Tier Monday 10 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL
 Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
Write your Examination Number here 2007. M. 43 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2007 BIOLOGY - ORDINARY LEVEL TUESDAY, 12 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in distilled water.
 The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
The diagram shows the same plant cell: after hour in distilled water after hour in strong sugar solution. Describe two ways in which the cell in the strong sugar solution is different from the cell in
Mark Scheme (Results)
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2F) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Biology (5BI2F) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body.
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Y10 POS Combined BIOLOGY 3Y
 08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Do Now Makeups. 4. In which organelle would water and dissolved materials be stored? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5. A. mitochondria B.
 Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
Examiners Report June GCSE Biology 5BI2H 01
 Examiners Report June 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range of qualifications
Examiners Report June 2013 GCSE Biology 5BI2H 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range of qualifications
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Absorption definition. Active transport. Aerobic respiration definition. Anaerobic respiration definition. Animal Cell features
 Absorption definition Active transport Aerobic respiration definition Anaerobic respiration definition The movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine into the blood or lymph
Absorption definition Active transport Aerobic respiration definition Anaerobic respiration definition The movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine into the blood or lymph
Intermediate 2. Biology. Learning Outcomes
 Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagrams show some organs in the human body. (a) Name the organs labelled A, B, C, D and E. A.... [1] B.... [1] C.... [1] D.... [1] E.... [1] (b) Which of the organs
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education BIOLOGY 0610/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
KS3 Science Assessment Framework: Year 7 Cells September 2015
 Assessment date Duration Learning Objectives Success criteria Misconceptions and Barriers to learning Working Scientifically Skill development Compulsory Practical Investigations Autumn 1 1 To identify
Assessment date Duration Learning Objectives Success criteria Misconceptions and Barriers to learning Working Scientifically Skill development Compulsory Practical Investigations Autumn 1 1 To identify
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist
 Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
Year 9 AQA GCSE Biology Revision Checklist Use this booklet to help you with your revision in preparation for your year 9 Biology exam and final examinations. This is the work that you will have covered
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as an aid
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
chloroplasts cell membrane nucleus nucleus cell wall vacuole cytoplasm Animal cell Plant cell Investigating Cells Summary Booklet page 1
 1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
1. General: state that cells are the basic units of living things. Sections of living tissue, when examined under a microscope are seen to be made up of similar units. These units consist of cytoplasm,
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
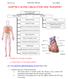 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes
 Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
2 Which of these statements best explains the process of energy conversion that takes place in the mitochondria?
 irst Semester Biology inal: 1. The technique known as chromosome painting is the result of scientific research. Scientists use chromosome painting to mark the locations of genes on human chromosomes with
irst Semester Biology inal: 1. The technique known as chromosome painting is the result of scientific research. Scientists use chromosome painting to mark the locations of genes on human chromosomes with
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
2014 Secondary Three Biology Curriculum Outline
 Week 1 Theory Week 2 2.1 Cell structure and Organization. Identify from prepared slides or from fresh preparations using appropriate temporary staining technique or on diagrams or photomicrographs, the
Week 1 Theory Week 2 2.1 Cell structure and Organization. Identify from prepared slides or from fresh preparations using appropriate temporary staining technique or on diagrams or photomicrographs, the
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes
 AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes Page 1 B2.1 Cells and Cell Structures Summary All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions.
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 2 Summary Notes Page 1 B2.1 Cells and Cell Structures Summary All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions.
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chemistry Regents Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
