Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Berenice Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN Available online at 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Post- Farangipete, Mangalore , Karnataka, India. ABSTRACT A multiple unit oral floating drug delivery system was developed to prolong gastric residence time, target stomach mucosa and increase drug bioavailability. Oral sustained release gastro-retentive dosage forms offer many advantages for drugs with absorption from upper parts of the gastro intestinal tract. Gastro retentive systems such as floating systems, mucoadhesive, high-density, expandable have developed to provide controlled delivery of drugs with prolonged gastric residence time. The present study attempts to give an insight into the gastro-retentive drug delivery systems, and gastric floating dosage forms, in particular. Due to their advantages over conventional dosage forms the study has attracted the formulators. The study highlights these advantages with reference to the various types of gastro retentive drug delivery systems, as well as provides an overview of the advances that have taken place in this area. Floating dosage forms are emerging as a promising dosage forms. Various attempts have been made to develop gastro retentive systems. Several approaches are currently utilized in the prolongation of the GRT Floating dosage forms can be prepared as tablets, capsules by adding suitable ingredients as well as by adding gas generating agent. In this review various techniques used in floating dosage forms along with current and recent developments of stomach specific floating drug delivery systems are discussed. Key Words: Floating drug delivery system, Buoyancy, Gastric residence time, Gastro retentive system. INTRODUCTION Gastric emptying of dosage types is a supremely variable process and ability to extend and control emptying time is a valuable benefit for dosage forms, which remain in the stomach for a longer period of time than conventional dosage forms. Oral controlled dosage forms are being originated due to their advantages. The controlled drug delivery system should basically be aimed at achieving more expectable and increased bioavailabilty of drugs. However the progressing process is challenged by several physiological obstacles, such as inability to restrain and locate drug in the particular regions of GI tract, due to the changeable gastric emptying and motility. Conventional oral dosage forms provide a certain drug concentration in systemic passage without offering any control over drug delivery. Controlled release drug delivery systems (CRDDS) produce drug release at a predetermined, expected and controlled rate. A main problem in oral CRDDS is that not whole drug candidates are absorbed uniformly throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Few drugs are absorbed uniformly throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Few drugs are absorbed in a specific portion of gastrointestinal tract only. Such drugs are said to have an Absorption window. After passing the absorption window, the liberated drug goes to waste with insignificant or no absorption. These discussions of CRDDS have guided to the development of oral GRDFs having gastric retention capabilities. 1 One of the most suitable and common approaches for fulfilling a prolonged and expected drug delivery profiles in gastrointestinal tract is gastro retentive dosage forms (GRDFs) that provide a new and better choice for drug therapy. Gastro retentive systems can prevail in the gastric region for long period of time and hence significantly extend the gastric residence period of drugs. Prolonged gastric retention enhances bioavailability, reduces drug waste, and enhances solubility for drugs that are less soluble in the high ph surroundings. Gastric retention will give new therapeutic possibilities and substantial advantages for patients. 2 The controlled gastric residing of solid dosage forms may be attained by the various efforts. Several gastro retentive drug delivery techniques being designed and improved, including: high density (sinking) systems that reside in the bottom of the stomach, low density (floating) systems that causes floatation in gastric fluids, mucoadhesive types that causes bioadhesion to stomach mucosa, unfoldable, extendible,
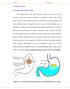
2 ISSN Available online at 45 or swellable systems which decreases emptying of the dosage forms through the pyloric sphincter of stomach, super porous hydrogel systems, magnetic systems etc. This review deals with various gastro retentive approaches that have recently become leading approaches in the field of site-specific oral controlled release drug delivery systems. 3 BASIC PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT The Gastrointestinal tract is a tube of about nine meters long that runs through the middle of the body, from the mouth to the anus and involves the throat (pharynx), oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (consisting of the duodenum, jejunum and ileum) and large intestine. The wall of the gastrointestinal tract has the identical common structure throughout most of its length from the oesophagus to the anus, with some local differences for each area. The stomach is an internal organ with a capacity for storage and blending. The stomach is located in the left upper part of the abdominal cavity instantly under the diaphragm. Its size varies depending on the amount of food taken: up to 1500 ml following a meal; after food has emptied, a fallen state is obtained with resting volume of ml. 4 Based on fasted and fed conditions of stomach, there are two different types of gastrointestinal motility. The fasted state is related with some cyclic contractile happenings commonly called as Migrating Myoelectric Complex (MMC) or The interdigestive motility pattern is commonly known as migrating motor complex ( MMC ) and is arranged in cycles of activity and quiescence. MMC wave begins from the stomach down the GI tract every minutes. A full cycle resides of four phases, starting in the lower oesophageal sphincter, continuing over the whole stomach, the duodenum and jejunum, and ends at the ileum. 5 Phase I: (basal phase) lasts from 40 to 60 minutes with several contractions. Phase II: (pre burst phase) It includes of fragmentary contractions that adequately increase in intensity as the phase develops and it lasts about 20 to 40 minutes. Phase III: (burst phase) lasts for 4 to 6 minutes. It considers intense and systematic contractions for small period. It is due to this wave that all the not digested material is moved out of the stomach down to the small intestine. It is also called as the housekeeper wave. Phase IV: This is a short temporary period of about 0 to 5 minutes, and the contractions vanish between the last part of phase III and quiescence of phase I. These contractions effect in reducing the size of food particles (to less than1mm) which are moved toward the pylorus in a suspension form. During the fed state onset of MMC is detained resulting in slowdown of gastric emptying rate. The studies finding gastric emptying rates says that orally administered controlled release dosage form are subjected to basically two problems that of short gastric residence time and incalculable gastric emptying rate. 6 Fig. 1: Anatomy of stomach
3 ISSN Available online at 46 Fig. 2: Gastro intestinal tract
4 ISSN Available online at 47 Need for Gastro retentive drug delivery system (GRDDs) Usually oral delivery is commonly utilized in pharmaceutical field to treat or prevent diseases. Although, conventional delivery had many obstacles and the major obstacle is non-site specificity. Gastro retentive delivery is a site-specific delivery for the confinement of drugs either at stomach or at intestine. It is obtained by residing dosage form in the stomach and the drug is delivered in a controlled manner to the specific site either in stomach or other parts of GI tract. Some drugs are absorbed at particular site. They need to be delivered at specific site or to be delivered such that maximum amount of drug reaches the specific site. Pharmaceutical field is now concentrating more towards such drugs which require particular site. 7 Factors affecting gastric retention 1. Nature of the meal of: Fats, particularly fatty acids retard gastric secretion and have a particular reductive effect on the rate of emptying. Proteins and starch are known to have inhibitory effect on gastric emptying, though to a less extent. As the viscosity of the gastric fluids is increased, there is a corresponding reduction in the rate of emptying Caloric content: Gastric residence time can be enhanced by 4-10 hours with a food that is rich in proteins and fats Density of dosage form: The density of a dosage form also affects the gastric emptying time and effects the location of the system in the stomach. 4. Frequency of the food: The GRT can be enhanced by over 400 minutes, when consecutive meals are given, due to the reduced frequency of MMC. 5. Size of dosage form: The mean gastric retention time of nonfloating dosage forms are highly variable and much more dependent on their size, which may be large, medium and small units. In most cases, the larger the dosage form the greater will be the gastric residence. In broad it is known that indigestible food particles > 1-2mm are retained in the stomach throughout the postprandial period, after which they are removed by cyclical recurring burst of interdigestive gastric contractions Single or multiple unit formulation: Multiple unit dosage forms show a more predictable release profile and unimportant impairing of performance due to failure of units allow co- administration of units with different release patterns or containing incompatible substances and permit a larger margin of safety against dosage form failure compared with single unit dosage forms. 7. Sex: Mean ambulatory GRT in males (3.4±0.6 hours) is less when measured with their age and race matched female counter parts (4.6±1.2 hours), nonetheless of the weight, height and body surface. 8. Emotional state of subject: The influence of psychological factors on gastric motility depending upon whether the emotional experience is of an aggressive or a depressive type. 9. Body posture: Gastric emptying is ideal while standing and by lying on the right side since the normal curvature of the stomach provides a hanging path whereas lying on the left side or in supine position reduces it Effect of drugs: Drugs that reduce gastric retention includes poorly soluble Antacids (Aluminium hydroxide), Anticholinergics (Atropine, Propantheline), Narcotic analgesics (Morphine) and Tricyclic antidepressants (Imipramine, amitryptiline).drugs such as Metoclopramide, Domperidone and Cisapride (Anti emetics) stimulates gastric emptying. 11. Exercise: Heavy physical activity retards gastric emptying. 12. Disease states: Diseases like gastric ulcer, pyloric stenosis, gastroenteritis, diabetes and hypothyroidism retard gastric emptying. Diseases like duodenal ulcer and hyperthyroidism promote gastric emptying rate. 12
5 ISSN Available online at 48 APPROACHES FOR GASTRIC RETENTION Fig. 3: Figure showing various approaches for gastro retentive drug delivery system. A) High Density Systems: It is also known as Sedimentation system. These systems with a density of about 3 g/cm3 will reside in the antrum part of the stomach and are capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements. This system is made by covering the drug or mixed with heavy inert substances such as titanium dioxide, barium sulfate, iron and zinc oxide powder. In the system, the formulation density exceeds the density of common stomach content (1.004 g/ml). The only major problem with such systems is that it is technically very difficult to manufacture such formulations with high amount of drug (>50%) and to achieve a density of about 2.8g/cm3. 13 B) Swelling and expanding system: One way to reside a dosage form in the stomach is by increasing its size. These are the dosage forms, which after engulfing, swells to an level that prevents their departure from the pylorus. As a outcome, the dosage form is retained in the stomach for extended or long period of time. These systems are also named as plug type systems. In this system, polymers are used with ideal molecular mass and swelling properties, which (in addition to imparting floatation) also helps in controlled and sustained drug release. This system undergoes contact with gastric media; the polymer absorbs water and swells. Eg: Developed swelling systems of Losartan tablets using sodium bicarbonate, sodium carboxy methyl cellulose (Na CMC), and hydroxyl ethyl cellulose (HEC). 14 C) Bioadhesive Systems: These systems are based on bioadhesive polymers, which adhere or bind to the mucin and / or epithelial surface. A bio/muco-adhesive substance is a natural or synthetic polymer, which is capable of developing an adhesive interaction based on hydration mediated, bonding mediated or receptor mediated adhesion with a mucus lining of GI mucosa. 15 D) Floating Drug Delivery systems and its mechanism: Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) or hydro-dynamically balanced systems have a bulk density lesser than gastric fluids and thus survive buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a long period of time. The system floats in the gastric fluid and the drug is slowly liberated at the required rate. This causes an increased GRT and a improved control of the fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. Several approaches or systems were used to develop an ideal FDDS. These buoyant formulations include hollow microsphere (micro balloons), granules, powders, tablets, pills, laminated film. To determine the floating force kinetics, ideal apparatus for determination of resultant weight has been mentioned in the literature. The apparatus works by measuring continuously the force equivalent to F (as a function of time) that is essential to maintain the submerged object or dosage form. The object floats better if F is on the greater positive side as shown in figure. This apparatus helps in optimizing FDDS with respect to stability and durability of floating forces produced in order to prevent the disadvantages of unforeseeable intragastric buoyancy capability imbalances. 16
6 ISSN Available online at 49 F = F buoyancy F gravity = (Df Ds) gv Where, F= total vertical force, Df = fluid density, Ds= object density, v = volume and g =acceleration due to gravity. F = F buoyancy F gravity = (Df Ds) gv Where, F= total vertical force, Df = fluid density, density, v = volume an g =acceleration due to gravity Ds= object Fig. 4: Mechanism of floating systems, GF=Gastric fluid Approaches to design floating dosage forms The following approaches have been used for the design of floating dosage forms of single and multiple unit systems. Single-Unit Dosage Forms: In low density systems, the globular shells, having lower density than that of gastric content or fluid can be used as a carrier for drug for its controlled rate release. A floating dosage form can also be derived by using a fluid-filled system that remains buoyant in the stomach. In coated shells or beads popcorn, poprice, and polystyrol have been used as drug carriers. Sugar polymeric materials such as methacrylic polymer and cellulose acetate phthalate have been utilized to undercoat these shells. These are additionally coated with a drug-polymer combination. The polymer of possible can be either ethylcellulose or hydroxypropyl cellulose, which depends on the type of released rate. Finally, the product remains buoyant on the gastric fluid while liberating the drug gradually over a prolonged period of time. Fluid filled floating chamber type of dosage forms includes incorporation of a gas filled floatation chamber in to a micro porous component that houses as a reservoir having apertures present at top and bottom walls through which the gastrointestinal tract fluid enters to dissolve the drug. 17 Hydrodynamically balanced systems (HBS) are designed to prolong the stay of the dosage form in the gastro intestinal tract and help in enhancing the absorption. Such systems are best acceptable for drugs having a ideal solubility in acidic environment and also for the drugs having particular site of absorption in the upper region of the small intestine. To exist in the stomach for a long period of time the dosage system must have a bulk density of less than 1. It should remain in the stomach, sustain its structural integrity, and release drug regularly from the dosage form. The outcome of HBS capsule as a better system is best explained with Chlordiazeopoxide hydrochloride. This drug is classical example of a solubility issue, wherein it exhibits a 4000-fold distinctness in solubility going from ph 3 to 6. But Singleunit formulations systems are associated with issues such as sticking together or being blocked in the gastrointestinal tract, which may have a possible danger of producing irritation. These forms are also unreliable in prolonging GRT in stomach when orally delivered, owing to their fortuitous (all or nothing) emptying process. 18 Multiple-Unit Dosage Forms: Multi particulate dosage forms are obtaining much favour over single-unit dosage forms. The potential advantages includes increased bioavailability; predictable, reproducible and normally short gastric residence time, no risk of dose dumping; reduced risk of local irritation, and the flexibility to mix pellets with different compositions or release models. In chasing of this endeavour many multiple unit floatable dosage systems have been designed. Microspheres have high storing capacity and numerous polymers have been used such as albumin, gelatin, starch, polymethacrylate, polyacrylamine, and poly alkyl cyanoacrylate. Spherical polymeric microsponges also called as microballoons have been
7 ISSN Available online at 50 prepared. Microspheres have internal hollow structure and show an excellent in vitro floatability or buoyancy. 19 CLASSIFICATION OF FLOATING SYSTEM Based on the mechanism of floating, the floating drug delivery systems are of following types: A) Non effervescent floating dosage form: These dosage forms or systems use a gel forming or swellable cellulose type of hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming polymers like polycarbonates, polymethacrylate and polystyrene. The formulation is done by blending the drug and the gel-forming hydrocolloid, after oral delivery of this dosage form swells while comes in contact with gastric fluids gains bulk density of <1. The air entrapped by the swollen polymer causes buoyancy to these dosage forms. Excipients used most frequently in these systems include hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), polyacrylate polymers, polyvinyl acetate, Carbopol, agar, sodium alginate, calcium chloride, polyethylene oxide and polycarbonates. 20 They are classified as: a. Colloidal gel barrier systems b. Micro porous compartment systems c. Alginate beads B) Effervescent floating dosage forms: These are the matrix type of floating dosage forms which are prepared by using swellable polymers like methyl cellulose, HPMC and chitosan based polymers as well as different effervescent compounds like Sodium carbonate, Calcium carbonate, Tartaric acid and Citric acid. They are developed in such a way that when in contact with the acidic gastric contents, C0 2 is liberated and gas entrapped in swollen hydrocolloids which provides buoyancy to the dosage forms. 21 They are classified as: a. Volatile liquid containing systems b. Gas generating systems Drugs suitable for GRDDS: 1. Drugs acting locally in the stomach E.g. Antacids and drugs for H. Pylori viz., Misoprostol 2. Drugs that are primarily absorbed in the stomach E.g. Amoxicillin 3. Drugs that is poorly soluble at alkaline ph E.g. Furosemide, Diazepam, Verapamil 4. Drugs with a narrow window of absorption E.g. Cyclosporine, Methotrexate, Levodopa, etc. 5. Drugs which are absorbed rapidly from the GI tract. E.g. Metronidazole, tetracycline. 6. Drugs that degrade in the colon. E.g. Ranitidine, Metformin HCl. 7. Drugs that disturb normal colonic microbes E.g. antibiotics against Helicobacter pylori. Drugs unsuitable for GRDDS: 1. Drugs that suffer instability in the gastric environment. E.g. Erythromycin etc. 2. Drugs intended for selective release in the colon. E.g. Amino salicylic acid and corticosteroids etc. 22 Merits of Floating Drug Delivery System 1. The floating drug delivery systems are advantageous for drugs absorbed through the stomach or proximal part of the small intestine. E.g. Ferrous salts, furosemide. 2. The ability of the medicaments administered utilizing the sustained release principle of floating formulation has been found to be independent of the site of particular medicaments. 3. The floating drug delivery systems are advantageous for drugs meant for local action in the stomach. E.g. antacids 4. Acidic substances like aspirin cause irritation on the stomach wall when come in contact with it. Hence HBS formulation may be useful for the administration of aspirin and other similar drugs. 5. Complete absorption of the drug from the floating dosage form is expected even at the alkaline ph of the intestine. The dissolution of the drug in gastric fluid occurs and then the dissolved drug is available for absorption in the small intestine after emptying of the stomach contents. 6. Enhanced bioavailability. 7. Sustained drug delivery/reduced frequency of dosing. 8. Reduced counter-activity of the body. 23
8 ISSN Available online at 51 Demerits of Floating Drug Delivery System: 1. Floating system is not suitable for those drugs that have solubility or stability problem in GI tract. 2. These systems require a high level of fluid in the stomach for drug delivery to float and work effectively. 3. Drugs such as nifedipine, which under goes first pass metabolism may not be suitable for the production of these types of systems. 4. Drugs which are annoyance to Gastric mucosa are also not suitable. 5. The drug substances that are unstable in the acidic environment of the stomach are not suitable candidates to be included in the systems. 23 POLYMERS USED IN FDDS Polymers are used in floating system so as to target the drug delivery at specific region in the GI tract i.e. stomach. Both synthetic and natural polymers are used in the floating drug delivery. Polymers are classified based on their source as follows. Natural polymers used in floating system are Guar gum, Chitosan, Xanthan gum, Gellan gum, Sodium alginate, etc. Synthetic polymers used for the floating drug delivery are HPMC, Eudragit, ethyl cellulose, etc. Natural polymers The use of natural polymers is ideal based on proven biocompatibility and safety margin. Natural gums are among the popular hydrophilic polymers since of their cost-effectiveness and regulatory approval. Polymers are generally used in floating drug delivery systems so as to target the drugs to a specific site in the gastro intestinal tract i.e. stomach. Moreover, these polymers are safe, nontoxic and capable of chemical moderation and gel forming nature. Natural polymer has advantages over synthetic polymer. They are as follows: 1. Biodegradable. 2. Biocompatible and non-toxic. 3. Low cost. 4. Environment friendly. 5. Local availability. Natural polymer has some disadvantages. They are as follows 1. Microbial contamination. 2. Batch to batch variation. 3. Uncontrolled rate of hydration. 4. Reduced viscosity on storage. 24 Synthetic polymers Synthetic polymers are important in pharmaceuticals. Use of synthetic polymers ranges from binder, film coating agent, etc. Synthetic polymers are either purely synthetic or they are modified form of natural polymers which are known as semi-synthetic. List of synthetic polymer used is as follows: 1. Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. 2. Eudragit. 3. Ethyl cellulose. Disadvantages of synthetic polymers are as follows: 1. High cost toxicity environmental pollution. 2. Acute and chronic adverse effect. 3. Poor biocompatible. 4. Inflammatory response and local reaction. 25
9 ISSN Available online at 52 Polymers used in GRDDS Polymers HPMC 4000, HPMC 100, HPMC K4M, CMC, PVA, Calcium alginate, Carbopol, Ethyl cellulose,eudragit RS and RL, acrylic polymer Buoyancy increasing agents Ethyl cellulose Release rate accelerants Mannitol, Lactose Release rate retardants Magnesium Stearate, Dicalcium phosphate, Talc Low density materials Polypropylene foam powder Inert fatty materials Fatty acids, Bees wax. Effervescent agents Tartaric acid, Citric acid, Sodium bicarbonate, Citroglycine METHODS OF PREPARATION OF FLOATING BEADS 1. Solvent evaporation method. 2. Emulsion gelation method. 3. Ionotrophic Gelation method. 1. Solvent evaporation method: Preparation of floating beads by solvent evaporation technique has been applied greatly in pharmaceutical industries for different purposes such as FDDS. This method includes the emulsification of an organic solvent which contains dissolved polymer and dissolved or dispersed drug in more amount of continuous phase, with the assist of an agitator or mixer. The concentration of the emulsifier exists in the aqueous phase will affect the particle size and its shape. When the desired or ideal droplet size is formed, the stirring or mixing rate is minimized and evaporation of the organic solvent is undertaken under atmospheric or reduced pressure at an ideal temperature. Subsequent evaporation of the solvent yields solid polymeric micro beads entrapping the drug. The solid beads are separated from the suspension by filtration, centrifugation, or lyophilisation. The polymers used for the development of such systems include, Cellulose acetate, Chitosan, Eudragit, Acrycoat, Methocil, Polyacrylates, Polyvinyl acetate, Carbopol, Agar, Polyethylene oxide and Polycarbonates. 26 Fig. 5: Schematic presentation of the preparation of floating micro-particles based on low-density foam powder, using (a) The solvent evaporation method or (b) The soaking method
10 ISSN Available online at Emulsion gelation method: In this method the polymer is added in to distilled/ demineralised water with stirring or mixing. Drug and different quantity of oil are then added to the polymeric solution. This solution containing drug and oil is dropped through 21G needle in to 5% calcium chloride solution and left at room temperature for 2h. The obtained hydrogel beads are washed twice with distilled/demineralised water and kept for dehydration at room temperature up to 12 hours Ionotrophic gelation method: Ionotropic gelation is a technique based on the capability of polyelectrolytes to cross link in the existence of counter ions to form hydrogel beads also known as gelispheres. Gelispheres are round crosslinked hydrophilic polymeric body that has ability of gelation and swelling in simulated biological fluid contents and thus the liberation of drug through it is managed by polymer relaxation. The hydrogel beads are formulated by dropping a drug-containing polymeric solution into the aqueous solvent of polyvalent cations. The cations try to diffuse into the drug-loaded polymeric drop of beads, which results in the formation of a three dimensional lattice of ionically crosslinked moiety. Biomolecules can also be loaded into these gelispheres under ideal conditions to retain their three dimensional structure. 28 Fig. 6: Ionotropic gelation method Characterization of floating gel beads include: a) Percentage Yield The prepared floating gel beads with given size range will be collected and weighed. The measured weight divided by total amount of non-volatile component which are used in the formulation gives percentage yield. 29 b) Size analysis of floating gel beads: The particle size of drug containing beads were measured by an optical microscope, with calibrated ocular and stage micrometer and particle size distribution was calculated. Around 50 particles or beads in five unlike areas were examined. 29 c) Drug Content and Drug Entrapment Efficiency: 100mg equivalent drug loaded polymer beads will be dissolved in suitable solvent. It will be stirred using magnetic stirrer. The resulting solution will be then filtered and filtrate will be suitably diluted with suitable solvent. Drug content can be determined spectrophotometrically. 30 Drug content and entrapment efficiency determined using equation:
11 ISSN Available online at 54 d) In vitro buoyancy study: Beads (300mg) were scattered over the USP XXIV dissolution apparatus type II containing 900 ml of 0.1 N HCl and 0.02% Tween 80. The medium was disturbed with a paddle revolving at 100 rpm for 12 hr. The floating and the immersed portions of beads were collected separately. The beads were dehydrated and weighed. Buoyancy percentage was measured as the ratio of the mass of the beads that remained buoyant and the total mass/weight of the beads. 31 %of buoyancy= Where, Qf = Weight of the floating Beads Qs = Weight of settled Beads e) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): Morphological examination of the surface and internal structure of the dried beads can be performed by using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). 31 f) In-vitro drug release study: The drug release analysis from beads is conducted by using USP dissolution apparatus Type I containing 900 ml of 0.1 N HCl as dissolution media (ph- 1.2) at 100 rpm and 37 C. 2 ml sample was taken at 1 hr. time interval for 12 hr. and same volume of fresh medium was replaced to maintain sink condition. Taken samples were assayed spectrophotometrically at suitable wavelength. The drug release was analyzed by UV spectrophotometer. 32 g) Stability studies: As per ICH guidelines, the beads filled in hard gelatin capsule shells, stability studies are performed on the formulations as short time stability study at 40 0 C±2 0 C and 70±5% RH for 3 months to assess their stability. 32 CONCLUSION Gastro retentive drug delivery systems have been extensively investigated in recent years. Gastro retentive drug delivery techniques are the most selected systems in order to target the drugs which have a narrow absorption site near the gastric region. Recently number of drug delivery systems are being developed which aim at liberating the drug at gastric region. A number of FDDS have been emerged, such as single and multiple unit HBS, single and multiple unit gas generating systems, hollow microspheres and raft forming systems. Development of sustained release dosage forms is advantageous in providing prolonged gastric retention and increased efficacy of the dosage forms. The floating ability of the low density drug delivery dosage forms could successfully be joined with valid control of the drug release manners in order to boast accurate bioavailability. Hence further more studies are required in this view in order to improve effective drug delivery systems. REFERENCES 1. Amit KN, Ruma M, Biswarup D. A review on gastro retentive drug delivery system. Asian J Pharm Clin Res.2010; 3(1): Yeole PG, Shagufta K, Patel VF. Floating drug delivery system: Need and development. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2005; 67(3): Sanjay P, Boldhane, Bhanudas S, Kuchekar. Development and optimization of metroprolol succinate gastro retentive drug delivery system. Acta Pharm. 2010; 60(1): Kataria S, Middha A, Bhardwaj S, Sandhu P. Floating drug delivery system: A review. Int Res J Pharm. 2011; 2(9): Majethiya KA, Patel MR. Review on gastro retentive drug delivery system. Int J Universal Pharm and Bio Sci. 2013; 2(1): Wasim F, Pankaj C, Tawseef HS. Gastro retentive drug delivery system: Research article. J of drug discovery and development. 2018; 2(1): Vedha H. The recent developments on gastric floating drug delivery systems: An overview. Int J Pharmtech. 2010; 2(1):
12 ISSN Available online at Khosla R, Feely LC, Davis SS. Gastrointestinal transit of non-disintegrating tablets in fed subjects. Int J Pharm 1989; 53: Amit JK, Umashankar H. A review on floating drug delivery system. Int J of Pharm studies and Res. 2011; 2(3): El-Kamel AH, Sokar MS, Al Gamal SS, Naggar VF. Preparation and evaluation of ketoprofen floating oral delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2001; 220: Monika S, Kapil K, Deepak T. Gastro-retentive floating beads a new trend of drug delivery system. J of Drug delivery and Therapeutics. 2018; 8(3): Lavanya M, Jayanth PC,Debarshi D. Gastroretentive drug delivery system. Indo American J of Pharm Sci. 2013; 3(9): Clarke G.M., Newton J.M., Short M.D. Gastrointestinal transit of pellets of differing size and density. Int. J. Pharm. 1993; 100(13): Klusner EA, Lavy E, Stepensley D, Friedman M, Hoffman A. Novel gastroretentive dosage form: evaluation of gastroretentivity and its effect on riboflavin absorption in dogs. Pharm Res. 2002; 19(15): Udaykumar T, Chordia MA, Udhumansha U. Design and development of bioadhesive gastroretentive drug delivery system of metroprolol succinate. Int J Res and development in Pharm and life Sci. 2013; 2(2): Durga J, Arundhati B, Indranil KY, Hari PS. Formulationa evaluation of floating gel beads of ranitidine hydrochloride. Int J of Pharm and Pharma Sci. 2009; 1(1): Asha P, Shubhabrata R, Ram ST. Invitro evaluation and optimization of controlled release floating drug delivery system of metformin hydrochloride. Daru J Pharm Sci. 2006; 14(2): Jonathan G, Francis V, Karim A. Development and evaluation of new multiple unit levodopa sustained release floating dosage forms. Int J of Pharm. 2007; 334(12): Brahma NS, Kwon H Kim. Floating drug delivery systems: An approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J of Controlled release. 2000; 63(3): Anand S, Rakhee KK. An overview on various approaches to oral controlled drug delivery system via gastroretention. Int J of Pharm Sci review and Res. 2010; 2(2): Kunal PN, Pratik U, Jayant D, Arohi RV, Nirav PC. A review on gastro retentive drug delivery systems and recent approaches. J Pharm Res opinion.2012; 2(1): Pandey A, Kumar G. A review on current approaches in gastro retentive drug delivery system. Asian J Pharm and Med SCi. 2012; 2(4): Chein YW. Novel drug delivery systems. Vol 50, Mracek Dekker Inc, New York, 1992;50: Sourabh J, Yadav SK, Patil UK. Preparation and evaluation of sustained release matrix tablet of furosemide using natural polymers. Res J Pharm and Tech. 2008; 1(4): Sandip B, Tiwari T, Krishna M, Raveendra P. Controlled release formulation of tramadol hydrochloride using hydrophilic and hydrophobic matrix system. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2003; 4(3): Nick J, Carroll, Shailendra B, Rathod. Droplet- based microfluidics for emulsion and solvent evaporation synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous silica microspheres. Langmuir. 2008; 24(1): Kumari A, Koland M, Giridhari J, Shaillendra, Charyulu N. Buoyant oil entrapped calcium pectinate gel beads of famotidine. IRJP.2012; 3(4): Mrunalini N, Praveen S, Atmaram P. Stomach specific controlled release gellan beads of acid soluble drug prepared by ionotropic gelation method. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2010; 11(1): Shravya, Shabaraya AR, Narasimharaj A. Design and development of floating gel beads of levodopa. Int J of Pharna and Chem Res. 2018; 4(3): Mowafaq MG, Zainab AR. Formulation and evaluation of Trimetazidine dihydrochloride floating beads.int J Pharm Sci. 2014; 6(2): Megha R, Shwetha S, Sumeet D, Raghavendra D. Formulation and evaluation of Glycyrrhizin alginate beads for stomach specific delivery. Asian J Med Pharm Res. 2017; 7(1): Sarvesh DP, Shruthi P, Amitha S, Mohd A, Shabaraya AR. A brief review on floating bilayer tablet as a convenient gastro retentive drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Chem Sci. 2014; 3(2):
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS
 Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
Formulation and evaluation of gastro-retentive floating microspheres bearing metformin HCl for treatment of diabetes mellitus
 2017; 6(10): 173-180 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating 2017: 5.03 TPI 2017; 6(10): 173-180 2017 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 22-08-2017 Accepted: 23-09-2017 Bijender Sagar Department
2017; 6(10): 173-180 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating 2017: 5.03 TPI 2017; 6(10): 173-180 2017 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 22-08-2017 Accepted: 23-09-2017 Bijender Sagar Department
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Pellets of Metronidazole
 Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Journal 16(1): 107-115, 2013 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Pellets of Metronidazole Shahriar Nowshad and Md. Saiful Islam Pathan Department of Pharmacy,
Bangladesh Pharmaceutical Journal 16(1): 107-115, 2013 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Pellets of Metronidazole Shahriar Nowshad and Md. Saiful Islam Pathan Department of Pharmacy,
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY FLOATING APPROCHES
 Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
Pooja et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 213, 3(3), 37-41 37 Available online at http://jddtonline.info RESEARCH ARTICLE MODULATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT TIME OF SALBUTAMOL SULPHATE BY
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate
 Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science
 Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
Research article Available online www.ijrpsonline.com ISSN: 2249 3522 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Tablet of Metoprolol Tartrate Patel
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media
 Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media Sandip B. Tiwari, Ph.D. Technical Director: South Asia Colorcon Asia Pvt. Ltd., Goa, India DISSO-INDIA 2013, May
Effect of Excipients on Dissolution: Case Studies with Bio-relevant/ Hydro-alcoholic Media Sandip B. Tiwari, Ph.D. Technical Director: South Asia Colorcon Asia Pvt. Ltd., Goa, India DISSO-INDIA 2013, May
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol. 2 (2), July-Sept,2012
 STUDIES ON EFFECT OF SUPERDISINTEGRANTS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS Chowdary K. P. R 1, Venugopal. K *2 1 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Vishakapattanam. 2 * Nirmala college
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF SUPERDISINTEGRANTS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS Chowdary K. P. R 1, Venugopal. K *2 1 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Vishakapattanam. 2 * Nirmala college
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
FLORITER. New Technology for Innovative Formulation Design.
 FLORITER New Technology for Innovative Formulation Design www.tomitaph.co.jp FLORITE Dramatically Change Your Formulation FLORITE is synthetic Calcium Silicate with exceptional liquid absorbency and excellent
FLORITER New Technology for Innovative Formulation Design www.tomitaph.co.jp FLORITE Dramatically Change Your Formulation FLORITE is synthetic Calcium Silicate with exceptional liquid absorbency and excellent
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 20, 637-646 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF NIMESULIDE BY CYCLODEXTRINS, POLOXAMER AND PVP K. P. R. CHOWDARY *, K.
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Chemate and Chowdary, IJPSR, 2012; Vol. 3(7): ISSN:
 IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF BILAYERED FLOATING TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE R.Margret Chandira*, P.Palanisamy,
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN AND SOLUTOL HS15
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF HYDROXY PROPYL β- CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF BCS CLASS II DRUGS
 JChrDD Vol 2 Issue 2 2011: 89-93 ISSN 2249-6785 Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery Received: August 06, 2011 Accepted: Sep 12, 2011 Original Research Paper FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF HYDROXY
JChrDD Vol 2 Issue 2 2011: 89-93 ISSN 2249-6785 Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery Received: August 06, 2011 Accepted: Sep 12, 2011 Original Research Paper FACTORIAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECTS OF HYDROXY
Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets of lisinopril
 Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE
 METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5901-5907 Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release K.P.R. CHOWDARY* and MALLURU SUBBA
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5901-5907 Preparation and Evaluation of Ethyl Cellulose Coated Microcapsules of Carbamazepine for Controlled Release K.P.R. CHOWDARY* and MALLURU SUBBA
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Excipient Quality & Trouble Shooting. By Seema Trivedi GM, Technical
 Excipient Quality & Trouble Shooting By Seema Trivedi GM, Technical Back Ground The Society for Pharmaceutical Dissolution Science (SPDS) had held its 6th Annual International Convention Disso India -
Excipient Quality & Trouble Shooting By Seema Trivedi GM, Technical Back Ground The Society for Pharmaceutical Dissolution Science (SPDS) had held its 6th Annual International Convention Disso India -
Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design.
 Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design. Adenike Okunlola a, Oluwatoyin A. Odeku a* and Rakesh P. Patel b a Department of Pharmaceutics
Formulation optimization of floating microbeads containing modified Chinese yam starch using factorial design. Adenike Okunlola a, Oluwatoyin A. Odeku a* and Rakesh P. Patel b a Department of Pharmaceutics
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Patel B et al. IRJP 1 (1)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article IMPROVEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF CINNARIZINE BY USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Patel Bipin*, Patel Jayvadan,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article IMPROVEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF CINNARIZINE BY USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Patel Bipin*, Patel Jayvadan,
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
