Alexander Staruschenko, PhD
|
|
|
- Ralph Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Role of the epithelial Na + channel (ENaC) in salt-sensitive hypertension and mechanisms of its regulation by EGF Alexander Staruschenko, PhD Department of Physiology Институт эволюционной физиологии и биохимии им. И. М. Сеченова РАН 26 декабря 212 г.
2 PCT Bowman s capsule CNT DCT CCD Glomerulus PST TAL OMCD tdlh talh IMCD Principal cell Intercalated cell Staruschenko (212) Comp. Physiol. 2(2):
3
4
5 The two-membrane model of epithelial transport in principal cells H 2 O AQP2 Na + ROMK K + URINE ENaC 3Na + H 2 O Na + /K + ATPase 2K + AQP3,4 BLOOD
6 Hormonal factors ENaC regulation Balance of ions Stretch Proteolytic cleavage Small GTPase-regulated processes Phosphorylation ROS production intracellular signaling Arachidonic acid metabolites PIP pathways Gene expression Cytoskeletal rearrangements Ubiquitylation ENaC Increased/decreased expression of the channels Changes in the open probability Altered trafficking
7 Kidney Physiological significance of ENaC Regulation of the body fluid volume Lungs sweat and salivary ducts Keeps the alveoli dry Clears the lungs of fluid at birth Retrieves salt from the sweat ENaC-associated diseases Liddle s syndrome hypertension hypokalemia metabolic alcalosis Pseudohypoaldosteronism type I salt wasting hyperkalaemia unresponsiveness to mineralocorticoids Cystic fibrosis, polycystic kidney disease etc
8 Role of ENaC in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive (SS) rats EGF and its related growth factors regulate ENaC Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins EGF might regulates ENaC via Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor RhoGDIα EGF modulates ENaC-mediated Na + transport in the ASDN and participate in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
9 Dahl SS rats Blood pressure salt-sensitivity Chronic kidney injury Reduced renal function Low renin hypertension SS.13 BN consomic rats developed at MCW exhibit only 2% allelic differences compared to the SS strain, but saltinduced hypertension and renal injury are greatly attenuated.
10 Mean arterial pressure (mmhg) Amiloride inhibits the blood pressure in the SS rats A.4% 8% high salt diet Vehicle or Amiloride (6mg.kg.day) infusion Measure blood pressure & collect urine daily Day 1 Start Day 3 Begin High salt Day 6 Begin Drug or Vehicle Day 17 End experiment Plasma/histology B 2 8% NaCl.4% NaCl Arterial pressure Vehicle C % NaCl Urine Na + /K + ratio 8% NaCl Amiloride Vehicle 15 Amiloride Na + /K Drug or vehicle Drug or vehicle
11 Mean arterial pressure (mmhg) Benzamil (given through drinking water 15 mg/l) attenuates the development of hypertension in SS rats.4% 4% diet Control Benzamil Benzamil/vehicle days
12 Relative abundance High salt diet increases ENaC expression SS rats (cortex) LS HS α-enac β-enac γ-enac GAPDH LS HS *** *** α-enac β-enac γ-enac
13 Im_scaled (pa) Im_scaled (pa) Time (s) Time (s) High salt diet increases ENaC activity LS HS 1 pa 2 s c o 1 o 2 c o 1 o 2 o 3 NP o ** n=8 n=7 LS HS
14 MAP (mmhg) Im_scaled (pa) Im_scaled (pa) Im_scaled (pa) Time (s) 34 NPo High salt diet increases MAP and ENaC activity in SS rats fed a high salt diet compare to SS.13 BN 1.5 SS.13 BN (LS) SS.13 BN (HS) c o 1 c * SS (HS) o pA 1s c o 1 o 2.5. n=4 n=9 n=1 SS.13 BN LS SS-13 BN HS SS HS Time (s) Time (s) * 1 SS SS-13 BN
15 Relative abundance High salt diet does not change ENaC expression in SS.13 BN rats LS HS α-enac β-enac γ-enac β-actin LS HS α-enac β-enac γ-enac
16 β-enac signal intensity (% of max) High salt diet increases ENaC abundance in the CCD of SS rats compare to SS.13 BN SS rats SS.13 BN * n=27 n=24 SS SS.13 BN
17 Servocontrolled Uncontrolled β-enac signal intensity ENaC expression is upregulated in chronic servo-controlled rats Control Servo-controlled (left) Uncontrolled (right) 1 * µm 6 5 n=1 n=1
18 Conclusion: Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats develop severe hypertension on high-salt diet and ENaC contributes to the development of hypertension in the SS rat strain.
19 Role of ENaC in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive (SS) rats EGF and its related growth factors regulate ENaC Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins EGF might regulates ENaC via Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor RhoGDIα EGF modulates ENaC-mediated Na + transport in the ASDN and participate in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
20 ErbB receptors and their ligands From: J Clin Invest. 27; 117:251 8
21 Relative current Biphasic effect of EGF on sodium transport in mpkccd c14 cells Control EGF (1 ng/ml) Amil Time, hours Levchenko et al. (21) J Cell Physiol. 223(1): Liu et al. (29) AJP Renal 296(6): F
22 Relative current Relative current EGF regulates Na + transport in a concentration-dependent manner Amil 1.8 EC 5 = ng/ml Control.1 ng/ml.1 ng/ml.5 ng/ml 1 ng/ml 1 ng/ml 1 ng/ml Time, hours EGF, ng/ml
23 Relative current Relative current Relative current Effect of growth factors in the EGF-family on Na + reabsorption across mpkccd c14 monolayer TGF-α Amil Control.5 ng/ml 1 ng/ml 1 ng/ml 1 ng/ml Time, hours Amil Amil Control HB-EGF (5 ng/ml).4 Control Amphiregulin (1 ng/ml) Time, hours Time, hours
24 Expression profiles of ErbB receptor family proteins in mpkccd c14 cells analyzed by Western Blot analysis A ErbB ErbB actin B ErbB actin
25 ErbB2 expression in rat kidney tissue control ErbB2 ErbB2 5 µm 4X 4X 1X Zheleznova et al. (211) BBA - Mol Basis Disease 48:
26 Relative current Relative current Relative current Effect of ErbB2 inhibitors (tyrphostin AG825 and ErbB2 Inhibitor II) on EGF-induced changes of amiloride-sensitive Na + absorption A B C Control EGF EGF+AG Time, hours hrs 48 hrs * * hrs *
27 Conclusions: Our data are consistent with the idea that EGF and its related growth factors (TGF-α, HB-EGF and amphiregulin) have a biphasic effect on sodium absorption in the mammalian kidney as represented by mpkccd c14 cells. In addition, we show that the EGF effect is mediated via the ErbB2 receptor, most probably via formation of ErbB2/EGFR heterodimers.
28 Role of ENaC in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive (SS) rats EGF and its related growth factors regulate ENaC Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins EGF might regulates ENaC via Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor RhoGDIα EGF modulates ENaC-mediated Na + transport in the ASDN and participate in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
29 IN 1 (mv) Time (ms) Sw eep:14 Visible:18 of 18 Current density (pa/pf) Rac1 but not Cdc42 enhances ENaC activity overexpressed in CHO cells 75 *** menac 6 *** 1nA 1 ms mv 6 mv -1 mv 4 mv 15 Whole-cell (CHO cells) Pavlov et al. 21 J Am Soc Nephrol. 21(5):
30 _Ipatch (pa) _Ipatch (pa) Vitality, % _Ipatch (pa) 3.5 Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity Cell-attached 3.5 A B C c -.52 o c o c o I NSC I (before NSC23766) II (after NSC23766) 1 Time (min) II 15 2 NP o pa 3 min/3 s. * control + NSC control + NSC Time (s) Karpushev et al. (211) Hypertension 57:
31 % Rac1 protein expression Creation of M-1 stable cell line with lentivirus-mediated knock down of Rac1 M-1 β-actin Rac *
32 I sc (μa/cm 2 ) _Ipatch (pa) _Ipatch (pa) Time (s) Time (s) 4 8 shrna-mediated silencing of Rac1 inhibit transepithelial Na + currents and ENaC activity in M-1 cells * c o 1 o 2 o 3 c o.5 pa 1 s control Rac1 shrna P o NS N *
33 Expression profiles of N-WASP/WAVEs in rat kidney tissue and in epithelial cells A B 75 WAVE1 control 5 μm 5 WAVE-2 N-WASP 75 WAVE-3 WAVE1 N-WASP Takenawa and Suetsugu Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8, mpkccd c14 M-1 WAVE2
34 Current density (pa/pf) Current density (pa/pf) Rac1 enhances ENaC activity via WAVE1 or WAVE2 A 8 6 * * * B 8 6 * * *
35 Conclusions: Co-expression of Rac1 with ENaC markedly increased channel activity, whereas co-expression of Cdc42 failed to change ENaC activity. Inhibition of Rac1-GEF interaction resulted in a decrease of ENaC activity in native principal cells. shrna-mediated silencing of Rac1 inhibits transepithelial current in M-1 cells via decrease in the number of channels at the plasma membrane. Rac1 and WAVE1/2 are parts of the same signaling pathway with respect to activation of ENaC. Thus, our findings suggest that Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins.
36 Role of ENaC in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive (SS) rats EGF and its related growth factors regulate ENaC Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins EGF might regulates ENaC via Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor RhoGDIα EGF modulates ENaC-mediated Na + transport in the ASDN and participate in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
37 Small GTPases cycle between a GDP- and GTP-bound state Nethe M, Hordijk P L J Cell Sci 21;123:
38 EGF upregulates RhoGDIα in mpkccd c14 cells mpkccd c14 actin RhoGDIα Control +EGF (1 ng/ml) 24 hrs
39 ENaC + Rho GDIα +Rac1 +Rac1 DN +Rac1 +Rho GDIα Current Density (pa/pf) RhoGDIα downregulates ENaC activity via Rac1 5 * * * # 1
40 % RhoGDIα protein expression Knockdown of RhoGDIα in M-1 cells upregulates ENaC expression A β-actin RhoGDIα C α-enac β-actin B 1 β-enac β-actin γ-enac 25 control * n=4 n=4 RhoGDIα shrna 5 37 β-actin
41 Conclusions: Chronic treatment with EGF increases RhoGDIα expression RhoGDIα downregulates ENaC activity via Rac1
42 Role of ENaC in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive (SS) rats EGF and its related growth factors regulate ENaC Rac1 is essential for ENaC activity and regulates the channel via WAVE proteins EGF might regulates ENaC via Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor RhoGDIα EGF modulates ENaC-mediated Na + transport in the ASDN and participate in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
43 EGF, ng/mg Level of EGF measured by ELISA in the cortex of SS rats fed a normal and high salt diets 6 4 * 2.4% NaCl (2 weeks) 4% NaCl (2 weeks)
44 MAP (mmhg) MAP (mmhg) Chronic intravenous infusion of EGF prevents development of hypertension in SS rats fed a HS diet A B 5 Day 1 Start C Day 1 Start 1% 4% high salt diet I/V vehicle or EGF (2μg/h) infusion Blood pressure measurements via arterial catheter Day 3 Begin High salt.4% Day 6 Begin Drug or Vehicle (intravenous infusion) 8% high salt diet I/V vehicle or EGF (2μg/h) infusion Blood pressure measurements via arterial catheter Day 3 Begin High salt and Drug or Vehicle (intravenous infusion) Day 13 (End) IHC, Biochemistry Day 9 (End) Electrophysiology D control * +EGF Control EGF * * *
45 Im_scaled (pa) Ipatch (pa) Time (s) Chronic intravenous infusion of EGF decreases ENaC activity in SS rats fed a high salt diet 3 c o o c o pa 2 s SS rat (high salt) EGF infusion 5 1 Time (s) NP o control * +EGF
46 Glomerular injury score Protein casts, % EGF attenuated renal glomerular and tubular damage A B C x 6 3 mm D 3 control * +EGF 4. 2x * 3.2 SS rat (8%; 2 weeks) 1 µm SS rat (8%; 2 weeks; + i/v EGF) 3. control +EGF
47 Conclusions: EGF concentration is reduced in the SS rats fed a high diet, which we propose would enhance ENaC activity, sodium retention and hypertension. Elevation of EGF is associated with diminished sodium reabsorption, an attenuation of hypertension, and a reduction of renal damage in Dahl SS rats fed high salt. EGF deficiency in the renal cortex contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension in Dahl SS rats via upregulation of ENaC activity Thus, elucidation of the interaction between EGF, small GTPases and ENaC will advance our understanding of the basic mechanisms of sodium regulation in salt-dependent forms of hypertension and might provide novel targets and strategies for their treatment.
48 SD rats Na + WAVE1/2 Rac1 RhoGDIα SS rats high salt Na + WAVE1/2 Rac1 RhoGDIα EGFR ErbB2 EGFR ErbB2 EGF, TGF-α, HB-EGF, amphiregulin EGF, TGF-α, HB-EGF, amphiregulin Na + retention Blood volume Cardiac output Arterial pressure
49 Thanks to: Tengis Pavlov, PhD Daria Ilatovskaya, PhD Vlad Levchenko, BS Allen W. Cowley, Jr., PhD Julian Lombard, PhD Andrey Sorokin, PhD David L. Mattson, PhD Nadezhda Zheleznova, PhD (MCW) Paul M. O Connor, PhD (GHSCU) Patricia D. Wilson, PhD (UCL) Research was supported by the American Heart Association, American Diabetes Association and NIH Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Отдельное спасибо фонду Династия Alexey Karpushev, PhD
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Essential role of Kir5.1 channels in renal salt handling and blood pressure control Oleg Palygin, Vladislav Levchenko, Daria V. Ilatovskaya, Tengis S. Pavlov, Oleh M. Pochynyuk,
Supplemental Information Essential role of Kir5.1 channels in renal salt handling and blood pressure control Oleg Palygin, Vladislav Levchenko, Daria V. Ilatovskaya, Tengis S. Pavlov, Oleh M. Pochynyuk,
Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction. Jun Ki Park 11/30/10
 Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction Jun Ki Park 11/30/10 Use of Lithium Mid 19 th century: treatment of gout Late 19 th century: used for psychiatric disorders Early 20 th century: sodium substitute to
Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction Jun Ki Park 11/30/10 Use of Lithium Mid 19 th century: treatment of gout Late 19 th century: used for psychiatric disorders Early 20 th century: sodium substitute to
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES
 THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose. Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health
 Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Normal Renal Function
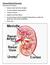 Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Cortical distal nephron Cl transport in volume homeostasis and blood pressure regulation
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305: F427 F438, 2013. First published May 1, 2013; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00022.2013. Review Cortical distal nephron Cl transport in volume homeostasis and blood pressure regulation
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305: F427 F438, 2013. First published May 1, 2013; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00022.2013. Review Cortical distal nephron Cl transport in volume homeostasis and blood pressure regulation
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
There is evidence that in hypertension, glomerular capillary
 Connecting Tubule Glomerular Feedback in Hypertension Hong Wang, Martin A. D Ambrosio, Jeffrey L. Garvin, Yilin Ren, Oscar A. Carretero See Editorial Commentary, pp 687 688 Abstract In Dahl salt-sensitive
Connecting Tubule Glomerular Feedback in Hypertension Hong Wang, Martin A. D Ambrosio, Jeffrey L. Garvin, Yilin Ren, Oscar A. Carretero See Editorial Commentary, pp 687 688 Abstract In Dahl salt-sensitive
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Sodium and chlorine transport
 Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
ERK1/2 controls Na,K-ATPase activity and transepithelial sodium transport in the principal. cell of the cortical collecting duct of the mouse kidney
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on September 28, 2004 as Manuscript M405674200 ERK1/2 controls Na,K-ATPase activity and transepithelial sodium transport in the principal cell of the cortical collecting
JBC Papers in Press. Published on September 28, 2004 as Manuscript M405674200 ERK1/2 controls Na,K-ATPase activity and transepithelial sodium transport in the principal cell of the cortical collecting
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
3/19/2009. The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load. Buffering of an acid load. A o B - + H + B - A o +OH - C +
 The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
PHSI3009 Frontiers in Cellular Physiology 2017
 Overview of PHSI3009 L2 Cell membrane and Principles of cell communication L3 Signalling via G protein-coupled receptor L4 Calcium Signalling L5 Signalling via Growth Factors L6 Signalling via small G-protein
Overview of PHSI3009 L2 Cell membrane and Principles of cell communication L3 Signalling via G protein-coupled receptor L4 Calcium Signalling L5 Signalling via Growth Factors L6 Signalling via small G-protein
ROS production as a common mechanism of ENaC regulation by EGF, insulin, and IGF-1
 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304: C102 C111, 2013. First published November 7, 2012; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00231.2012. ROS production as a common mechanism of ENaC regulation by EGF, insulin, and IGF-1 Daria
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304: C102 C111, 2013. First published November 7, 2012; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00231.2012. ROS production as a common mechanism of ENaC regulation by EGF, insulin, and IGF-1 Daria
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis
 Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Diuretics primarily prevent the reabsorption of K Na Cl I Don t know, Too busy with periodic exams! AIKTC - Knowledge
DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Diuretics primarily prevent the reabsorption of K Na Cl I Don t know, Too busy with periodic exams! AIKTC - Knowledge
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
BODY FLUID. Outline. Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid. Regulation of fluid homeostasis
 BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Your Goal. Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems. Paragraph 1: Introduction Goal introduce the paper. Paragraph 1: Introduction
 Your Goal Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems l Be able to tell the story of kidney evolution as an essay. Maintenance Introduction Goal introduce the paper l Homeostasis is the of Maintenance
Your Goal Animal s Urinary and Osmoregulatory systems l Be able to tell the story of kidney evolution as an essay. Maintenance Introduction Goal introduce the paper l Homeostasis is the of Maintenance
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance
 Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Epigenetic Control of ENaC
 Epigenetic Control of ENaC Transcription, Na + Metabolism and Blood Pressure Wenzheng Zhang, Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine The University of Texas Medical School at Houston International Conference
Epigenetic Control of ENaC Transcription, Na + Metabolism and Blood Pressure Wenzheng Zhang, Ph.D. Department of Internal Medicine The University of Texas Medical School at Houston International Conference
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Mechanisms Underlying Rapid Aldosterone Effects in the Kidney
 Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland e-publications@rcsi Molecular Medicine Articles Department of Molecular Medicine 1-2-2011 Mechanisms Underlying Rapid Aldosterone Effects in the Kidney Warren Thomas
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland e-publications@rcsi Molecular Medicine Articles Department of Molecular Medicine 1-2-2011 Mechanisms Underlying Rapid Aldosterone Effects in the Kidney Warren Thomas
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents:
 Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Low Efficacy Diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Osmotic diuretics. Miscellaneous
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Ch 19: The Kidneys. Functional unit of kidneys:?? Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM
 Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
Ch 19: The Kidneys Homeostatic regulation of ECF volume and BP Osmolarity 290 mosm Ion balance Na+ and K+, etc. ph (acid-base balance Excretion of wastes & foreign substances Hormone production EPO Renin
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life
 Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido Boerrigter, Horng C Chen, Fernando L Martin, and John C Burnett Jr
 Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Cardiorenal Enhancing and Aldosterone Suppressing Actions of a Novel Designer Natriuretic Peptide in Experimental Hypertension with Ventricular Pressure Overload Paul M McKie, Alessandro Cataliotti, Guido
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment of kidney failure.
 1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion
 Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids 2. Structure & Function of the Kidneys 3. Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration
Chapter 20. Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors. Three general types of extracellular signaling. endocrine signaling. paracrine signaling
 Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/80/80449526.jpg) 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
