Alveolar Histiocytosis. Non-infectious conditions of Rats. Alveolar Histiocytosis
|
|
|
- Terence Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Non-infectious conditions of Rats Charles B Clifford, DVM, PhD, DACVP Charles River Alveolar Histiocytosis Synonym: Alveolar lipidosis Prevalence: Very high in aged rats, moderate in younger animals may be >50% in F-344 rats, also common in SD. Grossly: visible as white to pale tan foci, usually about 1 mm in diameter, visible on the pleural surface foci may extend slightly above the pleural surface in uninflated lung may be numerous Alveolar Histiocytosis cause is unknown, not considered to be infectious should not be mistaken for any of the infectious pneumonias of rats, e.g., P. carinii animals are seronegative any lymphoid infiltrate is slight and localized perivascular lymphoid cuffing not a prominent feature hemosiderin is not a feature; would suggest previous hemorrhage
2 Eosinophilic Granulomatous Pneumonia of Brown Norway Rats Prevalence: Very high in Brown-Norway rats Observed in BN rats of all ages, from Asia, North America and Europe, and in rats of any health status, including gnotobiotic Cause is unknown, may be related to a hypersensitivity reaction special stains are negative, as are cultures and serology Chronic Progressive Nephropathy Synonyms: Chronic Progressive Nephrosis, Chronic Progressive Glomerulonephropathy, Progressive Renal Disease, and Old Rat Nephropathy Prevalence: Very high, especially in males May be minimal lesions by 3-6 months of age in some strains (F- 344, SD) Most important age-related disease of rat kidneys Among most common causes of death in rats in lifetime studies
3 Chronic Progressive Nephropathy Microscopically: glomerular changes are characterized by thickened basement membranes, thickening of the capillary tufts, adhesions to the parietal layer of Bowman s membrane, and segmental glomerulosclerosis. with progression, numerous tubules in both the cortex and medulla are often dilated and filled with eosinophilic proteinaceous casts can have mild multifocal nonsuppurative interstitial inflammation Secondary hyperparathyroidism may occur, resulting in widespread mineralization Chronic Progressive Nephropathy Etiopathogenesis poorly understood, probably multifactorial First, genetic predisposition Sprague-Dawley and F344 rats have high incidence Wistar and Long-Evans stocks have lower incidence Esp. high in hypertensive rats Second, sex Males have earlier onset, higher incidence at any given age, and greater severity of lesions than do females
4 Chronic Progressive Nephropathy Etiopathogenesis - continued Third, Diet - mechanism hypothesized to be: overfeeding >> prolonged increases in renal blood flow and GFR >> glomerular hypertrophy >> macromolecule filtration deficits, mesangial damage, glomerulosclerosis, and protein leakage Protein levels in diet may also play a secondary role Chronic Progressive Nephropathy Diet control to reduce CPN Regardless of actual mechanism, 25-30% caloric reduction: decreases incidence and severity of CPN in female rats decreases severity of CPN in male rats increases survival in both sexes Nephrocalcinosis Prevalence: High, especially in females Defined as the deposition of calcium phosphate in renal tissue Additional terms are sometimes employed to reflect location in cortex, medulla, etc. Nephrocalcinosis In addition to gender, the incidence varies with age and strain may occur in F-344 rats by 7 weeks incidence in F-344 rats may reach 50%, compared to 0 7% Sprague-Dawley and Wistars An especially high incidence and severity is observed in BDIX rats Nephrocalcinosis The incidence and severity of nephrocalcinosis may be increased by dietary manipulation high levels of calcium high phosphorus low calcium:phosphorus ratios low magnesium Unknown if dietary levels of these minerals cause spontaneous background incidence Nephrocalcinosis Grossly: Larger mineral depositis may appear as pale areas, and may be crepitous when cut Microscopically: Mineral deposition is observed most frequently at the corticomedullary junction, in cells of the pars recta and thin loops of Henle, as well as in the lumen of these tubules
5 Hydronephrosis Prevalence: Very high in Brown Norway, Gunn and Zucker Low to moderate in many other strains Generally higher in males than females Higher in right kidney than left Hydronephrosis Grossly: Appearance may vary from normal to greatly enlarged and translucent Associated with urothelial hyperplasia and hemorrhage resulting in hematuria in the Brown Norway and the Lewis x Brown Norway rat
6 Cardiomyopathy Synonyms: Murine Progressive Cardiomyopathy, Chronic progressive cardiomyopathy, myocardial degeneration and fibrosis Prevalence: A major cause of death in aged male rats of many strains, when fed ad libitum, including Sprague-Dawley and F-344. May be observed (minimal severity) as early as three months of age. Reported incidence varies greatly Probably different thresholds by different pathologists Cardiomyopathy Grossly, heart may be enlarged, occasionally with pale streaks increased heart weight correlates well with histologic severity Microscopically, myocardial necrosis interstitial infiltration of mononuclear cells later, fibrosis may be more prominent large reactive nuclei are also observed in myofibers most commonly affected sites are apex, papillary muscles, left ventricular free wall and interventricular septum Cardiomyopathy The incidence and severity of cardiomyopathy can also be dramatically reduced at any age by moderate dietary restriction, i.e., reduction of 25-30% of total caloric intake relative to ad libitum overfed rats
7 Arteritis Synonyms: Panarteritis nodosa, Periarteritis, Polyarteritis Prevalence: Moderate. Very high in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR), higher in males Grossly - thickened tortuous arteries, especially in mesenteric arcade Also suspensory connective tissue of spleen, pancreas and testis. Can occur in almost any tissue, but not reported in lung Microscopically Fibrinoid necrosis of intima and media, Mural leukocytic infiltration. Chronically - intimal hyperplasia, medial fibrosis and periarterial fibrosis and dense infiltrations of leukocytes. Arterial stenosis or thrombosis may occur. Hypertension Can lead to arteriosclerosis Common in aging rats of many strains Very common in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rat (SHR) Susceptible strains, e.g., SHR-SP, can also develop malignant hypertension Onion-skin appearance to affected vessels in heart, kidney.
8 Ringtail Prevalence: Sporadic and infrequent Affects rats and mice Primarily a disease of sucklings and weanlings Cause: Never experimentally reproduced (nothing in literature) Historically reported to be associated with low humidity Ringtail Grossly: tails swollen, with annular constrictions distal portions more severely affected may have distal necrosis Must distinguish from bite wounds, other trauma, infarcts, etc.
9 Ringtail Microscopically: Acanthosis, hyperkeratosis Subepidermal congestion Epidermis often intact (compared to ulcers with serocellular crusting in bite wounds) Age-related changes in the skin Prevalence: Very high Often observed but rarely reported Alopecia: especially on the dorsum very common in Brown Norway rats Age-related changes in the skin Old albino rats appear more yellow with age, due to accumulation of sebum The rings of scales covering tail increase with age to 190 at 1 year, and become more prominent and more yellow with time Yellowish material on the tail and at the base of the ear also may become black with time, probably from oxidation and/or bacterial action Age-related changes in the skin Male rats accumulate brown pigmented foci on the skin, termed scales, occasionally reported as freckles scales can be detached, and overlay skin of normal color found on the dorsum, and some on the tail and perineum scale formation is abrogated by gonadectomy nature of scale pigment is unclear, but may be oxidized lipid or amino acids
10 Auricular Chrondropathy Prevalence: Low to moderate Synonyms: Auricular chondritis, cauliflower ear Grossly: Nodular thickening and distortion of pinna May sometimes be associated with inflammation, triggered by eartags Also observed in rats without eartags Malocclusion Prevalence: Low to moderate Malocclusion of incisors most often observed in older rats, and may be associated with gingivitis It can be caused by lack of wear on incisors (powdered diet) Sporadically observed in younger rats, in which it may either be congenital or due to trauma
11 Osteoarthritis Synonym: Degenerative joint disease Prevalence: Moderate Cause unknown, but age-related, likely related to weight May also be induced experimental model - Collagen, adjuvant, etc. Osteoarthritis may have a higher incidence in animals housed in wire-bottom caging (rarely used now) Tarsal joints are affected most, and may appear grossly thickened Histologically, there is erosion of articular cartilage and degeneration of the matrix Tinctorial change, fibrillation, proliferation, necrosis, bone lysis, synovial hyperplasia, etc.
12 Endocrine Neoplasms Neoplasia Endocrine neoplasms are the most common spontaneous tumors of aged Sprague-Dawley, Wistar-Han, and F344 rats (except interstitial cell tumors and LGL leukemia in male F344) Pituitary Thyroid Adrenal Medulla Pituitary Neoplasms Tumors of the pars distalis are the most common tumors of the pituitary. Other tumors are infrequent Most are adenomas Most are chromophobe adenomas By immunohistochemistry, most secrete prolactin Pituitary Neoplasms Grossly, the pituitary is enlarged and often hemorrhagic Microscopically: adenomas are expansile and sharply delimited cells are larger than normal, with abundant pale cytoplasm (chromophobes) and have enlarged vesicular nuclei histologic pattern may vary mitoses are occasionally observed (low rate)
13 Pituitary Neoplasms Carcinomas are more infiltrative, but rarely metastasize. Criteria for carcinoma = metastasis or aggressive invasion (STP, 1990) Multicenter control group data for Sprague-Dawley (CD) rats show much variation in use of the term carcinoma some large studies have no carcinomas in control rats in others, most of the pituitary tumors are considered malignant total number of pituitary tumors (adenomas plus carcinomas) is fairly consistent at ~ 70-80% in females and 50-70% in males. Thyroid Neoplasms The most common thyroid tumors are C-cell neoplasms (>5%), followed by follicular cell tumors No sex predilection C-cell adenomas defined as compressive masses of C- cells, with diameter > 5 average follicular diameters Smaller C-cell proliferations are termed hyperplasia Thyroid Neoplasms C-cell adenomas: cells closely resemble normal, may be oblong if compressed Carcinomas: pleomorphic cells usually a high mitotic rate usually vascularized and may have areas of mineralization, necrosis and hemorrhage Key criteria for carcinomas = invasion, necrosis, metastasis
14 Pheochromocytomas Incidence in 2 year studies (benign + malignant) F-344 rats: ~ 26% in males, 6% in females CD rats: ~ 13% in males, 3% in females Wistar-Han rats: ~ 3% in males, 2% in females Pheochromocytomas Benign pheochromocytomas, synonymous with pheochromocytomas: defined as a discrete mass of cells arranged in islets or trabeculae may be confined to the medulla or may compress the cortex some atypia may be present, with cells smaller than normal, and with more basophilic cytoplasm mitotic rate is variable Malignant pheochromocytomas: defined as pheochromocytomas which invade the capsule or metastasize
15 Mammary Neoplasms Incidence: CD rats: > 50% of control female CD rats will usually have mammary tumors at the conclusion of a two-year study F344 and Wistar Han rats: up to 30% Incidence in male rats usually < 1% In females, most are fibroadenomas, with carcinomas being 2nd most common Age of onset delayed by caloric restriction Mammary Neoplasms Fibroadenomas: firm, circumscribed, lobulated, subcutaneous masses may be located anywhere along mammary chain may become massive and ulcerated if rats are not euthanized ulceration can cause anemia composed of varying ratios of fibrous tissue and ductal epithelium fibrous tissue appears mature ductal epithelium may vary from a single layer of cuboidal cells with no atypia to focal epithelial proliferation, pleomorphism, moderate atypia and increased mitotic rate. Cysts lined by attenuated epithelium may also be present.
16 Mammary Neoplasms Adenomas: discrete, circumscribed masses composed almost entirely of glandular epithelial structures with scant stroma if alveoli are formed, they may be empty or distended with secretions the epithelium is usually uniform, cuboidal to columnar cytoplasmic vacuolation may be present there is usually little or no atypia mitotic rate may be slightly elevated may have tubular, secretory, papillary or cystic papillary patterns Mammary Neoplasms Adenocarcinomas: distinction of adenoma vs. adenocarcinomas is controversial, as rat mammary tumors seldom metastasize or even invade locally tumors with marked atypia, a high nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, variable growth patterns, high mitotic rates or abnormal mitoses are considered malignant the rare tumors that invade or metastasize are unequivocally considered malignant adenocarcinomas may have multiple patterns; more common patterns are papillary, tubular, cribriform and comedo
17 Lymphoreticular Neoplasms Prevalence: CD and Wistar Han, both sexes: ~ 2-3% F344 rats: ~ 33% for males and 20% for females, virtually all of which are mononuclear cell leukemia Rat lymphoid neoplasms are NOT thought to be retroviral-associated Lymphoreticular Neoplasms Large Granular Lymphocyte leukemia: also called large granular lymphocytic leukemia, or LGL lymphoma or leukemia also reported in other rat strains, including Wistar and Wistar-Furth arise in marginal zone of spleen, soon spread to the liver, lung, lymph nodes previously thought to arise from NK cells, then thought to have a more heterogeneous lymphocyte origin, now seem to be considered NK cells Lymphoreticular Neoplasms Large Granular Lymphocyte leukemia: Grossly, usually marked splenomegaly and hepatomegaly, with variable lymphadenopathy Microscopically : cells are small, non-cohesive, pleomorphic relatively small amount of cytoplasm which stains reddish nuclei are irregular, round to reniform, and may be eccentric, with sparse chromatin and small nucleoli mitotic rate is low Neoplastic cells can diffusely involve the spleen, hepatic sinusoids, and pulmonary interstitium
18 Skin Neoplasms In CD, Wistar Han and F344 strains, male rats have approximately 10% incidence of skin neoplasms, compared to 5% in females. The most common tumors are fibromas and squamous cell neoplasms, especially the keratoacanthoma Fibromas: Skin Neoplasms benign tumors consisting of dense interwoven bands of collagen, with only a few fibroblasts, and little or no cellular pleomorphism or mitotic activity some care required, to insure that fibromas are distinguished from mammary fibroadenomas Fibrosarcomas are much less frequent in rat skin, and are easily distinguished by their much greater cellularity, often with much pleomorphism, a high mitotic rate, and local invasion Squamous cell neoplasms: papillomas: Skin Neoplasms resemble those in other species exophytic, with a well-differentiated stratified squamous epithelium covering a fibrovascular core Non-viral in origin
19 Skin Neoplasms Squamous cell neoplasms: keratoacanthomas (cutaneous horn is considered a variant): probably also arise from a squamous cell these are invaginations, sometimes multilocular, which communicate with the surface via a pore lined by thick stratified squamous epithelium and filled with keratinaceous epithelium may progress to squamous cell carcinoma
20 Skin Neoplasms Squamous cell neoplasms: Squamous cell carcinomas: invasive tumors which usually extend into the subcutis usually composed of multiple nests of pleomorphic cells may have markedly enlarged nuclei and prominent nucleoli may metastasize. Sebaceous adenoma of preputial gland Prevalence: Testicular Neoplasms common in aging rats of many strains ~ 88% in F344 rats ~ 3% in CD and Wistar Han rats most testicular tumors in the CD and Wistar Han and virtually all in the F344 rat are interstitial cell tumors Testicular Neoplasms Interstitial cell tumors: grossly: appear as circumscribed, yellow or white testicular masses, often hemorrhagic can be bilateral can be multiple within one testis
21 Testicular Neoplasms Interstitial cell tumors: Microscopically: interstitial cell masses < 3 seminiferous tubule diameters are considered focal hyperplasia can be seen at a high incidence in F344 rats < 1 year old adenomas are > 3 tubule diameters, compress adjacent tubules. cells show pleomorphism or an increased nucleus:cytoplasm cells enmeshed in endocrine-type sinusoidal network may have necrosis, hemorrhage, and pseudocysts Interstitial cell tumors: Microscopically: Testicular Neoplasms Almost all interstitial cell tumors are considered benign Malignant designation should be reserved for tumors that invade structures adjacent to the testis or metastasize
22 Mesotheliomas Often tabulated with testicular neoplasms, as they often arise on the tunica vaginalis. More properly, should be categorized as tumors of body cavities Prevalence: primarily in males < 1% in male CD rats ~ 3% in male Wistar Han and F344 rats Mesotheliomas All mesotheliomas are considered malignant Grossly visible as white or beige plaques on the tunica vaginalis or throughout the abdomen (spontaneous thoracic mesotheliomas are very rare) Mesotheliomas Microscopically: Neoplastic foci consist of complex papillary structures Prominent, well vascularized stroma covered by one or more layers of cuboidal cells Spread throughout the peritoneum is common Mesotheliomas must be distinguished from mesothelial hyperplasia, which is common Hyperplasia, usually not visible grossly, has focal thickening, occasionally papillary projections, but no stratification or fibrovascular stalk
23 More background tumor incidence data are available at: Thanks for your attention!
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
A neoplasm is defined as "an abnormal tissue proliferation, which exceeds that of adjacent normal tissue. This proliferation continues even after
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA
 Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features.
 Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Histopathology: Hypertension and diabetes in the kidney These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need
Dr. S. K. Vijayasarathi Head, Pathology Advinus, Bangalore
 PITUITARY IN PRECLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Dr. S. K. Vijayasarathi Head, Pathology Advinus, Bangalore Disclaimer The ideas and thoughts expressed in this presentation are purely that of the presenter and do not
PITUITARY IN PRECLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Dr. S. K. Vijayasarathi Head, Pathology Advinus, Bangalore Disclaimer The ideas and thoughts expressed in this presentation are purely that of the presenter and do not
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Pathology of Hypertension
 2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
2016-03-07 Pathology of Hypertension Honghe Zhang honghezhang@zju.edu.cn Tel:88208199 Department of Pathology ❶ Genetic predisposition ❷ Dietary factors ❸ Environmental factors ❹ Others Definition and
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult. by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department
 Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Spectrum of Preneoplastic and Neoplastic Cystic Lesions of the Kidney in Adult by dr. Banan Burhan Mohammed Lecturer in Pathology Department Various hereditary, acquired, and neoplastic conditions can
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data. March, 2003
 Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Salivary Gland Cytology
 Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
TUMOR,NEOPLASM. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Tinh hoàn
 Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE
 AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER. Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D.
 NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
NEOPLASIA-I CANCER Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. 1 2 Tumor in the hieroglyphics of the Edwin Smith papyrus (1,600 B.C., Breasted s translation 1930) 3 War on Cancer (National Cancer Act, 1971) 4 Cancer Acts in Korea
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
The stability of historical control data for common neoplasms in laboratory rats and the implications for carcinogenic risk assessment
 Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology xxx (2004) xxx xxx Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology www.elsevier.com/locate/yrtph The stability of historical control data for common neoplasms in laboratory
Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology xxx (2004) xxx xxx Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology www.elsevier.com/locate/yrtph The stability of historical control data for common neoplasms in laboratory
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers.!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1
 !! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
!! Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D.!! 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers!! Peak Incidence is 6th Decade!! M:F = 2:1!! Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule 1 !!Conventional RCC! Clear
Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update 5/29/2009
 Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder
 Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
Tumors of kidney and urinary bladder Overview of kidney tumors Benign and malignant Of the benign: papillary adenoma -cortical -small (0.5cm) -in 40% of population -clinically insignificant The most common
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis.
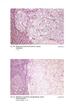 Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Palatal Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Palatal Lesions Palatal Masses Periapical Abscess Torus Palatinus Mucocele Lymphoid Hyperplasia Adenomatous Hyperplasia Benign Salivary Neoplasms Malignant Salivary
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
AN AUTOPSY CASE OF PARATHYROID CARC. Matsumoto, Koji; Ito, Masahiro; Sek. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) AN AUTOPSY CASE OF PARATHYROID CARC Hsu, Chao-Tien; Naito, Shinji; Shik Matsumoto, Koji; Ito, Masahiro; Sek Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) AN AUTOPSY CASE OF PARATHYROID CARC Hsu, Chao-Tien; Naito, Shinji; Shik Matsumoto, Koji; Ito, Masahiro; Sek Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia
 Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Demystifying Endometrial Hyperplasia A review from Diagnostic Histopathology 19:7 Dr R Hadden ST5 Histopathology Derriford Hospital Plymouth Endometrium Target for sex-steroid hormones Glands Stroma Proliferate
Outline 11/2/2017. Pancreatic EUS-FNA general aspects. Cytomorphologic features of solid neoplasms/lesions of the pancreas
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND GUIDED-FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF PANCREAS Khalid Amin M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Outline Pancreatic
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND GUIDED-FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF PANCREAS Khalid Amin M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology University of Minnesota Outline Pancreatic
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
 www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
www.ivis.org Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct. 17-19, 2008 Barcelona, Spain http://www.sevc.info Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC www.ivis.org
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
2015 Lab Animal 8/22/ Mouse. 2. Rat. 3. Mouse. Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse
 1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study. of Diphenylamine. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Title malignancy. Issue Date Right 209, 12, (2013)
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A case of intracystic apocrine papi malignancy Hayashi, Hiroko; Ohtani, Hiroshi; Y Citation Pathology - Research and Practice, Issue Date 2013-12 URL Right
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A case of intracystic apocrine papi malignancy Hayashi, Hiroko; Ohtani, Hiroshi; Y Citation Pathology - Research and Practice, Issue Date 2013-12 URL Right
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
