Objectives. Principles of Neurodynamics. Objectives. Foundations of Anatomy. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Structure Meets Function
|
|
|
- Jacob Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Neurodynamics Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT With contributions from: Leslie Nelson, PT Objectives Participant will review the relevant anatomy and function of the peripheral, central, and autonomic nervous systems Participant will describe the intraneural and extraneural factors contributing to nerve injury Objectives Participant will describe the tension points in the body where pathology is most likely to occur Participant will review a system of examination for adverse neural tension Foundations of Anatomy Continuous tissue tract Connective tissue interconnected Electrically interconnected neurons Chemical consistency Neurotransmitters Cytoplasm Structure Meets Function Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Accommodation of body movements Meninges (Endo, peri, epi)-neurium Impulse conduction Axons Myelin Axon Run undulatory course in endoneurial tubes Myelin
2 Peripheral Nervous System Diagram of Connective tissue coverings Central Nervous System Nerve roots Undulations Dural and epidural meninges Extrathecal attachments (low cervical, LS) Plugging by dorsal root ganglion Central Nervous System Spinal cord Undulations Movement in relation to neighboring vertebral segments Meninges Pia and arachnoid mater Dura mater Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic trunk and ganglia Pre-ganglionic neurons Head and neck C8-T5 UE T2-T10 LE T10-L2 Post-ganglionic neurons Efferent to smooth muscle and glands Intraneural Causes of ANT Vascular considerations Decreased blood supply to nervous system Disruptions in axonal transport Nociceptive stimulation of connective tissue coverings of nervous system 2% of body mass consumes 20% of available Oxygen CNS: Critical vascular zone exists from T4-T9 Narrow spinal canal PNS: Arrest of blood flow at 8% elongation, complete at 15%
3 Axonal transport systems Two-way movement of materials and substances in the cytoplasm Double crush Innervation of Connective Tissue Meninges Dura mater highly innervated ventrally Arachnoid/pia mater innervation uncertain (Endo, peri, epi)-neurium Intrinsic innervation Free nerve endings Extraneural Causes of ANT Intraneural versus Extraneural Symptom & Sign Differentiation Mechanical Interface Spinal foramen Muscle/fascia Joint Ligament Blood vessel Description of symptoms Physical signs Extraneural Catches, twinges around vulnerable areas Comparable signs with movement of interfacing structure Intraneural (Conducting) Burning, tingling, electric in innervation field Neurological signs and symptoms; palpation refers sx elsewhere; increased sx with tension testing Intraneural (Connective) Lines of pain, along trunks, nondermatomal Palpation elicits local pain; increased sx with tension testing Sites of Injury Tunnels Soft tissue, osseus or fibro-osseus tunnels Where the nervous system branches Where the system is relatively fixed Where the nerves pass over unyielding interfaces Tension points Median nerve in carpal tunnel Spinal nerve in intervertebral foramen Posterior interosseus nerve in arcade of Frohse
4 Branches Union of lateral and medial plantar nerves to form the common plantar digital nerve Fixed System Common peroneal nerve at head of fibula Dura mater at L4 Radial nerve to the head of radius Suprascapular nerve in scapular notch Unyielding Surface Cords of plexus over first rib Radial nerve in radial groove of humerus Dural sleeve at pedicles Unyielding Surfaces (continued) Greater occipital nerve through fascia Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve through fascia Nerves in feet through plantar fascia Tension Points Key points in the body where movement demands (and tension) are increased C6 T6 L4 Tibial nerve at posterior knee Median nerve at anterior elbow Neurodynamic Examination Tension testing Longitudinal deformation Elasticity intraneural Elasticity extraneural Palpation Perpendicular deformation Neurological testing
5 Tension Testing Palpation ULTT1 SLR Palpate nerves under tension Final thoughts The interconnectedness of the nervous system must be considered when evaluating and treating patients with adverse neural tension. These patients are often misdiagnosed, so check for adverse neural tension when treatment is not progressing as planned. Thank You
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 11: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed,
Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Classification of the nervous system. Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 2
 1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves mediate reactions to environmental changes. B. The spinal cord has several functions. 1. It processes reflexes. 2. It is
Chapter 13! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
With other members of your lab group, discuss the following questions: - The spinal cord connects directly to which part of the brain?
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ************************************************************************************************************************* SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, AND REFLEXES
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
The Nervous System PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System
 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System 50a A&P: Nervous System -! Peripheral Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:"
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System. DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy
 The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
The functional Anatomy of the Nervous System DR. OKSANA PETRICHKO Department of Human Anatomy Coordination and Regulation of Body Systems Nervous system. Conducts nerve impulses maintaining homeostasis
CNS & PNS Entrapment. Disclosure - Nothing
 Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
The Nervous System: The
 C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD
 THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
THE BACK THE SPINAL CORD The structures in the vertebral canal: the spinal cord spinal nerve roots spinal meninges the neurovascular structures THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord occupies the superior 2/3
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. C1. Cervical spinal ner ves. Thor acic. T12 Spinal nerve rootlets
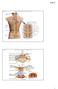 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlar gem ent C7 Cervical spinal ner ves Dural sheath Subarachnoi d space Thor acic spinal ner ves Vertebra (cut) Lum bar enlar gem ent Medullar y T12 rootlets cone Posterior median
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapters 12 and 13 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a function of the nervous system? A) sense the internal and external environments B) integrate sensory
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy. Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT
 Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical i l Orthopedic Rehabilitation ti Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to thoracic pain of red flag origin Discuss concepts
Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical i l Orthopedic Rehabilitation ti Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to thoracic pain of red flag origin Discuss concepts
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Nervous System. Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves
 Nervous System Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves neurology - study of the nervous system - nervous system and endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis - More than 80 major nerves and billions
Nervous System Overview, Tissues and Spinal Nerves neurology - study of the nervous system - nervous system and endocrine system work together to maintain homeostasis - More than 80 major nerves and billions
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy. Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT
 Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical i l Orthopedic Rehabilitation ti Education 1 Objectives Discuss red flag signs for the thoracic region Apply key concepts from the
Thoracic Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical i l Orthopedic Rehabilitation ti Education 1 Objectives Discuss red flag signs for the thoracic region Apply key concepts from the
Spinal Cord Protection. Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. External Anatomy of Spinal Cord. Structures Covering the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
Spinal Cord Protection Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves We are only going to cover Pages 420-434 and 447 Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Anatomy & Physiology (Part 2)
 Overview Endocrine System Skeletal System Muscle System Nervous System Endocrine System A system of glands & organs which produce hormones that biologically alter the function of the body Endocrine System
Overview Endocrine System Skeletal System Muscle System Nervous System Endocrine System A system of glands & organs which produce hormones that biologically alter the function of the body Endocrine System
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System. Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D.
 Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Early Development of Neural Tube Development of Medulla Spinalis and Peripheral Nervous System Assoc.Prof. E.Elif Güzel, M.D. Third week of Embryogenesis Primitive streak/pit appears on the epiblast (day
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
 Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
Link download :https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forfundamentals-of-anatomy-and-physiology-9th-edition-by-martini TEST BANK FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 9TH EDITION BY MARTINI
ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD. Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Structure of the spinal cord Tracts of the spinal cord Spinal cord syndromes The Nervous System Coordinates the activity of muscles, organs, senses, and actions Made
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar ** I did my best and sorry for any mistake ** the sheet does not contain pictures, tables and some slides so please be careful and go back to slides
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
HEAD AND NECK PART 2
 HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
Demonstrate the bony features of Cl and C2 vertebrae evident on this Xray
 SUBJECT: ANATOMY 7 September 2007 am. TOPIC: X-ray: Lateral C spine NUMBER: JL Demonstrate the bony features of Cl and C2 vertebrae evident on this Xray 1 Odontoid peg (dens) 2 Bodies of Cl andc2 3 anterior
SUBJECT: ANATOMY 7 September 2007 am. TOPIC: X-ray: Lateral C spine NUMBER: JL Demonstrate the bony features of Cl and C2 vertebrae evident on this Xray 1 Odontoid peg (dens) 2 Bodies of Cl andc2 3 anterior
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
