Cocaine Exposure Results in Formation of Dendritic Varicosity in Rat Primary Hippocampal Neurons
|
|
|
- Camron McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Infectious Diseases 5 (1): 26-30, 2009 ISSN Science Publications Cocaine Exposure Results in Formation of Dendritic Varicosity in Rat Primary Hippocampal Neurons 1 Honghong Yao, 1 Crystal Bethel-Brown, 2 Anil Kumar and 1 Shilpa Buch 1 Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, KS Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO Abstract: Problem statement: It has been well documented that drugs of abuse such as cocaine can cause enhanced progression of HIV-Associated Neuropathological Disorders (HAND), the underlying mechanisms mediating these effects remain poorly understood. Approach: In present study, we explored the impact of cocaine exposure (I and 10 µm) on the dendritic beading in rat primary hippocampal neurons. Using the approach of transfection with green fluorescent protein, we observed significant dendritic swelling in hippocampal neurons exposed to 10 µm but not 1 µm of cocaine when compared with the saline treated group. Results: Cocaine exposure also resulted in decreased expression of the synaptic plasticity gene, Arc as evidenced by Western blotting. Intriguingly, cocaine exposure of primary neurons in the presence of the neurotoxin-hiv envelope protein gp 120, resulted in increased enhancement of neuronal beading as compared with exposure of neurons to either agent alone. Conclusion: Taken together these findings imply that cocaine in co-operation with HIV protein exacerbates neuronal damage in the brains of HIV-infected cocaine abusers. Key words: Cocaine, HIV-1-associated neurological disorders, hippocampal neurons, dendritic swelling INTRODUCTION Mounting evidence suggests that drugs of abuse accelerate the incidence and progression of HIV-1- Associated Neurological Disorders (HAND) [1-3]. Drugabusing HIV-1 positive individuals exhibit more severe cognitive impairment compared with non drug-abusing HIV positive counterparts. Epidemiological studies on abused drug users and AIDS link abuse of cocaine (by different routes), even more than other drugs, to increased incidence of HIV prevalence and progression to AIDS [4-6]. Cocaine targets the CNS and is associated with brain dysfunction. Despite the recognized impact of the abuse of psychostimulants on the clinical course of HIV-1-associated brain pathology [1], mechanisms underlying the ability of these drugs to enhance the pathological effects of HIV-1 in the brain remain elusive. Neurologic impairment in patients with HAND correlates well with injury to dendrites and synapses [7]. This clinical phenomenon has been shown in Alzheimer disease [8] and dendritic injury in both the diseases is characterized by focal swelling or beading, loss of spines, and reductions in overall dendritic and synaptic areas [9,10]. Therefore, synaptic protection represents an area of considerable therapeutic interest. Previous study indicated that In vitro exposure of neurons to glutamate resulted in dendritic beading [11] and loss of synaptic transmission. Mechanism by which cocaine causes dendritic injury remains an enigma. A better understanding of how HIV-1 and drugs of abuse affect dendrites may lead to development of more effective therapeutic interventions for the interlinked epidemic of HIV and drug abuse. The current study is aimed at exploring the effect of cocaine and/or HIV proteins on neuronal health with emphasis on dendritic morphology. MATERIALS AND METHODS Primary neuronal cultures: Primary neurons were prepared as described earlier with slight modifications. Briefly, hippocampus tissues were dissected from embryonic day Sprague-Dawley rats and dissociated with a mild mechanical trituration. Corresponding Author: J. Shilpa Buch, Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, 5000 Wahl Hall East, University of Kansas Medical Center, 3901 Rainbow Blvd, Kansas City, KS Tel: (913) Fax: (913)
2 Dissociated cells were seeded first at cells well 1 on 24-well culture plates and maintained in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium/f12 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotic. One day later the cultures were supplemented with serum-free neurobasal medium containing B27 (50:1), 2 mm glutamax, and 1% antibiotic. After 7 days, the initial plating cultures consisted of 90% neuron-specific nuclear-proteinimmunereactive neurons. Green fluorescent protein transfection: Neurons were transfected at 2-3 d in culture with the Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) plasmid using the DOSPER Liposomal Transfection Reagent (Boehringer Mannheim, Indianapolis, IN) as described the previous study [7]. These conditions were selected to yield a transfection efficiency of 0.01%, permitting the study of individual neurons. Neuronal cell bodies expressed GFP the day after transfection with development of neuritis over subsequent days. GFP fluorescence was stable in a number of neurons for at least 3 weeks and revealed the neuronal arbor, including axons, dendrites, and dendritic spines. Western blotting Treated cells were lysed using the Mammalian Cell Lyses kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Western blots were then probed with antibodies recognizing the Arc antibody (Santa Cruz). The secondary antibodies were alkaline phosphates conjugated to goat anti mouse/rabbit IgG (1:5000). Signals were detected by chemiluminescence s (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Western blot experiments are repeated three times individually, representative examples are presented in the figures. Immunocytochemistry: For MAP-2 staining, neurons were fixed for 30 min with 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature. The fixed cells were permeabilized with 1% Triton X100 for 30 min, followed by staining with MAP-2 antibody. Briefly, after blocking with 3% normal goat serum, 0.1% Triton X-100 and 1% BSA, sections were incubated with rabbit anti-map-2 (1:1000, Chemicon, Temecula, CA), washed in PBS (0.1M) and incubated with secondary antibody. Statistical analysis: Data were expressed as mean±sd. Significance of differences between control and cocaine-treated samples was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Least-Significant- Difference (LSD) test. Values of p<0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS Cocaine caused dendritic varicosity in primary hippocampus neurons: To examine effects of cocaine exposure on dendrites, primary neurons were treated with different concentrations of cocaine followed by Am. J. Infect. Dis., 5 (1): 26-30, measuring dendritic varicosity. As shown in Fig. 1, 10 µm of cocaine caused dendritic varicosity throughout the dendritic arbors within 120 min of treatment, an effect that was not observed with 1 µm cocaine. 2. Cocaine regulated Arc expression in hippocampal neurons Since neuronal plasticity is exemplified by the expression of the Arc gene, we next sought to explore the expression of Arc Western blot analysis in parallel with the dendritic varicosity. Interestingly, exposure of neurons to 10 µm of cocaine, that resulted in enhanced dendritic varicosity, correspondingly demonstrated decreased Arc expression (Fig. 2). Rat primary neurons exposed to different concentrations of cocaine were monitored for cocainemediated Arc expression. Exposure of neurons to 10 µm of cocaine resulted in decreased Arc expression while exposure of cell to 1µM cocaine resulted in increased Arc expression. The figure is a representative image of three independent experiments Gp120 and cocaine caused enhanced dendritic varicosity formation: Drugs of abuse are known to accelerate the progress of HIV [1,12]. We next sought to explore the effect of both cocaine and the HIV protein gp120 on dendritic varicosity. Rat primary neurons cotreated with gp120 and cocaine were examined for somatodendritic microtubule-associated protein MAP2 using staining by immunofluoresence. Control group revealed neurons with round somata and an intricately branched dendritic arbor with smooth dendrites. Fig. 1: Cocaine exposure resulted in formation of dendritic varicosity in primary hippocampus neurons. Rat hippocampal neurons exposed to 10 µm but not 1µM cocaine developed dendritic varicosities. The image shown is a representative picture of three independent experiments. Images were captured on a timelapse confocal microscope. Arrows indicate the sites of dendritic varicosity formation
3 Fig. 2: Cocaine regulated Arc expression in hippocampal neurons (a) (b) Fig. 3: Gp120 and cocaine caused enhanced dendritic varicosity formation. (a) MAP2 immunofluorescence of primary hippocampal neurons exposed to cocaine, gp120 and cocaine plus gp120 demonstrated increased dendritic varicosity formation in the presence of both cocaine and gp120 as compared with neurons exposed to either agent alone. Arrows indicate the sites of dendritic varicosity formation. (b) Quantification of percentage of cells with dendritic varicosities. All the data are presented as mean±sd of four individual experiments. *p<0.05; **p<0.01 vs control group Am. J. Infect. Dis., 5 (1): 26-30, Exposure of neurons to either cocaine (10 µm) or gp120 (200 ng ml 1 ) alone for 120 min demonstrated the appearance of dendritic varicosity along the length of the dendrite. This effect was further enhanced in neurons exposed to both cocaine as well as gp120, with increased dendritic varicosity formation as shown in Fig. 3. DISCUSSION While there is ample evidence suggesting that drugs of abuse such as cocaine can co-operate with HIV-1 to induce neurotoxicity [3], the mechanisms involved in this process remain elusive. The present study demonstrated that cocaine exposure of hippocampal neurons resulted in increased neuronal beading. Further findings determined that the mechanisms underlying the cocaine exposure-mediated impairment of neuronal dendrites in primary hippocampal neurons involved down-regulation of the expression of the neuronal plasticity gene Arc. Additionally, exposure of neurons to HIV-1 envelope protein gp120 resulted in enhanced loss of dendrites of neurons exposed to cocaine. Acute dendritic swelling and spine loss are pathological hallmarks of brain injury and spine loss is associated with focal dendritic swelling [13]. In present study, we demonstrated that cocaine exposure damaged neuronal dendrites in cell culture, a finding that was consistent with the previous study demonstrating that in locus coeruleus neurons, cocaine treatment decreased both the number of cell initiating neuritis as well as the length of neuritis [14]. Although there are conflicting reports indicating that acute cocaine exposure increased spine density and synaptic plasticity of the dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area in vivo [15], the cellular mechanism(s) underlying the effects of cocaine on neuronal plasticity remain unclear. In our study, it was interesting to note that the spine loss occurred over short intervals following treatment with 10 µm of cocaine, but not with 1 µm of cocaine. These findings likely suggest dose-dependent differential effects of cocaine on neuronal plasticity. Long-lasting changes in synaptic efficacy are accompanied by the expression of immediate early genes, including the activity-regulated cytoskeletonassociated gene Arc, also known as Arg3.1 [16]. In the present study, we observed that different concentrations of cocaine exerted distinct effects on Arc expression, with1 µm of cocaine increasing Arc expression, while 10 µm of cocaine exhibiting the opposite effects. Based upon the effects of cocaine on the neuronal dendrites, down-regulation of Arc expression may contribute to
4 Am. J. Infect. Dis., 5 (1): 26-30, 2009 the damage of neuronal dendrites. Up-regulation of Arc expression following exposure of cells to 1uM cocaine (this concentration was identical to the physiological concentration) [17] was consistent with the previous reports demonstrating cocaine-mediated up-regulation of Arc expression primarily in striatum, prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus [18]. Neurologic impairment in patients with HAND correlates well with injury to dendrites and synapses [7]. Despite significant progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying HIV-1 infection and drug abuse-induced neurotoxicity, very few studies have directly examined the impact of HIV-1 infection on dendrites and whether such alterations may contribute to HIV-1-associated neurologic dysfunction. CONCLUSION Present study demonstrated enhanced neuronal beading in the presence of cocaine and HIV proteins as compared with neurons exposed to either agent alone thus shedding light on the exacerbated toxicity mediated by drugs of abuse such as cocaine in the presence of HIV-infection. A better understanding of how HIV-1 and drugs of abuse together can affect the molecular and cellular mechanisms of dendrite damage, can lead to development of new therapeutic approaches targeting preservation of dendrites. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This study was supported by grants RR016443, MH , DA020392, DA and DA from the National Institutes of Health (SB). REFERENCES 1. Aksenov, M.Y. et al., Cocaine-mediated enhancement of Tat toxicity in rat hippocampal cell cultures: The role of oxidative stress and D1 dopamine receptor. Neurotoxicology, 27: Gurwell, J.A. et al., Synergistic neurotoxicity of opioids and human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat protein in striatal neurons in vitro. Neuroscience, 102: Turchan, J. et al., Estrogen protects against the synergistic toxicity by HIV proteins, methamphetamine and cocaine. BMC Neurosci., 2: 3. DOI: / Anthony, J.C., et al., New evidence on intravenous cocaine use and the risk of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Am. J. Epidemiol., 134: /10/ Baldwin, G.C., M.D. Roth, and D.P. Tashkin, Acute and chronic effects of cocaine on the immune system and the possible link to AIDS. J. Neuroimmunol., 83: Doherty, M.C. et al., Correlates of HIV infection among young adult short-term injection drug users. AIDS, 14: Bellizzi, M.J. et al., Synaptic activity becomes excitotoxic in neurons exposed to elevated levels of platelet-activating factor. J. Clin. Invest., 115: DOI: /JCI Dekosky, S.T. and S.W. Scheff, Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann. Neurol., 27: Masliah, E. et al., Selective neuronal vulnerability in HIV encephalitis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 51: Masliah, E. et al., Synaptic and neuritic alterations during the progression of alzheimer's disease. Neurosci. Lett., 174: Park, J.S., M.C. Bateman and M.P. Goldberg, Rapid alterations in dendrite morphology during sublethal hypoxia or glutamate receptor activation. Neurobiol. Dis., 3: DOI: /nbdi Goodkin, K. et al., Cocaine abuse and HIV-1 infection: Epidemiology and neuropathogenesis. J. Neuroimmunol., 83: Hasbani, M.J. et al., Dendritic spines lost during glutamate receptor activation reemerge at original sites of synaptic contact. J. Neurosci., 21: Dey, S., et al., Specificity of prenatal cocaine on inhibition of locus coeruleus neurite outgrowth. Neuroscience, 139: DOI: /j.neuroscience
5 Am. J. Infect. Dis., 5 (1): 26-30, Sarti, F. et al., Acute cocaine exposure alters spine density and long-term potentiation in the ventral tegmental area. Eur. J. Neurosci., 26: Rodriguez, J.J., et al., Long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus is associated with enhanced Arc/Arg3.1 protein expression in spines, dendrites and glia. Eur. J. Neurosci., 21: Dey, S. and D.M. Snow, Cocaine exposure in vitro induces apoptosis in fetal locus coeruleus neurons through TNF-alpha-mediated induction of Bax and phosphorylated c-jun NH (2)-terminal kinase. J. Neurochem., 103: DOI: /j x 18. Fumagalli, F. et al., Corticostriatal upregulation of activity-regulated cytoskeletalassociated protein expression after repeated exposure to cocaine. Mol. Pharmacol., 70: DOI: /mol
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors
 Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Functional Development of Neuronal Networks in Culture -An in vitro Assay System of Developing Brain for Endocrine Disruptors Masahiro Kawahara and Yoichiro Kuroda Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Neuroscience
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization. Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience
 Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Developmental regulation of Medium Spiny Neuron dendritic arborization Lorene M. Lanier Department of Neuroscience Diversity in dendritic arbors Pyramidal Purkinje Medium Spiny http://youtu.be/_tqpca6wx84
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB
 Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
22 JWA :00-15:
 22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
22 JWA 2018 2018 7 7 13:00-15:00 1 2 1702004 2018 7 7 Saturday, 7 th July, 2018 12:30-2F 1 13:00-14:00 1 (SL-1) Special Lecture 1 Monoaminergic drugs vs. fast-acting antidepressants: effects on glutamate
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back
 Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION. Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre
 1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
1 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF DRUG ADDICTION Sylvane Desrivières, SGDP Centre Reward 2 Humans, as well as other organisms engage in behaviours that are rewarding The pleasurable feelings provide positive reinforcement
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus
 2018;68:111~115 Original N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus Shuchuan Miao 1, Noriko Koganezawa 1, Kenji Hanamura 1, Anggraeini Puspitasari 1,2
2018;68:111~115 Original N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Mediates X-irradiation-induced Drebrin Decrease in Hippocampus Shuchuan Miao 1, Noriko Koganezawa 1, Kenji Hanamura 1, Anggraeini Puspitasari 1,2
The Role of PSD-95 and Cypin in Morphological Changes in Dendrites Following Sublethal NMDA Exposure
 15468 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 26, 2011 31(43):15468 15480 Cellular/Molecular The Role of PSD-95 and Cypin in Morphological Changes in Dendrites Following Sublethal NMDA Exposure Chia-Yi Tseng
15468 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 26, 2011 31(43):15468 15480 Cellular/Molecular The Role of PSD-95 and Cypin in Morphological Changes in Dendrites Following Sublethal NMDA Exposure Chia-Yi Tseng
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India
 Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
Recent Findings from Analysis of HIV Clade C in India Pankaj Seth, Ph.D Associate Professor, Molecular & Cellular Neuroscience National Brain Research Centre (NBRC) Manesar, INDIA pseth@nbrc.res.in NeuroAIDS
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003
 Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury
 Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
Receptor-interacting Protein Kinases Mediate Necroptosis In Neural Tissue Damage After Spinal Cord Injury Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D., Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Kenichiro Yahata, M.D.,
and functional consequences
 Morphological effects of chronic drug use in the brain and functional consequences Christian P. Müller SGDP Center, Institute of Psychiatry King s College London normal behavioural repertoire: driven by
Morphological effects of chronic drug use in the brain and functional consequences Christian P. Müller SGDP Center, Institute of Psychiatry King s College London normal behavioural repertoire: driven by
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) cause degeneration of cytoskeleton and disrupt synaptic machinery of cultured cortical neurons
 Xu et al. Molecular Brain 2013, 6:29 RESEARCH Open Access Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) cause degeneration of cytoskeleton and disrupt synaptic machinery of cultured cortical neurons Fenglian Xu 1,2*, Cortt
Xu et al. Molecular Brain 2013, 6:29 RESEARCH Open Access Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) cause degeneration of cytoskeleton and disrupt synaptic machinery of cultured cortical neurons Fenglian Xu 1,2*, Cortt
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP. Reading: BCP Chapter 25
 Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
Memory Systems II How Stored: Engram and LTP Reading: BCP Chapter 25 Memory Systems Learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills. Memory is the retention of learned information. Many different
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain
 Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
CASE 49. What type of memory is available for conscious retrieval? Which part of the brain stores semantic (factual) memories?
 CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
CASE 49 A 43-year-old woman is brought to her primary care physician by her family because of concerns about her forgetfulness. The patient has a history of Down syndrome but no other medical problems.
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki
 TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
TNS Journal Club: Interneurons of the Hippocampus, Freund and Buzsaki Rich Turner (turner@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk) Gatsby Unit, 22/04/2005 Rich T. Introduction Interneuron def = GABAergic non-principal cell Usually
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity
 PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
PROPOSAL: Translational Safety Biomarker Assessment of Neurotoxicity Andreas Jeromin, PhD Chief Scientific Officer NextGen Sciences DX Boston, MA Emerging Issues Session HESI Annual Meeting 12 June 2012
Neuronal Development
 Neuronal Development stage1 stage2 stage3 stage4 Mature neuron 20 m Presynaptic axonal terminal Postsynaptic dendritic spine 5μm 20μm Mature synapse 脳の最小機能単位シナプス 外界からの刺激 シナプスの応答 脳の最小機能単位シナプス 外界からの刺激 シナプスの応答
Neuronal Development stage1 stage2 stage3 stage4 Mature neuron 20 m Presynaptic axonal terminal Postsynaptic dendritic spine 5μm 20μm Mature synapse 脳の最小機能単位シナプス 外界からの刺激 シナプスの応答 脳の最小機能単位シナプス 外界からの刺激 シナプスの応答
Session Goals. Principles of Brain Plasticity
 Presenter: Bryan Kolb Canadian Centre for Behavioural Neuroscience University of Lethbridge Date: January 12, 2011 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and
Presenter: Bryan Kolb Canadian Centre for Behavioural Neuroscience University of Lethbridge Date: January 12, 2011 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
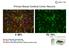 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Effect of Rhodamine-taxol conjugate on Caveolin dynamics
 Chapter 6 4 Effect of Rhodamine-taxol conjugate on Caveolin dynamics 1. Summary In the present study, Rhodamine- taxol conjugate treatment resulted in a transient recruitment of Caveolin-1 to the cell
Chapter 6 4 Effect of Rhodamine-taxol conjugate on Caveolin dynamics 1. Summary In the present study, Rhodamine- taxol conjugate treatment resulted in a transient recruitment of Caveolin-1 to the cell
The Adolescent Developmental Stage
 The Adolescent Developmental Stage o Physical maturation o Drive for independence o Increased salience of social and peer interactions o Brain development o Inflection in risky behaviors including experimentation
The Adolescent Developmental Stage o Physical maturation o Drive for independence o Increased salience of social and peer interactions o Brain development o Inflection in risky behaviors including experimentation
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide
 Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide Bruce H. Morimoto, Ph.D. Executive Director, Applied Translational Medicine Microtubules Microtubules essential for neuronal
Neuroprotection in preclinical models of Parkinson disease by the NAPVSIPQ peptide Bruce H. Morimoto, Ph.D. Executive Director, Applied Translational Medicine Microtubules Microtubules essential for neuronal
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb. by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral
 Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Elise Cook. BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology. BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology
 Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
Acute and chronic toxicity of methamphetamine exposure in cultured neuronal cells Elise Cook BForensics (Hons) Forensic Biology and Toxicology BSc Biomedical Science and Molecular Biology This thesis is
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
11/3/2014. Opiates: methadone, buprenorphine, heroin, prescription drugs: Vicodin, OxyContin, Percocet
 Estelle B. Gauda, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Senior Associate Dean of Faculty Development Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions UNDERSTAND HOW COCAI AND METHAMPHETAMIS HAVE ABUSE POTENTIAL UNDERSTAND WHY
Estelle B. Gauda, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Senior Associate Dean of Faculty Development Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions UNDERSTAND HOW COCAI AND METHAMPHETAMIS HAVE ABUSE POTENTIAL UNDERSTAND WHY
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
Supplementary Fig. 1
 PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
Supporting Information. FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce. apoptosis
 1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Hasbi et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903676106 SI Text Drugs. Dopaminergic agonists and antagonists SKF 83959, SKF 83822, dopamine, SCH 22390, and raclopride were purchased from Tocris Bioscience.
Supporting Information Hasbi et al. 10.1073/pnas.0903676106 SI Text Drugs. Dopaminergic agonists and antagonists SKF 83959, SKF 83822, dopamine, SCH 22390, and raclopride were purchased from Tocris Bioscience.
1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization
 Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Estrogen and Brain Development. Kyle Pemberton
 Estrogen and Brain Development Kyle Pemberton Estrogens and Estrogen Receptors GPER ERα Nucleus ERβ https://www.pharmacorama.com/en/sections/estrogens_progestins_hormonal_contraceptives_1_1.php Estrogen
Estrogen and Brain Development Kyle Pemberton Estrogens and Estrogen Receptors GPER ERα Nucleus ERβ https://www.pharmacorama.com/en/sections/estrogens_progestins_hormonal_contraceptives_1_1.php Estrogen
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Fig. 4. The activity of Pkc -transduced neurons is required for enhanced learning. After gene transfer, rats were tested on [] vs. +.
![Fig. 4. The activity of Pkc -transduced neurons is required for enhanced learning. After gene transfer, rats were tested on [] vs. +. Fig. 4. The activity of Pkc -transduced neurons is required for enhanced learning. After gene transfer, rats were tested on [] vs. +.](/thumbs/90/102196023.jpg) Research Interests Advanced cognitive learning is encoded in distributed circuits that span multiple forebrain areas. Further, synaptic plasticity and neural network theories hypothesize that essential
Research Interests Advanced cognitive learning is encoded in distributed circuits that span multiple forebrain areas. Further, synaptic plasticity and neural network theories hypothesize that essential
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation
 Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction. Alcohol. Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) School of Psychology. Tobias Bast.
 C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
C81ADD Psychology of Addiction Alcohol Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) Tobias Bast School of Psychology tobias.bast@nottingham.ac.uk 1 Selected aspects of the psychopharmacology of alcohol (ethanol) Primary neuropharmacological
Synaptic changes in dementia: links to cognition and behaviour
 Synaptic changes in dementia: links to cognition and behaviour Paul T Francis, PhD Professor of Neurochemistry Director, Brains for Dementia Research Agenda Discuss synaptic changes in various dementias
Synaptic changes in dementia: links to cognition and behaviour Paul T Francis, PhD Professor of Neurochemistry Director, Brains for Dementia Research Agenda Discuss synaptic changes in various dementias
Ontogeny of biochemical, morphological and functional parameters of synaptogenesis in primary cultures of rat hippocampal and cortical neurons
 Harrill et al. Molecular Brain (2015) 8:10 DOI 10.1186/s13041-015-0099-9 RESEARCH Open Access Ontogeny of biochemical, morphological and functional parameters of synaptogenesis in primary cultures of rat
Harrill et al. Molecular Brain (2015) 8:10 DOI 10.1186/s13041-015-0099-9 RESEARCH Open Access Ontogeny of biochemical, morphological and functional parameters of synaptogenesis in primary cultures of rat
6. TNF-α regulates oxidative stress, mitochondrial function and autophagy in neuronal cells
 6. TNF-α regulates oxidative stress, mitochondrial function and autophagy in neuronal cells 6.1 TNF-α induces mitochondrial oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. The dysregulation of mitochondria and oxidative
6. TNF-α regulates oxidative stress, mitochondrial function and autophagy in neuronal cells 6.1 TNF-α induces mitochondrial oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells. The dysregulation of mitochondria and oxidative
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse. Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver
 Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1
 Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation
 In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation Tamima Ashraf, PhD candidate Supervisor: Dr. Reina Bendayan University of Toronto, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy,
In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation Tamima Ashraf, PhD candidate Supervisor: Dr. Reina Bendayan University of Toronto, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy,
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
28/04/51. Introduction. Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood. Is accelerated brain aging a consequence of diabetes? chronic hyperglycemia
 Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
Introduction Insulin signaling effects on memory and mood (Review) Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both Long-term diabetes Lawrence
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
To: Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS) Final report. Daniela Busti
 To: Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS) Final report Daniela Busti e-mail address: daniela.busti@i-med.ac.at Contact information of home institution: Prof. Francesco Ferraguti, Innsbruck Medical
To: Network of European Neuroscience Schools (NENS) Final report Daniela Busti e-mail address: daniela.busti@i-med.ac.at Contact information of home institution: Prof. Francesco Ferraguti, Innsbruck Medical
Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways
![Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways](/thumbs/96/128474991.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Neuropathology of Neurodegenerative Disorders Prof. Jillian Kril
 Neurodegenerative disorders to be discussed Alzheimer s disease Lewy body diseases Frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies Huntington s disease Motor Neuron Disease 2 Neuropathology of neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative disorders to be discussed Alzheimer s disease Lewy body diseases Frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies Huntington s disease Motor Neuron Disease 2 Neuropathology of neurodegeneration
Fig. S1. High K+ increases intracellular calcium level.
 Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
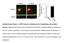 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
