Spongy Bone. Spongelike appearance formed by plates of bone called trabeculae. spaces filled with red bone marrow
|
|
|
- Alban Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spongy Bone Spongelike appearance formed by plates of bone called trabeculae spaces filled with red bone marrow Trabeculae have few osteons or central canals no osteocyte is far from blood of bone marrow Provides strength with little weight trabeculae develop along bone s lines of stress 1
2 Spongy Bone Structure and Stress 2
3 Bone Marrow In medullary cavity (long bone) and among trabeculae (spongy bone) Red marrow like thick blood reticular fibers and immature cells Hemopoietic (produces blood cells) in vertebrae, ribs, sternum, pelvic girdle and proximal heads of femur and humerus in adults Yellow marrow fatty marrow of long bones in adults Gelatinous marrow of old age yellow marrow replaced with reddish jelly 3
4 Intramembranous Ossification Condensation of mesenchyme into trabeculae Osteoblasts on trabeculae lay down osteoid tissue (uncalcified bone) Calcium phosphate is deposited in the matrix forming bony trabeculae of spongy bone Osteoclasts create marrow cavity Osteoblasts form compact bone at surface Surface mesenchyme produces periosteum 4
5 Intramembranous Ossification 1 Produces flat bones of skull and clavicle. 5
6 Intramembranous Ossification 2 Note the periosteum and osteoblasts. 6
7 Stages of Endochondral Ossification 7
8 Endochondral Ossification 1 Bone develops from pre-existing model perichondrium and hyaline cartilage Most bones develop this process Formation of primary ossification center and marrow cavity in shaft of model bony collar developed by osteoblasts chondrocytes swell and die stem cells give rise to osteoblasts and clasts bone laid down and marrow cavity created 8
9 Primary Ossification Center and Primary Marrow Cavity 9
10 Endochondral Ossification 2 Secondary ossification centers and marrow cavities form in ends of bone same process Cartilage remains as articular cartilage and epiphyseal (growth) plates growth plates provide for increase in length of bone during childhood and adolescence by early twenties, growth plates are gone and primary and secondary marrow cavities united 10
11 Secondary Ossification Centers and Secondary Marrow Cavities 11
12 The Metaphysis Zone of reserve cartilage = hyaline cartilage Zone of proliferation chondrocytes multiply forming columns of flat lacunae Zone of hypertrophy = cell enlargement Zone of calcification mineralization of matrix Zone of bone deposition chondrocytes die and columns fill with osteoblasts osteons formed and spongy bone is created 12
13 Fetal Skeleton at 12 Weeks 13
14 LAB 14
15 Pelvic Girdle Girdle = 2 hip bones Pelvis = girdle and sacrum Supports trunk on the legs and protects viscera Each os coxae is joined to the vertebral column at the sacroiliac joint Anteriorly, pubic bones are joined by pad of fibrocartilage to form pubic symphysis 15
16 Pelvic Inlet and Outlet False and true pelvis separated at pelvic brim Infant s head passes through pelvic inlet and outlet 16
17 Os Coxae (Hip Bone) Acetabulum is hip joint socket Ilium iliac crest and iliac fossa greater sciatic notch contains sciatic nerve Pubis body, superior and inferior ramus Ischium ischial tuberosity bears body weight ischial spine lesser sciatic notch between ischial spine and tuberosity ischial ramus joins inferior pubic ramus 17
18 Comparison of Male and Female Female lighter, shallower pubic arch( >100 degrees), and pubic inlet round or oval Male heavier, upper pelvis nearly vertical, coccyx more vertical, and pelvic inlet heart-shaped 18
19 Femur and Patella (Kneecap) Nearly spherical head and constricted neck ligament to fovea capitis Greater and lesser trochanters for muscle attachment Posterior ridge called linea aspera Medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles found distally Patella = triangular sesamoid 19
20 Tibia Tibia is thick, weightbearing bone (medial) Broad superior head with 2 flat articular surfaces medial and lateral condyles roughened anterior surface palpated below patella (tibial tuberosity) distal expansion = medial malleolus 20
21 Fibula Slender lateral strut stabilizes ankle Does not bear any body weight spare bone tissue Head = proximal end Lateral malleolus = distal expansion Joined to tibia by interosseous membrane 21
22 The Ankle and Foot Tarsal bones are shaped and arranged differently from carpal bones due to load-bearing role of the ankle Talus is most superior tarsal bone forms ankle joint with tibia and fibula sits upon calcaneus and articulates with navicular Calcaneus forms heel (achilles tendon) Distal row of tarsal bones cuboid, medial, intermediate and lateral cuneiforms 22
23 The Foot Remaining bones of foot are similar in name and arrangement to the hand Metatarsal I is proximal to the great toe (hallux) base, shaft and head Phalanges 2 in great toe proximal and distal 3 in all other toes proximal, middle and distal 23
24 END OF LAB 24
25 Bone Growth and Remodeling Bones increase in length interstitial growth of epiphyseal plate epiphyseal line is left behind when cartilage gone Bones increase in width = appositional growth osteoblasts lay down matrix in layers on outer surface and osteoclasts dissolve bone on inner surface Bones remodeled throughout life Wolff s law of bone = architecture of bone determined by mechanical stresses action of osteoblasts and osteoclasts greater density and mass of bone in athletes or manual worker is an adaptation to stress 25
26 Dwarfism Achondroplastic long bones stop growing in childhood normal torso, short limbs spontaneous mutation during DNA replication failure of cartilage growth Pituitary lack of growth hormone normal proportions with short stature 26
27 Mineral Deposition Mineralization is crystallization process osteoblasts produce collagen fibers spiraled the length of the osteon minerals cover the fibers and harden the matrix ions (calcium and phosphate and from blood plasma) are deposited along the fibers ion concentration must reach the solubility product for crystal formation to occur Abnormal calcification (ectopic) may occur in lungs, brain, eyes, muscles, tendons or arteries (arteriosclerosis) 27
28 Mineral Resorption from Bone Bone dissolved and minerals released into blood performed by osteoclasts ruffled border hydrogen pumps in membrane secrete hydrogen into space between the osteoclast and bone surface chloride ions follow by electrical attraction hydrochloric acid (ph 4) dissolves bone minerals enzyme (acid phosphatase) digests the collagen Dental braces reposition teeth and remodel bone create more pressure on one side of the tooth stimulates osteoclasts to remove bone decreased pressure stimulates osteoblasts 28
29 Calcium and Phosphate Phosphate is component of DNA, RNA, ATP, phospholipids, and ph buffers ~750 g in adult skeleton plasma concentration is ~ 4.0 mg/dl 2 plasma forms: HPO -2 4 and H 2 PO - 4 Calcium needed in neurons, muscle contraction, blood clotting and exocytosis ~1100g in adult skeleton plasma concentration is ~ 10 mg/dl 29
30 Ion Imbalances Changes in phosphate levels = little effect Changes in calcium can be serious hypocalcemia is deficiency of blood calcium causes excitability of nervous system if too low muscle spasms, tremors or tetany ~6 mg/dl laryngospasm and suffocation ~4 mg/dl with less calcium, sodium channels open more easily, sodium enters cell and excites neuron hypercalcemia is excess of blood calcium binding to cell surface makes sodium channels less likely to open, depressing nervous system muscle weakness and sluggish reflexes, cardiac arrest ~12 mg/dl Calcium phosphate homeostasis depends on calcitriol, calcitonin and PTH hormone regulation 30
31 Carpopedal Spasm Hypocalcemia demonstrated by muscle spasm of hands and feet. 31
32 Hormonal Control of Calcium Balance Calcitriol, PTH and calcitonin maintain normal blood calcium concentration. 32
33 Calcitriol (Activated Vitamin D) Produced by the following process UV radiation and epidermal keratinocytes convert steroid derivative to cholecalciferol - D3 liver converts it to calcidiol kidney converts that to calcitriol (vitamin D) Calcitriol behaves as a hormone that raises blood calcium concentration increases intestinal absorption and absorption from the skeleton increases stem cell differentiation into osteoclasts promotes urinary reabsorption of calcium ions Abnormal softness (rickets) in children and (osteomalacia) in adults without vitamin D 33
34 Calcitriol Synthesis and Action 34
35 Calcitonin Secreted (C cells of thyroid gland) when calcium concentration rises too high Functions reduces osteoclast activity as much as 70% increases the number and activity of osteoblasts Important in children, little effect in adults osteoclasts more active in children deficiency does not cause disease in adults Reduces bone loss in osteoporosis 35
36 Correction for Hypercalcemia 36
37 Parathyroid Hormone Glands on posterior surface of thyroid Released with low calcium blood levels Function = raise calcium blood level causes osteoblasts to release osteoclaststimulating factor (RANKL) increasing osteoclast population promotes calcium resorption by the kidneys promotes calcitriol synthesis in the kidneys inhibits collagen synthesis and bone deposition by osteoblasts Sporatic injection of low levels of PTH causes bone deposition 37
38 Correction for Hypocalcemia 38
39 Other Factors Affecting Bone Hormones, vitamins and growth factors Growth rapid at puberty hormones stimulate osteogenic cells, chondrocytes and matrix deposition in growth plate girls grow faster than boys and reach full height earlier (estrogen stronger effect) males grow for a longer time and taller Growth stops (epiphyseal plate closes ) teenage use of anabolic steroids = premature closure of growth plate and short adult stature 39
40 Fractures and Their Repair Stress fracture caused by trauma car accident, fall, athletics, etc Pathological fracture in bone weakened by disease bone cancer or osteoporosis Fractures classified by structural characteristics break in the skin multiple pieces 40
41 Types of Bone Fractures 41
42 Healing of Fractures 1 Normally 8-12 weeks (longer in elderly) Stages of healing fracture hematoma (1) - clot forms, then osteogenic cells form granulation tissue soft callus (2) fibroblasts produce fibers and fibrocartilage hard callus (3) osteoblasts produce a bony collar in 6 weeks remodeling (4) in 3 to 4 months spongy bone replaced by compact bone 42
43 Healing of Fractures 2 43
44 Treatment of Fractures Closed reduction fragments are aligned with manipulation and casted Open reduction surgical exposure and repair with plates and screws Traction risks long-term confinement to bed Electrical stimulation used on fractures if 2 months necessary for healing Orthopedics = prevention and correction of injuries and disorders of the bones, joints and muscles 44
45 Fractures and Their Repairs 45
46 Osteoporosis 1 Bones lose mass and become brittle (loss of organic matrix and minerals) risk of fracture of hip, wrist and vertebral column complications (pneumonia and blood clotting) Postmenopausal white women at greatest risk by age 70, average loss is 30% of bone mass black women rarely suffer symptoms 46
47 Osteoporosis 2 Estrogen maintains density in both sexes (inhibits resorption) testes and adrenals produce estrogen in men rapid loss after menopause, if body fat too low or with disuse during immobilizaton Treatment ERT slows bone resorption, but increases risk breast cancer, stroke and heart disease PTH (parathyroid hormone) slows bone loss if given daily injection Forteo increases density by 10% in 1 year may promote bone cancer best treatment is prevention -- exercise and calcium intake (1000 mg/day) between ages 25 and 40 47
48 Spinal Osteoporosis 48
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
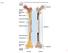 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
 C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6. Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 7
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 7 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 7 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. 1 SCCC BIO130 Lab 7 Appendicular Skeleton & Articulations
 The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
