THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Maurice Payne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
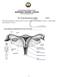
1 Hello and welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM We are going to be covering the FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM and all its mysteries in this presentation. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STD's) will also be included. The female reproductive system is located in the pelvis, below the small intestines as we see here in this image that shows a turquoise colored uterus and two blue ovaries. The female reproductive system: consists of: 1) The OVARIES 2) The FALLOPIAN TUBES 3) The UTERUS and its CERVIX 4) The VAGINA 5) The EXTERNAL GENITALIA (LABIA MAJORA AND MINORA) Now, let s talk about each part a little bit. 1) The OVARIES: the ovaries are two almond shaped organs, located in the upper and outer part of the pelvis like we see in the image. Just like their male counterparts, the testicles, the ovaries have a DOUBLE ROLE : A) ENDOCRINE ROLE: which they carry out by secreting the female hormones (ESTROGEN, PROGESTERONE) into the bloodstream. I'll come back and explain what these hormones do a little later. B) REPRODUCTIVE ROLE: because the ovaries produce the OVA (human eggs). We will explore that more in the Obstetrics presentation. 2) The FALLOPIAN TUBES: are two tubes that extend from the ovaries to the body of the uterus which are lined with mucous membrane (just like the membrane inside of your mouth). They possess finger-like projections called fimbriae that catch the ovum. Once inside the tube, the ovum is shuffled along by waves of contractions (peristalsis) down into the body of the uterus. We see here a cross section of the tube and ovary showing a progression of the ovum down the tube. This is about a 5 day journey and it's generally where the egg meets the sperm-boy meets girl! 3) The UTERUS: imagine the uterus like a hollow upside-down pear (fruit). Its function is to receive the fertilized egg and harbor it during the course of pregnancy. It is made of smooth muscle and also has an inner lining of mucous membrane. If pregnancy doesn't occur it sheds its inner lining called the ENDOMETRIUM and menstruation occurs.
2 The uterus is divided from top to bottom in 3 parts: -FUNDUS: area where the fallopian tubes are located. -BODY: the central portion. -CERVIX: the lowest part of the uterus; where it narrows as seen here which opens into the vagina through the EXTERNAL OS. 4) The VAGINA: is a muscular tube, about 3 inches long, that connects the uterus with the vulva. As we see in this image, the VAGINA sits between the BLADDER and the RECTUM. Right behind the upper back wall of the vagina lies the lowest part of the abdominal cavity (seen in gray) which explains why a sample of fluids from the abdominal cavity can be obtained by piercing this upper back wall of the vagina with a needle. A procedure called a: CULDOCENTESIS. The vagina contains folds of tissue called rugae which allow the vagina to stretch during intercourse and childbirth. The vagina is: the female organ of copulation part of the birth canal and serves as a passageway for the menstrual flow All this we have talked about: the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina are known as the INTERNAL GENITALIA. 5) The EXTERNAL GENITALIA aka VULVA: consist of: - MONS PUBIS: name given to the fatty tissue that covers the pubic region - LABIA MAJORA and MINORA: The labia majora are 2 folds of skin containing fatty tissue, containing hair that cover the entry to the vagina. The labia minora are two thin folds of tissue located within the labia majora (shaded in red in the sketch). - CLITORIS: is erectile tissue located up where both labia minora meet similar to the male penis (like a mini penis). - VESTIBULE: oval-shaped area seen when we separate the labia minora (shaded in yellow in sketch). It's the area which contains: A) URINARY MEATUS: which is the opening of the urethra, where urine flows out. B) VAGINAL ORIFICE aka INTROITUS: is the entry to the vagina. At birth the introitus is covered by a thin membrane called hymen which forms a border around the outer opening of the vagina. Its absence doesn't necessarily equate to lost virginity (since it can be torn during sports for example). C) BARTHOLIN'S GLANDS: these glands function is to lubricate the vagina. They are located on each side of the introitus and although you can see them in the sketch as yellow-red circles they are below the skin and not visible. - PERINEUM: diamond shaped area that extends from the vagina to the anus (area within the green lines seen in the sketch). I like to describe it as the in between the legs area! Composed of muscular and fibrous tissues that serve as a support for the vagina and other pelvic structures. Sometimes an incision is done at delivery time to avoid the tearing of the perineum during childbirth. That incision is called an EPISIOTOMY.
3 Let s give a brief summary of the actions of the female sex hormones: ESTROGEN is responsible for: - The MATURATION OF the OVARIAN FOLLICLES - The THICKENING OF THE ENDOMETRIUM in preparation to receive the fertilized egg every month. - The ONSET OF MENSTRUATION - and the appearance of the SECONDARY SEXUAL CHARACTERISTICS in puberty such as growth of the breasts, deposit of fat to give the rounded female look, the growth of pubic and axillary hair and the growth spurt. PROGESTERONE: As its name implies: PRO = FOR and GEST = PREGNANCY. - This hormone helps prepare for pregnancy. It provides SUPPORT FOR THE ENDOMETRIUM and THE PLACENTA. SOME SIGNS OF DISEASE: 1) PAIN or DISCOMFORT: in the lower quadrants of the abdomen, pelvis or vagina 2) VAGINAL DISCHARGE: clear or whitish fluid that comes out of the vagina 3) BLEEDING: that occurs in between periods or when heavier or more prolonged than usual. 4) VAGINAL ITCH and REDNESS 5) BAD ODOR 6) INFERTILITY: inability to get pregnant. 7) FEVER: body's temperature over 98.6 Fahrenheit SOME DISEASES: 1) OVARIAN CANCER: malignant tumor of the ovaries. Usually diagnosed in advanced stages due to non-specific symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain. 2) OVARIAN CYSTS: as we can see in the image there on the right side is a normal ovary which a normal amount of follicles inside it but on the left side we see a POLYCYSTIC OVARY where there is an excess of mature follicles. Associated with infertility and menstrual irregularities. 3) SALPINGITIS aka PELVIC INFLAMMATORY DISEASE (PID): is the inflammation of the Fallopian Tubes usually due to an infection in the tube. Leaves scars in tubes which can cause infertility or a tubal pregnancy if the ovum gets stuck when traveling down the scarred tube! 4) CONGENITAL DEFECT: better known as a birth defect. Not actually a disease. Some women may be born with a defect in their uterus where instead of the uterus angled forwardswhich is normal- it is bent back (retroversion) or where its top part is split in two-as we see here, a bicornuate uterus. These birth defects are rare but can make pregnancy difficult.
4 5) CERVICAL CANCER: a malignant tumor of the cervix. One of the most common cancers of the female reproductive system. Considered an STD because of its association with infection by the HPV. Seen in younger women. 6) CERVICITIS: inflammation of the cervix, can cause discharge and bleeding and is generally caused by gonorrhea, trichomoniasis or chlamydial infections. 7) ENDOMETRIAL CANCER: malignant tumor of the inner lining of the uterus. Seen in older women. 8) ENDOMETRIOSIS: means there are areas of endometrium outside of their normal location inside the uterus like in the ovary or in the small bowel. Main symptom is painful menses which doctors call: dysmenorrhea. 9) FIBROIDS: term commonly used to refer to benign growths of smooth muscle in the uterus. Their principal symptom is heavy bleeding during periods which can cause anemia. 10) CYSTOCELE: appears when bladder protrudes into vagina. 11) RECTOCELE: appears when rectum protrudes into the vagina 12) VAGINITIS aka VULVOVAGINITIS: is the inflammation of the vagina with symptoms like: discharge, itching, redness and pain. Can be caused by : a fungal infection of the vagina ( CANDIDIASIS) ( fungus = yeast same thing) a parasitic infection ( TRICHOMONIASIS) bacterial infection: (GARDNERELLA). FOREIGN BODY: retained in the vagina like a condom or tampon can also cause vaginitis or other IRRITANTS such as soaps, perfumes, semen, DOUCHES. 13) MENOPAUSE: not a disease. Just the shutting down of the ovaries which make less estrogen and stop producing ovum. Occurs between years of age the hormonal changes that occur during menopause give way to symptoms like: HOT FLASHES. SOME DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES: 1) GYNECOLOGICAL EXAM: SPECULUM: as we see here in this image there are different types of specula. A speculum introduced into the vagina opens the vaginal cavity so the cervix can be observed. 2) PAP SMEAR: screening test used to diagnose early stage cervical cancer. A speculum is inserted to permit access to the cervix which is then swabbed to obtain samples which are sent out to be analyzed under microscope by a pathologist. 3) COLPOSCOPY: as we see in this next image a gynecologist is having a peek at the vagina and cervix through the use of a colposcope. 4) CULDOCENTESIS: procedure we mentioned earlier, where a needle is passed through the back wall of the vagina in order to get a sample of fluid from the abdominal cavity for
5 testing. Used to help diagnose ectopic pregnancy or infection. 5) ENDOMETRIAL BIOPSY: another invasive procedure used to obtain a sample of the inner lining of the uterus. Used to diagnose endometrial hyperplasia and uterine cancer. Uterine hyperplasia means a thickening of the endometrium and is a risk factor for uterine cancer. 6) TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND: is a particular form of ultrasound used in gynecology which is done using a special transducer that is introduced into the vagina. It is very useful to check the ovaries. SOME TREATMENTS: 1) LAPAROSCOPY: is a surgical procedure done under general anesthesia. A small incision is made at the navel creating an opening called an umbilical port through which a gas (CO 2) is pumped into the abdomen, sort of like inflating the abdomen so as to separate the abdominal wall from the organs to make room for the surgeon to operate. The laparoscope (which is like a rod with a light and a camera on its tip) is also inserted through the umbilical port and then 2 or 3 trocars which are thin hollow tubes are put in at different parts of the abdomen so as to create other ports through which the surgeon can operate. In this photo you can see trocars sticking out of an abdomen and a scissor-like surgical instrument being introduced through one of the trocars. This type of procedure produces a short post-op. The patient can go home quickly and get back to his normal activities in a couple of weeks. 2) LAPAROTOMY: means regular, non-laparoscopic surgery (large incision is made). 3) HORMONES : given in the form of pills known as: oral contraceptives, for example, are useful in reducing pain in endometriosis 4) CANCER TREATMENTS : include -CHEMOTHERAPY -RADIATION -HORMONES 5) CONIZATION: Please look at the image in the upper left hand corner. It shows a LESION in the cervix. In the next image in the upper right hand corner an imaginary dotted line signals where the gynecologist will be cutting to remove the lesion. Then in the bottom left hand corner we see the doctor starting to remove the lesion. In the bottom right hand corner the procedure is finished. In between the 2 bottom images is the actual CONE shaped wedge of cervix which was removed and explains why this procedure is called a conization. This procedure is used to diagnose and treat precancerous lesions called dysplasia and noninvasive cervical cancer. The conization can be done : by burning the lesion ( through a loop excision) as seen in this image, by LASER or by cutting it out with a SCALPEL (cold knife conization). 6) CRYOSURGERY: surgical treatment where abnormal tissue is destroyed by freezing it.
6 7) HYSTERECTOMY: surgical removal of the uterus which may be total or partial. May include removal of the ovaries too. 8) ANTIBIOTICS: an example: METRONIDAZOLE 9) ANTIFUNGALS: an example : MICONAZOLE 10) Some patients opt for HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY to alleviate menopause symptoms (hot flashes, etc.). Now we'll begin the second part of this presentation where we'll briefly go over: SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDs) When we talk about STDs, we are talking about a group of diseases that are predominantly spread during sex (vaginal, anal or oral). The disease is spread from one person to another by contact with body fluids like blood, semen or vaginal secretions. The use of barriers (like a condom) to prevent contact with infectious sores or fluids helps reduce the risk of getting them. 1) AIDS: caused by a retrovirus called HIV (HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS) which I like to refer to as the microscopic giant, so tiny yet so immensely powerful! AIDS stands for: ACQUIRED IMMOUNODEFICIENCY SYNDROME. Untreated AIDS is a fatal illness. Roughly 2 million people die of AIDS every year. The virus infects the cells of the immune system, destroying the lymphocytes, cells that are in charge of protecting us from infections. Without their protection a patient falls prey to a wide range of OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS which is a medical term for infections that occur in patients with weak defenses, like for example : ORAL CANDIDIASIS aka THRUSH TOXOPLASMOSIS PNEUMOCYSTIS PNEUMONIA SHINGLES TUBERCULOSIS Other complications in patients with AIDS are cancers like LYMPHOMA and KAPOSI's SARCOMA AIDS can be CONTRACTED by: -UNPROTECTED SEX -SHARING NEEDLES -BREASTFEEDING -BLOOD TRANSFUSION Patients with no symptoms are known as HIV positive. HIV (+) = INFECTED BUT NOT SICK
7 HIV infection is diagnosed by: -DIAGNOSIS: lab tests: either an oral swab or blood tests. These tests detect the presence of HIV antibodies. -TREATMENT: today thanks to the arsenal of ANTIRETROVIRAL DRUGS like AZT, SAQUINAVIR, DDI and others, doctors are better able to manage the disease and patients stay alive longer; what's known as an increased life expectancy. The antiretroviral drugs are given together combined in what's called a drug cocktail to avoid the virus getting resistant to the drugs. Treatments are monitored by blood tests like: VIRAL LOAD, CD4 CELL COUNT. If a patient's viral load is low and CD4 counts high then the treatment is going well. 2) GONORRHEA: gonorrhea is an infection caused by a bacteria named GONOCOCCUS. Symptoms include painful urination and discharge. Infection can be asymptomatic in women and cause scarring of the Fallopian tubes leading to fertility problems, ectopic pregnancy. The presence of gonococcus in the birth canal can cause serious eye infections in the newborn reason why silver nitrate eye drops are placed in the newborn's eyes to prevent this. -TREATMENT: Antibiotics: CEFTRIAXONE 3) SYPHILIS: is a bacterial infection. In its initial stage, a painless sore called a chancre appears on genitals, anus or mouth (period known as primary syphilis), the chancre disappears on its own after a few weeks. About 2 months later a diffuse (all-over-the body) skin rash appears. This stage is known as secondary syphilis. Untreated it, too, will go away after a few weeks and after a long period of years passes, internal lesions called gummas develop in bones, liver, testicles and the central nervous system can be affected. This is the last period called tertiary syphilis. Syphilis can also be transmitted to the fetus causing serious birth defects (heart, bones, teeth). -DIAGNOSIS is generally done with blood tests like a: VDRL. -TREATMENT: antibiotics, for example: PENICILLIN. 4) GENITAL HERPES: is an infection caused by the HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS (HSV). Causes blisters on the genitals or anus. This virus also causes blisters on the lips called cold sores. Can be transmitted to the newborn during birth. Baby can develop encephalitis and other conditions. -TREATMENT: drugs that end in cyclovir are used to shorten outbreaks. Example: ACYCLOVIR. The virus can't be cured with current treatments. 5) HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS: there are many types of this virus. Some of these cause common skin warts like the one we see there on that pinky finger, when the warts appear on the genitals they're called CONDYLOMAS. The high-risk types such as types 16 and 18 can cause cervical cancer. There is now a vaccine (GARDASIL) available to prevent infection with these high risk types.
8 6) TRICHOMONIASIS: is caused by a parasite. Produces mild vaginal itching. At other times there may be pain with intercourse and foul smelling discharge (vaginitis). -TREATMENT: an antibiotic called METRONIDAZOLE is effective. 7) CHLAMYDIA: a bacterial infection. Possible symptoms are discharge (CERVICITIS) and painful intercourse in women and painful urination in men. Untreated it can cause PID in women and epididymitis in men. Can affect the newborn causing miscarriage, blindness, premature birth or pneumonia. -TREATMENT: antibiotics, for example AZITHROMYCIN. 8) OTHER STDs. I will only mention the following diseases which are also considered STDs : -HEPATITIS B -SCABIES -PUBIC LICE -CHANCROID -LYMPHOGRANULOMA VENEREUM The doctors who specialize in treating diseases of the Female Reproductive System are called GYNECOLOGISTS. The specialty is called GYNECOLOGY. In this presentation we have gone over many terms related to GYNECOLOGY while we discussed the anatomy of the FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. Signs and symptoms of sickness, diseases, diagnostic procedures and some treatments were also discussed. I hope you've enjoyed this lesson and come away with a better understanding of the field of GYNECOLOGY and the terms related to this field of medicine. Thank you for choosing InterpreterPrep.com
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS
 LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Sexually Transmitted Infections Introduction Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are some of the most common infectious diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases are also called sexually transmitted
Sexually Transmitted Infections Introduction Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are some of the most common infectious diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases are also called sexually transmitted
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s)
 Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s) STI s once called venereal diseases More than 20 STIs have now been identified most prevalent among teenagers and young adults.
Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s) STI s once called venereal diseases More than 20 STIs have now been identified most prevalent among teenagers and young adults.
Sexually Transmitted Infections. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Sexually Transmitted Infections Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI s). How they are transferred. High risk behavior. The most common STI s. How
Sexually Transmitted Infections Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI s). How they are transferred. High risk behavior. The most common STI s. How
MYTHS OF STIs True or False
 MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
MYTHS OF STIs True or False 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Birth control pills prevent the spread of STDs. 3. Douching will cure and STD. 4. Abstinence is the best way to prevent
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
How to Prevent Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Ch 24
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Ch 24 Statistics THERE ARE CURRENTLY 65 MILLION PEOPLE LIVING WITH INCURABLE STDs IN THE U.S. THERE ARE 15 MILLION NEW CASES REPORTED EACH YEAR SOURCE: CDC, 2000 REPORTS WHY
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Ch 24 Statistics THERE ARE CURRENTLY 65 MILLION PEOPLE LIVING WITH INCURABLE STDs IN THE U.S. THERE ARE 15 MILLION NEW CASES REPORTED EACH YEAR SOURCE: CDC, 2000 REPORTS WHY
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Reasons for Epidemic
 STI s STI s are diseases and infections which are capable of being spread from person to person through: sexual intercourse oral-genital contact IV drug Contact through cuts and sores Reasons for Epidemic
STI s STI s are diseases and infections which are capable of being spread from person to person through: sexual intercourse oral-genital contact IV drug Contact through cuts and sores Reasons for Epidemic
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1
 Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
STI Review. CALM: STI/HIV - Lesson One (Handout 3) Bacteria/ Transmission. Symptoms. Disease. Virus
 STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
STI Review Bacteria/ Virus? Transmission Chlamydia Bacteria Unprotected vaginal or anal sex with a person who has Chlamydia Genital Herpes Virus By direct contact with the sores or blisters of an infected
- (Have NO cure yet, but are controllable) - (Can be cured if caught early enough)
 Myths or Facts of STD s 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STD s. 3. If you get an STD once, and are treated, you can t get it again. 4. A
Myths or Facts of STD s 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STD s. 3. If you get an STD once, and are treated, you can t get it again. 4. A
University Health Services at CMU STI Awareness Month specials for students:
 University Health Services at CMU STI Awareness Month specials for students: -Free condoms during April (10 per student) -Free walk-in rapid HIV testing April 22-27 (no appointment needed) -STI Screening
University Health Services at CMU STI Awareness Month specials for students: -Free condoms during April (10 per student) -Free walk-in rapid HIV testing April 22-27 (no appointment needed) -STI Screening
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers
 Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Sexually Transmissible Infections (STI) and Blood-borne Viruses (BBV) A guide for health promotion workers Sexual & Reproductive Health Western Australia Chlamydia (bacterial infection) Unprotected vaginal
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases
 Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases Chapter Fourteen 2013 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Also known as sexually transmitted infections The Major STDs (STIs) HIV/AIDS Chlamydia Gonorrhea Human
Sexually Transmi/ed Diseases Chapter Fourteen 2013 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. Also known as sexually transmitted infections The Major STDs (STIs) HIV/AIDS Chlamydia Gonorrhea Human
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
toe... Chlamydia - CDC Fact Sheet Appendix K - Part 2
 Appendix K - Part 2 Chlamydia - CDC Fact Sheet What is chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common STD that can infect both men and women. It can cause serious, permanent damage to a woman's reproductive system,
Appendix K - Part 2 Chlamydia - CDC Fact Sheet What is chlamydia? Chlamydia is a common STD that can infect both men and women. It can cause serious, permanent damage to a woman's reproductive system,
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
SUMMARY TABLE OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
 1 of 5 SUMMARY TABLE OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Sexually Transmitted Infections How is it spread? How do I get tested? Can it be cured? fertility? pregnancy? a newborn? Can the mother breastfeed
1 of 5 SUMMARY TABLE OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS Sexually Transmitted Infections How is it spread? How do I get tested? Can it be cured? fertility? pregnancy? a newborn? Can the mother breastfeed
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Aim #58 STD's. What is the main difference between bacterial STD's and viral STD's? Why is Chlamydia nicknamed the "silent disease?
 Aim #58 STD's What is the main difference between bacterial STD's and viral STD's? Why is Chlamydia nicknamed the "silent disease?" PS - Quiz on Friday (20?'s) Birth control, STD's, and anatomy Genital
Aim #58 STD's What is the main difference between bacterial STD's and viral STD's? Why is Chlamydia nicknamed the "silent disease?" PS - Quiz on Friday (20?'s) Birth control, STD's, and anatomy Genital
STD Notes. Myths about STDs
 STD Notes Sexually transmitted diseases (STD's) or sexually transmitted infections (STI's) are infectious diseases that spread from person to person through intimate contact. STD's can affect males and
STD Notes Sexually transmitted diseases (STD's) or sexually transmitted infections (STI's) are infectious diseases that spread from person to person through intimate contact. STD's can affect males and
½ of all new infections are among people aged although this age group represents <25% of the sexually experienced population.
 Impact Almost 20 million - newly diagnosed STD s/sti s each year. $16 billion cost of treating STI s ½ of all new infections are among people aged 15-24 although this age group represents
Impact Almost 20 million - newly diagnosed STD s/sti s each year. $16 billion cost of treating STI s ½ of all new infections are among people aged 15-24 although this age group represents
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Sexually Transmitted Infections STI Director/ Centers for Disease Control Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: -Bacterial (Chlamydia, LGV,
Sexually Transmitted Infections STI Director/ Centers for Disease Control Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: -Bacterial (Chlamydia, LGV,
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS)
 SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS) CONTENTS Causes Prevention Methods of Transmission Decisions to Have Sexual Intercourse Signs and symptoms Screening Pop Quiz Diagnosis Management: Public Health
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIS) CONTENTS Causes Prevention Methods of Transmission Decisions to Have Sexual Intercourse Signs and symptoms Screening Pop Quiz Diagnosis Management: Public Health
In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
 Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007 In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007 In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity
 Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs. Sexually Transmitted Infections Reports
 UNIT NINE: UNDERSTANDING & PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs Overview When compared to the other industrialized
UNIT NINE: UNDERSTANDING & PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs Overview When compared to the other industrialized
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS)
 SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS) HIV/AIDS - TRANSMISSION Sexual intercourse Anal, oral, & vaginal Multiple partners Sharing needles Mother to infant Born or breast milk Blood transfusions Open
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS) HIV/AIDS - TRANSMISSION Sexual intercourse Anal, oral, & vaginal Multiple partners Sharing needles Mother to infant Born or breast milk Blood transfusions Open
What Causes Cervical Cancer? Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases What are they? Infections that spread from person to person through sexual contact More than 25 known STDs Most of the time those who have them may not realize it, hard to
Sexually Transmitted Diseases What are they? Infections that spread from person to person through sexual contact More than 25 known STDs Most of the time those who have them may not realize it, hard to
Sexually Transmitted Diseases STD s. Kuna High School Mr. Stanley
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases STD s Kuna High School Mr. Stanley Postponing sexual activity Postponing sexual activity until marriage and being mutually monogamous for the life of the marriage; you avoid
Sexually Transmitted Diseases STD s Kuna High School Mr. Stanley Postponing sexual activity Postponing sexual activity until marriage and being mutually monogamous for the life of the marriage; you avoid
Vaginitis. Antibiotics Changes in hormone levels due to pregnancy, breastfeeding, or menopause Douching Spermicides Sexual intercourse Infection
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Vaginitis Vaginitis is an inflammation of a woman s vagina. It is one of the most common reasons why women see their health care providers.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER
 INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
The Female Reproductive System
 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Sexually Transmitted Diseases This publication was made possible by Grant Number TP1AH from the Department of Health and Human Services,
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases This publication was made possible by Grant Number TP1AH000081-01-01 from the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Adolescent Health; its contents are solely
Sexually Transmitted Diseases This publication was made possible by Grant Number TP1AH000081-01-01 from the Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Adolescent Health; its contents are solely
STDs Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 STDs Sexually Transmitted Diseases Questions: (Ask Yourself) What would you do if you found out you had an STD? Who would you tell? Would you be angry at your partner? Is it their fault or yours? MYTHS
STDs Sexually Transmitted Diseases Questions: (Ask Yourself) What would you do if you found out you had an STD? Who would you tell? Would you be angry at your partner? Is it their fault or yours? MYTHS
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE!
 What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
What you need to know to: Keep Yourself SAFE! What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? How are they spread? What are the different types of STDs? How do I protect myself? STDs are infections or diseases
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
MYTHS OR FACTS OF STI s True or False
 Bacterial STI s MYTHS OR FACTS OF STI s True or False 1. Most people with an STI experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STIs. 3. If you get an STI once, and are treated,
Bacterial STI s MYTHS OR FACTS OF STI s True or False 1. Most people with an STI experience painful symptoms. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STIs. 3. If you get an STI once, and are treated,
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview frequent and more serious complications from STDs than men. Q: How do you get an STD? A: You can get and pass STDs through Q: What is a sexually transmitted vaginal,
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview frequent and more serious complications from STDs than men. Q: How do you get an STD? A: You can get and pass STDs through Q: What is a sexually transmitted vaginal,
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
Take out CST test corrections What do you know about STDs?
 Assignment #5 STDs LO: To understand sexually transmitted diseases. EQ: What are all of the ways to contract STDs? (4-5 sentences underlining key words) AGENDA 5/12-5/13 1. Group work 2. Notes Homework
Assignment #5 STDs LO: To understand sexually transmitted diseases. EQ: What are all of the ways to contract STDs? (4-5 sentences underlining key words) AGENDA 5/12-5/13 1. Group work 2. Notes Homework
Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015
 Female Reproduction Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015 Male Reproduction Reproduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7rsh2loiy8 1 About Sex How to use a condom Set Limits Think about how far you
Female Reproduction Sexuality/Reproduction CALM Summer 2015 Male Reproduction Reproduction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_7rsh2loiy8 1 About Sex How to use a condom Set Limits Think about how far you
Bursting Pelvic Inflammatory Disease.
 www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
www.infertiltysolutionsng.info/blog Disclaimer The information in this book is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to treat, diagnose or prevent any disease. The information in this
STDs. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Questions: (Ask Yourself)
 STDs Sexually Transmitted Diseases Questions: (Ask Yourself) What would you do if you found out you had an STD? Who would you tell? Would you be angry at your partner? Is it their fault or yours? MYTHS
STDs Sexually Transmitted Diseases Questions: (Ask Yourself) What would you do if you found out you had an STD? Who would you tell? Would you be angry at your partner? Is it their fault or yours? MYTHS
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
17a. Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17a Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17a Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Several of the most common STDs are often asymptomatic. Asymptomatic
 What Are STDs? Several of the most common STDs are often asymptomatic. Asymptomatic Individuals show no symptoms, or the symptoms are mild and disappear after the onset of the infection Common STDs There
What Are STDs? Several of the most common STDs are often asymptomatic. Asymptomatic Individuals show no symptoms, or the symptoms are mild and disappear after the onset of the infection Common STDs There
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Sexually Transmitted Infections What is a Sexually Transmitted Infection or STI? STI s are infections that are spread from person to person through intimate sexual contact. STI s are dangerous because
Sexually Transmitted Infections What is a Sexually Transmitted Infection or STI? STI s are infections that are spread from person to person through intimate sexual contact. STI s are dangerous because
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376
 374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
374 Cancer and Growths Chapter 24 In this chapter: Cancer 376 Causes of cancer 376 Cancer can be cured if found and treated early 376 Problems of the Cervix (the Opening of the Womb) 377 Common problems
Sexually Transmitted. Diseases
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases How can I get an STD? Many STDs are carried and transmitted through semen and vaginal fluids. Some STDs can be spread through skin to skin contact Mother to child STDs: Signs
Sexually Transmitted Diseases How can I get an STD? Many STDs are carried and transmitted through semen and vaginal fluids. Some STDs can be spread through skin to skin contact Mother to child STDs: Signs
Lesson Four HIV and STIs
 Unit Two Lesson Four Lesson Overview In this activity students learn about the types, symptoms, transmission methods and treatments for various STIs, and are made aware of how easily and comprehensively
Unit Two Lesson Four Lesson Overview In this activity students learn about the types, symptoms, transmission methods and treatments for various STIs, and are made aware of how easily and comprehensively
Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases
 Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases Chapter 12 Card game Lie Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexuality is an intrinsic part of human nature and affects many things People are not always honest about their
Preventing Sexual Transmitted Diseases Chapter 12 Card game Lie Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexuality is an intrinsic part of human nature and affects many things People are not always honest about their
STI Feud Instructions
 STI Feud Instructions This game works best with groups of 4 20. What you will need: The STI question cards, 2 easy buttons from staples, chart paper, markers (if no black or white board) 1. Break the group
STI Feud Instructions This game works best with groups of 4 20. What you will need: The STI question cards, 2 easy buttons from staples, chart paper, markers (if no black or white board) 1. Break the group
STD. Are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) different from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
 What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? STD Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases that can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. Depending on the STD, sexual contact that
What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? STD Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases that can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. Depending on the STD, sexual contact that
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
STI REVIEW. What are the Symptoms in Male? Many males experience no symptoms
 Chlamydia Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria. Chlamydia can also cause infection of the eyes, throat, joints and bloodstream. Chlamydia is a reportable infection. Chlamydia
Chlamydia Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria. Chlamydia can also cause infection of the eyes, throat, joints and bloodstream. Chlamydia is a reportable infection. Chlamydia
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology. Basic Structure of the Human Body. Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology
 Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Student Learning Guide Health Related Technology Basic Structure of the Human Body Name: Date: Course Title: Anatomy and Physiology Duty/Unit: Basic structure of the Human Body Objective: Upon completion
Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
The Truth About STDs/STIs. Presented by Denise Piper LPN School Based Health Ed.
 The Truth About STDs/STIs Presented by Denise Piper LPN School Based Health Ed. Family Planning Center of Ocean County Located Rt. #9 Lakewood Sliding fee scale Insurance accepted Confidential Quality
The Truth About STDs/STIs Presented by Denise Piper LPN School Based Health Ed. Family Planning Center of Ocean County Located Rt. #9 Lakewood Sliding fee scale Insurance accepted Confidential Quality
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System TESTES and EPIDIDYMIS Testes produce male gametes (SPERMATOZOA) and male sex hormone TESTOSTERONE Found in pouch of skin called a SCROTUM Size of a small egg Made up of 250 lobules,
Male Reproductive System TESTES and EPIDIDYMIS Testes produce male gametes (SPERMATOZOA) and male sex hormone TESTOSTERONE Found in pouch of skin called a SCROTUM Size of a small egg Made up of 250 lobules,
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Chapter Five. Female Sexual Anatomy
 Chapter Five Female Sexual Anatomy Agenda Discuss Female Sexual & Reproductive System Describe Female Maturation Cycle Discuss Female Reproductive and Sexual Health The Female Sexual and Reproductive System
Chapter Five Female Sexual Anatomy Agenda Discuss Female Sexual & Reproductive System Describe Female Maturation Cycle Discuss Female Reproductive and Sexual Health The Female Sexual and Reproductive System
Chronic Pelvic Pain. AP099, December 2010
 AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
AP099, December 2010 Chronic Pelvic Pain Pain in the pelvic area that lasts for 6 months or longer is called chronic pelvic pain. An estimated 15 20% of women aged 18 50 years have chronic pelvic pain
Sexually Transmitted
 CHAPTER 22 Infections, Including HIV Key Points for Providers and Clients People with sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV, can use most family planning methods safely and effectively.
CHAPTER 22 Infections, Including HIV Key Points for Providers and Clients People with sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV, can use most family planning methods safely and effectively.
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 NGO Initiatives to Prevent HIV/AIDS Sexually Transmitted Infections 5/F Unit 506, Tower II Cityland Condominium 10 154 H.V. dela Costa Street, Salcedo Village, Makati City 1227 Tel: 632 817-5049 Fax: 632
NGO Initiatives to Prevent HIV/AIDS Sexually Transmitted Infections 5/F Unit 506, Tower II Cityland Condominium 10 154 H.V. dela Costa Street, Salcedo Village, Makati City 1227 Tel: 632 817-5049 Fax: 632
Communicable Diseases
 Communicable Diseases Communicable diseases are ones that can be transmitted or spread from one person or species to another. 1 A multitude of different communicable diseases are currently reportable in
Communicable Diseases Communicable diseases are ones that can be transmitted or spread from one person or species to another. 1 A multitude of different communicable diseases are currently reportable in
What You Need to Know. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 What You Need to Know Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) What You Need to Know About STIs What are STIs? Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that spread through sexual contact. If you
What You Need to Know Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) What You Need to Know About STIs What are STIs? Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are diseases that spread through sexual contact. If you
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Fact Sheet comprises public domain material from the Office on Women s Health, U.S. Department of Health and
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Fact Sheet comprises public domain material from the Office on Women s Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Sexually Transmitted Infections: Overview
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Fact Sheet comprises public domain material from the Office on Women s Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Sexually Transmitted Infections: Overview
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings
 Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Terminology in Health Care and Public Health Settings Unit 10 Reproductive Systems 1 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Objectives Define, understand and correctly pronounce medical terms related to
Sexually Transmitted Infections in the Adolescent Population. Abraham Lichtmacher MD FACOG Chief of Women s Services Lovelace Health System
 Sexually Transmitted Infections in the Adolescent Population Abraham Lichtmacher MD FACOG Chief of Women s Services Lovelace Health System STI in the Adolescent High school students nationwide, 34.2% were
Sexually Transmitted Infections in the Adolescent Population Abraham Lichtmacher MD FACOG Chief of Women s Services Lovelace Health System STI in the Adolescent High school students nationwide, 34.2% were
