ChAPteR. Word Parts and Word Building Rules. objectives. lesson one. Materials to Be learned. ParTs of a MediCal TerM
|
|
|
- Ariel Harrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ChAPteR 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules lesson one: MaTerials To be learned Parts of a Medical Term Listings of Word Parts Prefixes, Word Roots with Combining Forms, and Suffixes lesson TWo: Progress CheCK ParT a Matching Spelling and Definition Defining Medical Word Elements Building Medical Words lesson TWo: Progress CheCK ParT b Matching Spelling and Definition Building Medical Words Defining Medical Terms objectives After completion of this chapter and the exercises, the student should be able to: 1. List the basic parts of a medical term. 2. Define the terms word root, combining vowel, combining form, prefix, and suffix. 3. State the rules for building medical terms. 4. Divide medical words into their component parts. 5. Build medical words using combining forms, prefixes, and suffixes. 6. Use multiple word roots in a compound word. lesson one ParTs of a MediCal TerM Materials to Be learned Words, including medical terms, are composed of three basic parts: word roots, prefixes, and suffixes. How the parts are combined determine their meaning. Changing any part of a word changes its meaning. Spelling and pronunciation also are very important because some medical terms sound similar, and some sound exactly alike but are spelled differently and therefore have different meanings. For example, the word phagia (fay-jee-ah) means eating or swallowing, and the word phasia (fay-zee-ah) means without speech. Examples of words that are pronounced exactly alike but spelled differently are the terms ileum (ill-ee-um) and ilium (ill-ee-um). Ileum is part of the small intestine, but ilium is part of the hipbone. 1. Prefix: the word or element attached to the beginning of a word root to modify its meaning. Not all medical words have a prefix. A prefix keeps its same meaning in every 5
2 6 Unit I Medical Terminology term in which it is used. When defining a medical term that has both a prefix and a suffix, define the suffix first, the prefix second, and the word root last. Note in the following example how the meaning of the word changes: peri- = prefix for around, cardi = root word for heart, and -itis = suffix for inflammation. Term: pericarditis Definition: inflammation around the heart (muscle) 2. Word root: the meaning or core part of the word. Medical terms have one or more roots. By adding prefixes and suffixes to a word root, the meaning of a word is changed. Most medical words have at least one word root, and some have several. Word roots are joined by a combining vowel. A word root will have the same meaning in every word that contains it. When a word root is joined to a suffix, or to other root words to make a compound word, it requires the use of a combining vowel. 3. Combining vowel: usually an o and occasionally an i, used between compound word roots or between a word root and a suffix. Combining vowels make word pronunciation easier. When a vowel is added to a root word, it is called a combining form. It is usually marked with a diagonal, e.g., arthr/o. Combining vowels are kept between compound words even if the second word root does begin with a vowel, e.g., gastr/oentero/logy. Compound words are two or more root words joined with a combining vowel. Compound words also may have a suffix, which is joined to the word by a combining vowel. When the suffix begins with a vowel (usually an i), the combining vowel on the root word is dropped. When the suffix begins with a consonant, the combining vowel is kept. Examples are: mening/o (root word and combining vowel) and -itis (suffix). The word is spelled meningitis, dropping the o. The term means inflammation of the meninges. hem/o (root word and combining vowel) and -rrhage (suffix). The word is spelled hemorrhage, keeping the o. The term means escape of blood from the vessels. If the suffix and the combining vowel are the same vowel, the duplicate vowel is also dropped, e.g., cardi/o (root word for heart) and -itis (suffix). The word is spelled carditis (only one i is used). It means inflammation of the heart (muscle). 4. Suffix: the word part or element attached to the end of a root word to modify its meaning. Not all root words have a suffix, and some words have two suffixes, e.g., psych/o/log/ic/al. When a medical term has two suffixes (as psychological does), they are joined and considered one suffix, that is, -ic/al = -ical. Some suffixes are attached to a prefix only, e.g., dia- (prefix) and -rrhea (suffix), or diarrhea. When they form a complete word, as in this example (diarrhea), the resulting word may be considered a root word, depending on its use. The literal meaning of a word may be shortened through usage, by common consent, or when understood without being expressed. Please note the following two premises when studying: 1. Many columns carry the heading word root. This is taken to mean that items under this column can be the word root itself or a word root with /o, that is, a combining form. This practice is to avoid excess repetition of the term combining form throughout the book. Confusing Medical Terminology -stasis Versus -stalsis -stasis = control, stop, e.g., hemostasis (he-mo-sta-sis) refers to the interruption of blood flow or arrest of bleeding by the physiological properties of vasoconstriction and coagulation or by surgical means -stalsis = contraction, e.g., peristalsis (per-uh-stawl-sis) refers to successive waves of involuntary contraction passing along the walls of a hollow muscular structure (as the esophagus or intestine) and forcing the contents onward
3 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 7 2. About 3 5% of the medical terms in this book that have not been presented in the lessons are included in the practice exercises. This is designed to: Encourage students to use the dictionary because the practice exercises are all open-book. Provide students an opportunity to practice dividing those words into their respective components according to the rules in the book. Give the instructor a choice whether to include these additional words. Some textbooks on medical terminology use the same technique; others do not. Feedback from students and instructors will be noted. Word parts combine in various ways, as can be seen in the accompanying table. Word Parts Examples Medical Terms prefix + word root word root + suffix combining form (word root + combining vowel) + suffix prefix + suffix prefix + root word + suffix compound word* + suffix anti- (prefix meaning against) + thyroid (root word for thyroid gland) gastr (word root for stomach) + -ic (suffix meaning pertaining to) cardi (root word for heart) + /o (a combining vowel) + -logy (suffix meaning study of ) an- (prefix meaning no, without) + -emia (suffix meaning blood) epi- (prefix meaning above, over) + gastr (root word for stomach) + -algia (suffix meaning pain) ot/o (root word for ear) + rhin/o (root word for nose) + laryng/o (root word for throat or larynx) + -logy (suffix meaning study of ) antithyroid literal definition: against the thyroid actual usage: (agent) suppressing thyroid activity gastric definition: pertaining to the stomach cardiology definition: study of the heart anemia literal definition: without (or no) blood actual usage: decreased number of red blood cells or decreased hemoglobin in the cells epigastralgia literal definition: pain above the stomach actual usage: pain in the upper region of the abdomen otorhinolaryngology definition: the branch of medicine dealing with diseases of the ear, nose, and throat * Two or more root words connected with a combining vowel. Listing of Word Parts You may or may not know most of the words presented in the table. Do not be concerned if you don t. There will be plenty of opportunity to learn more about them. In the next section, you are provided with listings of word parts. Many of the prefixes, combining forms, word roots, and suffixes are indicated. Eventually, you will have to be familiar with all of them. Here are some steps that will help you to learn: 1. Go through the lists of word parts once or twice. 2. Check your knowledge by covering all but the first column and see if you can provide meanings for some of the words. Confusing Medical Terminology ante- Versus antiante- = before, forward, e.g., antepartum (an-te-par-tum) refers to occurring before childbirth anti- = against, counter, e.g., anticoagulant (an-te-ko-ag-u-lant) is an agent that slows down the clotting process
4 8 Unit I Medical Terminology Prefixes, Word Roots with Combining Forms, and Suffixes Table 2-1 Prefixes Commonly Used in Medicine Prefix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition a-, an- no, not, without, lack of, apart anoxia an-ok -se-ah lack of sufficient oxygen in the blood ad- toward, near, to adhesion ad-he -zhun union of two surfaces that are normally separate bi- two, double bicuspid bi-kus -pid having two cusps de- down, away from degenerate de-jen -er-ate to change from a higher to a lower form di- two, double diplopia di-plo-pe-ah double vision dia- through, between dialysis di-al -i-sis diffusion of solute molecules through a semipermeable membrane dif-, dis- apart, free from, separate diffusion di-fu -zhun state or process of being widely spread dys- bad, difficult, painful dysfunctional dis-fungk -zhun-al disturbance, impairment, or abnormality of an organ ec-, ecto- out, outside, outer ectoderm ek-to-derm outermost of the three primitive germ layers of the embryo end-, endowithin, inner endometrium en-do-me -tre-um mucous membrane lining the uterus ep-, epi- upon, over, above epidural ep-i-du-ral situated upon or outside the dura mater eu- good, normal euphoria u-fo -re-ah an exaggerated feeling of mental and physical well-being ex-, exo- out, away from excrete ek-skreet to throw off or eliminate, as waste matter, by normal discharge extra- outside, beyond extrauterine ek-strah-u -ter-in situated or occurring outside the uterus hyper- above, beyond, excessive hypertension hi-per-ten -shun persistently high blood pressure hypo- below, under, deficient hypodermic hi-po-der -mik beneath the skin in- in, into, not infusion in-fu -zhun steeping a substance in water to obtain its soluble principles mega- large, great megalgia meg-al-je-ah a severe pain meta- para- beyond, over, between, change beside, alongside, abnormal metastasis me-tas -tah-sis transfer of a disease from one organ to another not directly connected to it paracolitis par -ah-ko-li -tis inflammation of the outer coat of the colon poly- many, much, excessive polycystic pol -e-sis -tik containing many cysts
5 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 9 Table 2-1 Prefixes Commonly Used in Medicine (continued ) Prefix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition post- after, behind postnatal post-na -tal occurring after birth, with reference to the newborn pre- before, in front of premenstrual pre-men -stroo-al preceding menstruation pro- before, in front of prootic pro-ot -ik in front of the ear super- above, beyond supernutrition soo-per-nu-trish un excessive nutrition supra- above, beyond supracostal soo-prah-kos -tal above or outside the ribs Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition abdomin/o abdomen abdominocystic ab-dom -i-no-sis-tic pertaining to the abdomen and gallbladder aden/o gland adenitis ad -e-ni-tis inflammation of a gland an/o anus anoplasty an -oh-plas-te plastic repair of the anus andr/o men android an-droid resembling a man angi/o vessel angiectomy an -je -ek-to-me excision of part of a blood vessel or lymph vessel appendage attached to or outgrowth appendectomy ah-pen-dek -to-me excision of the vermiform appendix appendic/o appendix appendicolysis ah-pen-di-kol -i-sis surgical separation of adhesions binding the appendix arteri/o artery arteriogram ar-te-re-o-gram an x-ray picture of an artery arthr/o joint arthrocele ar-thro-sel a joint swelling cardi/o heart cardiology kar-de-ol -ogy study of the heart cephal/o head cephalic se -phăl-ic pertaining to the head cerebr/o cerebrum (part of the brain) cerebral ser -e-bral pertaining to the brain cyst/o bladder cystocele sis-toh-seel hernia of the bladder into the vagina cyt/o cell cytology si -toh-lōgy study of the body cells encephal/o brain encephaloma en-sef -ah-lo-mah a swelling or tumor of the brain (continues)
6 10 Unit I Medical Terminology Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition enter/o intestines enteritis en-ter-i -tis inflammation of the intestine (usually small intestine) esophag/o esophagus esophagism e-sof-ah-jism spasm of the esophagus gastro/o stomach gastropathy gas-trop-ah-the any disease of the stomach gloss/o tongue glossodynia glos -o-din-e-ah pain in the tongue gyne woman gynephobia jin -e-fo-be-ah morbid aversion to women hem/o blood hematoma he-ma-toh -mah blood clot in an organ or under the skin hepat/o liver hepatocele hep-ah-to-sel hernia of the liver hyster/o uterus hysterolith his-ter-o-lith a uterine calculus (stone) ile/o ileum (small intestine) Ileus il-e-us intestinal obstruction irid/o iris (eye) iridomalacia ir -i-do-mah-la-sheah softening of the iris kerat/o lamina, lamin/o cornea of eye; horny substance thin, flat part of vertebra keratorrhexis ker -ah-to-rek-sis rupture of the cornea laminotomy lam -i-not-o-me transection of a vertebral lamina lapar/o abdominal wall laparorrhaphy lap -ah-ror-ah-fe suture of the abdominal wall lingua tongue nigralingua ni-gra-ling-gwah black tongue lob/o lobe, as of lung or brain lobotomy lo-bot-o-me cutting of nerve fibers connecting a lobe of the brain with the thalamus mamm/o breast mammogram mam-o-gram x-ray recording of breast tissue mast/o breast mastitis mas-ti-tis inflammation of the breast my/o muscle myocarditis mi -o-kar-di-tis inflammation of the heart muscle myel/o bone marrow; spinal cord myelocyte mi-e-lo-sit immature cell of bone marrow myring/o eardrum myringoplasty mi-ring-o-plas -te surgical reconstruction of the eardrum nephr/o kidney nephritis ne-fri-tis inflammation of the kidney neur/o nerve neuralgia nu-ral-je-ah pain in a nerve oophor/o ovary oophorocystosis o-of -o-ro-sis-to-sis formation of an ovarian cyst ophthalm/o eye ophthalmorrhagia of-thal -mo-ra-je-ah hemorrhage from the eye orchi/o testicle orchiopathy or -ke-op-ah-the any disease of the testes
7 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 11 Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition orchid/o testicle orchidorrhaphy or -ki-dor-ah-fe surgical fixation of an undescended testis into the scrotum by suturing oste/o bone osteoporosis os -te-o-po-ro-sis abnormal thinning of the skeleton ot/o ear otitis o-ti-tis inflammation of the ear pancreat/o pancreas pancreatogenous pan -kre-ah-toje-nus arising in the pancreas pharyng/o pharynx pharyngismus far -in-jis-mus muscular spasm of the pharynx phleb/o vein phlebotomy fle-bot-o-me incision of a vein pneum/o lungs (air or gas) pneumonectomy nu -mo-nek-to-me excision of lung tissue proct/o rectum proctodynia prok -to-din-e-ah pain in the rectum prostat/o prostate gland prostatitis pros -tah-ti-tis inflammation of the prostate pyel/o pelvis of kidney pyelectasis pi -e-lek-tah-sis dilation of the renal pelvis rect/o rectum and/or anus rectocele rek-to-sel hernial protrusion of part of the rectum into the vagina ren/i renal (kidney) reniform ren-i-form kidney-shaped rhin/o nose rhinitis ri-ni-tis inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose sacr/o sacrum sacrolumbar sa -kro-lum-bar pertaining to the sacrum and loins salping/o fallopian tube salpingocyesis sal-ping -go-ci-e-sis development of an embryo in the uterine tube; a tubal pregnancy splen/o spleen splenoptosis sple-nop-to-sis downward displacement of the spleen spondyl/o vertebra spondylodymus spon -di-lod-i-mus twin fetuses united by the vertebrae steth/o chest stethospasm steth-o-spasm spasm of the chest muscles stomat/o mouth stomatomalacia sto-mah-to-ma-lashe-ah softening of the structures of the mouth ten/o tendon tendolysis ten-dol-i-sis the freeing of tendon adhesions thorac/a thorax (chest) thoracentesis tho -rah-sen-te-sis surgical puncture and drainage of the thoracic cavity thyr/o thyroid gland thyroxine thi-rok-sin a hormone of the thyroid gland that contains iodine trache/o trachea tracheoscopy tra -ke-os-ko-pe inspection of the interior of the trachea (continues)
8 12 Unit I Medical Terminology Table 2-2 Word Roots and Combining Forms for Body Parts (continued ) Word Part Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition tympan/o eardrum tympanum tim-pah-num part of the cavity of the middle ear, in the temporal bone ureter/o ureter ureteropathy u-re -ter-op-ah-the any disease of the ureter vas/o vessel vascular vas-ku-lar pertaining to blood vessels ven/i vein venipuncture ven -i-punk-chur surgical puncture of a vein Table 2-3 Suffixes Used in Surgery Suffix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition -age related to tri/age (three) tre-ahzh sorting out and classification of casualties to determine priority of treatment -centesis surgical puncture arthro/centesis (joint) ar -thro-sen-te-sis puncture of a joint cavity for aspiration of fluid -cid kill germi/cidal (germ) jer-mi-si-dal destructive to pathogenic microorganisms -cis cut, kill, excise circum/cision (around) ser-kum-sizh -un surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis -clasis to break down, refracture oste/oclasis (bone) os -te-ok-lah-sis surgical fracture or refracture of bones -desis binding, stabilization arthr/odesis (joint) ar -thro-de-sis surgical fusion of a joint -ectomy excision, removal append/ectomy ap -en-dek-to-me excision of the vermiform appendix -iatry healing (by a physician) psych/iatry (mind) si -ki-ah-tre healing of the mind -ion process excerebration (brain) ek-ser-e-bra -shun process of removal of the brain -lysis loosen, free from adhesions, destruction enter/olysis (intestine) en -ter-ol-i-sis surgical separation of intestinal adhesions -osis condition of necr/osis (death) ne-kro-sis death of cells or tissues -os/tomy mouth, forming an opening col/ostomy (colon) ko-los-to-me the surgical creation of an opening between the colon and the body surface -pexy fixation, suspension gastro/pexy (stomach) gas-tro-pek -se surgical fixation of the stomach -plasty formation, plastic repair rhino/plasty (nose) ri-no-plas -te plastic surgery of the nose
9 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 13 Table 2-3 Suffixes Used in Surgery (continued ) Suffix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition -stasis stop/control hemo/stasis (blood) he-mo-sta -sis stopping the escape of blood by either natural or artificial means -therapy treatment chemo/therapy (drug) ke-mo-ther -ah-pe treatment of illness by medication -tomy incision, to cut into phlebo/tomy (vein) fle-bot-o-me incision of a vein -tripsy to crush litho/tripsy (stone) lith-o-trip -se the crushing of a stone in the bladder Table 2-4 Suffixes for Diagnoses and Symptoms Suffix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition -algia pain cephal/algia (head) sef -a-lal-je-ah headache -cele hernia, swelling hepat/ocele (liver) hep-ah-to-sel hernia of the liver -dynia pain cephal/odynia (head) -ectasis dilation, expansion bronchi/ectasis (bronchus) -emia blood poly/cyth/emia (many) -gen producing, beginning carcin/o/gen (cancer) -gram record, picture encephal/o/gram (brain) sef -ah-lo-din-e-ah brong -ke-ek-tah-sis pol-e-si-the -me-ah car-sin-o-jen en-sef-ah-lo-gram pain in the head chronic dilation of one or more bronchi increase in total red cell mass of the blood any substance that causes cancer the x-ray film obtained by encephalography -graph instrument for recording cardi/o/graph (heart) kar-de-o-graf an instrument used for recording electrical activity of the heartbeat -graphy process of recording roentgen/o/ graphy rent -gen-og-rah-fe x-ray films (roentgenograms) of internal structures of the body -iasis abnormal condition, formation of, presence of chole/lith/iasis (gallstone) ko -le-li-thi-ah-sis the presence or formation of gallstones -itis inflammation gastr/itis (stomach) gas-tri-tis inflammation of the stomach (continues)
10 14 Unit I Medical Terminology Table 2-4 Suffixes for Diagnoses and Symptoms (continued ) Suffix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition -logy study of bio/logy (life) bi-ol-o-je scientific study of living organisms -malacia softening oste/o/malacia (bone) -megaly enlargement hepat/o/megaly (liver) softening of the bones resulting from vitamin D deficiency enlargement of the liver -meter instrument for measuring crani/o/meter (cranium) kra -ne-om-e-ter an instrument for measuring skulls -metry process of measuring pelvi/metry (pelvis) pel-vim-e-tre measurement of the capacity and diameter of the pelvis -oid resemble lip/oid (fat) lip-oid fatlike; lipid (resembling a fat) -oma tumor aden/oma (gland) ad -e-no-mah a benign skin tumor in which the cells are derived from glandular epithelium -osis abnormal condition dermat/osis (skin) der -mah-to-sis any skin disease, especially one not characterized by inflammation -pathy disease nephr/o/pathy (kidney) -penia decrease, deficiency leuk/o/cyto/penia (white) (cell) -phagia eating, swallowing dys/phagia (difficult) -phasia speech a/phasia (without) -phobia fear acr/o/phobia (extremities or top) ne-frop-ah-the os -te-o-mah-lashe-ah hep -aht-o-megah-le loo-ko-sit-o-pene-ah dis-fa-je-ah ah-fa-zhe-ah ak -ro-fo-be-ah disease of the kidneys reduction of the number of leukocytes (white blood cells), the count being 5,000/mm 3 or less difficulty in swallowing or eating defect or loss of the power of expression by speech, writing, or signs, or of comprehending spoken or written words morbid fear of heights -plegia paralysis hemi/plegia (half ) hem -e-ple-je-ah paralysis of one side of the body -ptosis prolapse, falling, dropping hyster/o/ptosis (uterus) his -ter-op-to-sis metroptosis; downward displacement or prolapse of the uterus -rrhage burst forth hem/o/rrhage (blood) -rrhea discharge, flow men/o/rrhea (menses) -rrhexis rupture angi/o/rrhexis (blood vessel) hem-o-rij men -o-re-ah an -je-or-ek-sis the escape of blood from the vessels; excessive bleeding normal menstruation rupture of a vessel, especially a blood vessel
11 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 15 Table 2-4 Suffixes for Diagnoses and Symptoms (continued ) Suffix Definition Word Example Pronunciation Definition -sclerosis hardening arteri/o/sclerosis (artery) ar-te -re-o-skle-ro-sis a group of diseases characterized by thickening and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls -scopy examination, view oto/scopy (ear) o-tos-ko-pe examination of the ear by means of the otoscope -spasm involuntary contraction, twitching of a muscle blephar/o/spasm (eyelid) blef-ah-ro-spazm spasm of the eyelids In summary, the important elements of a medical term are: 1. Root: the foundation of the term 2. Prefix: the word beginning 3. Suffix: the word ending 4. Combining vowel: a vowel that links the root word to the suffix or to other root words 5. Combining form: a combination of the root word(s) and the combining vowel The rules for building medical words from these elements are as follows: 1. A prefix is always placed at the beginning of the word. 2. A suffix is always placed at the end of the word. 3. When more than one root word is used, it is a compound word and requires the use of a combining vowel to separate the words, even if the root word begins with a vowel. 4. When defining medical terms, begin with the suffix and read backward. 5. If the word also contains a prefix, define the suffix first, prefix second, and root word(s) last. 6. When using compound words that relate to parts of the body, anatomic position determines which root word comes first. Confusing Medical Terminology an/o Versus ana- Versus anan/o = anal origin or anus, e.g., anorectal (a-no-rek-tal) refers to the anal opening of the rectum ana- = back, again, up, e.g., anaplasia (an-uh-pley-zhuh) refers to a reversion (back, again) of differentiation in cells and is characteristic of malignant tumors an- = no, not, or without, e.g., anacusis (anah-ku-sis) refers to without hearing Lesson TWO Progress Check Part A Matching Match the following word elements with their meaning: 1. aden/o 2. bronch/o 3. encephal/o 4. gloss/o 5. hyster/o 6. irid/o 7. lapar/o 8. oste/o a. brain b. uterus c. abdominal wall d. bronchus e. bone f. gland g. tongue h. iris
12 16 Unit I Medical Terminology Spelling and Definition Circle the letter of the correct spelling and then define the combining form: 1. (a) oophor/o (b) ophoor/o (c) oorphor/o 2. (a) prosct/o (b) proct/o (c) prost/o 3. (a) neuphr/o (b) neprect/o (c) nephr/o 4. (a) rhinit/o (b) rhin/o (c) rhen/o 5. (a) orchi/o (b) oorch/o (c) orche/o 6. (a) salcr/o (b) salp/o (c) sacr/o 7. (a) salpr/o (b) salping/o (c) salpen/o 8. (a) myring/o (b) mirang/o (c) myleng/o 9. (a) pharang/o (b) pharyng/o (c) pragyn/o 10. (a) spongyl/o (b) sphondyl/o (c) spondyl/o 11. (a) urotor/o (b) uroter/o (c) ureter/o 12. (a) chondr/o (b) cholondr/o (c) chodol/o 13. (a) chost/o (b) cost/o (c) costol/o 14. (a) vast/o (b) vas/o (c) vein/o 15. (a) ven/o (b) vin/o (c) vein/o 16. (a) erythr/o (b) eythry/o (c) erythrey/o
13 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 17 Defining Medical Word Elements Provide the medical root word for the following terms: 1. man 2. woman 3. heart 4. head 5. chest 6. bone 7. brain 8. stomach 9. liver 10. gallbladder 11. mouth 12. tongue 13. breast 14. muscle 15. nerve Building Medical Words Using all word elements necessary, build medical words that mean: 1. inflammation of a tendon 2. removal of the thyroid gland 3. incision into the trachea 4. any disease of the intestine 5. pain in the nerves 6. inflammation in the urinary bladder 7. inflammation in a joint 8. removal of the spleen 9. an eye specialist 10. an x-ray picture of a blood vessel 11. stones in the gallbladder 12. an obstructed artery 13. removal of a lung 14. an x-ray picture of the spinal cord 15. instrument for examining the ear 16. incision into a vein 17. removal of the prostate gland 18. rupture of a vessel in the cerebrum 19. inflammation of the esophagus 20. incision into the thorax 21. excessive sugar in the blood
14 18 Unit I Medical Terminology Lesson TWO Progress Check Part B Matching Match the following word elements with their meaning: 1. -ectomy 2. -ostomy 3. -otomy 4. -rrhaphy 5. -rrhage 6. -rrhea 7. -rrhexis 8. -oid 9. -oma 10. -osis a. tumor b. abnormal condition c. rupture d. resembling e. discharge f. burst forth g. cut into h. suture i. surgical removal j. mouth, surgical creation Spelling and Definition Circle the letter of the correct spelling and then define the word element: 1. (a) -centesis (b) -centisis (c) -senticis (d) -cinteses 2. (a) -clysis (b) -clasis (c) -claxis (d) -clasy 3. (a) -ectasy (b) -ectosis (c) -ectasis (d) -eclasis 4. (a) -malachi (b) -melacia (c) -malazia (d) -malacia 5. (a) -plegia (b) -plagia (c) -phlagia (d) -pelagia 6. (a) -tosis (b) -ptosis (c) -protosis (d) -tsosis 7. (a) -slerosis (b) -schlerosis (c) -sclerosis (d) -shlerosis 8. (a) -magaly (b) -mejally (c) -magely (d) -megaly 9. (a) -cele (b) -cely (c) -cili (d) -ceal 10. (a) -isis (b) -iasis (c) -iatis (d) -iesis
15 Chapter 2 Word Parts and Word Building Rules 19 Building Medical Words Using all word elements necessary, build medical words that mean: 1. a headache 2. taking x-ray films of internal body structures 3. inflammation of the stomach 4. formation of gallstones 5. increase in red cell mass 6. softening of the bones 7. surgical puncture of a joint 8. removal of blood from a vein 9. repair of a broken nose 10. scientific study of living organisms 11. enlargement of the liver 12. any skin disease 13. excision of the appendix 14. healing of the mind 15. incision into the brain 16. treatment of illness by medication 17. stopping the flow of blood 18. a substance that causes cancer 19. disease of the kidneys 20. loss of the power of speech Defining Medical Terms Define the following medical terms: 1. osteoclasis 2. enterolysis 3. lithotripsy 4. necrosis 5. circumcision 6. adenoma 7. dysphagia 8. leukopenia 9. hemiplegia 10. acrophobia
pertaining to the abdomen and gallbladder abdominocystic inflammation of a gland adenitis adenoma
 abdominocystic pertaining to the abdomen and gallbladder acrophobia morbid fear of heights adenitis inflammation of a gland adenoma a benign skin tumor in which the cells are derived from glandular epithelium
abdominocystic pertaining to the abdomen and gallbladder acrophobia morbid fear of heights adenitis inflammation of a gland adenoma a benign skin tumor in which the cells are derived from glandular epithelium
English Term Greek or Latin Term* Word Root Word Analysis. cutane pertaining to the skin A term that describes an anatomical structure kidney.
 Medical Terminology lecture 3 Word Parts and Word Building Rules Word Roots A word root is the foundation of a medical term and contains its primary meaning. All medical terms have at least one word root.
Medical Terminology lecture 3 Word Parts and Word Building Rules Word Roots A word root is the foundation of a medical term and contains its primary meaning. All medical terms have at least one word root.
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. Understanding Suffixes. Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 2 Understanding Suffixes Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the suffixes often used in medical terminology. Identify suffixes
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS
 CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
Medical Terminology The Fun in Deciphering Words. Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012
 Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
Julie A. Shay, RHIA Santa Fe HIT Program Director AAPC Conference September 29, 2012 Back to the Basics Pieces, Parts, Whole Body Systems Musculoskeletal Cardiovascular Solve the Puzzle 1. Word roots
Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system
 SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Terminology MATCHING Match each definition with the correct word part. a. abnormal condition b. deficient c. excessive d. pain e. surgical removal 1. -algia 2. -ectomy
List as many as you can think of Go To --Student Worksheet Med Terms I am going to start you off
 Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
Medical Terminology You may fear learning medical terminology thinking of it as a whole new language. Actually it is just a combination of terms many of which you are familiar with. Each student needs
prolapse, falling, dropping
 Section X Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The functions of the system are to produce and eliminate urine and to maintain homeostasis or the balance
Section X Urinary System The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. The functions of the system are to produce and eliminate urine and to maintain homeostasis or the balance
Respiratory System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview. Pulmonology
 Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Upon completion of this continuing education course, the professional should be able to:
 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is designed for individuals working in medical support services (e.g., billing, insurance, transcription, records, medical assisting, etc.) to review, refine, and expand
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
The Digestive System Combining Forms Append/o appendix Hepat/o liver Appendic/o appendix Lingu/o tongue Col/o colon Myc/o fungus Dent/o teeth Odont/o teeth Enter/o intestine Or/o mouth Esophag/o esophagus
Chapter 2. Organization of the Body. Copyright 2012, 2009, 2005, 2003, 1999, 1991 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 2 Organization of the Body 1 Learning Objectives Name the body systems and their functions. Identify body cavities and specific organs within them. List the divisions of the back. Identify three
Chapter 2 Organization of the Body 1 Learning Objectives Name the body systems and their functions. Identify body cavities and specific organs within them. List the divisions of the back. Identify three
Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided.
 CC306M: Medical Terminology Quiz 1 June 4, 2012 Section 1: Defining Terms Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided. 1. carcinophobia a. cancer-eating
CC306M: Medical Terminology Quiz 1 June 4, 2012 Section 1: Defining Terms Directions: For each of the following terms, select the best definition from the options provided. 1. carcinophobia a. cancer-eating
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. All answers to questions asking for a combining form must be written in the combining form style,
8 Digestive System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview
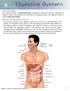 8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
8 Digestive System Gastroenterology The medical practice of gastroenterology encompasses treatment of diseases affecting the digestive system. The physician who specializes in treating disorders of the
Appendix B English Terms
 Appendix B English Terms English Word Abnormal condition Abnormal condition (produced by something specified) above, upon above adrenal glands after, behind against air air, lung anterior, front anus,
Appendix B English Terms English Word Abnormal condition Abnormal condition (produced by something specified) above, upon above adrenal glands after, behind against air air, lung anterior, front anus,
Medical Terminology. 1 P a g e
 Medical Terminology 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Medical Terminology Assignment Guidelines When terms are assigned, primarily the Latin or Greek word parts will be given; however, combined forms of the word parts
Medical Terminology 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Medical Terminology Assignment Guidelines When terms are assigned, primarily the Latin or Greek word parts will be given; however, combined forms of the word parts
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function
 study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
study of body structure & Physiology study of body function Medical Words Made up of Latin, Greek, French, German, Dutch, Scandinavian, Italian, English, etc.. Common Medical Roots, Prefixes & Suffixes
Spelling & Pronunciation
 Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
UNIT 1. Introduction
 UNIT 1 Introduction Grading A grade is an inadequate report of an inaccurate judgment by a biased and variable judge of the extent to which a student has attained an undefined level of mastery of an unknown
UNIT 1 Introduction Grading A grade is an inadequate report of an inaccurate judgment by a biased and variable judge of the extent to which a student has attained an undefined level of mastery of an unknown
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. The Skeletal and Muscular Systems Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal and Muscular Systems Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create medical terms for the skeletal
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal and Muscular Systems Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create medical terms for the skeletal
9 Review. Labeling Exercise. Blood high in oxygen. Blood low in oxygen. Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195
 Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Gastrectomy: a. Gastric resection b. Intestinal incision c. Tumor of the stomach d. Incision of the stomach e. Resection of the intestine A
Chapter 1: Basic Word Structure Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Gastrectomy: a. Gastric resection b. Intestinal incision c. Tumor of the stomach d. Incision of the stomach e. Resection of the intestine A
saliva, salivary glands
 Section IX Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source
Section IX Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source
1-Choose the correct answer
 Course No: DSEC 1201 Course Title: Medical Terminology Date: 16/1/2017 No. of Questions: (5) Time: 2 hour final Exam2016/2017 Total Grade: ------------- Instructor Name: Dr. Fuad M. Nijim Student No.:
Course No: DSEC 1201 Course Title: Medical Terminology Date: 16/1/2017 No. of Questions: (5) Time: 2 hour final Exam2016/2017 Total Grade: ------------- Instructor Name: Dr. Fuad M. Nijim Student No.:
Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam. PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer:
 Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Testing Services and School of Allied Health & Communicative Disorders HSCI 318 Proficiency Examination Medical Terminology COURSE DESCRIPTION: A study of the basic language
FAQ: Foundations of Medical Terminology
 Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
Medical Terminology made easy...
 Medical Terminology made easy... well, sort of... What is medical terminology? describes parts of the body locations in the body bodily functions (physiology) diseases procedures instruments Why so complicated?
Medical Terminology made easy... well, sort of... What is medical terminology? describes parts of the body locations in the body bodily functions (physiology) diseases procedures instruments Why so complicated?
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Biomedical Terminology. Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System
 Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology
 Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil1@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orientation) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology. 2. Levels of structural
Human Anatomy and Physiology CLS 224 Lama Alzamil Email: lalzamil1@ksu.edu.sa 3 rd floor/ office #119 Lecture 1: The Human Body (an orientation) 1. An overview of anatomy and physiology. 2. Levels of structural
C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly
C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System
 C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly spell
C h a p t e r 9 Urinary System Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly spell
The Skeletal System. Support Systems Unit 2
 The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 Vocabulary- combining forms Arthr/o joint Sacr/o Sacrum Cervic/o neck Spondyl/o vertebrae Chondr/o cartilage Stern/o Sternum Cost/o rib Ten/o, Tend/o, Tendon
The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 Vocabulary- combining forms Arthr/o joint Sacr/o Sacrum Cervic/o neck Spondyl/o vertebrae Chondr/o cartilage Stern/o Sternum Cost/o rib Ten/o, Tend/o, Tendon
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS:
 PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS: Use Avery 8471 Business Cards. 10 cards per sheet x 220 cards = 22 sheets. (You can also reformat to fit other size cards). Just be careful to align word parts with definitions
PRINTABLE FLASHCARD DIRECTIONS: Use Avery 8471 Business Cards. 10 cards per sheet x 220 cards = 22 sheets. (You can also reformat to fit other size cards). Just be careful to align word parts with definitions
Title: Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F
 Course Number and Title: Instructor: Credit Hours: Course Description: Due Dates: Required Textbook: AH 290 Medical Terminology Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F pamela.skipworth@wku.edu
Course Number and Title: Instructor: Credit Hours: Course Description: Due Dates: Required Textbook: AH 290 Medical Terminology Pamela Chandler M.Ed, RHIT, CDIP Academic Complex 411F pamela.skipworth@wku.edu
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Suffix can mean a condition, procedure, surgery, treatment. ia/ism/sis/y condition or status
 Chapter 2 suffix Outline: condition suffix specialty suffix surgical suffix diagnostic suffix disease suffix Adjective suffix Introduction about suffix suffix are always at the word ending When added to
Chapter 2 suffix Outline: condition suffix specialty suffix surgical suffix diagnostic suffix disease suffix Adjective suffix Introduction about suffix suffix are always at the word ending When added to
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
The Lymphatic System Combining Forms Aden/o Angi/o Hem/o Hist/o Immun/o Lymph/o Splen/o Thym/o Tox/o gland vessel (blood or lymph) blood tissue immune lymph spleen thymus gland poison Prefixes / Suffixes
The Language Of Medicine
 The Language Of Medicine 11 th edition Davi Ellen Chabner Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011, 2007 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Additional Suffixes and Digestive System Terminology Copyright
The Language Of Medicine 11 th edition Davi Ellen Chabner Copyright 2017, 2014, 2011, 2007 Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. 1 Chapter 6 Additional Suffixes and Digestive System Terminology Copyright
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ
 Chapter 3 38 Chapter 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ Name: In the box write the letter of the choice that is the definition of the term or best answers the question. There is only one correct
Chapter 3 38 Chapter 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ Name: In the box write the letter of the choice that is the definition of the term or best answers the question. There is only one correct
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
The Body s Organization
 Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
TEST 5. Module 9 & 10
 TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
TEST 5 Module 9 & 10 Questions from the GVLS website 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels 4. Circulation 5. Blood Pressure 6. Respiratory system 7. Lungs 8. Oxygen 9. Carbon Dioxide 10. The heart is made
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
A Sound Track to Reading
 A Sound Track to Reading Blending Flashcards Prepared by Donald L Potter June 1, 2018 Mr. Potter prepared these cards to be used with Sister Monica Foltzer s advanced intensive phonics program and reader,
A Sound Track to Reading Blending Flashcards Prepared by Donald L Potter June 1, 2018 Mr. Potter prepared these cards to be used with Sister Monica Foltzer s advanced intensive phonics program and reader,
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ
 Chapter 3 38 Chapter 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ Name: In the box write the letter of the choice that is the definition of the term or best answers the question. There is only one correct
Chapter 3 38 Chapter 3 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUIZ Name: In the box write the letter of the choice that is the definition of the term or best answers the question. There is only one correct
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours. Animal Form. AP Biology Rapid Learning Series
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
 TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY CHAPTER 1 The Instructor Resources teaching tools for this chapter include: The answer key for the Learning Exercises for the chapter, located
TEACHING TOOLS FOR CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY CHAPTER 1 The Instructor Resources teaching tools for this chapter include: The answer key for the Learning Exercises for the chapter, located
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion?
 Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
Section 1.1: What is the function of digestion? When you have completed this section, you should be able to: Describe the overall function of the GI tract. Describe the processes involved in digestion.
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
