Anacardic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, modulates LPS-induced IL-8 expression in a human alveolar epithelial cell line A549
|
|
|
- Austen Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Anacardic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, modulates LPS-induced IL-8 expression in a human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 [version 1; referees: 2 approved] Tetsuo Yasutake, Hiroo Wada, Manabu Higaki, Masuo Nakamura, Kojiro Honda, Masato Watanabe, Haruyuki Ishii, Shigeru Kamiya, Hajime Takizawa, Hajime Goto Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, , Japan v1 First published: 6 Mar 213, 2:78 (doi: /f1research.2-78.v1) Latest published: 6 Mar 213, 2:78 (doi: /f1research.2-78.v1) Abstract Objective and design: The histone acetylation processes, which are believed to play a critical role in the regulation of many inflammatory genes, are reversible and regulated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs), which promote acetylation, and histone deacetylases (HDACs), which promote deacetylation. We studied the effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on histone acetylation and its role in the regulation of interleukin (IL)-8 expression. Material: A human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 was used in vitro. Methods: Histone H4 acetylation at the IL-8 promoter region was assessed by a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. The expression and production of IL-8 were evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and specific immunoassay. Effects of a HDAC inhibitor, trichostatin A (TSA), and a HAT inhibitor, anacardic acid, were assessed. Results: Escherichia coli-derived LPS showed a dose- and time-dependent stimulatory effect on IL-8 protein production and mrna expression in A549 cells in vitro. LPS showed a significant stimulatory effect on histone H4 acetylation at the IL-8 promoter region by ChIP assay. Pretreatment with TSA showed a dose-dependent stimulatory effect on IL-8 release from A549 cells as compared to LPS alone. Conversely, pretreatment with anacardic acid inhibited IL-8 production and expression in A549 cells. Conclusion: These data suggest that LPS-mediated proinflammatory responses in the lungs might be modulated via changing chromatin remodeling by HAT inhibition. Open Peer Review Referee Status: 1 2 version 1 published 6 Mar 213 Bruce Rubin, Children s Hospital of Richmond USA Shu Hashimoto, Nihon University School of Medicine Japan Discuss this article Comments (1) Invited Referees 1 2 report report Corresponding author: Hajime Takizawa ( htakizawa.alg@gmail.com) How to cite this article: Yasutake T, Wada H, Higaki M et al. Anacardic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, modulates LPS-induced IL-8 expression in a human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 [version 1; referees: 2 approved] F1Research 213, 2:78 (doi: /f1research.2-78.v1) Copyright: 213 Yasutake T et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Licence, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Data associated with the article are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero "No rights reserved" data waiver (CC 1. Public domain dedication). Grant information: This work was supported in part by the scientific grants from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science and Culture (Hajime Goto, M.D., Ph.D.: grant number , and Hiroo Wada, M.D., Ph.D.: grant number ). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Competing interests: No relevant competing interests were disclosed. First published: 6 Mar 213, 2:78 (doi: /f1research.2-78.v1) F1Research Page 1 of 1
2 Introduction Pneumonia is an important socio-medical problem and one of the leading causes of death in the world 1. Gram-negative rods, crucial pathogens in hospital- as well as community-acquired pneumonia, produce and release endotoxins which constitute lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Once inhaled via respiratory routes, LPS stimulate alveolar structural as well resident cells to release many kinds of bioactive agents such as proinflammatory cytokines into local microenvironments 2. Recent studies have emphasized a crucial role for the lung epithelium as an important sentinel and effector system of innate immunity 3 5. Upon infectious agents and their products being inhaled into the respiratory systems, activated lung epithelium may contribute to the regulation of the immune response as the first-line defense mechanism 6. Among those defense responses, it seems important that alveolar epithelial cells express and release a variety of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines into alveolar microenvironments 6,7. A CXC chemokine, interleukin (IL)-8, plays an important role in the acute recruitment of immune/inflammatory cells, especially neutrophils, to the site of infection in the lung 8,9. LPS bind to Tolllike receptors (TLR) and thereby activate downstream signal transduction pathways which ultimately phosphorylate cytosolic I-κB kinase 1,11. Then, I-κB is phosphorylated to induce free-form of NF-κB, which translocates into the nucleus. The NF-κB binds to its specific binding sites on the promoter regions and enhances the expression of IL-8 gene 12,13. Increasing evidence has indicated that the expression of many inflammatory genes involves the remodeling of the chromatin structure provided by histone proteins 14,15. Remodeling of chromatin within the nucleus is controlled by the degree of acetylation/deacetylation of histone residues on the histone core around which DNA is coiled. Histone acetylation results in the unwinding of the chromatin structure, which enhances the binding of transcription factors to their specific promoter sites on the DNA 16. Nuclear histone acetylation is a reversible process and is regulated by a group of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) which promote acetylation, and histone deacetylases (HDACs) which promote deacetylation 17,18. The loosening of DNA-histone interactions and the subsequent unmasking of transcription factor binding sites is controlled by specific covalent modifications of accessible N-terminal histone tails 19. Among the four core histone proteins that comprise the central chromatin core (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), acetylation processes on H3 and H4 seem particularly important in gene regulation. For example, Gilmour and associates 2 found that acetylation on H4 played an important role in environment particle-induced IL-8 production in A549 cells. Viable Listeria monocytogenes-stimulated endothelial cells showed increased expression of IL-8, and that process depended on modifications of H3 and H4 21. Although the host response in pneumonia is characterized by massive cytokine production, and altered histone modifications have been observed in diseased lungs 22, it is not fully elucidated how histone modifications contribute to innate immune regulation in the lung. In this study, we tried to determine whether Escherichia coliderived LPS, one of the mainstream stimuli upon bacterial respiratory infection, altered histone acetylation/deacetylation balance, and to see whether the modulation of HDACs or HATs by their specific inhibitors (i.e. trichostatin A [TSA] for HDACs and anacardic acid for HATs) affected IL-8 gene expression and protein production in an alveolar epithelial cell line A549 in vitro. Materials and methods Cell culture and stimulation Human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) via DS Pharma Biomedical Co., Ltd (Tokyo, Japan). A549 cells were cultured in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium (Sigma- Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) containing 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY, USA) and 1% penicillinstreptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, St, Louis, MO, USA), and incubated at 37 C in 5% CO 2 atmosphere. Cells were cultured to 8% confluency as judged under inverted microscopy before the medium was replaced with serum-free Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium and incubated for a further 15 h. The cells were stimulated with different concentrations of E.coli-derived LPS (26:B6, Sigma- Aldrich, St, Louis, MO, USA) for further experiments. To evaluate the effects of HDAC and HAT inhibitors, cells were pre-treated with TSA or anacardic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St, Louis, MO, USA; dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO] and further diluted for use) at the concentrations indicated, 1h prior to stimulation with LPS (1 μg/ml). Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qrt-pcr) Total RNA from A549 cells was isolated with the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Hamburg, Germany), and cdna was prepared using the Im Prom II reverse transcription system (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for reverse transcription, and all procedures were conducted according to the manufacturers instructions. Gene transcript levels of IL-8, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were quantified by real-time PCR using a reaction mixture with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, Tokyo, Japan) on a 75 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The primer sets for IL-8 were: (forward) 5 -CTGATTTCTGCAGCTCT- GTG-3 ; (reverse) 5 -TTCACTGGCATCTTCACTG-3 and for GAPDH were: (forward) 5 -TGAACGGGAAGCTCACTGG-3 (reverse) 5 -TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA-3 The relative amount of gene transcript was estimated after normalization by dividing the calculated value for the gene of interest by the GAPDH value. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (ChIP assay) Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed using Millipore s ChIP kit (Billerica, Massachusetts, USA) with an acetyl-histone H4 antibody. Cells were cultured to 8% confluency in 1mm culture plates. Cells were cross-linked by adding 1% formaldehyde for 1 minutes at room temperature in shaking. Then, 1ml of 1 glycine was added to 1ml of growth media to each dish to quench unreacted formaldehyde at room temperature for 5 minutes. Cells were washed twice with cold 1ml phosphate buffered saline (PBS). One ml PBS containing 1 protease inhibitor cocktail II prepared in the ChIP kit was added to each dish. Cells were scraped from each dish into a conical tube. The tubes were centrifuged at 7 g at 4 C for 5 minutes to pellet cells. Each cell pellet was resuspended in 1ml Page 2 of 1
3 of SDS lysis buffer containing 1 protease inhibitor cocktail II prepared in the ChIP kit. Chromatin was sonicated to an average DNA length of 2 1 bp using an Ultrasonic Disruptor UD-2 sonicator (TOMY, Tokyo, Japan). Sonicated samples were centrifuged and the supernatant was collected. Samples (1μl) of the extracted chromatin were diluted with 9μl ChIP Dilution Buffer (.1% SDS, 1.1% Triton X-1, 1.2mM EDTA, 16.7mM Tris-HCl, ph 8.1, 167mM NaCl), precleared (1 hour) by incubation with 6μl Protein G Agarose containing 1 protease inhibitor cocktail II, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with a specific antibody with rotation overnight at 4 C. The antibody used for ChIP assays was antiacetyl histone H4 antibody (Millipore, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA). Immunocomplexes were collected by adsorption onto 6μl Protein G Agarose and the beads were washed five times sequentially with Low Salt Immune Complex Wash Buffer (.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-1, 2mM EDTA, 2mM Tris-HCl, ph 8.1, 15mM NaCl), High Salt Immune Complex Wash Buffer (.1% SDS, 1% Triton X-1, 2mM EDTA, 2mM Tris-HCl, ph 8.1, 5mM NaCl) and LiCl Immune Complex Wash Buffer (.25M LiCl, 1% IGEPAL CA63, 1% deoxycholic acid (sodium salt), 1mM EDTA, 1mM Tris, ph 8.1), which were prepared in the ChIP kit. Precipitates were washed twice with TE Buffer (1mM Tris-HCl, ph 8., 1mM EDTA), and antibody-chromatin fragments were eluted from the beads with 1% sodium dodecyl sulphate in.1 M NaHCO 3. Crosslinks were reverted by adding 2mM NaCl and heating at 65 C for 5 hours. In total, 1mg/ml RNase A were added and samples were then incubated for 3 minutes at 37 C. 1mg/ml proteinase K, 1mM EDTA and 4mM Tris-HCl were added and samples were then incubated for 2 hours at 45 C. A total of 1ml of Bind Reagent A was added to each sample, and mixed well by pipetting. The sample was transferred up to a spin filter placed in a collection tube, and was centrifuged for 3 seconds at 12 g. Then, 5μl of Wash Reagent B was added to each spin filter placed in a collection tube, and was centrifuged for 3 seconds at 12 g. Then, 5μl of Elution Buffer C was added to each spin filter placed in a clean collection tube, and was centrifuged for 3 seconds at 12 g to recover purified DNA. The IL-8 enhancer regions were quantified by real-time PCR using a reaction mixture with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, Tokyo, Japan) on a 75 realtime PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The primer sets for IL-8 were: (forward) 5 - CAGAGACAGCA- GAGCACAC-3 ; (reverse) 5 - ACGGCCAGCTTGGAAGTC-3. All PCR signals from immunoprecipitated DNA were normalized to PCR signals from non-immunoprecipitated input DNA. ELISA for IL-8 measurement The concentration of IL-8 in the media was determined by sandwich ELISA kit (R&D Systems, San Diego, CA) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Statistical analysis Data were analyzed with the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 17. for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Values are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE). Mann-Whitney U test was performed for comparisons between groups. A P-value <.5 was considered significant. All P-values were two-sided. Results LPS stimulated production of IL-8 in A549 cells We analyzed IL-8 production in LPS stimulated A549 cells. A549 cells were stimulated by different concentrations of LPS (1 ~ 2μg/ml) for indicated time periods. As shown in Figure 1, LPS showed a time- and dose-dependent stimulatory effect on IL-8 release. LPS induced expression of IL-8 gene in A549 cells A549 cells were stimulated by 1μg/ml LPS, and the time course in levels of IL-8 mrna was analyzed by qrt-pcr. IL-8 mrna levels showed a gradual increase in response to LPS, reaching a maximum level 2 h after initial stimulation with 1μg/ml, which then decreased after that point (Figure 2). IL-8 pg/ml LPS (µg/ml) 12hr 24hr 48hr Figure 1. The dose- and time- dependent interleukin-8 (IL-8) release from A549 cells in vitro. A549 cells were cultured until 8% confluence and stimulated by different concentrations of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 ~ 2μg/ml). LPS showed a time- and dose-dependent stimulatory effect on IL-8 release at each concentration. Data were expressed in mean±sem. *P<.5, compared to LPS unstimulated cells at each concentration and time point (Mann-Whitney U test), n=4. Page 3 of 1
4 IL-8/GAPDH (h) Figure 2. Time course analysis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene expression in A549 cells in vitro. A549 cells were cultured until subconfluence and stimulated by LPS at 1μg/ml. After ~ 8 hrs, IL-8 mrna expression was analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qrt-pcr). The IL-8 mrna levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels. Data were expressed in mean±sem. *P<.5: compared to LPS hr stimulated cells (Mann- Whitney U test), n=4. LPS induced histone acetylation in A549 cells Based on the previous reports showing that modifications of histones, in particular acetylation of H4, seem to contribute to the regulation of inflammatory genes such as IL-8 2, we assessed acetylation of H4 after stimulation of LPS in A549 cells. We analyzed histone modifications at the IL-8 gene promoter by ChIP assay. A549 cells were stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) for min to 3 h. LPS induced a time-dependent increase of acetylation of H4 at the IL-8 promoter, and this increase peaked after 1 h (P<.5, Mann-Whitney U test), and then decreased after 3 h of LPS stimulation (Figure 3). Histone acetylation regulates IL-8 expression in LPSstimulated A549 cells Next, we wondered whether inhibition of HDACs by TSA or blocking of HATs by anacardic acid impacts on LPS-induced IL-8 expression. We increased global histone acetylation by incubation of A549 cells with TSA (1nM, 24 h) which did not induce IL-8 secretion per se (Figure 4). Preincubation for 1 h with TSA (1nM) before subsequent treatment with LPS significantly increased IL-8 release as compared to LPS alone (Figure 4). Pretreatment with TSA (1nM) showed a tendency to increase IL-8 mrna levels as assessed by qpcr analysis, but did not reach statistical significance (Figure 5). Suppression of histone acetylation by blocking of HATs via anacardic acid showed a dose-dependent inhibitory effect on LPSstimulated IL-8 production (Figure 6), indicating that histone deacetylation regulates IL-8 expression in LPS-treated epithelial cells. The effects of anacardic acid on IL-8 mrna expression were analyzed by qrt-pcr. Anacardic acid at 1μM administered 1 h H4 acetylation at IL-8 promoter % input Figure 3. Time course analysis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced histone H4 acetylation at the promoter region of the interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene in A549 cells in vitro. A549 cells were stimulated ~ 3 hr with LPS (1μg/ml). The results presented are from ChIP analyses using anti-acetyl H4 antibodies. All PCR signals from immunoprecipitated DNA were normalized to PCR signals from non-immunoprecipitated input DNA. Results are expressed as percentage of the input. Data were expressed in mean±sem. *P<.5: compared to LPS hr stimulated cells (Mann-Whitney U test), n=4. Page 4 of 1
5 8 7 6 IL-8 pg/ml LPS 1µg/ml TSA (nm) Figure 4. Effect of trichostatin A (TSA) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) release from A549 cells in vitro. TSA at 1 ~1nM treated 1 hr before LPS stimulation (1μg/ml) showed a significant stimulatory effect on LPS-induced IL-8 release. Data were expressed as mean±sem. *P<.5: compared to LPS-stimulated cells (Mann-Whitney U test), n= LPS(1µg/ml) TSA(1nM)+LPS (1µg/ml) IL-8/GAPDH (h) Figure 5. Time course analysis of trichostatin A (TSA) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene activation from A549 cells in vitro. TSA at 1nM treated 1 h before LPS stimulation (1μg/ml) tended to show a stimulatory effect on LPS-induced IL-8 gene activation. After ~ 8 h, the levels of IL-8 mrna were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qrt- PCR). The IL-8 mrna levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels, n= IL-8 pg/ml LPS 1µg/ml Anacardic acid (µm) DMSO Figure 6. Effect of anacardic acid on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) release from A549 cells in vitro. Anacardic acid at 1 ~ 1μM treated 1 hr before LPS stimulation showed a significant inhibitory effect on LPS-induced IL-8 release. Data were expressed as mean±sem. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide used for solvent. *P<.5: compared to LPS (1μg/ml) stimulated cells (Mann- Whitney U test), n=4. Page 5 of 1
6 before LPS (1μg/ml) stimulation showed a significant inhibitory effect on LPS-induced IL-8 mrna levels (Figure 7). These observations indicated that modulation of histone acetylation by anacardic acid regulated LPS-stimulated IL-8 gene expression in A549 cells. Raw data for figures Data Files Discussion In the present study, we demonstrated that E. coli-derived LPS stimulate human alveolar epithelial A549 cells to express and release IL-8, an important chemokine for the local recruitment of neutrophils as an initial defense mechanism 8,9. The specific histone acetylation processes were evaluated by ChIP assay, which clearly showed that LPS induced histone H4 acetylation in A549 cells. Next, we studied the effects of TSA, a HDAC inhibitor on LPS-induced IL-8 expression. TSA showed a significant stimulatory effect on IL-8 production, whereas this agent tended to increase, although not significantly, IL-8 mrna levels in LPS-stimulated A549 cells. Finally, a HAT inhibitor, anacardic acid, significantly decreased IL-8 mrna levels as well as protein release in a dose-dependent fashion. These results suggested that LPS-induced IL-8 gene expression is, at least in part, regulated by histone H4 acetylation/ deacetylation balance at the IL-8 promoter region. It has been reported that alveolar epithelial cells respond to bacterial products such as LPS to produce a variety of inflammatory cytokines and mediators including IL-8 2. We 23,24 and others 9,25,26 have previously shown that airway and alveolar epithelial cells, including A549 cells, are activated by a variety of endogenous agents such as cytokines as well as exogenous stimuli including LPS and fine particles, and express biologically active compounds including cytokines and chemokines. The transcription of many genes is known to correlate with levels of acetylated nuclear histone proteins The expression of many inflammatory genes involves the remodeling of the chromatin structure provided by histone proteins. Histone acetylation causes the unwinding of the chromatin structure, thereby enabling transcription factors to bind to their specific promoter sites on the DNA. Such acetylation processes are reversible and regulated by HATs, which promote acetylation, and HDACs, which promote deacetylation 18,19. Proinflammatory gene transcription regulation is a multifaceted process that requires integrated sequential molecular events for maximal gene transcription to occur. Activation of specific gene expression needs to be associated with co-operated chromatin remodeling by histone acetylation and binding of transcription factors to their specific binding sites on DNA. In the present experiments, the levels of histone H4 acetylation peaked 1 h after LPS stimulation followed by the maximal levels of IL-8 mrna at 2 h; such a time course was consistent with the above scenarios. Our study supports a hypothesis that histone H4 acetylation could play a key role in inflammatory gene transcription such as IL-8 in A549 cells caused by LPS; however, the role of acetylation of the other histones in this model is yet to be established. It has been reported that a variety of histone acetylations are involved in cytokine transcriptional processes. Miyata et al. 27 have shown that H3 and H4 are acetylated in murine epithelial cells in response to granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) at the myeloperoxidase gene promoter site, a response dependent on MAPK activation LPS (1µg/ml) Anacardic acid (1µM) +LPS (1µg/ml) IL-8/GAPDH (h) Figure 7. Time course analysis of anacardic acid on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene activation in A549 cells in vitro. Anacardic acid at 1μM treated 1 hr before LPS (1μg/ml) stimulation showed a significant inhibitory effect on LPS-induced IL-8 gene activation. After ~ 8hrs, the levels of IL-8 mrna were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qrt-pcr). The IL-8 mrna levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels. Data were expressed as mean±sem. *P<.5 (Mann-Whitney U test), n=4. Page 6 of 1
7 Anacardic acid is a bioactive phytochemical found in the nutshell of Anacardium occidentale 28. The promising effect of anacardic acid on IL-8 gene regulation in the current study has already been reported by Schmeck and associates 29 in Legionella pneumophiladerived flagellin-induced IL-8 expression. Although the available records are promising, more detailed investigation into the therapeutic properties of anacardic acid, particularly the anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities, are needed 3. LPS-mediated IL-8 production is generally expected to act as a defense mechanism which recruits neutrophils in the local environment and facilitates bacterial elimination. However, it is now also known that excessive accumulation of activated neutrophils in the lung is likely to cause excessive inflammatory changes that damage lung tissues 8. In this context, appropriate control of local inflammation would be an important strategy for the management of severe pneumonia 22. Recently, it has been attracting attention that macrolide antibiotics added to guideline-based therapy has shown a better outcome than respiratory quinolones among intensive care unit (ICU) hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia and/or sepsis 31. It has been speculated that certain anti-inflammatory actions of macrolides were involved in such clinically beneficial effects 32. Therefore, the suppressive effects of anacardic acid on IL-8 gene expression and production might become a novel strategy for controlling excessive inflammation in order to lessen the risks of acute lung injury and, ultimately, respiratory failure to death. In conclusion, we have shown that E. coli-derived LPS-induced expression and release of IL-8 are associated with increased acetylation of histone H4 expression. The HDAC inhibitor TSA increased IL-8 release. In contrast, a HAT inhibitor, anacardic acid, significantly decreased IL-8 mrna levels as well as protein release in a dosedependent fashion. These results suggested that regulation of HDAC and HAT activity by low molecular weight agents might become a novel strategy for the appropriate control of inflammation by modulating inflammatory mediators such as IL-8. Author contributions TY, HW, HT and HG conceived the study. TY and MH designed the experiments. TY, MN, KH, MW and HI carried out the research. SK contributed to the design of experiments and provided expertise in ChIP experiments. TY, HW and HT prepared the first draft of the manuscript. MW and HI contributed to the experimental design and preparation of the manuscript. All authors were involved in the revision of the draft manuscript and have agreed to the final content. Competing interests No relevant competing interests were disclosed. Grant information This work was supported in part by the scientific grants from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science and Culture (Hajime Goto, M.D., Ph.D.: grant number , and Hiroo Wada, M.D., Ph.D.: grant number ). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Acknowledgements We thank Ms Makiko Sakamoto for technical assistance during this project. We also thank Ms Yumiko Date for secretarial assistance. References 1. Mizgerd JP: Acute lower respiratory tract infection. N Engl J Med. 28; 358(7): Free Full Text 2. Thorley AJ, Grandolfo D, Lim E, et al.: Innate immune responses to bacterial ligands in the peripheral human lung--role of alveolar epithelial TLR expression and signalling. PLoS One. 211; 6(7): e Free Full Text 3. Gilmour PS, Rahman I, Hayashi S, et al.: Adenoviral E1A primes alveolar epithelial cells to PM(1)-induced transcription of interleukin-8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 21; 281(3): L598 L66. PubMed Abstract 4. Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, et al.: Diesel exhaust particles activate p38 MAP kinase to produce interleukin 8 and RANTES by human bronchial epithelial cells and N-acetylcysteine attenuates p38 MAP kinase activation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2; 161(1): Nakamura H, Yoshimura K, Jaffe HA, et al.: Interleukin-8 gene expression in human bronchial epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266(29): PubMed Abstract 6. Chuquimia OD, Petursdottir DH, Rahman MJ, et al.: The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in Initiating and Shaping Pulmonary Immune Responses: Communication between Innate and Adaptive Immune Systems. PLoS One. 212; 7(2): e Free Full Text 7. Sanders CJ, Doherty PC, Thomas PG: Respiratory epithelial cells in innate immunity to influenza virus infection. Cell Tissue Res. 211; 343(1): Chollet-Martin S, Montravers P, Gibert C, et al.: High levels of interleukin-8 in the blood and alveolar spaces of patients with pneumonia and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Infect Immun. 1993; 61(11): PubMed Abstract Free Full Text 9. Li B, Dong C, Wang G, et al.: Pulmonary epithelial CCR3 promotes LPS-induced lung inflammation by mediating release of IL-8. J Cell Physiol. 211; 226(9): Akira S: Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 23; 278(4): Mitchell JA, Paul-Clark MJ, Clarke GW, et al.: Critical role of toll-like receptors and nucleotide oligomerisation domain in the regulation of health and disease. J Endocrinol. 27; 193(3): Henkel T, Machleidt T, Alkalay I, et al.: Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993; 365(6442): Park GY, Christman JW: Nuclear factor kappa B is a promising therapeutic target in inflammatory lung disease. Curr Drug Targets. 26; 7(6): Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, et al.: Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 24; 429(699): Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Ito K: Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 25; 25(3): Kuo MH, Allis CD: Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation. Bioessays. 1998; 2(8): Tang YA, Wen WL, Chang JW, et al.: A novel histone deacetylase inhibitor exhibits antitumor activity via apoptosis induction, F-actin disruption and gene acetylation in lung cancer. PLoS One. 21; 5(9): e Free Full Text Page 7 of 1
8 18. Claus R, Fliegauf M, Stock M, et al.: Inhibitors of DNA methylation and histone deacetylation independently relieve AML1/ETO-mediated lysozyme repression. J Leukoc Biol. 26; 8(6): Grunstein M: Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription. Nature. 1997; 389(6649): Gilmour PS, Rahman I, Donaldson K, et al.: Histone acetylation regulates epithelial IL-8 release mediated by oxidative stress from environmental particles. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 23; 284(3): L Schmeck B, Beermann W, van Laak V, et al.: Intracellular bacteria differentially regulated endothelial cytokine release by MAPK-dependent histone modification. J Immunol. 25; 175(5): PubMed Abstract 22. Goodman RB, Strieter RM, Martin DP, et al.: Inflammatory cytokines in patients with persistence of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996; 154(3 Pt 1): Takizawa H, Ohtoshi T, Kawasaki S, et al.: Diesel exhaust particles induce NFkappa B activation in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro: importance in cytokine transcription. J Immunol. 1999; 162(8): PubMed Abstract 24. Yamauchi Y, Okazaki H, Desaki M, et al.: Methotrexate induces interleukin-8 production by human bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells. Clin Sci (Lond). 24; 16(6): Arae K, Hirata M, Kurata S, et al.: Mycoplasma pneumoniae induces interleukin-8 production via the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Microbiol Immunol. 211; 55(1): Schleimer RP, Kato A, Kern R, et al.: Epithelium: at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 27; 12(6): Free Full Text 27. Miyata Y, Towatari M, Maeda T, et al.: Histone acetylation induced by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in a map kinase-dependent manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 21; 283(3): Sullivan JT, Richards CS, Lloyd HA, et al.: Anacardic acid: molluscicide in cashew nut shell liquid. Planta Med. 1982; 44(3): Schmeck B, Lorenz J, N'quessan PD, et al.: Histone acetylation and flagellin are essential for Legionella pneumophila-induced cytokine expression. J Immunol. 28; 181(2): PubMed Abstract 3. Hemshekhar M, Sebastin Santhosh M, Kemparaju K, et al.: Emerging Roles of Anacardic Acid and Its Derivatives: A Pharmacological Overview. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol Asadi L, Eurich DT, Gamble JM, et al.: Guideline adherence and macrolides reduced mortality in outpatients with pneumonia. Respir Med. 212; 16(3): Mouktaroudi M, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ: Macrolides for the therapy of nosocomial infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 212; 25(2): Page 8 of 1
9 Open Peer Review Current Referee Status: Version 1 Referee Report 11 March 213 doi:1.5256/f1research.871.r83 Shu Hashimoto The Department of Respiratory Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan This manuscript is well written and conducted. The data and conclusions are clear and worthwhile for the readers. I have read this submission. I believe that I have an appropriate level of expertise to confirm that it is of an acceptable scientific standard. Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed. Referee Report 7 March 213 doi:1.5256/f1research.871.r817 Bruce Rubin Department of Pediatrics, Children s Hospital of Richmond, Richmond, VA, USA This is an extremely well conducted study from a top research group. Takizawa and colleagues clearly demonstrate the role of histone acetylation in airway epithelial cell signal transduction after exposure to bacterial endotoxin. These findings are novel and may help in identifying novel targets for modulating chronic airway inflammation. I have read this submission. I believe that I have an appropriate level of expertise to confirm that it is of an acceptable scientific standard. Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed. Discuss this Article Version 1 Author Response ( F1Research Advisory Board Member ) 14 Mar 213 F1Research Page 9 of 1
10 Hajime Takizawa, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Japan I greatly appreciate both of two reviewers for giving us such kind and encouraging comments. After my article was published, the open post publication peer review process was extremely quick! My article received two reviews in the space of just 5 days, which is a refreshing change from the traditional reviewing system. I believe this type of review system will become a new standard for scientific publications in the near future. Competing Interests: None to be reported F1Research Page 1 of 1
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Host cell activation
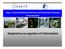 Dept. of Internal Medicine/Infectious and Respiratory Diseases Stefan Hippenstiel Epigenetics as regulator of inflammation Host cell activation LPS TLR NOD2 MDP TRAF IKK NF-κB IL-x, TNFα,... Chromatin
Dept. of Internal Medicine/Infectious and Respiratory Diseases Stefan Hippenstiel Epigenetics as regulator of inflammation Host cell activation LPS TLR NOD2 MDP TRAF IKK NF-κB IL-x, TNFα,... Chromatin
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Antibodies: LB1 buffer For 50 ml For 10ml For 30 ml Final 1 M HEPES, ph 2.5 ml 0.5 ml 1.5 ml 50mM. 5 M NaCl 1.4 ml 280 µl 0.
 Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit
 HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1320 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1320 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format:
 Supplementary Protocol 1. Adaptor preparation: For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format: Per reaction X96 10X NEBuffer 2 10 µl 10 µl x 96 5 -GATC
Supplementary Protocol 1. Adaptor preparation: For the 5 GATC-overhang two-oligo adaptors set up the following reactions in 96-well plate format: Per reaction X96 10X NEBuffer 2 10 µl 10 µl x 96 5 -GATC
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Global Histone H4 Acetylation Assay Kit. Base Catalog # P-4009 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Global Histone H4 Acetylation Assay Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H4 Acetylation Assay Kit is suitable for specifically measuring global
EpiQuik Global Histone H4 Acetylation Assay Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H4 Acetylation Assay Kit is suitable for specifically measuring global
SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72084 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect HDAC activity. Enhanced Value: It provides
SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72084 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect HDAC activity. Enhanced Value: It provides
Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit
 Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0633 96 assays Version: 06 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0633 96 assays Version: 06 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit
 HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit Item No. 600150 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit Item No. 600150 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit. Base Catalog # P-4008 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit is suitable for specifically measuring global
EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Acetylation Assay Kit is suitable for specifically measuring global
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Item. Catalog No Manufacturer
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
SOP: Nuclei isolation from tissue and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 090923 Modified by: P. Sabo. (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei from tissue. Ordering Information Item.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit
 HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit Item. 10011563 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit Item. 10011563 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit
 HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Item No. 10011564 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Item No. 10011564 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
ab Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab156064 Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Histone Deacetylase activity in cell lysates This product is for research
ab156064 Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Histone Deacetylase activity in cell lysates This product is for research
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples:
 Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit
 HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit Item No. 600150 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
HDAC Cell-Based Activity Assay Kit Item No. 600150 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Geneaid DNA Isolation Kit
 Instruction Manual Ver. 02.21.17 For Research Use Only Geneaid DNA Isolation Kit GEB100, GEB01K, GEB01K+ GEC150, GEC1.5K, GEC1.5K+ GET150, GET1.5K, GET1.5K+ GEE150, GEE1.5K, GEE1.5K+ Advantages Sample:
Instruction Manual Ver. 02.21.17 For Research Use Only Geneaid DNA Isolation Kit GEB100, GEB01K, GEB01K+ GEC150, GEC1.5K, GEC1.5K+ GET150, GET1.5K, GET1.5K+ GEE150, GEE1.5K, GEE1.5K+ Advantages Sample:
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Catalog # Lot # 16875
 MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric*
 SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit
 Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS
 TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
TMM,5-2011 PREPARATION OF IF- ENRICHED CYTOSKELETAL PROTEINS Ice-cold means cooled in ice water. In order to prevent proteolysis, make sure to perform all steps on ice. Pre-cool glass homogenizers, buffers
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads
 Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads HBM-BOLF-##/##-# HBM-BOLC-##/##-# HBM-BTLF-##/##-# Overall Exosome capture from Human Biological fluids Overall Exosome capture from
Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunobeads HBM-BOLF-##/##-# HBM-BOLC-##/##-# HBM-BTLF-##/##-# Overall Exosome capture from Human Biological fluids Overall Exosome capture from
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4034 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4034 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. D4076 Highlights High-quality DNA, including cell-free, is easily and robustly purified from up to 10 ml of serum/plasma, up to 1 ml amniotic
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-cfDNA Serum & Plasma Kit Catalog No. D4076 Highlights High-quality DNA, including cell-free, is easily and robustly purified from up to 10 ml of serum/plasma, up to 1 ml amniotic
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit(Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit(Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Colorimetric) is very suitable for
EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit(Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Colorimetric) is very suitable for
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Total Histone Extraction Kit. Base Catalog # OP-0006 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Total Histone Extraction Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Total Histone Extraction Kit is suitable for a quick preparation of total histone extracts
EpiQuik Total Histone Extraction Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Total Histone Extraction Kit is suitable for a quick preparation of total histone extracts
HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit
 HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit Item. 10011563 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
HDAC Fluorometric Activity Assay Kit Item. 10011563 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 4 Precautions
Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The Epigenase HDAC Activity/Inhibition Direct Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells
 EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR (1167)
 From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS
 292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
292 Tang, An, Du, Zhang, Zhou 292 IN VITRO HORMESIS EFFECTS OF SODIUM FLUORIDE ON KIDNEY CELLS OF THREE-DAY-OLD MALE RATS Qin-qing Tang, a Xiao-jing An, a Jun Du, a Zheng-xiang Zhang, a Xiao-jun Zhou a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual
 Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Item Catalog Number Manufacturer 1,4-Dithioerythritol (1 g) D9680 Sigma-Aldrich
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunoplates
 Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunoplates HBM-POF-##/## HBM-POC-##/## Overall Exosome capture from Biological fluids (plasma, urine) Overall Exosome capture from Cell culture
Product Insert Exosomes Immunocapture and Isolation Tools: Immunoplates HBM-POF-##/## HBM-POC-##/## Overall Exosome capture from Biological fluids (plasma, urine) Overall Exosome capture from Cell culture
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Cell Lysis Buffer. Catalog number: AR0103
 Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
10.00 PBS OVA OVA+isotype antibody 8.00 OVA+anti-HMGB1. PBS Methatroline (mg/ml)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
INSTRUCTION MANUAL. RNA Clean & Concentrator -5 Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016. Highlights. Contents
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016 Highlights Quick (5 minute) method for cleaning and concentrating RNA. Ideal for purification of RNA from aqueous phase following an acid phenol extraction.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Catalog Nos. R1015 & R1016 Highlights Quick (5 minute) method for cleaning and concentrating RNA. Ideal for purification of RNA from aqueous phase following an acid phenol extraction.
Transfection of Sf9 cells with recombinant Bacmid DNA
 Transposition Bacmid DNA Mini Culturing baculo cells Transfection of Sf9 cells with recombinant Bacmid DNA Amplification of the virus Titration of baculo stocks Testing the expression Transposition 1.
Transposition Bacmid DNA Mini Culturing baculo cells Transfection of Sf9 cells with recombinant Bacmid DNA Amplification of the virus Titration of baculo stocks Testing the expression Transposition 1.
Data Sheet. Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068
 Data Sheet Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068 DESCRIPTION: The Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit is a complete assay system designed to measure histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8 activity for screening
Data Sheet Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068 DESCRIPTION: The Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit is a complete assay system designed to measure histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8 activity for screening
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Data Sheet. NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621
 Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4 Related Products..
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA MidiPrep Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Exo-spin Exosome Purification Kit For cell culture media/urine/saliva and other low-protein biological fluids
 Exo-spin Exosome Purification Kit For cell culture media/urine/saliva and other low-protein biological fluids Cat EX01 Protocol Version 1.1 1 Contents 1. Storage 3 2. Kit contents 3 3. Product Information
Exo-spin Exosome Purification Kit For cell culture media/urine/saliva and other low-protein biological fluids Cat EX01 Protocol Version 1.1 1 Contents 1. Storage 3 2. Kit contents 3 3. Product Information
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture
 Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik HDAC2 Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4006 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik HDAC2 Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC2 Assay Kit is very suitable for measuring HDAC2 levels from various fresh tissues and
EpiQuik HDAC2 Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC2 Assay Kit is very suitable for measuring HDAC2 levels from various fresh tissues and
Human IL-2. Pre-Coated ELISA Kit
 Human IL-2 (Interleukin 2) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2083 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 31.2 2000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 18.75 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
Human IL-2 (Interleukin 2) Pre-Coated ELISA Kit Catalog No: 90-2083 1 96 well Format (96 tests) Detection Range: 31.2 2000 pg/ml Sensitivity: < 18.75 pg/ml This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro
HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA0627 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background...
HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA0627 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background...
20X Buffer (Tube1) 96-well microplate (12 strips) 1
 PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) is very suitable for
EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik HDAC Activity/Inhibition Assay Kit (Fluorometric) is very suitable for
Transcription factors in airway diseases
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0023-6837/06 $30.00 www.laboratoryinvestigation.org Peter J Barnes Section of airway diseases, National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College, London, UK Transcription
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0023-6837/06 $30.00 www.laboratoryinvestigation.org Peter J Barnes Section of airway diseases, National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College, London, UK Transcription
Trident Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Product Manual. Omni-Array Sense Strand mrna Amplification Kit, 2 ng to 100 ng Version Catalog No.: Reactions
 Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
Genetic Tools and Reagents Universal mrna amplification, sense strand amplification, antisense amplification, cdna synthesis, micro arrays, gene expression, human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, cloning Omni-Array
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit. Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C
 Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit provides a rapid and accurate determination of total
Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit Catalog Number SIALICQ Storage Temperature 2 8 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The Sialic Acid Quantitation Kit provides a rapid and accurate determination of total
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
