Anatomy Neuroanatomy & Physiology. Michelle Heard, Katie McGrath & Shannon Woo
|
|
|
- Reynard King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy Neuroanatomy & Physiology Michelle Heard, Katie McGrath & Shannon Woo
2 Table of Contents Respiration: Structures & Processes Phonation: Structures & Processes Resonation and Articulation: Structures & Processes Neurons & Neural Transmission Peripheral & Autonomic Nervous Systems Central Nervous System a. b. c. d. e. Brainstem, RAS, Diencephalon, Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum Review Activity Cerebrum Review Activity Pyramidal & Extrapyramidal Activity Fibers, Ventricles & Layers Activity CSF & Blood Supply Activity
3 Respiration Structure & Processes Review Activity
4 Respiration- Anatomy Structures Lungs Bronchi Made of cartilage Extends from lungs to trachea. Trachea The right one is bigger 20 cartilaginous rings Extends from the larynx to the right and left bronchi Rib cage 12 pairs
5 Spinal Column consists of individual vertebrae: 7 cervical vertebrae (C1 - C 7) 12 thoracic vertebrae (T 1 - T 12) 5 lumbar vertebrae (L 1- L 5) 5 sacral vertebrae (S 1- S 5, fused in adults) 3-4 coccygeal vertebrae (fused and called the coccyx). Sternum or breastbone consists of three parts: Manubrium-uppermost part of sternum, provides attachment for the clavicle and the first rib. Corpus (Body)- long and narrow, cartilages of ribs 2-7 attach here. Xiphoid Process- small cartilaginous structure found at bottom of the body
6 The process of respiration...who can describe what happens?
7 Muscles of Inhalation
8 Muscles of Exhalation
9 Video Link of the muscles involved in respiration... Muscles of the thorax
10 Phonation Structure & Processes
11 Phonation Larynx Adduct: moves toward midline ABduct: moves away from midline Biological function Closure so that food and other substances does not enter the lungs Production of the cough reflex Closure to build subglottic pressure necessary for physical tasks
12 Phonation- Structures of the larynx Hyoid bone U shaped Muscles of the tongue and various muscles of the mandible, skull, and larynx attaches to the hyoid Epiglottis During the swallow the epiglottis retroflexes to cover the larynx What is the epiglottis made of?
13 Phonation- Structures of the larynx Thyroid cartilage Cricoid cartilage Forms the lateral and anterior walls of the larynx Protects the larynx Linked with the thyroid and paired with the arytenoids Completely surrounds the trachea Arytenoid cartilages Pyramid shaped cartilages Connected to the cricoid through the cricoarytenoid joint which allows sliding and circular movements
14 Phonation- Structures of the larynx Corniculate cartilages Sit on apex of arytenoid Assist in reducing the laryngeal opening when a person is swallowing Cuneiform cartilages Located under the mucous membrane that covers the aryepiglottic folds Stiffens and tenses the aryepiglottic folds
15
16 Phonation- Structures of the larynx Vocal folds 3 Layers (or 5) Aryepiglottic folds Epithelium, lamina propria (deep, medial and superficial) and the vocalis muscle Composed of rings of connective tissue and muscle Extend from the tips of the arytenoid to the larynx Separate the laryngeal vestibule from the pharynx Helps preserve the airway Ventricular (false) vocal folds Vibrate only at a low fundamental frequency and usually not during typical phonation Compress during activities such as coughing and lifting
17 Phonation- Intrinsic Laryngeal Muscles Muscles (CN) Function Thyroarytenoid (X) Vibrates and produces sound Lateral cricoarytenoid (X) Adducts vocal folds Transverse arytenoid (X) Adducts vocal folds Oblique arytenoid (X) Pulls arytenoids medially Cricothyroid (X) Lengthens and thickens vocal folds Posterior Cricoarytenoid (X) ABducts vocal folds
18 Phonation- Extrinsic Laryngeal Muscles Elevators (CN) Depressors (CN) Digastric (V, VII) Thyrohyoid (XII) Geniohyoid (XII) Omohyoid Mylohyoid (V) Sternothyroid Stylohyoid (VII) Sternohyoid Hyoglossus (XII) Genioglossus (XII)
19 Physiology of Phonation Myoelastic-Aerodynamic Theory Vocal fold vibrate because of the forces and air pressure of air and the elasticity of the vocal folds Subglottic air pressure blows the vocal folds apart which sets the folds into vibration The pressure between the edges of the vocal folds decrease and the folds are sucked together Bernoulli Effect Caused by the increased speed of air passing between the folds Results in the folds sucking back together; this cycle occurs 100x second Mucosal Wave Action The epithelium and lamina propria (all three layers) slide and produce the mucosal wave Without the mucosal wave there is no ability to phonate Surgery can stiffen the vocal folds and limit the mucosal wave
20 Phonation- Neuroanatomy of the Vocal Mechanism Cortical Areas Area 4 (primary motor cortex) Area 44 (Broca s area) Areas 1, 2, 3 (somatosensory cortex Area 6 (supplemental motor cortex) Cerebellum Regulates motor movement Crucial for phonation and all other speech systems Cranial Nerves CN VII: innervates the posterior belly of the digastric muscle CN X SLN Internal branch: sensory information the larynx External branch: motor innervation to the cricothyroid RLN All motor innervation all of the other intrinsic muscles Supplies all sensory information below the vocal folds
21 Resonation & Articulation Structures & Processes
22 Resonance & Articulation Fundamentals of Resonation The modification of laryngeal tone by selective dampening or enhancing specific frequencies Laryngeal tone is modified by the pharynx, nasal cavity and oral cavity Nasal cavity: /m/, /n/ & /ŋ/ Oral cavity: all of the other sounds Source Filter Theory Energy from the vibrating vocal folds (source) is modified by the resonance characteristics of the vocal tract (filter)
23 Resonance & Articulation Fundamentals of Articulation The movement of joined anatomic parts, as well as the production of speech sounds that result from such movements What are the structured needed for resonance and articulation?
24 Resonation & Articulation Structures Pharynx Soft Palate Hard Palate Mandible Teeth Tongue Face: Lips & Cheek
25 Articulation- Pharynx Made up of of three structures: Laryngopharynx Oropharynx Begins superior to the larynx and ends at the base of the tongue Extends from the base of the tongue to the soft palate Nasopharynx Ends where the two nasal cavities begin Innervated by CN X and XI via the pharyngeal plexus Pharyngeal plexus- formed by the joining of CN X and XI
26 Articulation- Pharyngeal Muscles Muscle (CN) Function Salpingopharyngeus (X, XI) Elevates lateral pharyngeal wall Stylopharyngeus (IX) Elevates and opens pharynx Superior pharyngeal constrictor (X, XI) Constricts pharyngeal diameter Middle pharyngeal constrictor (X, XI) Narrows diameter of pharynx Cricopharyngeus (X, XI) Constricts superior orifice of esophagus Thyropharyngeus (X, XI) Reduces diameter of lower pharynx
27 Articulation- Soft Palate (aka the velum) Definition: a flexible muscular structure at the juncture of the oropharynx and the nasopharynx Uvula: a small cone shaped located at the tip of the velum The velum can be elevated or lowered Velopharyngeal closure: The soft palate is raised and the muscles of the pharynx move inward creating closure. Lack of adequate velopharyngeal closure results in a nasal sounding voice
28 Articulation- Muscles of the Soft Palate Muscle (CN) Function Levator veli palatini (X, XI) Elevates velum Tensor veli palatini (V) Tenses velum, elevates eustachian tube Palatoglossus (X, XI) Elevates and depresses velum Palatopharyngeus (X, XI) Narrows pharyngeal cavity, lowers velum
29 Articulation- Hard Palate Roof of mouth/floor of nasal cavity Premaxilla: most anterior portion of the palate, houses the four upper incisors Palatine Process: largest part of the palate, two portion fuse to midline during time in utero Failure to fuse causes a cleft palate Alveolar Process: houses the teeth
30 Articulation- Mandible Also known as the lower jaw Houses the lower teeth and forms the floor of the mouth Serves as the framework for the tongue and lower lip Function Open and closes the mouth Chewing food Hinged to the skull with muscles and tendons via the temporomandibular joint
31 Articulation- Muscles of the Mandible Elevators Muscle (CN) Function Masseter (V) Elevates mandible Temporalis (V) Elevates mandible Medial pterygoid (V) Elevates mandible Lateral pterygoid (V) Protrudes mandible
32 Articulation- Muscles of the Mandible Depressors Muscle Function Anterior belly of digastric (V) Depresses mandible, pulls hyoid forward Posterior belly of digastric (VII) Depresses mandible, pulls hyoid back Geniohyoid (XII) Depresses mandible Mylohyoid (V) Depresses mandible
33 Articulation- Teeth Major function of the teeth Baby teeth Appear usually around 6 to 9 months Babies usually have 20 teeth (10 per arch) Adult teeth 32 (16 per arch) Of the 16, 4 are incisors, 2 are canine, 4 are premolar, and 6 are molar) Occlusion Deciduous teeth Mastication Articulation: Labiodentals Refer to the way the two arches come together when the person bites down Normal if symmetrical and aligned Malocclusion Deviation in the position of individual teeth and the shape and relationship of the upper and lower dental arches Three different types of malocclusion
34 Articulation- Tongue Job of the tongue Sound production Linguadentals Lingua-alveolars Lingua palatal (fricative & affricates) Divided into 4 parts Eating Articulation Tip: thinnest and most flexible part of the tongue Blade: in resting position, it is the portion that lies inferior to the alveolar ridge Dorsum: largest part of tongue that lies in contact with the hard and soft palate Root: back and bottom portion of the tongue Lingual Frenulum: Connects the mandible with the tongue
35 Articulation- Muscles of the Tongue Intrinsic Muscle (CN) Function Superior longitudinal muscle (XII) Shortens tongue Inferior longitudinal muscle (XII) Shortens tongue Transverse muscles (XII) Narrows and elongates tongue Ventricular muscle (XII) Flattens tongue
36 Articulation- Muscles of the Tongue Extrinsic Muscle (CN) Function Genioglossus (XII) Forms bulk of tongue, retracts tongue Styloglossus (XII) Draws tongue up and back Hyoglossus (XII) Retracts and depresses tongue Chondroglossus (XII) Depresses tongue Palatoglossus Elevates tongue
37 Articulation- Muscles of the Lips & Cheeks Sound production: /m/, /p/, and /b/ Muscle Function Mentalis (VII) Pulls lower lip out Platysma (VII) Depresses mandible Risorius (VII) Retracts lips at corners Buccinator (VII) Constricts oropharynx Depressor labii inferioris (VII) Pulls lip down and out to dilate orifice Depressor anguli oris (VII) Presses upper and lower lip together, depresses corners of mouth
38 Articulation- Muscles of the Lips & Cheeks Muscle Function Zygomatic minor (VII) Elevates upper lip Zygomatic major (VII) Retracts and elevates angles of mouth Orbicularis oris (VII) Pulls lip together, serves as a point of insertion for other muscles Levator anguli oris (VII) Draws corner of mouth upward and toward medial Levator labii superioris (VII) Elevates upper lip Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (VII) Elevates upper lip
39 Neurons & Neural Transmission Review Activity
40 Neurons & Neural Transmission Afferent neurons carry sensory/motor impulses away/toward the brain. Efferent neurons carry sensory/motor impulses away/toward the brain. Afferent= Sensory Efferent= Motor (think takes effort to move) The neuron cell has two main parts: Nerve fibers Soma (cell body)
41 QUARTERBACK Dendrites: RECEIVE impulses Axons: SEND OUT impulses RECEIVER Neurons communicate via SYNAPSES
42 Peripheral & Autonomic Nervous System Review Activity
43 Peripheral Nervous System The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a collection of nerves that are outside the skull and spinal column. These nerves carry motor/sensory impulses which originate in the peripheral sense organs, to the brain, and motor/sensory impulses which originate in the brain, to the glands and muscles of the body. The PNS contains three types of nerves: Cranial- 12 pairs Spinal- 31 pairs Autonomic
44
45 Damage to CN s result in... Trigeminal (V) - mixed nerve possible inability to close the mouth, difficulty in chewing, and trigeminal neuralgia (sharp pain in facial area). Facial (VII) - mixed nerve a mask-like appearance with minimal or no facial expression. Vestibulocochlear (VIII)sensory nerve Hearing loss, problems with balance, or both. Glossopharyngeal (IX) mixed nerve Difficulty in swallowing, unilateral loss of the gag reflex, and loss of taste and sensation from the posterior third of the tongue. Vagus (X) - mixed nerve Difficulty swallowing, paralysis of the velum, and voice problems. Spinal Accessory (XI) motor nerve Neck weakness, paralysis of the sternocleidomastoid, and consequent inability to turn heard as well as an inability to shrug the shoulders or raise the arm above shoulder level.
46 Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls and regulates the internal environment of our bodies with it s two branches: Sympathetic- regulates the fight or flight, accelerates heart rate, dialates pupils, raises the blood pressure Parasympathetic- brings the body back to a state of relaxation, lowers blood pressure, slows the heart rate, increases activity within the stomach.
47 Central Nervous System
48 Central Nervous System Composition Spinal cord Enclosed within vertebral column Brain Pop Review: What is contained in the PNS? Enclosed in the skull Function Command center for planning, originating and carrying out messages Gathers info from the PNS Sends impulses that lead to actions
49 Roadmap Cerebrum Cerebellum Basal Ganglia Diencephalon Brainstem Reticular Activating System Pyramidal & Extrapyramidal Fibers Ventricles Blood Supply
50 CNS - Brainstem Connects spinal cord & brain Internal Structures: Longitudinal fiber tracts Cranial nerve nuclei Reticular formation External Structures: Midbrain Pons Medulla
51 CNS - Brainstem 1. Midbrain - Mesencephalon a. b. c. d. 2. Midbrain & pons connect cerebellum to other structures Controls postural & visual reflexes, eye movement Help connect brainstem to cerebellum Substantia nigra runs along it CN IV & CN III (not involved in speech) Pons - Metencephalon a. b. c. d. Movement info from cerebral hemispheres to cerebellum Contains descending motor fibers Involved in hearing & balance Houses nuclei for: i. V: trigeminal ii. VII: facial /medium_thumbs/cdr jpg
52 CNS - Brainstem 3. Medulla - Myelencephalon a. b. c. d. Uppermost part of spinal cord Centers that control bodily functions i. Breathing, digestion, HR and BP Motor information to CN nuclei i. VIII: vestibulocochlear ii. IX: glossopharyngeal iii. X: vagus iv. XI: accessory v. XII: hypoglossal Contains pyramidal tracts i. Decussation
53 CNS - Reticular Activating System AKA Reticular Formation Structure within midbrain, brainstem and upper spinal cord Integrates efferent motor info with afferent sensory info Mechanism of attention & consciousness Sleep-wake cycles, alertness
54 CNS - Diencephalon Between brainstem & cerebral hemispheres Thalamus Hypothalamus Regulates sensory information Receives motor info from cerebellum Consciousness & alertness Controls emotions Integrates ANS Third Ventricle CSF
55 CNS - Basal Ganglia Structures deep in brain, near thalamus Related to control of background movement & initiation of movement patterns Damage = movement disorders Corpus striatum I/AAAAAAAADVY/1bEQrvUhrBMYV-jisJQtSfiLHh8CkJTU gclcbgas/s1600/bg%2bchooses.jpg Lenticular nucleus Globus pallidus Putamen Caudate Nucleus Part of extrapyramidal system Substantia nigra is functionally related
56 CNS - Cerebellum The little brain - two hemispheres Cerebellar peduncles Helps coordinate and regulate impulses Both efferent & afferent Regulates Superior, middle & inferior Connect to brainstem Equilibrium Body posture Coordinate fine motor movements Very important for speech production Damage = ataxia
57 Brainstem, RAS, Diencephalon, Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum Review Questions
58 CNS - Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Wrinkled surface Gyrus - ridge Sucus - shallow valley Fissure - deep valley Main fissures/sulci Gray matter 6 layers billion neurons Longitudinal fissure Central sulcus/fissure Sylvian/lateral sulcus Four lobes 0dd1e0e5a3a9a719f2e70b
59 Frontal Lobe 1. Higher-level thinking, problem-solving conscious behavior, social interaction 2. Primary motor cortex a. b. c. d. 3. Supplementary motor cortex 4. Broca s area a. b. Precentral gyrus, anterior to central sulcus Contralateral motor control All muscles of body are connected to this strip Pyramidal system Motor movements for speech Anterior to primary motor cortex
60 Parietal Lobe Primary somatic sensory area Sensory cortex/strip Postcentral gyrus Supramarginal gyrus Integrates and controls sensory impulses Damage = conduction aphasia and/or agraphia Angular gyrus Damage = writing, reading and naming difficulties, sometimes transcortical sensory aphasia lan_1b.jpg
61 Occipital Lobe Primary visual cortex Not very relevant to speech and hearing Expect maybe for lip reading
62 Temporal Lobe Primary auditory cortex Superior temporal gyrus Receives sound stimuli from CN VIII Auditory association area Synthesizes info so it can be recognized Dominant hemisphere (L) Analyzes speech sounds Recognize words & sentences Nondominant hemisphere Primary auditory cortex & association area sometimes called Heschl s gyri Environmental noise & music Wernicke s area Posterior 2/3rds of superior temporal gyrus Comprehension of written & spoken language
63 Label the Brain Word Bank: Frontal Lobe Parietal Lobe Temporal Lobe Occipital Lobe Cerebellum Pons Medulla Central Sulcus Lateral Sulcus Precentral gyrus What else is this called? Postcentral gyrus What else is this called?
64 1. Lower Motor Neurons a. b. Upper & Lower Motor Neurons 2. Upper Motor Neurons a. b. c. 3. Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Within the CNS Pyramidal system i. Corticospinal tract ii. Corticobulbar tract Extrapyramidal system Summary a. b. UMN communicate with LMN LMN carry message to muscles
65 CNS - Pyramidal System Direct motor activation pathway Corticospinal tract Voluntary muscle movement Cerebral cortex spinal cord Spinal nerves innervate muscles Decussate at medulla anterior horn of vertebrae Corticobulbar tract Cerebral cortex brainstem (CN nuclei) Voluntary movement of speech muscles
66 CNS - Extrapyramidal System Indirect activation system Transmits impulses that control postural support needed for voluntary movement Anything not in the pyramidal system Subcortical nuclei, basal ganglia, substantia nigra (cerebellum contributes too probably) Includes pathways between these structures Influences lower motor neurons Helps maintain posture and tone Damage = involuntary movement disorders
67 Pyramidal & Extrapyramidal Review Questions
68 CNS - Connecting Fibers in the Brain Projection Fibers Association Fibers Commisural Fibers Connect cortex with subcortical structures like cerebellum, basal ganglia, brainstem Connect areas within the same hemisphere Connect corresponding areas of the 2 hemispheres Arcuate fasiculus connects Broca s area with Wernicke s area Corpus callosum connects hemispheres at their base Internal capsule contains concentrated PFs Intrahemispheric Originate in frontal lobe and form UPN system of pyramidal tract Afferent fibers fan out into corona radiata Damage = disconnection syndromes Interhemispheric
69 CNS - Cerebral Ventricles System of interconnected cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) CSF facts Made by choroid plexus Circulates and nourishes neural tissue Cushions brain Regulates pressure Removes waste Four ventricles Lateral (2) - inferior to corpus callosum Third - behind lateral at top of brainstem Fourth - between cerebellum and pons 3 & 4 connected by cerebral aqueduct
70 CNS - Protective Layers of the Brain 1. Layer of skin 2. Skull bones 3. Layers of tissue - meninges a. b. c. 4. Dura mater - thick and tough Arachnoid - thin and delicate, vascularized Pia mater - adheres to brain surface Where is the CSF? a. b. Between arachnoid & pia mater Subarachnoid space
71 CNS - Central Blood Supply Anterior System Posterior System Aorta common carotid arteries Aorta vertebral arteries Carotid arteries split into internal & external branches Vertebral arteries join & become basilar artery External branch supplies face Internal divides into anterior & middle cerebral arteries Basilar artery divides into posterior cerebral arteries Middle supplies lateral surface of cortex Anterior supplies medial surfaces of hemispheres Supply inferior surface of brain
72 CNS - Circle of Willis Base of brain Carotid & vertebral arteries join Circle completed by communicating arteries Blockage Below the circle - minimal damage Above the circle -bad news
73 Another visualization of Circle of Willis
74 Fibers, Ventricles, Layers, CSF & Blood Supply Questions
75
Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream
 1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Protection of the Brain. Overview of the Brain. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober. Chapter 13. Lecture 20
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Cranial Nerves VII to XII
 Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. 1) List the anatomical subdivisions.
 S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Upper Respiratory Tract
 Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
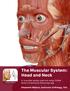 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Anatomy and Physiology app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES A. Watch the video 13.1 Muscular System Overview and observe
Stanley Pruisinger 1980's
 Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system
 Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Module 5 : Anatomy The nervous system In this module you will learn: The main parts of the nervous system The different sections of the brain and how it functions The structure and function of the spinal
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
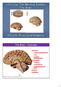 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Embryonic Brain Development
 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord membrane covering the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three membrane Meninges
Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord membrane covering the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three membrane Meninges
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Big Ideas. (e.g. puberty, immune function (autoimmune disorders)) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Central Nervous System. January 7, 2016
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
