Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
|
|
|
- Alexina Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
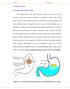
1 ISSN Available online at 73 Review Article REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Ashwini T *, Shabaraya AR and Vineetha K Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas College of Pharmacy, Valachil, Post- Farangipete, Manglore , Karnataka, India. ABSRACT Oral controlled release and site specific drug delivery system has been of great interest in pharmaceutical field to improve therapy with several important drugs. Concept of novel drug delivery system arose systems to overcome physiological adversities such as short gastric residence times and unpredictable gastric emptying times. Gastro retentive drug delivery system is one of such novel approaches to prolonged and continuous release of the drug to the upper part of Gastro intestinal tract (GIT) and this significantly extend the duration of drug release and improve bioavailability of drugs that have narrow therapeutic window, by this way they prolong dosing interval and increase compliance of the patient. In this review we have been discussed the gastro retentive drug delivery (GRDD), factors related to GRDD, its advantages disadvantages, various approaches of gastro retentive drug delivery system, various polymers used for gastro retention. INTRODUCTION The goal of any drug delivery system is to provide a therapeutic amount of drug to the proper site in the body to achieve and maintain the desired drug concentration. The oral route is the most preferred route of administration of drugs because of low cost of therapy, ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Effective oral drug delivery may depend upon the factors such as gastric emptying process, gastrointestinal transit time of dosage form, drug release from the dosage form and site of absorption of drugs. Most of the oral dosage forms possess several physiological limitations such as variable gastrointestinal transit, because of variable gastric emptying leading to non-uniform absorption profiles, variation of ph in different segments of gastrointestinal tract (GIT), incomplete drug release and shorter residence time of the dosage form in the stomach. This leads to incomplete absorption of drugs having absorption window especially in the upper part of the small intestine, as once the drug passes down the absorption site, the remaining quantity goes unabsorbed 2. To overcome this physiological problem, several drug delivery systems with prolonged gastric retention time have been investigated. Attempts are being made to develop a controlled drug delivery system that can provide therapeutically effective plasma drug concentration levels for longer durations, thereby reducing the dosing frequency and minimizing fluctuations in plasma drug concentration at steady state by delivering drug in a controlled and reproducible manner 3. FDDS are widely explored for gastro retention purposes and have a bulk density lower than gastric fluids and thus remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time so that system is floating on gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at a desired rate from the system. To achieve controlled gastric retention of dosage unit in stomach many approaches have emerged like bio adhesive systems, swelling and expanding systems, floating systems, modified shape systems, high-density systems and other delayed gastric emptying devices 2,3,4. BASIC GIT PHYSIOLOGY Anatomically the stomach is divided in to three regions Fundus, Body and Antrum (pylorus). The proximal part made of fundus and body acts as a reservoir for undigested materials, whereas the antrum is the main site for mixing motions and acts as a pump for gastric emptying by propelling actions 5 (Yie W. Chein et al, 1992, Sanjay Garg et al, 2003). Gastric emptying occurs in both the fasting and fed states. During the fasting state an inter digestive series of electrical events take place which cycle both through stomach and intestine every 2-3 hrs, which is called as inter digestive myoelectric cycle or migrating myoelectric cycle (MMC) which is further divided in to four phases After the ingestion of a mixed meal, the pattern of contractions changes from fasted to that of fed state which is also termed as digestive motility pattern 6,7 (Fig1) 1. Phase 1-(Basic phase)-last from minutes with rare contractions.
2 ISSN Available online at Phase 2-(Pre burst phase)-last for minutes with intermittent action potential and contractions. 3. Phase 3-(Burst phase) - last for minutes which includes intense and regular contractions for short period. 4. Phase 4-last for 0-5 minutes and occurs between phase 2 and 1 of 2 consecutive cycles 7 (Fig1) Fig. 1: GIT Physiology Fig. 2: schematic representation of inter digestive motility Factors affecting gastric retention of dosage forms A. Formulation factors Shape and Size of the Dosage Form Shape and size of the dosage forms are important factor which affects gastric emptying process. Small tablets are emptied quickly from the stomach during the digestive phase, but larger ones will not quickly pass through the pyloric antrum into the intestine 8,9. The diameter of the dosage unit is also equally important as a formulation parameter in which dosage forms that are having a diameter of more than 7.5mm show a better gastric residence time compared with one having 9.9 mm 9. The shape of dosage form is one of the factors that affect its gastric residence time. Six shapes (ring tetrahedron, clover leaf, string, pellets and disk)were screened in vivo for their gastric retention potential. The tetrahedron (each leg 2cm long) ri ngs (3.6cm in diameter) exhibit nearly 100%retention at 24hrs Density of dosage forms The density of a dosage form also important factor which affects the gastric emptying rate and determines the location of the dosage form in the stomach. A buoyant dosage formshavinga density of less than 1.004g/ml i.e. less than that of gastric contents floats, since it is away from the pyloric sphincter, the dosage unit is retained in the stomach for a prolonged period 9. Viscosity grade of polymer Viscosity of polymers and their interaction greatly affects the drug release rate and floating properties of FDDS. Low viscosity polymers (e.g., HPMC K100 LV) enhance floating properties compared to high viscosity polymers (e.g., HPMC K4M). In addition, high viscosity polymers show decrease in the release rate of the drug from the system 12. B. Idiosyncratic factors Gender Men have faster gastric emptying time than women. Mean ambulatory GRT in males (3.4 ± 0.6 hours) is less compared with their age and race matched female counterparts (4.6 ± 1.2 hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface 13. Age Geriatric people have slower gastric emptying time as well as longer GRT. Intrasubject and intersubject variations also are observed in gastric and intestinal transit time 13.
3 ISSN Available online at 75 Posture a. Upright position An upright position protects floating forms against postprandial emptying because the floating form remains above the gastric contents irrespective of its size 14. b. Supine position This position offers no reliable protection against postprandial emptying. The floating dosage form remain buoyant experience prolonged retention anywhere between lesser and greater curvature of the stomach. On moving distally, compared to upright subjects significant reduction in GRT is seen due to the units may be swept away by the peristaltic movements that propel the gastric contents towards the pylorus 15. C. Concomitant intake of drug The coadministration of GI motility decreasing drugs can increase gastric emptying time 15. Concomitant intake of drugs affects the performance of FDDS. For eg: Drugs such as prokinetic agents (e.g., metoclopramide and cisapride) decrease GRT, anti Cholinergics (e.g., atropine or propantheline) increase GRT. D. Disease state: Gastric ulcer, diabetes and hypothyroidism enhance the GRT. Hyperthyroidism and duodenal ulcers decrease the GRT. E. Fed or unfed state: Under fasting conditions, gastro intestinal motility is characterized by periods of strong motor activity that occurs every 1.5 to 2 hours and GRT of the unit will be very short if the timing of administration of the dosage form coincides with that of the MMC. Under fed state, MMC is delayed and GRT is significantly longer 18. F. Feeding regimen and Nature of meal In the presence of food there is increase in gastric residence time, leading to increased drug dissolution of the dosage form at the most favourable site of absorption. After a meal of fats and proteins a GRT of 4 10 hr has been reported 16. Feeding of indigestible polymers or fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate. G. Caloric content: GRT can be enhanced by 4 to 10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats 18. H. Frequency of feed: When successive meals are given there is increase in GRT by over 400 minutes due to low frequency of MMC. I. Food intake and its nature Food intake, viscosity and volume of food, caloric value and frequency of feeding have an effect on the gastric retention of dosage forms. Usually the presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) increases the gastric retention time (GRT) of the dosage form and thus, the drugs absorption increases. Again, increase in acidity and caloric value decreases gastric emptying time (GET), which can improve the gastric retention of dosage forms 18.
4 ISSN Available online at 76 APPROACHES TO GASTRO RETENTION Several techniques are reported in the literature to increase the gastric retention of drugs
5 ISSN Available online at FLOATING SYSTEMS Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remai n buoyant in the stomach, the drug releases slowly from the system at the predetermined rate for a prolonged period of time without affecting the gastric emptying rate. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach results in an increased gastric retention time (GRT). This results in better control of the fluctuation in plasma drug concentration and better bioavailabilty 19. This delivery systems is desirable for drugs with an absorption window in the stomach or in the upper small intestine 20. The major requirements for floating drug delivery system are 18 : It should release contents in controlled manner to serve as a reservoir. the specific gravity of the system must be more than that of gastric contents (specific gravity of gastric contents: gm/cm3). the system must form a cohesive gel barrier. A. Effervescent system a. Volatile liquid containing systems The volatile liquid containing systems consists of inflatation chamber made up of bio erodible polymer (PVA, polyethylene etc,) that gasifies at body temperature to cause the inflatation of the chamber in the stomach 21. I. Intragastric floating gastrointestinal drug delivery system In these system a floatable chamber is incorporated, which may be vacuum or filled with air or a harmless gas results in inflatation of chamber in the stomach, while drug reservoir is encapsulated inside a microporous compartment 22. II. Inflatable gastrointestinal delivery system These systems are fabricated by loading the inflatation chamber with drug reservoir, which can be a drug, impregnated polymeric matrix, then encapsulated in a gelatine capsule. The inflatation chamber contains a volatile liquid (e.g. ether, cyclopentane,) that gasifies at body temperature to cause the inflatation of the chamber in the stomach and the bio erodible polymer filament (copolymer of PVA, polyethylene) gradually dissolves causes the drug reservoir to retain in the gastric fluid finally results in controlled release of drug 23.
6 ISSN Available online at 78 III. Intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery system 24 This system is composed of an osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device and an inflatable floating support. In the stomach, the capsule quickly disintegrates to release the intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery device. The osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device consists of two components: drug reservoir compartment and an osmotically active compartment. The drug reservoir compartment is enclosed by a pressure responsive collapsible bag, which is impermeable to vapour and liquid and has a drug delivery orifice. The osmotically active compartment contains an osmotically active salt and is enclosed within a semi-permeable housing. In the stomach, the water in the GI fluid is continuously absorbed through the semi-permeable membrane into osmotically active compartment to dissolve the osmotically salt. An osmotic pressure is then created which acts on the collapsible bag and in turn forces the bag reservoir compartment to reduce its volume and activate the drug release of a drug solution formulation through the delivery orifice. The floating support is also made to contain a bio-erodible plug that erodes after a predetermined time to deflat the support. The deflated drug delivery system is then emptied from the stomach. b. Matrix system: Single matrix tablet is prepared by incorporation of bicarbonates in matrix forming hydrocolloid gelling agent and drug. Bilayer matrix tablet can also be prepared by gas generating matrix in one layer and second layer with drug for its SR effect. Floating capsule can also prepared by using such mixtures. Triple layer matrix tablet can also prepared having first swell able floating layer, second sustained release layer of 2 drug, third rapid dissolving bismuth salt. b. Gas generating system These buoyant systems utilize matrices prepared with the help of swellable polymers such as methylcellulose and polysaccharides (e.g. Chitosan), effervescent components (e.g. sodium bicarbonate, citric acid or tartaric acid). The optimal stoichiometric ratio of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate for generation of gas is reported to be 0.76:1. These systems are formulated in such a way that when dosage form come in contact with the acidic gastric contents, CO 2 is liberated and gets entrapped in swollen hydrocolloids, which causes formulation to float in the stomach 25. I. floating capsules These are prepared by formulating mixture of sodium bi carbonate and sodium alginate. On exposure to acidic environment, CO 2 gas is generated which is trapped in the hydrating gel network and makes the system to float.
7 ISSN Available online at 79 II. Floating pills These are multiple types of unit dosage forms which releases drug in controlled and sustained manner. These pills consists of two layers in which inner layer consist of effervescent agents which is surrounded by outer swellable membrane. The system when reaches to acidic environment of the stomach get swell due to swelleble membrane and then sink. Due to presence of effervescent agent, CO 2 is released and the system floats. III. Floating system with ion exchange resin: The most common approach for formulating these systems involves ion exchange resin beads loaded with bi carbonates as gastro retentive drug delivery systems. This is then coated with polymer which is usually insoluble but permeable to water. In the presence of hydrochloric acid bicarbonate was liberated, which formed carbon dioxide. The later was trapped inside the membrane resulting in flotation of the resin particle 26. B. Non Effervescent Systems The non-effervescent FDDS based on mechanism of swelling of polymer or bio adhesion to mucosal layer in GI tract. The most commonly used excipients in non-effervescent FDDS are gel forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming material such as polycarbonate, polyacrylate, polymethacrylate, polystyrene as well as bio-adhesive polymer such as chitosan and carbopol. The various type of this systems are as follows: a. Single layer floating tablets This single layer tablets mainly consists of gel forming hydrocolloid and drug, which swells in contact with gastric fluid and maintain bulk density of less than unity as figure A. The air trapped by the swollen polymer confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. b. Bilayer floating tablets A bilayer tablet contains two layer such as immediate release layer and sustain release layer as figure B. Immediate release layer releases initial dose from system while the another sustained release layer absorbs gastric fluid, forming an impermeable colloidal gel barrier on its surface, and maintain a bulk density of less than unity and thereby it remains buoyant in the stomach. 40 c. Alginate beads Multi unit floating dosage forms are developed from freeze dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm diameter can be prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing precipitation of calcium alginate leading to formation of porous system, which can maintain a floating force for over 12 hours. When compared with solid beads, which gave a short residence, time of 1 hour, and these floating beads gave a prolonged residence time of more than 5.5 hours.
8 ISSN Available online at 80 d. Hollow microspheres Hollow microspheres (microballons) loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells were prepared by simple solvent evopration or solvent diffusion or evaporation methods. The ethanol: dichloromethane solution of drug and enteric acrylic polymer was poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that was thermally controlled at 40 0 C. The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane formed an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. The microballons floated continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for more than 12 hours in vitro. 2. NON-FLOATING SYSTEM: These gastro retentive drug delivery systems do not float in the stomach however they remain retained there by different mechanism A. High density systems These systems possess density greater than the gastric fluids results in dosage form gets retained in the rugae of the stomach and capable of withstanding its peristaltic movement. Such high density formulations can be formulated by coating drug on heavy inert materials like zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, iron powder, etc. B. Swelling system These systems are also called as plug-type system. These non floating gastroretentive drug delivery system which when enter to stomach, dosage form on contact with gastric fluid the polymer imbibes water and swells to an extent that their exit from the pylorus is prevented, as a result the dosage form is retained in the stomach for a prolonged period of time. Controlled and sustained release may be achieved by selection of swellable polymers. The physical chemical cross links in the hydrophilic polymer network results in extensive swelling of these polymers retards the dissolution of the polymer and thus maintain the physical integrity of the dosage form 28. C. Mucoadhesive & bioadhesive systems Bio adhesive and mucoadhesive drug delivery systems contain a polymer that adheres to gastric mucosal layer results in localization of delivery device within the lumen to enhance the drug absorption in a site specific manner. This approach involves the use of bio adhesive polymers, which can adhere to the epithelial surface in the stomach. These polymers can be natural such as sodium alginate, gelatine, guar gum etc. semisynthetic polymers such as HPMC, carbopol, sodium carboxy methyl cellulose.
9 ISSN Available online at 81 The adhesion of polymers with mucous membrane may be mediated by hydration, bonding, or receptor mediated 27. a. Hydration mediated adhesion Certain hydrophilic polymers have the tendency to imbibe large amount of water and become mucoadhesive and sticky, results in prolonged gastro retention of the mucoadhesive drug delivery system is further controlled by the dissolution rate of the polymer. b. Bonding mediated adhesion Adhesion of polymers to mucus/epithelial cell surface involves varying bonding mechanism. Physical or mechanical bonds can result from deposition and inclusion of the polymeric material in the crevices of the mucosa. Secondary chemical bonds, may involve ionic or covalent bonds or Vander Waal forces between the polymer molecule and the mucous membrane. c. Receptor -mediated adhesion Receptor mediated adhesion takes place between certain polymers and specific receptors expressed on gastric cells hence enhancing gastric retention of the dosage form 28. D. Expendable system: These systems are formulated as a capsule containing folded and compact dosage form which is capable of expanding and retain in the stomach for longer periods. these capsules after being exposed to stomach environment, capsule shell disintegrates and dosage form expands preventing its exit through the stomach. By using a suitable polymer, sustained and controlled drug delivery can be achieved 29. Polymers Polymer are used in floating system so as to target the drug delivery at specific region in the GI tract i.e. stomach. Both synthetic and natural polymers are used in the floating drug delivery. Natural polymer used in floating system are Guar gum, Chitosan, xanthum gum, Gellan gum, Sodium alginate, etc. Synthetic polymer used for the floating drug delivery are HPMC, Eudragit, ethyl cellulose, etc. 30,34 Natural polymers Natural gums (obtained from plants) are hydrophilic carbohydrate polymer of high molecular weight. They are generally insoluble in organic solvents like hydrocarbon, ether. Gums either water soluble or absorb water and swell up or disperse in cold water to give a viscous solution or jelly 30. List of natural gum given below: List of Natural Polymer Used In Floating Drug Delivery System 30 S. No. Polymer Source 1 guar gum Endosperm of seed of cynopsis tetragonolobus 2 Chitosan Shell of marine invertibrates 3 xanthum gum Fermentation of glucose Xanthomonas compestris 4 gellan gum Pseudomonas elodea 5 sodium alginate Laminaria hyperboria Natural polymer has advantages over synthetic polymer. They are as follows: 1. Biodegradable. 2. Biocompatible and non-toxic. 3. Low cost. 4. Environment friendly processing. 5. Local availability(especially in developing countries). 6. They have better patient tolerance as well aspublic acceptance. Natural polymer has some disadvantages. They are as follows: 1. Microbial contamination. 2. Batch to batch variation. 3. Uncontrolled rate of hydration. 4. Reduced viscosity on storage.
10 ISSN Available online at Guar gum Guar gum is naturally occurring galactomannan polysaccharide. Guar gum has ability to hydrates rapidly and swells in cold water to attain uniform and high viscous colloidal dispersions at relatively low concentrations. This gelling property retard the drug release and make it a flexible carrier for extended release Dosage forms 31. In pharmaceutical guar gum is used as disintegrants and as a polymer in floating drug delivery system. Properties of guar gum 1. It is soluble in hot and cold water but insoluble in most organic solvents. 2. Strong hydrogen bond property. 3. Excellent thickening, emulsion, stabilizing and film forming property. 4. Ability to control rheology. Advantages of guar gum in floating drug delivery system It has been reported that polymer swelling play an important role to prolong gastric residence time and increase drug bioavailability. It was found that guar gum formulation were relatively insensitive to changes in stirring speed during in vitro drug dissolution testing and dissolution profile were not affected significantly Chitosan Chitosan is natural and versatile polymer obtained by deacetylation of chitin. It has favourable biological properties such as nontoxic, biodegradable to normal body constituents, safe, haemostatic, anticancerogen, anticholesteremic, biocompatible. It is a bio adhesive polymer and have anti-bacterial properties thus make it suitable for site specific delivery 32. Chitosan is high molecular weight polycationic weak base with pka value of the D-glucosamine residue of about and therefore, is insoluble a neutral and alkaine ph values. On addition to acidic ph of 1.2 it become buoyant in nature and provide control release. By increasing thickness of chitosan film release rate can be decreased.
11 ISSN Available online at 83 Advantages of chitosan 1. Chitosan granules and chitosan laminated preparations could be helpful in developing DDS that will reduce the effect of gastrointestinal transit time. 2. Most of the Hallow microcapsule tended to float on gastric fluid for more than 12hrs. 3. Release of drug followed zero order kinetics and controlled by both diffusion and erosion mechanism Xanthum gum Xanthan gum is a high molecular weight extracellular hetero-polysaccharide produced by pure culture aerobic fermentation of carbohydrate with bacterium xanthomonas campestris. Xanthan is a long chained polysaccharide with large number of trisaccharide side chains. Gum also has an excellent solubility and stability under acidic and alkaline conditions and in the presence of salts and resists common enzymes. 31 Advantages of Xanthum gum 1. It is used to increase or decrease rate of release of drug from formulation. 2. Soluble in water. 3. High viscosity at low concentration. 4. It has potential advantage of drug release at zero order kinetics. 5. Some tablet containing xanthum gum and citric acid show buoyancy for more than 24hrs. 4. Gellan gum Gellan gum is an anionic, high molecular weight, deacetylated extracellular linear polysaccharide comprising glucuronic acid, rhamnose and glucose. This gum has an outstanding flavour release, high gel strength, an excellent stability, process flexibility, high clarity, good film former and thermally reversible gel characteristics. Gellan gum is produced as a fermentation product from spingomonas elodea. 30 Advantages of Gellan gum 1. It has excellent flavour release, high gel strength, and excellent stability. 2. It forms gel when positively charged ions are added. 3. It is used in food product as thickening agent or stabilizing agent. 34 Structure of Gellan gum
12 ISSN Available online at Sodium alginate Sodium alginates have been used and investigated as stabilizers in emulsions, suspending agents, tablets binders and tablet disintegrants. Sodium alginate consists chiefly of the sodium salt of alginic acid, which is a mixture of polyuronic acids composed of residues of dmannuronic acid and L guluronic acid. The block structure and molecular weight of sodium alginate Samples have been investigated. 32 Typical Properties Acidity/alkalinity ph 7.2 (1% w/v aqueous solution). Solubility: Practically insoluble in ethanol (95%), ether, chloroform, and ethanol/water mixtures in which the ethanol content is greater than 30%. Also, practically insoluble in other organic Solvents and aqueous acidic solutions in which the ph is less than 3. Slowly soluble in water, forming a viscous colloidal Solution. 34 Viscosity (dynamic): Various grades of sodium alginate are commercially available that yield aqueous solutions of varying Viscosity. Typically, a 1% w/v aqueous solution, at 208C, will have a viscosity of mpa s (20 400cp). Viscosity may vary depending upon concentration, ph, temperature, or the Presence of metal ions. Above ph 10, viscosity decreases. 35 Structure of sodium alginate [24] Pectin Pectin is non toxic and economic polysaccharide extracted from apple pomaces and citrus peels. Actually it is a D- galacturonic acid with 1-4linkages. 36 It is used as bulking agent,food additive and gelling agentdue the pectin ability to form gel based ondegree of esterification and molecular suze, it is alluring candidate for pharmaceutical care, for example, as a drug carrier for the controlled release application. 37 Advantages of pectin 1. Pectin gel beads have been shown to be an effective medium for controlling the release of drug within GI tract. 2. Pectin are used as nutritional aspects as source of fibers, anticancer action, cholesterol regulation, prebiotics effect. Synthetic polymers Synthetic polymer are becoming increasingly important in pharmaceuticals. Use of synthetic polymer ranges from binder, film coating agent, etc. Polymer are macromolecule having very large, contain a variety of functional group. Synthetic polymers are either purely synthetic or they are modified form of natural polymer know as semi-synthetic.
13 ISSN Available online at 85 List of synthetic polymer used is as follows: 1. Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. 2. Eudragit. 3. Ethyl cellulose. Disadvantages of synthetic polymer are as follows: 1. High cost toxicity environmental pollution. 2. Acute and chronic adverse effect. 3. Poor biocompatible. 4. Inflammatory response and local reaction. 1. Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose ethers belong to an extensive family of white to off-white, odourless, water soluble polymers that bind, retain water, thicken, form films, lubricate. It is a semi synthetic, inert, viscoelastic polymer, used as an excipient and controlled-delivery component in oral medicaments, found in a variety of commercial products. Synonym for hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is Hypromellose. Properties General properties common to the Hypremellose are listed below. Individual type exhibits these properties to varying degrees and may have additional properties that are desirable for specific applications. 1) Apparent density: 0.25~0.70g/cm 3. 2) The refractive index= ) Surface tension: 42 to 56mn/m. 4) Solubility: dissolve in water and some solvent. Advantages 1. Water soluble and most abundant polymer in nature. 2. Used as a thickener, film former and water retention agent. 3. Hydrophilic matrix is the simplest sustained release technology for oral dosage form. 2. Eudragit 38 Polymethacrylates (Eudragit) are primarily used in oral capsule and tablet formulations as film-coating agents. Depending on the type of polymer used, films of different solubility characteristics can be produced. Soluble in gastric fluid below ph 5. Eudragit RL, RS, NE 30D, NE 40D, andnm30d are used to form water-insoluble film coats for sustainedrelease products. Eudragit RL films are more permeable than those of Eudragit RS, and films of varying permeability can be obtained by mixing the two types together. In contrast, Eudragit L, S and FS types are used as enteric coating agents because they are resistant to gastric fluid. Different types of enteric coatings are soluble at different ph values: e.g. Eudragit L is soluble at ph >6 whereas Eudragit S and FS are soluble at ph >7.Polymethacrylates are also used as binders in both aqueous and organic wet-granulation processes. Larger quantities (5 20%) of dry polymer are used to control the release of an active substance from a tablet matrix. Solid polymers may be used in direct compression processes in quantities of 10 50%. Polymethacrylates polymers may additionally be used to form the matrix layers of transdermal delivery systems and have also been used to prepare novel gel formulations for rectal administration.
14 ISSN Available online at Ethyl cellulose 33,39 Ethocel (Ethyl cellulose polymers) has been widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for over 50 years. Ethyl cellulose has been used for choice in pharmaceutical formulations for various purposes, such as taste-masking of bitter actives, moisture protection, stabilizer, extended release multi particulate coating, micro-encapsulation of actives, extended release binder in inert matrix systems, solvent and extrusion granulation. Ethyl cellulose is an ideal polymer for the formation of products allowing modified drug release. It is insoluble at any ph that occurs in organism, but in the presence of the gastric Juice it undergoes swelling. This makes it suitable for improved patient compliance. Several types of such Ethyl cellulose exist, e.g. Ethocel 4, Ethocel 10 and Ethocel 45, which differ in the length of the polymer chains. CONCLUSION Based on the literature, it may be concluded that drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract is a highly variable process and prolonging gastric retention of the dosage form extends the time for drug absorption. Gastro retentive drug delivery systems have emerged as current approaches to prolong the continuous delivery of drug and improve the bioavailability of many drugs and enhancing bioavailability. Gastroretentive drug delivery approaches comprised mainly of floating, non floating, bioadhesive, swelling, high density systems etc. These systems not only provide controlled release of the drug but also present the drug in an absorbable form at the regions of optimal absorption. All these drug delivery systems have their own advantages and drawbacks. To design a successful GRDDS, it is necessary to take into consideration. GRDDS have multiple advantages that include greater flexibility and adaptability of dosage forms which give clinicians and pharmacists powerful tools to optimize pharmacotherapy. The increasing growth of delivery technology will ensure the development of increasing number of GRDDSs in order to optimize the delivery of drugs that exhibit narrow absorption window, low bioavailability and extensive first pass metabolism. The control of gastro intestinal transit could be the focus of the future studies and may result in new therapeutic capacities with considerable benefits for patient and hence it is very probable that these systems can gain popularity. To design a successful GRDDS, it is necessary to take into consideration.
15 ISSN Available online at 87 REFERENCES 1. Chandel A, Chauhan K, Parashar B, Kumar H, Arora S. Floating drug delivery systems: A better approach. International Current Pharmaceutical Journal.2012;1(5): Singh B, Kim K. Floating drug delivery systems: An approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J Control Rel. 2000;63: Jassal M, Nautiyal U, Kundlas J, singh D, Deshpande AA, Rhodes CT, Shah NH, Malick AW. A review: Gastro retentive drug delivery system (grdds). Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research. 2015; 3(1): Adibkia K, Ghanbarzadeh S, Mohammadi G, Atashgah RB, Sabzevari A. Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Journal of Reports in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2013;2(2): Yie W, Chein; Novel Drug Delivery System 2nd ed. Marcel dekker ;Inc. New York. 1992; Garg S, Sharma S. Gastro retentive Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmatech.2003; Hari V. The Recent Developments on Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems: An Overview. Int Journal pharmtech Res.2010;2(1): Oth M, Franze M, Timmermans J, Moes A. The bilayer-floating capsule: a stomach directed drug delivery system for misoprostol. Pharm res., 1992;9: Timmermans J, Andre JM. Factors controlling the buoyancy and gastric retention capabilities of floating matrix capsules: new data for reconsidering the controversy. J Pharm Sci. 1994;83:18Y Gergogiannis YS, Rekkas DM, Dallos PP, Chailis NH. Floating and swelling characteristics of various excipients used in controlled release technology. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1993;19: Cargill R, Cadwell LJ, Engle K, Fix JA, Porter PA, Gardner CR. Effects of physical properties on gastric residence times of non-disintegrating geometric shapes in beagle dogs. Pharm Res. 1988; 5: Li S, Lin S, Daggy BP, Mirchandani HL, Chien YW. Effect of HPMC and Carbopol on the release and floating properties of gastric floating drug delivery system using factorial design. Int J Pharm. 2003; 253: Mojaverian P, Vlasses PH, Kellner PE, Rocci ML. Effects of gender, posture and age on gastric residence time of indigestible solid: pharmaceutical considerations. Pharm Res. 1988; 10: Timmermans J, Moes AJ. Factors controlling the buoyancy and gastric retention capabilities of floating matrix capsules: new data for reconsidering the controversy. J Pharm Sci. 1994; 83: Chawla G, Gupta P, Koradia V, Bansal AK. Gastro retention: A Means to address regional variability in intestinal drug absorption. Pharm Tech, 2003; 27: Muller Lissner SA, Blum AL. The effect of specific gravity and eating on gastric emptying of slowrelease capsules. New Engl J. 1994; 83: Singh BN, Kim KH. Floating drug delivery system: An approach to the controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J Control Release, 2000; 63: S. P. Vyas and Roop K. Khar, Controlled Drug Delivery, Concepts & Advances, Vallabh Prakashan, Delhi (2012). 19. Sing BN, Kim KH. Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention. J Control Rel. 2000; 63: Sungthongjeen S, Paeratakul O, Limmatvapirat S, Puttipupathachorn S. Preparation and in-vitro evaluation of multiple-unit floating drug delivery system based on gas formation technique. Int J Pharm. 2006; 324: A S Michael, J D Bishaw, A Zaffaroni. Gastro inflatable drug delivery device. US Pat 3; 901; 232: Atyabi F,Sharm HL, Mohammad HAH, Fell JT. Controlled Drug Release from Coated Floating Ion Exchange Resin Beads. J. Control. Release,1996;42: Bhardwaj V, Nirmala SL. Harikumar. Floating Drug Delivery System: a review. Pharmacophore. 2013;4 (1): Brahmankar D.M., Biopharmaceutics and pharmacokinetics, vallabh prakashan, New Delhi, pg Shah SH, Patel JK, Patel NV. Stomach specific floating drug delivery system: A review. Int J Pharm Res. 2009; 1(3): Yao H, Xu L, Han F, et al. A novel riboflavin gastro-mucoadhesive delivery system based on ion exchange fibre. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2008;364:21-6.
16 ISSN Available online at Jaleh varshosaz, N.Tavakoli,and F. Rooz bahani:formulation and in vitro characterization of ciprofloxacin floating and bio adhesive- extended release tablets, drug delivery journal,2006;13: Arza R.A,C.S Roa Gonugunta, Veerareddy P.R. formulation and evaluation of swellable and floating gastroretentive ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablets. American association of pharmaceutical scientists.2009;10(1): Klausner, E.A.; Lavy, E., Friedman, M.; Hoffman, A.; Expandable Gastro retentive Dosage Forms. J. Control. Release. 2003;90: Singh, kumar A. role of natural polymers used in floating drug delivery system floating drug delivery system. j. pharm. sci. innov. 2012; 1: Nokano M, Ogata A. In invitro release characteristic of matrix tablets: Study of Karaya gum and Guar gum as release modulators. Ind.J.Pharm.Sc.2006;68(6): Sarmento B, Ribeiro A, Veiga F, Sampaio P, Neufeld R, Ferreira D. Alginate/Chitosan nanoparticles are effective for oral insulin delivery. Pharm. Res. 2007; 24: Remuñán López C, Portero A, Vila-Jato J L, Alonso MJ. Design and evaluation of chitosan/ ethylecellulose mucoadhesive bilayered devices for buccal drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release. 1998;55(2): Gandhi KJ, Deshmane SV, Biyani KR. Polymer in pharmaceutical drug delivery system: A Review. International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research. 2012;14(2): Ching, A.L, Liew, C.V, Heng, P.W.S, Chan, L.W. Impact of crosslinker on alginate matrix integrity and drug release.int. J. Pharm. 2008;355: Ridley, B.L, O Neill, M.A, Mohnen, D.Pectins:structure, biosynthesis and oligogalacturonide related signaling. Phytochrmistry. 2001;57: Mohnen, D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 11, 2008;11: Patra CN, Priya R, Swain S, Kumar Jena G, Panigrahi KC, Ghose D. Pharmaceutical significance of Eudragit: A review, Future Journal of Pharmaceutical sciences doi: /j.fjps Hegyesi, D. Study of the widely used ethylcellulose polymer as film forming and matrix former Ph. D. Thesis Diána Hegyesi Pharmacist, Sarvesh DP, Shruthi P, Amitha S, Mohd A, Shabaraya AR. A brief review on floating bilayer tablet as a convenient gastro retentive drug delivery system. Int Pharm Chem Sci. 2014: 3(2):
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides
 Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
Non-Food Uses of Polysaccharides John Mitchell John.Mitchell@biopolymersolutions.co.uk Acknowledgements Fundamentals of Hydrocolloid Technology Course (2003-2009) Rob Winwood Colin Melia Steve Harding
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE
 METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
METOLOSE: CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface What is Metolose Substitution types Specifications 1) Available grades & viscosity 2) Nomenclature 3) Packaging Characteristics of Metolose Properties of Metolose 1) Powder
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Gellan Gum. Rm.1702, West Unit, No. 41, Donghai Xi Rd, Qingdao, China Post Code:
 Gellan Gum Gellan gum (E418) is a bacterial exopolysaccharide, prepared commercially by aerobic submerged fermentation from Sphingomonas elodea (previously called Pseudomonas elodea), in a manner similar
Gellan Gum Gellan gum (E418) is a bacterial exopolysaccharide, prepared commercially by aerobic submerged fermentation from Sphingomonas elodea (previously called Pseudomonas elodea), in a manner similar
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
ANNEXURE -2. Excipients profiles of Compritol ATO 888, Gelucire 43/01, HPMC and PVP and have been described in the following section.
 2. EXCIPIENTS PROFILES ANNEXURE -2 Excipients profiles of Compritol ATO 888, Gelucire 43/01, HPMC and PVP and have been described in the following section. 2.1. COMPRITOL 888 Non proprietary names BP:
2. EXCIPIENTS PROFILES ANNEXURE -2 Excipients profiles of Compritol ATO 888, Gelucire 43/01, HPMC and PVP and have been described in the following section. 2.1. COMPRITOL 888 Non proprietary names BP:
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 4
 (A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
(A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives
 Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives 2.1 Introduction According to the Food Protection Committee of the Food and Nutrition Board, food additives
Paper No.: 13 Paper Title: Food Additives Module 2. Functional Classification of Food Additives 2.1 Introduction According to the Food Protection Committee of the Food and Nutrition Board, food additives
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS
 Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Direct Compression. With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process
 Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
Dow Wolff Cellulosics. Using ingenuity and savvy. TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow
 Dow Wolff Cellulosics Pharmaceutical Excipients Using ingenuity and savvy to help design healthcare solutions TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Enhancing
Dow Wolff Cellulosics Pharmaceutical Excipients Using ingenuity and savvy to help design healthcare solutions TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Enhancing
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
Chemate and Chowdary, IJPSR, 2012; Vol. 3(7): ISSN:
 IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol
 Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
Formulation Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating tablets of Atenolol K.Viveksarathi, K.Kannan*, S.Selvamuthu Kumar, R.Manavalan Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Engineering
CHAPTER-2 DRUG AND POLYMER PROFILES
 57 CHAPTER-2 DRUG AND POLYMER PROFILES 58 2.1 DRUG PROFILES 2.1.1 Lamivudine (3TC) 85 US FDA approval date: November 1995 Structural formula of lamivudine Physicochemical properties of lamivudine 1. Description
57 CHAPTER-2 DRUG AND POLYMER PROFILES 58 2.1 DRUG PROFILES 2.1.1 Lamivudine (3TC) 85 US FDA approval date: November 1995 Structural formula of lamivudine Physicochemical properties of lamivudine 1. Description
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics
 Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Critical material properties for the design of robust drug products : excipient functionality related characteristics Dr Liz Meehan, Pharmaceutical Development, Macclesfield UK 1 Excipients Definition
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Innovations in Design: NIA-West. Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017
 Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE
 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM FOR NEVIRAPINE Mahajan Ashwini *, Dr. Sarode S. M., Prof. Sathe B.S., Dr. Vadnere G.P. Department Of Pharmaceutics. Smt. S.S.
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al.6 (2007), Chaudhari et al.7 (2011), Sivabalan M et al.8 (2011), Punitha et al.9 (2010), Patel et al.
 1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
1. LITERATURE REVIEW Jaimini et al. 6 (2007), prepared floating tablets of famotidine by using Methocel K 15 M and Methocel K 100 M as gel forming agent and combination of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
 PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 974-434 Vol.2, No.1, pp 341-347, Jan-Mar 1 FORMULATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF TELMISATAN SOLID DISPERSIONS Kothawade S. N. 1 *, Kadam
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper
 D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN( USA): IJPRIF ISSN : 0974-4304 Vol.1, No.3, pp 634-638, July-Sept 2009 FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF ER METOPROLAOL SUCCINATE TABLETS K. Reeta Vijaya
Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels
 Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels O Gums--Food functions Gums can control or determine the texture of many food products Gums--General functions Thickening All gums do this to
Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels O Gums--Food functions Gums can control or determine the texture of many food products Gums--General functions Thickening All gums do this to
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Gums--Food functions. Gums--General functions. Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels
 Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels Gums--Food functions Gums can control or determine the texture of many food products Gums--General functions Thickening All gums do this to some
Behaviors of Polysaccharide Solution, Dispersions and Gels Gums--Food functions Gums can control or determine the texture of many food products Gums--General functions Thickening All gums do this to some
KURARAY POVAL & EXCEVAL
 Characteristics Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) having varying degree of polymerization and. Recommended Uses Ranging from emulsion polymerization aid to binder for pigments in paper applications. Form supplied
Characteristics Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) having varying degree of polymerization and. Recommended Uses Ranging from emulsion polymerization aid to binder for pigments in paper applications. Form supplied
Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
ISSN 2395-3411 Available online at www.ijpacr.com 44 Review Article FLOATING BEADS: A NEW TREND OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Rakshith M*, Viresh KC and Shabaraya AR Department of Pharmaceutics, Srinivas
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. s film coating products are one-step coating systems for pharmaceutical
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. s film coating products are one-step coating systems for pharmaceutical
Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Science Yadav et al., Int J Res Pharm Sci 2016, 6(2) ; 19 24 Review Article Gastroretentive drug delivery system: a concise review Yadav S 1,2, Nyola NK
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY
 LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
