Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology
|
|
|
- Randolph Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology Rajan Patel, MD Director, Pediatric Neuroimaging Assistant Professor, Division of Neuroradiology
2 DISCLOSURE No financial disclosure.
3 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Overview of different imaging modalities in Pediatric Neuroradiology To learn the basic differences in CT & MRI of the Brain in Pediatrics as compare to adults. Brief discussion of role of imaging in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy(HIE), Seizure, Metabolic Disorders
4 IMAGING MODALITIES USG: Brain: Evaluate for IVH, hydrocephalus for preterm and newborn (<6 months) Spine: Spinal Dysraphism, concern for tethered cord CT: Brain: Screening exam in acute setting/er with neurological deficit, Trauma, suspected child abuse MR: Neurological deficit, Developmental delay, Suspected congenital abnormality, Metabolic Disorders.
5 Head Ultrasound Why? No radiation Can be performed at bed-side Non-invasive Requires no sedations Relatively inexpensive No contraindications
6 Head Ultrasound - Limitations Operator dependent Age of child Can t be performed once anterior fontanelle closed. Limited evaluation for early parenchymal abnormalities
7 Head Ultrasound - Indications Germinal matrix hemorrhage - Preterm infants Periventricular Leukomalacia (PVL) Macrocephaly Follow up hydrocephalus Concern for presence of vascular anomalies Vein of Galen Malformation
8 Watershed Zones: Pre-term Vs. Full term Penetrating arteries that arise from the surface of the brain and extend toward lateral ventricles. Lack of collaterals. Pre-Term Full Term Vessels start to grow from the lateral ventricles outward toward the surface. Moves the watershed area more peripherally. Difficulty with auto regulation in response to hypoxia or ischemia. Chao, C. et al. Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy: Multimodality Imaging Findings. RadioGraphics 2006.
9 Patterns of brain injury in HIE Mild to moderate HIE: Blood flow is shunted from the watershed areas to the more hypervascular areas of the brain including the basal ganglia, thalamus, brainstem. Classic periventricular WM findings in preterm and deep WM in full term. Severe HIE: Deep brain structures such as basal ganglia involvement.
10 HIE in the Pre-term Neuroimaging findings of the HIE depend on the severity of the insult: Mild to moderate HIE: Germinal matrix hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) Periventricular Leukomalacia (PVL) Severe HIE: Injuries involving the deep gray matter structures (basal ganglia) or brainstem, which are similar to findings of HII in term infants Huang BY, Castillo M. Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury: Imaging Findings from Birth to Adulthood. Radiographics 2008
11 Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage and IVH Sagittal Coronal Grade I: Hemorrhage confined to caudothalamic groove
12 Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage and IVH Sagittal Coronal Grade II: Grade I + extension into the lateral ventricles without hydrocephalus
13 Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage and IVH Sagittal Coronal Grade III: Grade II with hydrocephalus
14 Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage and IVH Sagittal Coronal Grade IV: Grade III + extension into the adjacent parenchyma/hemorrhagic venous infarcts
15 PERIVENTRICULAR LEUKOMALACIA (PVL) 5% of infants born before 32 weeks and 15-20% of infants born before 28 weeks will develop cerebral palsy (1). PVL is an important prognostic sign as more than 50% of infants with exhibit some form of cerebral palsy or cognitive/behavioral deficit (2). 2 Types of PVL: Focal PVL will be more associated with cerebral palsy Diffuse PVL will be more associated with cognitive/behavioral deficit 1. Huang BY, Castillo M. Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury: Imaging Findings from Birth to Adulthood. Radiographics Volpe J. Cerebral White Matter Injury of the Premature Infant- More Common Than You Think. AJP 2003; 112;
16 PERIVENTRICULAR LEUKOMALACIA (PVL) Coronal Coronal Axial T2
17 Spine Ultrasound Best in newborn/early infancy Limited value after 6 months due to ossification of bony elements
18 Spine Ultrasound - Indications Evaluation of lumbosacral stigmata known to be associated with spinal dysraphism Midline or paramedian soft tissue masses Hair tufts Hemangiomas Paramedian, Deep sacral dimples Evaluation of suspected defects such as Cord Tethering, Diastematomyelia, Syrinx
19 Spine Ultrasound - Indications
20 Spine Ultrasound - Indications
21 Pediatrics CT HEAD
22 Radiation Risk
23 Radiation Risk
24 Radiation Risk
25 Radiation Risk
26 Radiation Risk
27 Decreased Dose kvp>ma>collimation. Increase ma with age. 0 to 2 years years years 210. > 6 years 240 Low dose CT for shunt evaluation, PNS, Temporal bone Use other alternatives if possible such as MRI for shunt evaluation.
28 Unique about Pediatrics CT HEAD White matter is difficult to evaluate in the neonate Better evaluated with US and MR Marked white matter hypodensity until age of 2 months Basal ganglia indistinct until 4 months Cortex should be well seen no matter what age Hyperdense dural venous sinuses in neonates from increased hematocrits Prominence of the subarachnoid spaces Normal or macrocephalic
29 3 week old with Seizure
30 7 week old with Fever
31 3 year old with Seizure
32 3 week old with Seizure
33 3 year old with Seizure, Weakness Which side is abnormal? Question
34
35
36 3 week old with Altered consciousness
37
38 3 week old with Fever, Seizure
39 14 month old with macrocephaly - Normal or Abnormal - Which compartment fluid is located?
40 6 month old with macrocephaly - Normal or Abnormal - Which compartment fluid is located?
41 Case 1 Case 2 - Normal or Abnormal - Which compartment fluid is located?
42 Anterior Extra-axial Fluid Subarachnoid versus Subdural Subarachnoid Symmetric Vessels (bridging veins) coarse through No mass effect Subdural Asymmetric Vessels displaced towards cortex Underlying mass effect.
43 4 months, Girl with 1 st time seizure & 5 mins of passing out, CPR by Dad Social History: - Wanted child only child - Socially well adjusted family No History of trauma Unclear diagnosis! - Epilepsy? Strong family history - Cardiac problem? - Metabolic etiology?
44 4 months, Girl with 1 st time seizure & 5 mins of passing out, CPR by Dad Clinical examination: Bruise on the both sides of chest H/o CPR by Dad at home
45 Disease/accident vs. Abuse - a question of balance? CT report: Normal Seizure without trauma Socially well adjusted family No report of trauma Abuse Disease/Accident
46 4 months, Girl with 1 st time seizure & 5 mins of passing out, CPR by Dad
47 Disease/accident vs. Abuse - a question of balance? Seizure without trauma Socially well adjusted family Disease/Accident CT report: Clear! - Bilat. SDH suggesting violent, recurring trauma Positive Retinal Hemorrhage Abuse
48 SDH: Time course Vs. Change of attenuation(hu) 85 HU 45 Normal Brain 0 CSF Weeks 5 Adapted from K. Ericson
49 Retinal haemorrhages Acute on chronic SDH Cerebral edema Child Abuse Speaks in very strong favour Shaken Baby Syndrome (> 95 %) Reiber: Fatal falls in Childhood. Am J Forensic Med & Pathol 1993:3;
50 Bridging Veins
51 SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME Repeated accelerations decelerations Brain comes in motion relative to the skull and meninges. Torn bridging veins Subdural haematoma
52 HEAD TRAUMA
53 Pediatrics MRI HEAD
54 White Matter Myelination T1 WM increases relative to GM Newborn 2 year old T2 WM decreases relative to GM Newborn 2 year old
55 White Matter Myelination Caudal to Cranial Central to Peripheral Posterior to Anterior
56 Simplified Pattern Approach ANATOMIC REGION T1 T2 Middle Cerebellar Peduncle, Posterior Limb of IC, Birth Birth 2 Month Deep Cerebellar WM (DCW) Birth 3 Month 3 5 Month Anterior Limb of IC 2-3 Month 8-11 Month Splenium, Corpus Callosum 3-4 Month 4-6 Month Genu, Corpus Callosum 4-6 Month 6-8 Month Frontal White Matter, Central 4-6 Month Month Frontal White Matter, Peripheral 6-11 Month Month Barkovich et al. Normal maturation of the neonatal and infant brain:mri at 1.5 T Radiology 1988;166: 173.
57 Simplified Pattern Approach ANATOMIC REGION T1 T2 Middle Cerebellar Peduncle, Posterior Limb of IC, Birth Birth 2 Month Deep Cerebellar WM (DCW) Birth 3 Month 3 5 Month Anterior Limb of IC 2-3 Month 8-11 Month Splenium, Corpus Callosum 3-4 Month 4-6 Month Genu, Corpus Callosum 4-6 Month 6-8 Month Frontal White Matter, Central 4-6 Month Month Frontal White Matter, Peripheral 6-11 Month Month Up to 6 months: Use T1-W; Use T2-W > 6 months
58 Simplified Pattern Approach ANATOMIC REGION T1 T2 Middle Cerebellar Peduncle, Posterior Limb of IC, Birth Birth 2 Month Deep Cerebellar WM (DCW) Birth 3 Month 3 5 Month Anterior Limb of IC 2-3 Month 8-11 Month Splenium, Corpus Callosum 3-4 Month 4-6 Month Genu, Corpus Callosum 4-6 Month 6-8 Month Frontal White Matter, Central 4-6 Month Month Frontal White Matter, Peripheral 6-11 Month Month Up to 6 months: Use T1-W; Use T2-W > 6 months
59 Simplified Pattern Approach ANATOMIC REGION T1 T2 Middle Cerebellar Peduncle, Posterior Limb of IC, Birth Birth 2 Month Deep Cerebellar WM (DCW) Birth 3 Month 3 5 Month Anterior Limb of IC 2-3 Month 8-11 Month Splenium, Corpus Callosum 3-4 Month 4-6 Month Genu, Corpus Callosum 4-6 Month 6-8 Month Frontal White Matter, Central 4-6 Month Month Frontal White Matter, Peripheral 6-11 Month Month Up to 6 months: Use T1-W; Use T2-W > 6 months
60 Splenium 6 months 8 months T1 Weighted Sequence 11 months months Genu MCP, DCW Splenium 3 months 4 months 6 months 8-11 months T2 Weighted Sequence Genu ALIC
61 Role of imaging in Epilepsy To identify possible epileptic focus MRI, MEG, SPECT/PET To confirm lateralization fmri, WADA testing
62 MRI: EPILEPSY PROTOCOL Imaging MUST BE acquired on a 3T scanner. High resolution T2-weighted coronal oblique images 3D T1-weighted MPRAGE volumetric images Coronal FLAIR images
63 WHY 3T? 1.5 T, Coronal T2 Oblique Images
64 WHY 3T? 3 T, Coronal T2 Oblique Images Abnormally thickened right insular cortex Abnormally thickened superior temporal gyrus Right temporal subependymal heterotopia.
65 CAUSE >61 Cerebral Hypoxia Inborn error of Metabolism Congenital Malformation X X X X Infection X X Phakomatosis X X Primary seizures X MTS X X Vascular Malformation Post-traumatic Epilepsy X X X X X X Tumor X X X Stroke X X
66 MALFORMATION OF CORTICAL DEVELOPEMENT Malformation due to abnormal neuronal and glial proliferation - Focal cortical dysplasia - Hemimegalancephaly - Neoplasm (DNET, Ganglioglioma) Malformation due to abnormal neuronal migration - Lissencephaly - Heterotopias Malformation due to abnormal late migration and organization - Polymicrogyria - Schizencephaly
67 MALFORMATION OF CORTICAL DEVELOPEMENT Malformation due to abnormal neuronal and glial proliferation - Focal cortical dysplasia - Hemimegalancephaly - Neoplasm (DNET, Ganglioglioma) Malformation due to abnormal neuronal migration - Lissencephaly - Heterotopias Malformation due to abnormal late migration and organization - Polymicrogyria - Schizencephaly
68 FCD: KEY MR IMAGING FINDINGS Key MRI Features of FCD: Abnormal gyral pattern
69 FCD: KEY MR IMAGING FINDINGS Key MRI Features of FCD: Abnormal gyral pattern Increased cortical thickness Increased cortical signal
70 FCD: KEY MR IMAGING FINDINGS Key MRI Features of FCD: Abnormal gyral pattern Increased cortical thickness Increased cortical signal Blurring of gray matter / white matter junction Increased white matter signal
71 FCD: KEY MR IMAGING FINDINGS Key MRI Features of FCD: Abnormal gyral pattern Increased cortical thickness Increased cortical signal Blurring of gray matter / white matter junction Increased white matter signal Transmantle signal changes
72 Mesial Temporal Sclerosis(MTS) Left hippocampus T2 hyperintensity Left hippocampal atrophy Compensatory enlargement of the adjacent temporal horn Coronal T2
73 Pediatric Metabolic Disorders Genetic Tests Clinical Data Lab Tests Imaging
74 Pediatric Metabolic Disorders Genetic Tests Clinical Data Lab Tests Imaging
75 MRI based approach to Pediatric Metabolic Ds. 1) Disorders of Hypomyelination 2) Disorders affecting subcortical WM 3) Disorders affecting periventricular + deep WM 4) Disorders affecting combined WM and GM 5) Disorders affecting GM with some WM
76 *Disorders of Hypomyelination* Pelizaeus Merzbacher disease (PMD) Fucosidosis Sialic acid storage disorder Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum Hypomyelination, hypodontia, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Hypomyelination and congenital cataract Hypomyelination with monocarboxylate transporter-8 deficiency Folate receptor defect Tremor-ataxia with central hypomyelination
77 2y/M, Hypotonia,Developmental Delay T1 T2 Markedly delayed myelination of the cerebral white matter on T2.
78 *Disorders affecting Predominantly Subcortical WM* Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Cysts (MLC) / Van der Knaap Disease Vanishing White Matter Disease Galactosemia Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome
79 Vanishing White Matter Ds. (Childhood ataxia with central hypomyelination)
80 Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Cysts (MLC) / Van der Knaap Disease
81 *Disorders affecting Predominantly Periventricular + Deep WM* X-linked ALD Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) Lowe Syndrome Cockayne Syndrome X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth Syndrome Leukoencephalopathy with Brainstem and Spinal cord involvement (LBSL)
82 X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD)
83 Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
84 *Disorders affecting Combined White and Gray Matter* Alexander Disease Canavan Disease Krabbe Disease Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) GM1/GM2 Gangliosidosis Organic Acidopathies e.g. Propionic acidemia, Glutaric aciduria type I, Methylmalonic acidemia, L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria
85 Alexander Disease
86 Canavan Disease 13 months old, increased head circumference
87 Canavan Disease Elevated NAA : Creatine ratio 2.72
88 *Disorders affecting Predominantly Gray Matter with some WM* Mitochondrial Disorders Leigh Syndrome Kearns-Sayre Syndrome Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, Stroke like symptoms (MELAS) Urea Cycle Disorders
89 Leigh Syndrome
90 SUMMARY Use helpful resources if any uncertainty regarding which imaging study to order in pediatric patients. ACR appropriate criteria, Call Radiologists Significant difference in appearance of CT Head (up to 6 months) & MRI of head (up to 2 year) as compared to adults. Learn from your colleagues. i.e. multidisciplinary conferences
91 Thank you for your attention
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter. Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
 Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review
 Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy. Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA
 Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA Neuroimaging in Childhood Neuroimaging issues are distinct from adults Sedation/anesthesia Motion
Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA Neuroimaging in Childhood Neuroimaging issues are distinct from adults Sedation/anesthesia Motion
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes
 Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review
 Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures:
 3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Course objectives. Head Ultrasound. Introduction
 Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Imaging of the pediatric brain, spinal cord and muscle: Tools and clinical applications Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section
Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting September 10-13, 2014 Imaging of the pediatric brain, spinal cord and muscle: Tools and clinical applications Andrea Poretti, MD Research Associate Section
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW
 NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Neuro. Development. Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC. ! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation. ! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months!
 Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Disclosures None. Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters. Macrocephaly Low Back Pain Sacral Dimple Concussion Chiari Malformation
 Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters When to Manage, When to Refer Andrew Jea MD FAAP Professor and Chief of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Indiana University School
Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters When to Manage, When to Refer Andrew Jea MD FAAP Professor and Chief of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Indiana University School
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Neurosurgery. Neurosurgery
 Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development
 Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
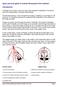 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011
 Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Spine and spinal cord
 NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects
 Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Appendix 3.5 A3.5-1 Case Definition Appendix 3.5 Case Inclusion Guidance for Potentially Zika-related Birth Defects Contents
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES)
 AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
Insults to the Term Brain
 Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
 Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy MRI. Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation
 Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Imaging of Pediatric Epilepsy Epilepsy: Nonacute Situation MR is the study of choice Tailor MR study to suspected epileptogenic zone Temporal lobe Extratemporal A. James Barkovich, MD University of California
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound
 Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page
 EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page Please find enclosed the EGI Clinical Data Form for my patient. This form was completed by: On (date): _ Page 1 of 14 EGI Clinical Data Form Patient Name: Date
EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page Please find enclosed the EGI Clinical Data Form for my patient. This form was completed by: On (date): _ Page 1 of 14 EGI Clinical Data Form Patient Name: Date
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Padmaja K. Naidu, M.D. Usha D. Nagaraj, M.D. William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. AOCR Annual Conference 2018 Scottsdale, Arizona @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Padmaja K. Naidu, M.D. Usha D. Nagaraj, M.D. William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. AOCR Annual Conference 2018 Scottsdale, Arizona @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
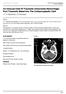 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge
 Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury. Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford
 Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Cerebellar Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI
 Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Brain Involvement in Salla Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:433 443, March 1999 Brain Involvement in Salla Disease Pirkko Sonninen, Taina Autti, Tarja Varho, Mirja Hämäläinen, and Raili Raininko BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose was to
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:433 443, March 1999 Brain Involvement in Salla Disease Pirkko Sonninen, Taina Autti, Tarja Varho, Mirja Hämäläinen, and Raili Raininko BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose was to
Prevalence of "Compressed" and Asymmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic
 Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System
 NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
NEURORADIOLOGY Kinga Karlinger, MD, PhD Associate Professor Semmelweis University, Budapest Diagnostic modalities of the Central Nervous System X-ray: screening is not used any more, x-ray images instead
Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI.
 Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI. Doctors Nicolás Sgarbi, Osmar Telis Clinical Radiology Department Hospital de Clínicas Montevideo- Uruguay ABSTRACT Epilepsy is one of the most frequent neurological
Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI. Doctors Nicolás Sgarbi, Osmar Telis Clinical Radiology Department Hospital de Clínicas Montevideo- Uruguay ABSTRACT Epilepsy is one of the most frequent neurological
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist
 mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
