Sonography of the iliotibial band: spectrum of findings *
|
|
|
- Penelope Payne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review rticle rend CF / Sonography of the iliotibial band Sonography of the iliotibial band: spectrum of findings * Ultrassonografia do trato iliotibial: espectro de achados Carlos Frederico rend 1 rend CF. Sonography of the iliotibial band: spectrum of findings. Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1): bstract Iliotibial band lesions constitute a potential source of discomfort and are frequently confounded with other conditions which cause pain on the lateral aspect of the hip, thigh and knee. Ultrasonography is usually regarded as a first-line imaging modality in the assessment of such conditions because of its excellent diagnostic accuracy, low cost and wide availability. The correct identification of the structure involved in the production of symptoms leads to an appropriate management and to a higher probability of resolution of the clinical complaint. The present article is aimed at reviewing the different sonographic presentations of iliotibial band syndromes. Keywords: Sonography; Iliotibial band; Iliotibial band friction syndrome. Resumo Lesões no trato iliotibial constituem potencial fonte de desconforto e são frequentemente confundidas com outras enfermidades causadoras de dor na face lateral do quadril, coxa e joelho. ultrassonografia é reconhecida como um método de imagem de primeira linha na investigação destas alterações, em virtude da excelente capacidade diagnóstica, baixo custo e ampla disponibilidade. correta identificação da estrutura geradora dos sintomas resulta em tratamento específico e maior probabilidade de resolução da queixa clínica. O objetivo deste artigo é revisar as diferentes apresentações ultrassonográficas de doença do trato iliotibial. Unitermos: Ultrassonografia; Trato iliotibial; Síndrome do trato iliotibial. INTRODUCTION The iliotibial band is a dense fibrotic structure that is found exclusively in the human species, originating in the iliac tubercle, extending to the outer aspect of the thigh, where the fascia latae tensor, gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles insert (1), and contributing to the postural control and monopodal equilibrium (2). Its distal perigenicular insertion is complex and includes fibers which extend toward the tibial tubercle, as described by Gerdy (2). The incidence of iliotibial band syndromes is unknown, considering the high number of patients with subclinical lesions. The most frequent presentation is iliotibial band syndrome that is accepted as the most common cause of lateral gonalgia in long-distance athletes (3,4). However, several other less common alterations may also be observed in such structure, both proximally and distally in relation to the usual affected site in cases of distal iliotibial band syndrome. The present study is aimed at reviewing the different sonographic findings of iliotibial band syndrome. THE ROLE OF ULTRSONOGRPHY Ultrasonography is recognized as a first-line imaging method in the investigation of iliotibial band injuries because of its excellent diagnostic capability, low cost and wide availability (5). dditionally, 10 MHz linear transducers utilized * Study developed at Radimagem Diagnóstico por Imagem, Porto legre, RS, razil. 1. MD, Radiologist, Radimagem Diagnóstico por Imagem, Porto legre, RS, razil. Mailing ddress: Dr. Carlos Frederico rend. venida Cristóvão Colombo, 1691, Floresta. Porto legre, RS, razil, carlos_arend@hotmail.com. Received July 30, ccepted after revision July 12, as standard devices in many imaging diagnosis centers, allow for an investigation with an immense wealth of details, achieving axial resolution of 150 µm (6). For the purposes of comparison, such an axial resolution is three times better than the 469 µm obtained with commercially available 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging apparatuses (7). Theoretically, transducers with frequencies above 10 MHz can generate a much better imaging resolution with less depth penetration. However, as this method is operator-dependent and based on subjective criteria, the emphasis for the sonographic diagnosis should not be put on the transducer frequency, but on the education of the sonographer to recognize the signs of the disease (8). SCN TECHNIQUE In the authors routines, the scan is performed with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer, utilizing only one focal zone adjusted for the tract depth. The positioning of the patient varies according to the region of interest. In the assessment of the proximal iliotibial band, the patient is positioned in lateral decubitus over the symptomatic side, with semi-flexed knee; in the assessment of the distal band, dorsal decubitus with extend knee is preferable. The longitudinal plane allows for a more intuitive interpretation as compared with transverse images, except for snapping hip syndrome investigation, and the agreement with the anatomic alteration with the site of greatest pain sensitivity reported by the patient greatly increases the diagnostic reliability. Contrary to what many patients believe, the contralateral assessment is not mandatory for the diagnosis, although it may be useful in dubious cases or in scans performed with educational purposes (5). Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1): Colégio rasileiro de Radiologia e Diagnóstico por Imagem
2 SPECTRUM OF SONOGRPHIC FINDINGS Iliotibial band syndrome manifestations liable to be documented by ultrasonography shall be individually described in the present article. Generally, there is a resistance to consider hypoechogenicity alone as a criterion of disease due to the ubiquitous anisotropy. Most frequently the diagnosis requires a combination of thickening and hypoechogenicity or, eventually, alterations at dynamic scan. Proximal iliotibial band syndrome Proximal iliotibial band syndrome is an uncommon entity caused either by aging or overuse. Thus, it is most common in women because they present with wider pelvic girdle and shorter femur as compared with men, which leads to a greater mechanical overload on the iliotibial band as a stabilizer element during ambulation (9). Clinically, the discomfort tends to be restricted to the iliac tubercle area, worsening with physical activity. t sonographic evaluation focused on the site of pain reported by the patient, the process is detected as a thickening and hypoechogenicity of the structure (Figure 1). anterior edge of the gluteus maximus muscle are located posteriorly located in relation to the greater trochanter and slightly displace anteriorly during progressive flexion of the thigh, even in healthy individuals. The diagnostic criterion of such abnormality is not the displacement itself, but the snapping of the structure over the greater trochanter. Pain caused by thigh flexion is the most frequent reason for clinical complaints (Figure 2). Figure 1. Proximal iliotibial band syndrome. Female, 27-year-old patient, professional athlete, presenting with focal pain adjacent to the right iliac crest that intensifies during physical activity. Longitudinal image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer demonstrating thickening and hypoechogenicity of the iliotibial band origin (arrow heads) adjacent to the iliac tubercle (it). Snapping hip syndrome The abnormal anterior motion of the iliotibial tract over the greater trochanter of the femur is a common cause of snapping hip syndrome. Reliable statistics on the prevalence of such a condition in the general population are not available, but it is known that it is most common in women at the age range between 15 and 40 years (8). lthough usually such snaps do not trigger any symptom, in some cases such abnormality generates disabling pain and a specific diagnosis allows for appropriate treatment and greater chances of resolution of the clinical complaints. t ultrasonography, the patient is assessed with the thigh extended, in lateral decubitus lying on the asymptomatic side, with the transducer transversely positioned over the greater trochanter. In this position, the posterior edge of the iliotibial band and the 34 Figure 2. Snapping hip syndrome. Male, 16-year-old, asymptomatic patient referred by his mother for assessment due to chronic snapping in the peritrochanteric region. : Transverse image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer, with extended thigh, demonstrates the iliotibial band, the gluteus medius (gm) and the greater trochanter (Gt). Note the posterior edge of iliotibial band located posteriorly to the trochanter. : With progressive flexion of the thigh, there is a sudden anterior migration of the band and emergence of the gluteus maximus (gm) on the evaluation plane. The arrow indicates the direction of the iliotibial band displacement. Iliotibial band syndrome Iliotibial band syndrome is the most common presentation of iliotibial band disease. It results from overuse that is most common in athletes, particularly marathoners and cyclists (10,11), due to chronic compression of the iliotibial band over a thin layer of fat richly innervated interposed between the iliotibial band and the lateral femoral condyle (12). natomical factors, namely, genu varum, excessive internal tibial Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1):33 37
3 rotation, hip abductor muscle weakness and foot pronation may also contribute to increase the tension over the iliotibial band, predisposing to the syndrome onset (13,14). In older descriptions, the injury was attributed to a cyclic antero-posterior movement of the band over the lateral condyle (15,16), in a mechanism that has, most recently, been questioned. In fact, the iliotibial tract is a distinctive anatomical structure but rather a region of the fascia latae connected with the rough line of the femur by the intermuscular septum, which prevents its anteroposterior motion (17). Thus, currently the most accepted etiopathogenesis of this syndrome is compressive and not frictional (12,17). The typical clinical sign is pain in the region of the lateral femoral condyle, particularly acute at 30 flexion and exacerbated during the physical examination at local knee motion palpation (18). The compression of the iliotibial band over the fat layer occurs with genicular flexion of approximately 30, corresponding to the angle at the moment the foot touches the ground and justifies the maximum pain in most patients at that very instant (17). t imaging, it is easier to start the scan with the transducer longitudinally positioned over the tibial tubercle, where the band insertion can be readily identified. Then, the structure can be proximally followed up to the region of the lateral femoral condyle, where the disease manifestations are concentrated. t its early stage, iliotibial band syndrome manifests as heterogeneity and increased echogenicity of the fat tissue interposed between the band and the femur (Figure 3), which evolves with development of contiguous bursa adventitious caused by the chronic compression (Figure 4). The assessment must be performed with mere apposition of the transducer and extended knee, considering that both genicular flexion and the untimely compression of the transducer against the skin surface tend to displace the fluid, making the diagnosis less intuitive (Figure 5). t more advanced stages, thickening and heterogeneity of the iliotibial band itself are observed in the region of the lateral femoral condyle (Figure 6). Insertional iliotibial band tendinosis Insertional iliotibial band tendinosis is considered as a separate entity, located distally to the lateral femoral condyle and with no relation with chronic compression. The physio- Figure 4. Iliotibial band syndrome. Male, 42-year-old patient, recreational marathoner, presents with intermittent pain in the lateral aspect of his knee, proximally to the joint line. : Longitudinal image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer, with extended knee, demonstrates adventitious bursitis in a typical location (asterisks), interposed between the normal iliotibial band (arrow heads) and the lateral femoral (fem) condyle. : Magnetic resonance imaging coronal, STIR sequence confirming the sonographic findings. t magnetic resonance imaging, the iliotibial band is identified as an elongated structure with low signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted sequences, while the neobursa presents a fluid intensity signal. tib, tibia. Figure 3. Early stage of iliotibial band syndrome. Male, 37-year-old patient, amateur cyclist, presenting with pain in the lateral aspect of his knee that intensifies during physical activity. Longitudinal image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer demonstrating increased echogenicity of the fat tissue (arrow head) interposed between the iliotibial band (itb) and the femur (fem). tib, tibia. Figure 5. Iliotibial band syndrome. Male, 47-year-old patients, recreational marathoner, with constant pain in the lateral aspect of the knee. : Transverse image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer, at the level of the lateral femoral (fem) condyle, with extended knee, demonstrating typical adventitious bursitis (asterisks) deeply located in the normal iliotibial band (arrow heads). : Compressive study demonstrating bursal walls apposition which may generate false-negative results. Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1):
4 Figure 6. Iliotibial band syndrome. Male, 57-year-old, amateur cyclist, reporting chronic, intermittent pain in the lateral aspect of the knee. : Longitudinal image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer, demonstrating thickening and hypoechogenicity of the iliotibial band (asterisk) at the level of the lateral femoral (fem) condyle. lso, observe the normal distal band (arrow heads) inserting into the tibia tibia (tib). : Comparative contralateral image demonstrating the normality along the entire course of the iliotibial band (arrow heads). pathogenesis of such a condition involves aging and overuse, the latter common in unstable joints due to osteoarthrosis. Innumerable orthopedic misalignments may also increase the tension over the iliotibial band and catalyze the degenerative process over the years. From the clinical point of view, the discomfort epicenter tends to be more distal as compared with the above described iliotibial band syndrome, with eventual proximal irradiation along the lateral aspect of the thigh. The population at risk includes elderly and mid-aged individuals usually sedentary due to the associated genicular osteoarthrosis. t ultrasonography focused on the site of highest sensitivity to pain reported by the patient, insertional tendinosis is seen as thickening and hypoechogenicity of the iliotibial band in the region of the tibia (Figure 7). prolonged orthostatism, high-impact activities, or actions like running, climbing stairs and crossing legs. Pain is more common in women between their fourth and sixth decades of life than in men (19), at a 4:1 ratio (20 22). In about 50% of patients, the pain irradiates over the lateral aspect of the thigh, rarely surpassing the knee (23). Populational studies estimate its prevalence around 10 25% in industrialized countries (24 26). In individuals with lumbar pain, the syndrome prevalence increases to 20 35% (27,28). In the context of primary health care, its incidence is approximately 1.8:1,000 patients/ year (25). Causes are innumerable and include tendon and bursal conditions, and triggering points, only to mention some examples. dditionally, the clinical complaint may be, in truth, a reported pain originating from coxofemoral disease and/or spinal condition. namnesis and clinical examination do not allow a safe differentiation amongst the different etiologies, so imaging evaluation is usually indicated to guide the therapy, particularly in cases refractory to the initial management. Historically, iliotibial band syndrome has been preponderantly attributed to a bursal inflammatory process, recognized as trochanteric bursitis. However, with the popularization of imaging methods, the medical professionals have progressively perceived that the main anatomical trigger of symptoms seems to be tendinous rather than bursal, affecting the insertion of the gluteus medius and minimus muscles that are abductors of the lower limb. ecause of its anatomical proximity, the iliotibial band may play a significant role in the genesis of the tendon or bursal lesion causing the syndrome due to the chronic friction during ambulation (Figure 8). CONCLUSION Ultrasonography is a rapid, accurate and widely available method capable of demonstrating a wide spectrum of iliotibial band alterations. The iliotibial band as a catalyst of peritrochanteric syndrome Peritrochanteric syndrome is a term utilized to describe a clinical condition characterized by chronic and persistent pain in the region of the greater trochanter of the femur that may be exacerbated by decubitus over the symptomatic side, Figure 7. Insertional iliotibial band tendinosis. Male, 89-year-old, sedentary patient, presents with pain epicenter in the lateral aspect of his knee, with proximal irradiation, with no apparent motive. Longitudinal image acquired with a 5-13 MHz linear transducer, demonstrating juxtainsertional thickening and hypoechogenicity of the iliotibial band (arrow heads) adjacent to the tibia (tib). Figure 8. Iliotibial band as a catalyst of peritrochanteric syndrome. Female, 69- year-old, sedentary patient, presenting with chronic peritrochanteric pain. : Transverse image acquired with a 5 13 MHz linear transducer demonstrating thickening of the iliotibial band (arrow heads), as well as signs of gluteus medius (gm) tendinosis adjacent to its insertion into the greater trochanter of the femur (Gt). 36 Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1):33 37
5 REFERENCES 1. Muhle C, hn JM, Yeh L, et al. Iliotibial band friction syndrome: MR imaging findings in 16 patients and MR arthrographic study of six cadaveric knees. Radiology. 1999;212: Terry GC, Hughston JC, Norwood L. The anatomy of the iliopatellar band and iliotibial tract. m J Sports Med. 1986;14: Macera C, Pate RR, Powell KE, et al. Predicting lower-extremity injuries among habitual runners. rch Intern Med. 1989;149: Marti, Vader JP, Minder CE, et al. On the epidemiology of running injuries. The 1984 ern Grand-Prix study. m J Sports Med. 1988;16: rend CF. MSTER Ultrassonografia musculoesquelética. 2ª ed. Rio de Janeiro: Revinter; Neumann T, Ermert H. Schlieren visualization of ultrasonic wave fields with high spatial resolution. Ultrasonics. 2006;44 Suppl 1: e Link TM, Majumdar S, Peterfy C, et al. High resolution MRI of small joints: impact of spatial resolution on diagnostic performance and SNR. Magn Reson Imaging. 1998;16: rend CF. Top ten pitfalls to avoid when performing musculoskeletal sonography: what you should know before entering the examination room. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82: Sher I, Umans H, Downie S, et al. Proximal iliotibial band syndrome: what is it and where is it? Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40: Khaund R, Flynn SH. Iliotibial band syndrome: a common source of knee pain. m Fam Physician. 2005;71: Fredericson M, Cookingham CL, Chaudhari M, et al. Hip abductor weakness in distance runners with iliotibial band syndrome. Clin J Sport Med. 2000;10: Fairclough J, Hayashi K, Toumi H, et al. The functional anatomy of the iliotibial band during flexion and extension of the knee: implications for understanding iliotibial band syndrome. J nat. 2006;208: Noble C. Iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners. m J Sports Med. 1980;8: Ferber R, Noehren, Hamill J, et al. Competitive female runners with a history of iliotibial band syndrome demonstrate atypical hip and knee kinematics. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40: Holmes JC, Pruitt L, Whalen NJ. Iliotibial band syndrome in cyclists. m J Sports Med. 1993;21: Orchard JW, Fricker P, bud T, et al. iomechanics of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners. m J Sports Med. 1996;24: Fairclough J, Hayashi K, Toumi H, et al. Is iliotibial band syndrome really a friction syndrome? J Sci Med Sport. 2007;10: Fredericson M, Wolf C. Iliotibial band syndrome in runners: innovations in treatment. Sports Med. 2005;35: Shbeeb MI, Matteson EL. Trochanteric bursitis (greater trochanter pain syndrome). Mayo Clin Proc. 1996;71: nderson TP. Trochanteric bursitis: diagnostic criteria and clinical significance. rch Phys Med Rehabil. 1958;39: Krout RM, nderson TP. Trochanteric bursitis: management. rch Phys Med Rehabil. 1959;40: Silva F, dams T, Feinstein J, et al. Trochanteric bursitis: refuting the myth of inflammation. J Clin Rheumatol. 2008;14: Gordon EJ. Trochanteric bursitis and tendinitis. Clin Orthop. 1961; 20: Segal N, Felson DT, Torner JC, et al. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome: epidemiology and associated factors. rch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;88: Lievense, ierma-zeinstra S, Schouten, et al. Prognosis of trochanteric pain in primary care. r J Gen Pract. 2005;55: Collée G, Dijkmans, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (trochanteric bursitis) in low back pain. Scand J Rheumatol. 1991;20: Tortolani PJ, Carbone JJ, Quartararo LG. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome in patients referred to orthopedic spine specialists. Spine J. 2002;2: Collée G, Dijkmans, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. clinical epidemiological study in low back pain. Description of two clinical syndromes. r J Rheumatol. 1990;29: Radiol ras Jan/Fev;47(1):
Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome. Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton
 Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton Introduction The Iliotibial Band (IT Band) Thick strip of connective tissue connecting several muscles in the thigh The IT band stabilizes
Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton Introduction The Iliotibial Band (IT Band) Thick strip of connective tissue connecting several muscles in the thigh The IT band stabilizes
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings
 The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome
 2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section
 The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section of the femoral fascia (or fascia lata). The problem
The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section of the femoral fascia (or fascia lata). The problem
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology
 Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
Greater Trochanter: Anatomy and Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties:
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound Guided Steroid Injection
 Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 October; Vol. 26, No. 4: 387-391 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.387 Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound
Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 October; Vol. 26, No. 4: 387-391 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.387 Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
 Iliotibial Band Syndrome Definition and Home Stretches Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov Iliotibial Band: Definition The iliotibial band (ITB) is a dense fibrous band running from the lateral pelvis
Iliotibial Band Syndrome Definition and Home Stretches Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov Iliotibial Band: Definition The iliotibial band (ITB) is a dense fibrous band running from the lateral pelvis
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Technical Note. Arthroscopic Anatomy and Surgical Techniques for Peritrochanteric Space Disorders in the Hip
 Technical Note Arthroscopic Anatomy and Surgical Techniques for Peritrochanteric Space Disorders in the Hip James E. Voos, M.D., Jonas R. Rudzki, M.D., Michael K. Shindle, M.D., Hal Martin, D.O., and Bryan
Technical Note Arthroscopic Anatomy and Surgical Techniques for Peritrochanteric Space Disorders in the Hip James E. Voos, M.D., Jonas R. Rudzki, M.D., Michael K. Shindle, M.D., Hal Martin, D.O., and Bryan
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome
 Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Mikaela J. Mooney. Clinical Case Report Competition. West Coast College of Massage Therapy. New Westminster. First Place Winner
 Massage Therapists Association of British Columbia Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy New Westminster April 2014 First Place Winner Mikaela J. Mooney Is lengthening
Massage Therapists Association of British Columbia Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy New Westminster April 2014 First Place Winner Mikaela J. Mooney Is lengthening
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in. Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome. Aspiring Kid, PhD
 Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
Assessment of stretch effectiveness of the iliotibial tract in Ober and modified Ober
 Assessment of stretch effectiveness of the iliotibial tract in Ober and modified Ober maneuvers; an ultrasonographic study. Hsing-Kuo Wang, Jau-Yih Tsauo, Tiffany Ting-Fang Shih, Tyng-Guey Wang 1 Abstract
Assessment of stretch effectiveness of the iliotibial tract in Ober and modified Ober maneuvers; an ultrasonographic study. Hsing-Kuo Wang, Jau-Yih Tsauo, Tiffany Ting-Fang Shih, Tyng-Guey Wang 1 Abstract
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
 The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome A Capstone Project for PTY 768 Presented to the Faculty of the Physical Therapy Department Sage Graduate School
The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome A Capstone Project for PTY 768 Presented to the Faculty of the Physical Therapy Department Sage Graduate School
The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking
 1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
Move Well, Live Well Newsletter
 Move Well, Live Well Newsletter April 11, 2016 Volume 4, Number 4 In This Issue: Physical Therapy Improves Outcomes of Pelvic Surgery Iliotibial Band Pain in Runners: Is Inflammation the cause or a symptom?
Move Well, Live Well Newsletter April 11, 2016 Volume 4, Number 4 In This Issue: Physical Therapy Improves Outcomes of Pelvic Surgery Iliotibial Band Pain in Runners: Is Inflammation the cause or a symptom?
Iliotibial band revisited. The long and not-so-winding road...
 Iliotibial band revisited. The long and not-so-winding road... Poster No.: C-0992 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Burdiles, O. Contreras; Santiago/CL Keywords: Diagnostic procedure,
Iliotibial band revisited. The long and not-so-winding road... Poster No.: C-0992 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Burdiles, O. Contreras; Santiago/CL Keywords: Diagnostic procedure,
RECOVERING FROM ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME IN FEMALE RUNNERS
 RECOVERING FROM ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME IN FEMALE RUNNERS Huibri Schalkwyk November 2017 Course Date: 25 January 2017 Pretoria, South Africa This research paper addresses the benefits of an ongoing BASI
RECOVERING FROM ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME IN FEMALE RUNNERS Huibri Schalkwyk November 2017 Course Date: 25 January 2017 Pretoria, South Africa This research paper addresses the benefits of an ongoing BASI
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Strength and Stress Fractures
 Strength and Stress Fractures by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published Jan. 1, 2012 by Dynamic Chiropractor Magazine In any given year, more than one in five runners will sustain a stress fracture (1). In the
Strength and Stress Fractures by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published Jan. 1, 2012 by Dynamic Chiropractor Magazine In any given year, more than one in five runners will sustain a stress fracture (1). In the
The evaluation and management of patients with
 Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND EXAM OF THE HIP, GROIN AND THIGH Peter G Gerbino, MD, FACSM Orthopedic Surgeon Monterey Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Monterey, CA TPC, San Diego, 2017 The lecturer has no
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH
 ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
ANATOMY TEAM GLUTEAL REGION & BACK OF THIGH OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to identify and discuss: Contents of gluteal region: Groups of Glutei muscles and small muscles
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management
 Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management Rachael Mary McMillan Physiotherapist, Alphington Sports Medicine Clinic & FFA Australian Women s National Football Teams PhD Candidate
Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (GTPS): Assessment & Management Rachael Mary McMillan Physiotherapist, Alphington Sports Medicine Clinic & FFA Australian Women s National Football Teams PhD Candidate
The iliotibial (IT) tract,
 Use of an Inclinometer to Measure Flexibility of the Iliotibial Band Using the Ober Test and the Modified Ober Test: Differences in Magnitude and Reliability of Measurements Nancy B. Reese, PT, PhD 1 William
Use of an Inclinometer to Measure Flexibility of the Iliotibial Band Using the Ober Test and the Modified Ober Test: Differences in Magnitude and Reliability of Measurements Nancy B. Reese, PT, PhD 1 William
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip. Joseph H. Dimon
 Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
Hip joint and pelvic girdle. Lower Extremity. Pelvic Girdle 6/5/2017
 Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Muscles of Gluteal Region
 1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
1 The Gluteal Region In the gluteal region the skin is tough with many layers underneath. Directly under it is the superficial fascia followed by the deep fascia then the muscles and the bones of the thigh.
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
The Problem of Patellofemoral Pain. The Low Back Pain of the Lower Extremity. Objectives. Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA
 Mechanisms Underlying Patellofemoral Joint Pain: What have we learned over the last 20 years? Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory Objectives 1. Highlight recent research
Mechanisms Underlying Patellofemoral Joint Pain: What have we learned over the last 20 years? Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory Objectives 1. Highlight recent research
Evaluating hip pathology in trochanteric pain syndrome
 August 27, 2008 By Chris Dougherty, DO [1] and John J. Dougherty, DO [2] Patients may have greater trochanteric pain syndrome for years without knowing a defining cause or seeing pain improvement. Pathology
August 27, 2008 By Chris Dougherty, DO [1] and John J. Dougherty, DO [2] Patients may have greater trochanteric pain syndrome for years without knowing a defining cause or seeing pain improvement. Pathology
In comparison to anterior and lateral knee pain, chronic. Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain.
 [ Primary Care ] Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain William E. Bylund, BS,* and Kevin de Weber, MD Context: Semimembranosus tendinopathy (SMT) is an uncommon cause
[ Primary Care ] Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain William E. Bylund, BS,* and Kevin de Weber, MD Context: Semimembranosus tendinopathy (SMT) is an uncommon cause
Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle Does the Iliotibial Band Move? Elena J. Jelsing, MD, Jonathan T. Finnoff, DO, Andrea L. Cheville, MD, Bruce
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle Does the Iliotibial Band Move? Elena J. Jelsing, MD, Jonathan T. Finnoff, DO, Andrea L. Cheville, MD, Bruce
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY
 ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
Immediate effects of static stretching versus myofascial release in iliotibial band tight- ness in long distance runners-a randomised clinical trial
 Immediate effects of static stretching versus myofascial release in iliotibial band tight- ness in long distance runners-a randomised clinical trial A. Muragod 1, V.R.Patil 2, P. Nitsure 3 1Assistant Professor
Immediate effects of static stretching versus myofascial release in iliotibial band tight- ness in long distance runners-a randomised clinical trial A. Muragod 1, V.R.Patil 2, P. Nitsure 3 1Assistant Professor
Hip and Knee Approaches
 Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Hip and Knee Approaches Professor VLADIMIR STAVREV, MD, PhD, DMSc GEORGI MINEV MD DEPARTMENT OF ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY, MEDICAL UNIVERSITY -PLOVDIV Anterior View Hip Joint Posterior View - Hip Joint
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
HIP_CASE 2_OA. Hip Forces. Function of the Hip. Property of VOMPTI, LLC. For Use of Participants Only. No Use or Reproduction Without Consent 1
 HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
HIP_CASE 2_OA Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Eric Magrum DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT 62 yo female AM stiffness Hip pain diffuse, variable ant>lateral>post Gradual onset Tennis
Do Persons with PFP. PFJ Loading? Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle. Patellofemoral Pain: A Critical Review
 Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance Institute
Biomechanical Factors Contributing to Patellomoral Pain: The Dynamic Q Angle Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance Institute
River City Running Symposium Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy
 River City Running Symposium 2015 Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy A Brief History of my Running Career Then and... Now Common Running Injuries- Prevention and Treatment Jenelle
River City Running Symposium 2015 Jenelle Deatherage, PT, OCS Rock Valley Physical Therapy A Brief History of my Running Career Then and... Now Common Running Injuries- Prevention and Treatment Jenelle
Extraarticular Snapping Hip: Sonographic Findings
 Vincent Pelsser 1 Étienne Cardinal 1 Roger Hobden 2 enoit ubin 1 Michel Lafortune 1 Received September 22, 1999; accepted after revision June 8, 2000. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, CHUM-St-Luc
Vincent Pelsser 1 Étienne Cardinal 1 Roger Hobden 2 enoit ubin 1 Michel Lafortune 1 Received September 22, 1999; accepted after revision June 8, 2000. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, CHUM-St-Luc
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Trochanteric Bursitis After Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Trochanteric Bursitis After Total Hip Arthroplasty Incidence and Evaluation of Response to Treatment Kevin W. Farmer, MD, Lynne C. Jones, PhD, Kirstyn E.
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Trochanteric Bursitis After Total Hip Arthroplasty Incidence and Evaluation of Response to Treatment Kevin W. Farmer, MD, Lynne C. Jones, PhD, Kirstyn E.
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
DISCLOSURE. The contributing authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
 DISCLOSURE The contributing authors have no financial relationships to disclose. INTRODUCTION Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS); formerly trochanteric bursitis Common condition, wide differential
DISCLOSURE The contributing authors have no financial relationships to disclose. INTRODUCTION Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS); formerly trochanteric bursitis Common condition, wide differential
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies
 Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Non-arthritic anterior hip pain in the younger patient: examination and intervention strategies Melodie Kondratek, PT, DScPT, OMPT Bryan Kuhlman, PT, DPT, OMPT Oakland University Orthopedic Spine and Sports
Apophysis. Apophyseal Avulsion. Apophyseal avulsion injuries 3/2/2017
 Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
Apophysis 0 Differentiate from Epiphysis: The end of long bones which undergo endochondral ossification to produce longitudinal growth of the bones. i.e. growth plates 0 Apophysis refers to any eminence,
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Anterior knee pain.
 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology
 Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Downloaded from by on 12/22/17 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.205.8 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.205.8. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Pictorial Essay MR Imaging of the natomy of and Injuries
4/1/2016. Total Hip Arthroplasty. DAHR Procedure. Direct Anterior Hip Replacement. DAHR Procedure. DAHR Procedure
 Mercy Orthopedist Types of Approaches Total Hip Arthroplasty Mercy Has a total of 16 Orthopedist that perform all three different approaches Posterior Anterior Lateral Direct Anterior Direct Anterior Hip
Mercy Orthopedist Types of Approaches Total Hip Arthroplasty Mercy Has a total of 16 Orthopedist that perform all three different approaches Posterior Anterior Lateral Direct Anterior Direct Anterior Hip
Research Theme. Cal PT Fund Research Symposium 2015 Christopher Powers. Patellofemoral Pain to Pathology Continuum. Applied Movement System Research
 Evaluation and Treatment of Movement Dysfunction: A Biomechanical Approach Research Theme Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FAPTA Understanding injury mechanisms will lead to the development of more effective
Evaluation and Treatment of Movement Dysfunction: A Biomechanical Approach Research Theme Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FAPTA Understanding injury mechanisms will lead to the development of more effective
The effects of medial and lateral wedges on iliotibial band strain during overground running
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2015 The effects of medial and lateral wedges on iliotibial band strain during overground running Evan M. Day Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2015 The effects of medial and lateral wedges on iliotibial band strain during overground running Evan M. Day Iowa State University Follow this and additional
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents.
 Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Apophysiolysis of the pelvic area in adolescents. Poster No.: C-0077 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Derks, R. E. Westerbeek, R. Van Dijk; Deventer/NL Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
What This Is! What This Isn t! Insights Into Functional Training 5/27/15. #ideaworld. Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Thank you for coming!!!
 Insights Into Functional Training Insights Into Functional Training 2015 IDEA Health & Fitness Association. All Rights Reserved. www.ideafit.com/world P R E S E N T E D B Y Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Human Motion
Insights Into Functional Training Insights Into Functional Training 2015 IDEA Health & Fitness Association. All Rights Reserved. www.ideafit.com/world P R E S E N T E D B Y Chuck Wolf, MS, FAFS Human Motion
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know
 Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
Imaging in Groin Pain What the Team Physician Needs to Know Üstün Aydıngöz, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara, Turkey ustunaydingoz@yahoo.com No conflicts of interest
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems
 Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
Evaluation of Gait Mechanics Using Computerized Plantar Surface Pressure Analysis and it s Relation to Common Musculoskeletal Problems Laws of Physics effecting gait Ground Reaction Forces Friction Stored
Dynamic Stabilization of the Patellofemoral Joint: Stabilization from above & below
 Dynamic Stabilization of the Patellofemoral Joint: Stabilization from above & below Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance
Dynamic Stabilization of the Patellofemoral Joint: Stabilization from above & below Division Biokinesiology & Physical Therapy Co Director, oratory University of Southern California Movement Performance
5/14/2013. Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury:
 Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
Snapping Hip and Impingement
 Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Mohammad Ashraf. Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 - 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
- 7 Mohammad Ashraf Abdulrahman Al-Hanbali Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Structures under the cover of Gluteus Maximus: 1-Bones: Ileum, Femur (Head, greater trochanter and gluteal tuberosity), Ischium (ischial
Running Injuries. Lower Extremity
 Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
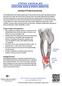 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Hip Arthroscopy Indications and Latest Techniques
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hip-arthroscopy-indications-and-latesttechniques/3801/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hip-arthroscopy-indications-and-latesttechniques/3801/
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Gluteus Medius facilitation using Kinesio Taping in the Treatment of Chronic Iliotibial Band Syndrome
 Gluteus Medius facilitation using Kinesio Taping in the Treatment of Chronic Iliotibial Band Syndrome Abstract: Objective: To determine whether Kinesio Taping (KT) can effectively facilitate Gluteus Medius
Gluteus Medius facilitation using Kinesio Taping in the Treatment of Chronic Iliotibial Band Syndrome Abstract: Objective: To determine whether Kinesio Taping (KT) can effectively facilitate Gluteus Medius
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
