Spine Trauma- Part B
|
|
|
- Brandon Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spine Trauma- Part B
2 Cervical Spine Injuries Atlanto- Occipital Dislocation Hyperextension and distraction mechanism Down s syndrome, RA more susceptible Asymmetric lateral masses on odontoid view Widened predens space Treatment- Often fatal Highly unstable If not fatal avoid traction, definitive fusion occiput to C1
3 Atlanto-axial Dislocation Hyperextension injury Children>adults Head slips forward on C1 Usually fatal
4 Atlas Fractures Neural Arch Fracture of C1 Most common fracture of C1 Hyperextension injury Not associated with neurologic deficit May be confused with congenital anomaly
5 Atlas Fractures Jefferson fracture Burst fracture of atlas (C1) Usually bilateral breaks in ant/ post arches Vertical compression/ axial load injury Widened lateral masses of C1 on open-mouth odontoid view Widened predens space Moderately unstable Neuro deficits uncommon Associated with: Fractures of C7 (25%) Fractures of C2 pedicle (15%) Extraspinal fractures (58%)
6 Transverse Ligament Ruptures May occur alone or with fracture atlas or atlantoaxial subluxation Transverse lig is the main restraint to ant motion of C1 Mechanism- due to flexion Widening of normal distance between ant ring of atlas and dens less than 3mm Unstable
7 Axis Fractures Incidence: 6% of cervical spine fractures Associated with atlas fractures in 8% Hyperextension Often forward subluxation of C1 on C2 Odontoid fracture Type I Avulsion of tip of odontoid (5-8%) Difficult to detect; required CT Type II Fracture through base of dens (54-67%) Complication: nonunion Type III Subdental injury (30-33%) Prognosis: good
8 Hangman s Fracture Most common fracture of C2 Bilateral fracture of pedicles of axis (C2) Anterior slip of C2 on C3 Mechanism: Sudden deceleration with hyperextension May or may not have anterior subluxation Unstable Neuro deficits variable Teardrop fracture of inferior aspect of C2 or C3 is clue
9 Tear Drop Fracture Avulsion of antero-inferior corner of cervical vertebral body by anterior ligament Most severe and unstable injury of the C-spine Mechanism: may be secondary to hyperflexion or hyperextension sudden, forceful flexion Often the result of diving into shallow water Typically at C2 Unstable with ligamentous instability Remainder of body displaced backward into spinal canal Facet joint and interspinous distances usually widened Disk space may be narrowed Neuro deficit in up to 70%
10 Teardrop
11 Teardrop
12 Compression Fracture Flexion injury Anterior wedging of 3mm or more suggests fracture Usually involves superior endplate of vertebral body
13 Unilateral facet dislocation Mechanism: flexion, combined flexion/ rotation Anterior dislocation of one vertebral body by 25-30% on lateral view Stable if anterior displacement on lateral less than ½ width of VB Only 30% associated with neurologic defect
14 Unilateral facet dislocation AP view-disruption of spinous process line Oblique- disruption of the tilting of the lamina Superior articulating facet impinges in neural foramina
15 Unilateral Facet Dislocation AP view- spinous processes of the vertebrae above the dislocation displaced towards the side of the dislocated facet
16 Unilateral Facet Dislocation Bowtie Sign
17 Bilateral Facet Dislocation Mechanism: flexion, combined flexion/ rotation Anterior dislocation of one vertebral body by 50% on lateral view Unstable Neurologic deficits common Seen in up to 85%
18 Bilateral Facet Dislocation
19 Clay Shoveler s Fracture Avulsion fracture of posterior spinous process of C7 or T1 Mechanism: sudden load on a flexed spine or secondary to rotational injury Shoveling snow, clay Very stable
20 Clay Shoveler s Fracture
21 Cervical Spine Fracture Stability Failure of middle column bony structures indicated by- Wide pedicles More than 25% loss of post body ht Fracture lines through post body cortex Failure of middle column ligamentous structures indicated by- Interspinous or intervertebral angulation 11 deg more than than adjacent segment Horizontal translation more than 3.5 mm Intervertebral disc space separation more than 1.7 mm
22 Cervical Ligamentous Injury Mechanism is flexion/distraction Clues to diagnosis Disk space narrower anteriorly than posteriorly Widening of the interspinous distance Widening of the facet joint Usually the posterior aspect
23 Thoracic Spine Rigid Spinal canal narrower than cervical or lumbar spine Large spinal cord diameter relative to canal diameter increases the risk of cord injury Injury, usually significant (complete), less common than in other regions Association between fractures of the thoracic spine and severe pulmonary injuries,mediastinal hemorrhage
24 Thoracic Spine Fractures
25 Thoracic Spine Injuries Compression fracture Injury to anterior column due to anterior or lateral flexion Middle, posterior column remains intact X-ray - decreased height anterior vertebral body, post body ht normal Amount of ant compression usually less than 40% of post body height Clinically - stable, cord injury rare
26 Thoracic Compression Fracture Unstable if: Loss of vertebral ht > 50% Angulation more than 20 deg Multiple adjacent compression fractures
27 Thoracic Spine Injuries Burst Disruption of the middle column Mechanism- axial loading Varying degrees of retropulsion into the neural canal X-ray- spreading of post elements If post elements involved- 50% have neuro injury Neurologic injury more common in: Loss of vertebral ht > 50% Angulation > 20 deg Canal compromise more than 40%
28 Lumbar Spine 1. Vertebral body 2. Spinal cord 3. Conus medullaris 4. Intervertebral disc 5. Filum terminale 6. Subarachnoid space
29 Lumbar Spine Fractures Thoracolumbar spine and lumbar spine are the most common sites for fractures due to the high mobility of the lumbar spine compared to the more rigid thoracic spine Injury to the cord or cauda equina occurs in approximately 10-38% of adult thoracolumbar fractures and in as many as 50-60% of fracture dislocations. Most occur in people younger than 30 years Nearly 60% of patients have serious disabling deficits Etiology- 40% caused by motor vehicle accidents, 20% by falls, and 40% by gunshot wounds, sporting accidents, industrial accidents, and farming accidents
30 Lumbar Spine Injury Lower lumbar spine is the most mobile Isolated fractures of the lower lumbar spine rarely result in complete neurologic injuries Injuries usually complete cauda equina lesions or isolated nerve root injuries
31 Sacro-coccygeal Injuries Sacral spine, nerve root injuries unusual Frequently associated with fractures of the pelvis Transverse fx through the body are most significant May cause injury to part or all of the cauda equina If there is involvement of the central sacral canal, however, bowel or bladder dysfunction may also occur Longitudinal fx may cause radiculopathy Rectal examination to assess anal sphincter tone and the bulbocavernosus reflex Often associated with fractures of the pelvis
32 Sacral Fractures
33 Sacral Fractures
34 Sacro-coccygeal Injuries Careful neurologic evaluation is essential Rectal examination will assess anal sphincter tone and the bulbocavernosus reflex Patients with complete damage to the sacral portion of the cord Loss of control of bowel and bladder function Paralysis of the lower extremities with preservation of some movement of the hips and knees and preserved knee jerks and sensation in the lumbar dermatomes.
35 Sacro-coccygeal Injuries Coccygeal injuries are usually associated with direct falls onto the buttocks Diagnosis of fracture is made on rectal exam Pain with of the coccyx X- rays are not needed Rarely a bony injury Treatment symptomatic Analgesics, rubber doughnut pillow
36 Penetrating Spine Trauma Majority caused by gunshot wounds. Most gunshot wounds result in stable vertebral injuries Cord lesions are often complete. Stabbing injuries are much less common Prognosis better than similar paralysis with GSW Majority of stab wounds involve incomplete Brown- Séquard lesions of the thoracic cord Best prognosis of incomplete spinal injuries
37 Penetrating Injuries Most vertebral injuries to the spine following penetrating trauma are stable and require only symptomatic treatment Progressive neurologic deficits warrant surgical decompression Bullet removal controversial in patients with stable cervical and thoracic spinal cord lesions Bullet removal from the thoracolumbar spine improved motor recovery in both complete and incomplete injuries
38 Anterior Cord Syndrome Flexion compression of anterior cord or ischemia to anterior spinal artery Motor paralysis, loss of pain and temperature distal to the lesion Posterior columns spared Light touch, motion, vibration, gross proprioception preserved Prognosis poor
39 Central Cord Syndrome Hyperextension injury in older patients, spondylosis, cervical stenosis Buckling of ligamentum flavum into cord during extension Partial cord syndrome Weakness greatest in hands Greater in arms than legs Variable sensory sensory and bladder involvement Treatment usually nonoperative with relatively good prognosis
40 Brown Sequard Syndrome Injury to one side of the cord Usually penetrating wound, hematoma, lateral disk Ipsilateral paralysis, loss of proprioception and vibratory sense Contralateral loss of pain and temperature Prognosis good
41 Cauda Equina Syndrome Cauda equina Composed of lumbar, sacral, coccygeal nerve roots Peripheral nerve injury rather than a spinal cord injury cord Symptoms Variable motor and sensory loss in the lower extremities Sciatica Bowel and bladder dysfunction Saddle anesthesia Loss of pain sensation over the perineum Prognosis for recovery better than spinal cord lesions
42 Pediatric Spine Injury Pediatric spine has increased mobility Laxity of the interspinous ligaments and joint capsules Horizontal orientation of facet joints, incompletely ossified wedge-shaped vertebrae Underdeveloped neck, paraspinous muscles Spinal injury occur less commonly in the pediatric population Usually secondary to mechanisms involving considerable force High degree of neurologic compromise at presentation
43 SCIWORA Spinal cord stretching leads to neuronal injury or even complete severing of the cord Accounts for up to 70 % of peds SC cord injuries Most common in kids < 8 years Paralysis may be present on arrival Up to 30 % have a delayed onset of neurologic abnormalities May not occur until up to 4-5 days after injury Many have neurologic symptoms at the time of the injury, such as paresthesias or weakness, that have subsequently resolved
44 SCIWORA Most have a complete recovery Especially if the onset is delayed MRI defines cord anatomy, helps prognosticate
45 Treatment Airway Chin lift, in-line immobilization, cricoid pressure, RSI Patient with an injury at C5 or above should be intubated
46 Hemodynamic Spinal Shock Seen with cervical or thoracic cord injury Relative hypotension due to the sudden loss of sympathetic tone below the level of the lesion Warm, dry skin and normal capillary refill, paradoxical bradycardia Must exclude blood loss Concurrent in 30% blunt trauma, 90% penetrating lesions Treat with direct acting pressors Norepinephrine > dopamine
47 Spinal Shock Partial or complete injury Typically at the T 6 level or above Temporary block of ascending/ descending communication past injured cord segment Clinical signs Areflexia, loss of sensation, flaccid paralysis below level of lesion Loss of rectal tone Bradycardia,hypotension Priapism implies a complete spinal cord injury
48 Spinal Shock Traumatic spine lesions not complete until spinal shock has resolved Lasts variable amount of time- typically ~ 24 hours Bulbocavernosus first reflex to return Elicited when squeezing or tugging on the glans penis with reflex contraction of the anal sphincter Cremasteric reflex suggests some spinal cord integrity Tested by running a pin/ blunt instrument up medial thigh with scrotum rising in response Anal wink reflex suggests some sacral sparing Tested by touching skin around anus with a pin with reflex wink (contracture of anal sphincter)
49 Treatment Methylprednisolone Load with 30 mg/kg as a bolus, followed by a continuous drip of 5.4 mg/kg/hour for the subsequent 23 hours Shown to lead to a statistically significant improvement in blunt trauma in neurologic outcome Not studied in penetrating trauma Resulted in improvement of both motor and sensory function in complete and incomplete lesions
50 Conclusion Cervical spine CT in Elderly with degenerative disease Neuro deficits Concurrent severe head injury MRI in GCS <8, ICH Suspected cord injury, especially children
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services OBJECTIVES DEFINITION 11/8/2017. Identify SCIWORA.
 SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Outline. Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures
 C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
Sir William Asher ANATOMY
 SPINAL CORD INJURY BASICS RELATED TO LIFE CARE PLANNING Lesson 1 Sir William Asher Picture the pathetic patient lying long abed, the urine leaking from his distended bladder, the lime draining from his
SPINAL CORD INJURY BASICS RELATED TO LIFE CARE PLANNING Lesson 1 Sir William Asher Picture the pathetic patient lying long abed, the urine leaking from his distended bladder, the lime draining from his
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Spinal Trauma. Dr T G Kruger
 Spinal Trauma Dr T G Kruger Epidemiology Spine injury in 6% of trauma patients Multiple levels involved in 20% of cases 80% of spinal cord injury patients have concurrent other system injuries 41% have
Spinal Trauma Dr T G Kruger Epidemiology Spine injury in 6% of trauma patients Multiple levels involved in 20% of cases 80% of spinal cord injury patients have concurrent other system injuries 41% have
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification Mark L Prasarn MD University of Texas Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Houston, Texas Updated 7/2016 Anatomy of the Spine
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification Mark L Prasarn MD University of Texas Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Houston, Texas Updated 7/2016 Anatomy of the Spine
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
SPECIFIC CATEGORIES OF INJURIES
 Página 1 de 20 Copyright 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Hickey, Joanne V. Clinical Practice of Neurological & Neurosurgical Nursing, 5th Edition SPECIFIC CATEGORIES OF INJURIES Part of "Chapter 19
Página 1 de 20 Copyright 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Hickey, Joanne V. Clinical Practice of Neurological & Neurosurgical Nursing, 5th Edition SPECIFIC CATEGORIES OF INJURIES Part of "Chapter 19
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 EPC Ch 24 Quiz w-key Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following best explains the presentation and prognosis of
EPC Ch 24 Quiz w-key Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following best explains the presentation and prognosis of
Thorasic and lumbar spinal injury. Dr.Abrisham
 Thorasic and lumbar spinal injury Dr.Abrisham Goal : alignment Stability Preserve neuologic function early mobilization Incidence: most site is thoraco lumbar 50% T 11 to L 1 30% L 2 to L 5 Motor vehicle
Thorasic and lumbar spinal injury Dr.Abrisham Goal : alignment Stability Preserve neuologic function early mobilization Incidence: most site is thoraco lumbar 50% T 11 to L 1 30% L 2 to L 5 Motor vehicle
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Acute spinal cord injury
 Acute spinal cord injury Thakul Oearsakul Songklanagarind hospital Hat Yai Songkhla Introduction New SCI 10000-12000 cases Approximately 4.0-5.3 per 100000 population Common causes of traumatic SCI :Motor
Acute spinal cord injury Thakul Oearsakul Songklanagarind hospital Hat Yai Songkhla Introduction New SCI 10000-12000 cases Approximately 4.0-5.3 per 100000 population Common causes of traumatic SCI :Motor
Surgery. Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes. Anatomy. See online here
 Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine. Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation
 Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Chapter 24 Spinal Trauma Introduction to Spinal Injuries (1 of 2) Annually 15,000 permanent spinal cord injuries Commonly men years old
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 24 Spinal Trauma Introduction to Spinal Injuries (1 of 2) Annually 15,000 permanent spinal cord injuries Commonly men 16-30 years old Mechanism of Injury: Vehicle crashes: 48% : 21%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 24 Spinal Trauma Introduction to Spinal Injuries (1 of 2) Annually 15,000 permanent spinal cord injuries Commonly men 16-30 years old Mechanism of Injury: Vehicle crashes: 48% : 21%
The craniocervical junction
 Anver Jameel, MD The craniocervical junction A biomechanical and anatomical unit that extends from the skull base to C2 Includes the clivus, foramen magnum and contiguous occipital bone, the occipital
Anver Jameel, MD The craniocervical junction A biomechanical and anatomical unit that extends from the skull base to C2 Includes the clivus, foramen magnum and contiguous occipital bone, the occipital
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
SPINAL CORD INJURY-GSW
 SPINAL CORD INJURY-GSW Wayne Cheng, MD Bones and Spine 1 EPIDEMIOLOGY-mechanism Most common cause of traumatic cord inj.: #1 MVA (45%) #2 Fall (22%) #3 Violence (16%) #4 Sports (13%) After 1990, Gsw now
SPINAL CORD INJURY-GSW Wayne Cheng, MD Bones and Spine 1 EPIDEMIOLOGY-mechanism Most common cause of traumatic cord inj.: #1 MVA (45%) #2 Fall (22%) #3 Violence (16%) #4 Sports (13%) After 1990, Gsw now
Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines
 6/15/2018 Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines Benjamin Oshlag, MD, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor of Sports Medicine Columbia University Medical Center Nothing to Disclose
6/15/2018 Cervical Spine Injury Guidelines Benjamin Oshlag, MD, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor of Sports Medicine Columbia University Medical Center Nothing to Disclose
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Imaging of Trauma to the Spine. Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic
 Imaging of Trauma to the Spine Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Jefferson Fracture Yee, LL: The Jefferson Fracture, Radiology Cases in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
Imaging of Trauma to the Spine Orthopedic Diplomate Program University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Jefferson Fracture Yee, LL: The Jefferson Fracture, Radiology Cases in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES
 AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
MDCT and MRI evaluation of cervical spine trauma
 Insights Imaging (2014) 5:67 75 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0304-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW MDCT and MRI evaluation of cervical spine trauma Michael Utz & Shadab Khan & Daniel O Connor & Stephen Meyers Received: 10
Insights Imaging (2014) 5:67 75 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0304-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW MDCT and MRI evaluation of cervical spine trauma Michael Utz & Shadab Khan & Daniel O Connor & Stephen Meyers Received: 10
3/10/17 Spinal a Injury 1
 Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Spinal Injury 1 'Paralysed' Watmough vows he'll have the backbone for Game Two after treatment for neck injury Watmough will have cortisone injected into his spine this morning to speed up the recovery
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
256 Spinal Cord Injuries
 Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2004 McGraw-Hill Tintinalli, Judith E., Kelen, Gabor D., Stapczynski, J. Stephan Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 6th Edition 256 Spinal Cord Injuries Bonny J.
Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2004 McGraw-Hill Tintinalli, Judith E., Kelen, Gabor D., Stapczynski, J. Stephan Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 6th Edition 256 Spinal Cord Injuries Bonny J.
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
1/15/2012. Cervical Spine Trauma. Who to Image. Who to Image. Who to Image. Who to Image. Trauma Cx Spine Protocols NEXUS. CCR and Nexus CCR CCR
 Trauma Cx Spine Protocols Cervical Spine Trauma Issues The clinically negative Cx-spine Does everyone need a CT Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of
Trauma Cx Spine Protocols Cervical Spine Trauma Issues The clinically negative Cx-spine Does everyone need a CT Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma C Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology and Adjunct Professor of Health Services University of Washington, Harborview Medical Center Salary support: AHRQ grant
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma C Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology and Adjunct Professor of Health Services University of Washington, Harborview Medical Center Salary support: AHRQ grant
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
3/3/2016. International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI)
 International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
International Standards for the Neurologic Classification of Spinal Cord Injury (ISNCSCI) American Spinal Injury Association International Spinal Cord Society Presented by Adam Stein, MD Chairman and Professor
Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms.
 RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc. Copyright 2014, 2011, 2006 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc.
 Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
Spinal Cord Injury Transection Injury, Spinal Shock, and Hermiated Disc 1 Spinal Cord Injury Results from fracture and/or dislocation of vertebrae // Compresses, stretches, or tears spinal cord Cervical
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients
 Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
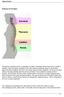 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
PREPARED FOR. Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016. REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr.
 Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
Accent on Health Chiropractic 405 Firemans Ave PREPARED FOR Marsha Eichhorn DATE OF INJURY : N/A DATE OF ANALYSIS : 12/14/2016 DATE OF IMAGES : 12/8/2016 REFERRING DOCTOR : Dr. David Bohn This report contains
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE
 The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery Diagnosis/Imaging/Surgery of Lumbar Spine Disorders Objectives Identify the most common
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery Diagnosis/Imaging/Surgery of Lumbar Spine Disorders Objectives Identify the most common
SCI EXAM & FUNCTIONAL PROGNOSIS
 SCI EXAM & FUNCTIONAL PROGNOSIS MARCH 20, 2015 JUAN L ASANZA, MD STAFF PHYSICIAN VA PUGET SOUND HEALTH CARE SYSTEM SPINAL CORD INJURY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON PHYSICAL MEDICINE & REHABILITATION OBJECTIVES
SCI EXAM & FUNCTIONAL PROGNOSIS MARCH 20, 2015 JUAN L ASANZA, MD STAFF PHYSICIAN VA PUGET SOUND HEALTH CARE SYSTEM SPINAL CORD INJURY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON PHYSICAL MEDICINE & REHABILITATION OBJECTIVES
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Cervical Spine Trauma 2016 Nordic Trauma Society
 Cervical Spine Trauma 2016 Nordic Trauma Society Stuart E. Mirvis. M.D., FACR Department of Radiology and Maryland Shock-Trauma Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Topics to Review Definition
Cervical Spine Trauma 2016 Nordic Trauma Society Stuart E. Mirvis. M.D., FACR Department of Radiology and Maryland Shock-Trauma Center University of Maryland School of Medicine Topics to Review Definition
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
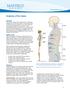 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018
 EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries
 Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position
 275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
275 Anterior Cervical Subluxation: An Unstable Position, 1 A. T. Scher1 The radioiogic signs of cervical anterior subluxation are subtle. Even when recognized, the injury may not be considered significant.
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Chapter 20: The Spine The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
The Positive Findings In Neck Injuries. American Journal of Orthopedics. August-September, 1964, pp
 The Positive Findings In Neck Injuries 1 American Journal of Orthopedics August-September, 1964, pp. 178-187 Ruth Jackson, MD This author analyzed 5,000 patients with disorders and found the following:
The Positive Findings In Neck Injuries 1 American Journal of Orthopedics August-September, 1964, pp. 178-187 Ruth Jackson, MD This author analyzed 5,000 patients with disorders and found the following:
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
The Spine.
 The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
HIGH LEVEL - Science
 Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Thoracolumbar spine trauma classifications: evolution or more confusion
 Thoracolumbar spine trauma classifications: evolution or more confusion Poster No.: C-1713 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Salazar, J. Halaburda Berni, C. Torrents, L. Casas;
Thoracolumbar spine trauma classifications: evolution or more confusion Poster No.: C-1713 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. P. Salazar, J. Halaburda Berni, C. Torrents, L. Casas;
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
Physical and Radiographic Examination of the Spine
 Physical and Radiographic Examination of the Spine Christopher M. Bono, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Boston University School of Medicine, Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA
Physical and Radiographic Examination of the Spine Christopher M. Bono, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Boston University School of Medicine, Boston Medical Center, Boston, MA
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
Anatomy of the Nervous System. Brain Components
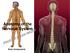 Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Anatomy of the Nervous System Brain Components NERVOUS SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Is the master system of human body, controlling the functions of rest of the body systems Nervous System CLASSIFICATION A. Anatomical
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State
 Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11
 Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11 Anatomy Spinal column Vertebrae Cervical (7) convex anteriorly Thoracic (12) concave anteriorly Lumbar (5) convex anteriorly Sacral (5 fused) concave
Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11 Anatomy Spinal column Vertebrae Cervical (7) convex anteriorly Thoracic (12) concave anteriorly Lumbar (5) convex anteriorly Sacral (5 fused) concave
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
BACK PAIN. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine
 NAME OF PATIENT: CASE STUDY 4 DATE OF REPORT: DATE OF EXAMINATION: REFERRING PHYSICIAN: TESTING FACILITY: Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine 1. In the neutral lateral projection: Shows reversal of the
NAME OF PATIENT: CASE STUDY 4 DATE OF REPORT: DATE OF EXAMINATION: REFERRING PHYSICIAN: TESTING FACILITY: Digital Motion X-ray Cervical Spine 1. In the neutral lateral projection: Shows reversal of the
Orthopadic cors. Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis)
 Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
