True / False Question 4. During the process of bone remodeling osteoblasts resorb existing bone and osteoclasts form new bone.
|
|
|
- Gervase Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 5 This chapter has 50 questions. Scroll down to see and select individual questions or narrow the list using the checkboxes below. 0 questions at random and keep in order s - (23) Odd Numbered - (25) / Questions - (23) Even Numbered - (25) s - (4) 1. Both the size and shape of bones can limit or allow movements. 2. There are approximately 552 muscles in the human body. 3. The shape of bones does not limit movement. 4. During the process of bone remodeling osteoblasts resorb existing bone and osteoclasts form new bone. 5. Cortical bone has a low degree of porosity which consists of approximately 5-30% mineralized tissue. 6. The medullary canal is located at the ends of long bones. 7. The scapula is an example of an irregular bone. 8. One of the functions of articular cartilage is to separate the diaphysis and epiphysis. 9. Typical bony features include tendons, epiphysis, and articular cartilage. 10. Epiphyseal plates generally close by age 18 but some may be present until age Diagonal abduction is movement by a limb through a diagonal plane away from midline of body. 12. Most outer bone is composed of cortical bone with cancellous bone underneath. 13. Cancellous bone is stiffer and therefore can withstand greater stress but less strain than cortical bone. 14. Collagen in bone provides flexibility and strength to resist tension.
2 Page 2 of Longitudinal bone growth continues as long as epiphyseal plates are open. 16. Osteoclasts are specialized cells that form and resorb new bone. 17. Aging induces a progressive increase of collagen in bone that results in an increase in brittleness. 18. Bone size and shape are influenced by both the direction and magnitude of applied forces. 19. Bones reshape themselves based upon the stresses that are placed upon them. 20. Ligaments through their bone to bone connections provide dynamic stability to diarthrodial joints. 21. Diarthrodial joints are also known as synovial joints. 22. /extension is an example of movement in a coronal plane about an anteroposterior axis. 23. Of all the movements possible in the joints of the body, flexion/extension is the most commonly occurring. 24. Which of the following is true regarding circumduction? Combination of flexion, extension, adduction, and abduction Synonymous with rotation Occurs only one joint Combines flexion and extension 25. Which of the following is the correct definition of biomechanics? Study of motion of human movement Study of the human musculoskeletal and musculotendinous systems Application of mechanical physics to human motion Study of muscles as they are involved in the science of movement 26. Which of the following is the correct definition of kinesiology? Study of anatomy (active and passive structures), physiology, and mechanics in relation to human movement Study of the human musculoskeletal and musculotendinous systems Application of mechanical physics to human motion Study of muscles as they are involved in the science of movement 27. Which of the following is not an example of a movement in the sagittal plane? Lateral flexion Plantar flexion
3 Page 3 of The frontal plane divides the body into. right and left halves front and back halves top and bottom halves medial and lateral halves 29. Movements in the transverse plane occur around which axis? Mediolateral Anteroposterior Vertical Horizontal 30. Elbow extension takes place in what plane? Sagittal Frontal Transverse Longitudinal 31. Abduction takes place around which axis? Anteroposterior Mediolateral Longitudinal Horizontal 32. Shaking the head "No" occurs in which plane? Sagittal Frontal Transverse Oblique 33. Each of the following joints allows a slight amount of motion to occur except? Gomphosis Syndesmosis Synchondrosis Symphysis 34. Which of the following movements occur at the shoulder joint but not at the knee? Circumduction Rotation 35. During an underhand softball pitch that does not involve a windmill windup, the hand holding the ball is moved to a posterior position with respect the torso prior to the forward swing of the arm that releases the ball. In what order do the movements occur at the shoulder joint to make this motion possible? Abduction, adduction Adduction, abduction, flexion, extension 36. What term is used to describe the motion of bringing the dorsum of the foot closer to the anterior leg? Dorsiflexion Plantar flexion 37. Which of the following best describes the anatomical location of the head with respect to the left arm? Superior and medial
4 Page 4 of 5 Anterior and medial Distal and lateral Inferior and lateral 38. Bone is composed of all but one of the following constituents. Protein Calcium Phosphorus Water 39. Which of the following is not a function performed by the skeletal system? Protection of internal organs Support to maintain posture Mineral Storage Production of heat 40. Motion of the bones relative to the three cardinal planes resulting from physiological movements is known as. osteokinematic motion arthrokinematic motion accessory motion osteochondral motion 41. The three specific types of accessory motions are described as. slip, slide, and roll spin, twirl, and glide rock, slide, and circumfusion roll, spin, and glide 42. If the knee were not able to slide, the femur would when going from flexion to extension on a stationary tibia. roll off the back of the tibia roll off the front of the tibia spin more internally on the tibia spin more externally on the tibia 43. Motion between the articular surfaces of bone is known as. kinetics osteokinematics arthrokinematics biomechanics 44. Forward movement of the shoulder girdle in the horizontal plane away from the spine is. pronation protraction retraction reduction 45. Movement of the little finger side of the hand toward the forearm in the lateral plane is. palmar flexion radial flexion ulnar flexion volar flexion 46. An instrument used to measure the change in joint angles is a(an). flexometer jointmeter arthrometer goniometer
5 Page 5 of List the six (6) types of diarthrodial/synovial joints. 1. Arthrodial 2. Condyloidal 3. Enarthrodial 4. Ginglymus 5. Seller 6. Trochoidal 48. Using proper joint terminology list the name and position of each joint involved upon completion of the following multiple joint movement. Starting from the anatomical position, reach with your right arm and touch the ipsilateral side of your head with the palm of your hand. 49. List three (3) of the terms that are used to describe bone markings. 50. List two of the most commonly occurring movements for each of the following planes. sagittal, frontal, transverse.
9/26/2012. Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & Arthrokinematics (how the joints move) Planes & Axes. Planes & Axes continued
 Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Main Menu. Introduction Kinesiology click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Introduction to Kinesiology click here Main Menu K.1 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k1entry.htm[3/23/18, 11:31:26 AM] Kinesiology The scientific study of muscular activity and the anatomy,
1 Introduction to Kinesiology click here Main Menu K.1 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k1entry.htm[3/23/18, 11:31:26 AM] Kinesiology The scientific study of muscular activity and the anatomy,
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
Student Objectives. When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives:
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy
 Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education
 CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
6.4 The Ankle. Body Divided into Planes. Health Services: Unit 6 Arms and Legs. Body Movement Vocabulary
 6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
Kinesiology & Body Mechanics
 Kinesiology & Body Mechanics Chapter 1 Foundations of Structural Kinesiology Kinesiology - study of motion or human movement Anatomic kinesiology - study of human musculoskeletal system & musculotendinous
Kinesiology & Body Mechanics Chapter 1 Foundations of Structural Kinesiology Kinesiology - study of motion or human movement Anatomic kinesiology - study of human musculoskeletal system & musculotendinous
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction. Sentenced to Life in the Joint
 Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS
 CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints
 Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 9 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Joints can be classified structurally as A) bony. B) fibrous. C) cartilaginous. D) synovial. E) All of the answers are correct. 2)
9.1 Joints. Objectives Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints
 Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Body Planes & Positions
 Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Introduction. Physiology. Classification of Bones. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Skeletal System and Joint Movements.
 Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Medical Terminology. Unit 2
 Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Joints. Judi Laprade. Illustrations from: Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA3) Moore, K. and Agur, A. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2007
 Slide 1 Joints Judi Laprade Illustrations from: Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA3) Moore, K. and Agur, A. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2007 Grant s Atlas of Anatomy 12 th ed. (GA12) Agur, A.
Slide 1 Joints Judi Laprade Illustrations from: Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA3) Moore, K. and Agur, A. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2007 Grant s Atlas of Anatomy 12 th ed. (GA12) Agur, A.
The Skeletal System: Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology ROM & GONIOMETRY
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology & GONIOMETRY MSAK201-II Session 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology & GONIOMETRY MSAK201-II Session 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will
Chapter 7 - Joints. Think About It: Describe the two structural classifications of joints. Describe the three functional classifications of joints.
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 7 - Joints Think About It: Describe the two structural classifications of joints. a. b. Describe the three functional classifications of joints. a. b. c. Checkpoint
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 7 - Joints Think About It: Describe the two structural classifications of joints. a. b. Describe the three functional classifications of joints. a. b. c. Checkpoint
The Articular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
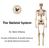 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
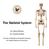 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Kinesiology & Body Mechanics Foundations of Structural Kinesiology
 Kinesiology & Body Mechanics Foundations of Structural Kinesiology KINE 3300 Applied Kinesiology Kinesiology - study of motion or human movement Anatomic kinesiology - study of human musculoskeletal system
Kinesiology & Body Mechanics Foundations of Structural Kinesiology KINE 3300 Applied Kinesiology Kinesiology - study of motion or human movement Anatomic kinesiology - study of human musculoskeletal system
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY Prof. Oluwadiya KS MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) http://www.oluwadiya.com What is anatomy? The study of the gross structure of the human body with the naked eyes and as well as microscopy.
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY Prof. Oluwadiya KS MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) http://www.oluwadiya.com What is anatomy? The study of the gross structure of the human body with the naked eyes and as well as microscopy.
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Chapter 6 part 2. Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement
 Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement Classification of joints is by functional group (the amount of movement possible), and structural group (how the bones are held together). Functional Group Structural
Chapter 8 Joints & Skeletal Movement Classification of joints is by functional group (the amount of movement possible), and structural group (how the bones are held together). Functional Group Structural
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Basics of Joint Design and Function
 Basics of Joint Design and Function 1 Joint Overview Joint (articulation): connects parts of a structure. Design depends on function. Function depends on design. Effective body function depends on integrated
Basics of Joint Design and Function 1 Joint Overview Joint (articulation): connects parts of a structure. Design depends on function. Function depends on design. Effective body function depends on integrated
Diagnostic Test Skeletal Words Made Easy Match the terms on the right with the terms on the left.
 CHAPTER 5 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 2003. All material is copyright protected. It is illegal to copy any of this material. This material may be used only in a course of study in which Exercise
CHAPTER 5 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 2003. All material is copyright protected. It is illegal to copy any of this material. This material may be used only in a course of study in which Exercise
Introduction to Human Anatomy. Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili
 Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems
 Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Dorsal surface-the upper area or top of the foot. Terminology
 It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
Movement Terminology. The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space.
 Movement Terminology The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space. In exercise it allows us to communicate with other movement professionals so we can describe
Movement Terminology The language of movement is designed to allow us to describe how the body moves through space. In exercise it allows us to communicate with other movement professionals so we can describe
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Articulations Chapter 9
 Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Lecture 9: Arthrology
 Lecture 9: Arthrology M/O Chapter 9 45. Classify joints based on the degree of movement allowed and give examples of each classification. 46. Classify joints based on anatomical structure and give examples
Lecture 9: Arthrology M/O Chapter 9 45. Classify joints based on the degree of movement allowed and give examples of each classification. 46. Classify joints based on anatomical structure and give examples
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect. Two classification methods are used to categorize joints:
 Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
Chapter 9 Articulations Articulations joints where two bones interconnect Two classification methods are used to categorize joints: Functional classification Structural classification Functional classification
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary.
 Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
2/4/2017. The Anatomical Position. Body Movement. Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement
 Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement PSK 4U North Grenville DHS S. Kelly The Anatomical Position The starting point for describing ALL anatomical and physiological features Upright, standing
Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement PSK 4U North Grenville DHS S. Kelly The Anatomical Position The starting point for describing ALL anatomical and physiological features Upright, standing
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques. Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright
 Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity
 THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
Upper Limb Biomechanics SCHOOL OF HUMAN MOVEMENT STUDIES
 Upper Limb Biomechanics Phases of throwing motion 1. Wind up Starts: initiate first movement Ends: lead leg is lifted & throwing hand removed from glove COG raised 2. Early Cocking Start: lead leg is lifted
Upper Limb Biomechanics Phases of throwing motion 1. Wind up Starts: initiate first movement Ends: lead leg is lifted & throwing hand removed from glove COG raised 2. Early Cocking Start: lead leg is lifted
Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing
 Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing Description of Movement While the movement required for a golf swing requires many muscles, joints, & ligaments throughout the body, the
Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing Description of Movement While the movement required for a golf swing requires many muscles, joints, & ligaments throughout the body, the
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints. Structural Classifica5on of Joints 10/26/14
 Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT
 INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT UNIT THREE Despite the certified athletic trainer s best efforts toward injury prevention, injuries do still occur. It is important for the ATC to be able to recognize,
INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT UNIT THREE Despite the certified athletic trainer s best efforts toward injury prevention, injuries do still occur. It is important for the ATC to be able to recognize,
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints. Structural Classifica5on of Joints. Fibrous Joints. Fibrous Joints: Sutures 10/26/14
 Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System
 Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
Introduction. Rarely does a single muscle act in isolation at the shoulder complex.
 Shoulder complex 1 Introduction Our study of the upper limb begins with the shoulder complex, a set of four articulations involving the sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, and humerus. Rarely does a single
Shoulder complex 1 Introduction Our study of the upper limb begins with the shoulder complex, a set of four articulations involving the sternum, clavicle, ribs, scapula, and humerus. Rarely does a single
Introduction. Fibrous Joints. 8.1: Types of Joints. Cartilaginous Joints. Fibrous Joints 12/14/2016. Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
Course Objectives. HUMAN MOTION -- Osteokinematics. Classification of Joints - based on anatomic structure and movement potential
 Course Objectives Kinesiology 2017#2: Huei-Ming Chai, Ph.D., PT School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University To review components of synovial joint To identify planes of motions and its relative
Course Objectives Kinesiology 2017#2: Huei-Ming Chai, Ph.D., PT School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University To review components of synovial joint To identify planes of motions and its relative
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomical Introduction. - Basic Terms. Anatomical terms. -Positions :
 Anatomical Introduction - Basic Terms : Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts in the body. * (ology ) is a suffix means science. Physiology: the science that
Anatomical Introduction - Basic Terms : Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts in the body. * (ology ) is a suffix means science. Physiology: the science that
9/26/2012. Basic Terminology. Basic Terminology continued. Kinesiology Terminology. Kinesiology = The study of movement
 Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
PTA Applied Kinesiology 1
 Western Technical College 10524156 PTA Applied Kinesiology 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Introduces basic principles of musculoskeletal
Western Technical College 10524156 PTA Applied Kinesiology 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Introduces basic principles of musculoskeletal
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Joints. Vi Michelle Austin
 Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Joints Vi Michelle Austin Joints Overview A joint, otherwise known as an articulation, is a point at which points connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull bones) and provide mechanical
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) Answers to Activity Questions
 Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
