Please answer the following questions:
|
|
|
- Kimberly May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Benha University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Dept. of Theriogenology Time allowed: 3 hours Date: Tuesday, June 21, 2011 Total Marks ( 50) Fourth Year exam (Andrology and Abortion Diseases,2011) Please answer the following questions: 1) Define and enumerate venereal diseases. Recognize the clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and line of treatment of one of them? (10 marks) 2) Impotentia generandi is largely influence the male fertility without apparent effect on the mating ability or sexual desire. Describe and Judge the changes in semen picture in different conditions that lower fertilizing capacity of the male. (10 marks) 3) Interpret on: a. Species-specific patterns of courtship in the male (3 marks) b. Contribution of the reproductive organs to seminal plasma. (3 marks) c. Factors influence the thermo-regulatory mechanism of the testes. (2 marks) d. Unilateral acute orchitis in a bull. (2 marks) 4) WRITE ON THE MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR: a. Hormonal control of testes function. (5 marks) b. Erection, Emission and Ejaculation in a bull. (5 marks) c. Vibriosis in inducing abortion (5 marks) d. Leptospirosis in inducing abortion (5 marks)
2 Benha University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Dept. of Theriogenology Time allowed: 3 hours Date: Tuesday, June 21, 2011 Total Marks ( 50) Fourth Year exam (Andrology and Abortion Diseases, 2011) - Model Please answer the following questions: 1) Define and enumerate venereal diseases. Recognize the clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and line of treatment of one of them? (10 marks) Venereal diseases are those diseases transmitted only through coitus such as Tichomoniasis, Vibriosis, Epi-Vag, IBR-IPVand IBP. The clinical symptoms, diagnosis, and line of treatment of trichomoniasis: - Clinical symptoms: In females days after infection a moderate vulvo-vaginitis and cervicitis. 2- Increase the number of services per conception which may reach about 10 services during the high time of infection. 3- Prolonged period between estrous periods after 4- Mild inflammation of the endometrium with mucopurulant exudate. 5- If the parasite enter the uterus early.unobserved abortion If the parasite multiplies in the vagina and not enter the uterus. the pregnancy continue normal (incidence 25%). If the parasite enter the uterus after formation of the fetus. it attack the placenta abortion between 2-7 months of gestation (av. 4 th month) with liquefaction of the fetus.. Converted with the fetal fluid into pus and the cervix remain closed (closed pyometra). 6- In case of sub-acute form; repeat breeding of cows. Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 2
3 7- Closed Pyometra (10%): the pyometra exudate is characterized by thin yellow grey, watery fluctuant consistency often containing yellowish flakes of pus and shreds of fetal tissues resemble a potato soup in color and consistency. 8- In chronic stage: sporadic abortion and irregular estrous In bull No clinical signs are not seen in bulls but mild balanoposthitis may be present for a short period from the first infection. - Diagnosis: 1- History: a problem of infertility characterized by failure of conception, prolonged period between the estrous, occurrence of early abortion and pyometra. 2. Demonstration of the organism in infected animal or immunological reactions due to local immunity developed in the genital tract of the female cow. 3. In bulls: examination of the preputial smegma or wash which must be repeated for sure diagnosis 14 successive examinations, weekly interval. - Treatment In the cows 1- Trichomoniasis is self-limiting in cows; a cow that passed through 3 unbred estrous periods and breeding under carefully supervised program usually is sufficient. 2- Cows with pyometra by PGF 2α with local and systemic antibiotic administration. In the bulls 1- Bovoflavin oint 80 gm should be rubbed into all exposed mucosa of extended penis after washing for 20 minutes. The urethra is flushed with ml of 0.01% trypoflavin solution repeated in days 2- Aci-iflavin ointment: 0.5% ointment applied to the exposed penis and 0.5% solution injected into the urethra as in Bovoflavin. 3- Iodine ointment Intravenous administration of 0.5 gm sodium iodide per 100 lbs. body weight in 500 ml sterile distilled water every 48 hours 5 doses. 4- Oral administration of mgl kg body weight of dimetridazol daily for 5 days proved effective Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 3
4 2) Impotentia generandi is largely influence the male fertility without apparent effect on the mating ability or sexual desire. Describe and Judge the changes in semen picture in different conditions that lower fertilizing capacity of the male. (10 marks) Clinical condition Semen picture Judgment A-Cytogenetic defects: normal semen Bull should be B- Congenital abnormalities: Anorchidy: Cryptorchidism Testicular hypoplasia - In unilateral anorchidy: oligospermia - In bilateral anorchidy: aspermia - Unilaterally cryptorchid animals are usually fertile but have reduced sperm concentration, alkaline ph and giant cells and cellular debris are found in semen. - Bilaterally cryptorchid animals are sterile and has azoospermia. - In unilateral case: Sever form: watery semen and contains few or no spermatozoa. Moderate form: Reduction in the sperm output and concen. to about 1/2-2/3. Mild form: Oligospermia - In bilateral sever form: azoospermi. Bull should be Bull should be Bull should be Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 4
5 Segmental aplasia of the Wolffian ducts C- Pathological affections: Testicular degeneration Orchitis Epididymitis Seminal vesiculitis - In bilateral: azoospermia. - In unilateral case: Oligospermia. - Oligospermia. - Decrease semen and sperm motion. - Lowered live sperm %. - Increased abnormal sperm. Mild form: proximal droplets. Moderate form: proximal drops, and nuclear craters. Sever form: Large number of Giant cell with rich chromatin - In acute form: no semen due to Impotentia Coeundi. - In chronic form: nearly normal semen volume, alkaline ph, decreased motility, oligospermia, high sperm abnormalities; Giant cells, blood and pus cells. - increased tailless heads and neutrophils leucocytes. - In Closed epidydimis; semen pic. Depend on the function of the other testis and epididymis. - Semen contains pus floccules and reduced motility. - High catalase activity, lowered fructose content Bull should be Variable, in early condition good prognosis Variable, in early condition good prognosis Variable, in early condition good prognosis Variable, in early condition good prognosis Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 5
6 D. Immunologic infertility - complete absence of the sperm motility under the microscope Bull should be 3) Interpret on: a. Species-specific patterns of courtship in the male (3 marks) Behavior Cattle Sheep Goat Swine Horse Sniffing Sniffing to female genitalia and urine Sniffing to females head Ritualized reaction to females urine Flehmen male stands rigidly and holds his head in horizontal position which he may move slowly from side to side with his neck extended and upper lip raised Flehmen lasts seconds. Absent Same as in cattle. Sheep and goat Urination No No Frequent micturition on foreleg during excitement Vocalization No Courting grunts during sexual approach Rhythmic emission of urine during sexual excitement Courting grunts Marks with urine the place where a mare has urinated Neighing during sexual excitement Tactile stimulation of female Licks females genitalia Noses females flanks Licks female s body bites back and neck Postures during copulation Presses head on female s back leap at ejaculation Rapid movement backwards of head at ejaculation Motionless during ejaculation, scrotal contraction Biters female s neck Post-coital reactions No Stretches head and neck Licks penis No No Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 6
7 b. Contribution of the reproductive organs to seminal plasma. (3 marks) (1) Testis: 1- The viable and normal male gametes, spermatozoa. 2- The cellular fragments that have been cast off by spermatozoa in their maturation. 3- The rete fluid containing higher levels of isolates, potassium and chloride than the blood plasma. (2) Epididymis: 1- Secretion of GPG, carnitine and sialic acid. 2- High level of lactate as an oxidizable substrate. (3) Ampulla ductus deferens: 1- Partial secretion of fructose and citric acid. 2- Secretion of ergothioneine. 3- Lipochrome pigments. (4) Prostate gland: 1- The main source of sperm cell anti-agglutinin. 2- Secretion of sodium, chloride, magnesium. (5) Seminal vesicles: 1- The main contributor of fructose, citric acid and ascorbic acid. 2- Addition of the riboflavin pigments. c. Factors influence the thermo-regulatory mechanism of the testes. (2 marks) 1- The skin of the scrotum has both sweat and sebaceous glands which are more active during the hot weathers. Evaporation of the secretion of these glands cools the scrotum and thus the testes. 2- The tunica dartos and cremasteric muscles are very sensitive to temperature as follows: Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 7
8 a. During cold weather, contraction of these muscles causes the scrotum to wrinkle and the spermatic cord to shorten, drawing the testes closer to the body. b. During hot weather, these muscles relax, permitting the scrotum to stretch and the spermatic cord to lengthen, dropping the testes away from the body. It has been found that the thermostatic effect of tunica dartos and cremasteric muscles does not appear before reaching the male puberty. It must be sensitized by testosterone to the change in ambient temperature. 3- The position of the testicular artery. In all farm animals the testicular artery is a convoluted structure in the form of a cone, the base of which rests on the cranial or dorsal apex of the testis. The so-called pampiniform plexus of testicular veins surrounds these arterial coils. In this countercurrent mechanism, arterial blood entering the testes is cooled by the venous blood leaving the testes. The greater the abdominaltesticular temperature gradient, the greater is the length of the convoluted testicular artery and its surrounding venous plexus, or the smaller is the caliber of the testicular artery. d. Unilateral acute orchitis in a bull. (2 marks) It is generally considered wisest to slaughter bulls affected with brucellosis. If slaughter is not compulsory, in the case of some valuable bulls, pressure is brought to bear on the veterinarian to attempt treatment. If the ampulla or seminal vesicles are not involved a closed castration may remove the source of the infertility and the brucella organisms in one operation. To improve the chance of eliminating the organisms heavy doses of streptomycin plus tetracycline should be given. Some months will elapse before regeneration of the remaining testis occurs Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 8
9 4) WRITE ON THE MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR: a. Hormonal control of testes function. (5 marks) 1- The hypothalamus secretes a hormone-releasing factor (GnRH), which stimulates the secretion of LH and FSH from the anterior pituitary gland. 2- The LH (ICSH) stimulates the interstitial cells of leydig to produce androgens mainly testosterone. 3- The androgens suppress GnRH, LH and FSH secretion by negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus. 4- The FSH interacts with receptors on the sertoli cells to cause production of ABP, conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone and estrogen, stimulation of spermatocytogensis, completion of sperm release (spermeation) and secretion of inhibin. 5- Inhibin secreted into the blood stream has a negative feedback effect on FSH, but not on LH secretion. b. Erection, Emission and Ejaculation in a bull. (5 marks) 1- Erection of the penis is essentially an extension and increase in the turgidity of the organ caused by a greater inflow than outflow of blood, with the resultant increase in the pressure within the penis. Vasodilatation of arteries caused by stimulation of the nervi ergentis from the pelvic plexus and a decrease in the venous drainage from the veins are the main factors in producing erection. The penis of ruminants and swine erects chiefly by straightening of the sigmoid flexures and the length and diameter of the penis remain nearly the same as in the relaxed condition. When the penis of the horse and dog erects, an increase in diameter as well as in length occurs because these species have a relatively large amount of erectile tissue or cavernous tissue. When the erected penis of the bull is protruded, the spinal arrangement of the fibrous architecture of the penile integument causes the penis to spiral, and the urethral orifice turns in a counter-clockwise direction through 300 degrees as ejaculation occurs. The terminal part of the boar penis is spiraled like a corkscrew and during erection the whole protruded length of the free Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 9
10 end of the penis becomes spiraled around its long axis like a twisted rope. The spiral deviation of the protruded penis during erection does not occur in the ram and male goats. 2- Emission: is a physiological event takes place immediately before ejaculation. It consists of movement of the spermatic fluid along the ductus deferens from the tail of the epididymis to the pelvic urethra where it is mixed with secretions of the accessory glands. It is caused by activation of the smooth muscles lining the duct system under the control of the autonomic nervous system. It has been observed that the sexual excitement and ejaculation are accompanied by activation of the peristaltic contractions of the cauda epididymis and ductus deferens. 3- Ejaculation is the passage of the semen along the penile urethra. It is brought about by striated muscles under the control of somatic efferent compartments in the sacral nerves (deep perineal nerve). During ejaculation, the bulbospongiosum muscle compresses the penile bulb and so pumps blood from the penile bulb into the remainder of the corpus spongiosum penis. The waves of pressure passing down the penile urethra may help to transport ejaculate. c. Vibriosis in inducing abortion (5 marks) Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 10
11 d. Leptospirosis in inducing abortion (5 mark) Andrology and Diseases causing abortion-4 th year exam-2011 Model Page 11
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Male Reproductive Physiology
 Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6: Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23
 AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
AnS 214 SI Multiple Choice Set 4 Weeks 10/14-10/23 The following multiple choice questions pertain to material covered in the last two weeks' lecture sets. Answering the following questions will aid your
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act
 Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
Male reproductive system The physiology of sexual act Gabriella Kékesi 65. The development and physiology of the male reproductive system. The physiology of the sexual act Define chromosomal, gonadal and
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Physiologic Anatomy of the Male Sexual Organs
 Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
Reproductive and Hormonal Functions of the Male The reproductive functions of the male can be divided into three major subdivisions: (1) spermatogenesis, which means simply the formation of sperm; (2)
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop
 Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Male Reproductive System. Figure 80-1 Copyright 2011 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
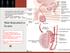 Male reprodctive system anatomy: briefly: composed of testis and external genetilia, the testis seminefrous tubules with space for spermatogenesis...the path is from the epidedimys-->vas defans-->prostatic
Male reprodctive system anatomy: briefly: composed of testis and external genetilia, the testis seminefrous tubules with space for spermatogenesis...the path is from the epidedimys-->vas defans-->prostatic
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
The Reproductive System. Presenter: Dr. Jim Hurrell
 The Reproductive System Presenter: Dr. Jim Hurrell A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 Veterinary Technician/NURSE Oath 4 5 Come Hang Out with Us in Our Awesome Facebook
The Reproductive System Presenter: Dr. Jim Hurrell A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 Veterinary Technician/NURSE Oath 4 5 Come Hang Out with Us in Our Awesome Facebook
Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals. Lecture Six. Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive System II
 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals Lecture Six Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive System II 1 The male reproductive system Two testes Scrotum Spermatic cords Accessory glands Penis Prepuce
Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals Lecture Six Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive System II 1 The male reproductive system Two testes Scrotum Spermatic cords Accessory glands Penis Prepuce
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 WELCOME University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology
WELCOME University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and Mineral Physiology
Diseases of the Reproductive Tract of the Male. Penis and Prepuce
 Diseases of the Reproductive Tract of the Male Penis and Prepuce Bulls Hematoma of the Penis (Broken Penis) Pertinent Anatomy Pressure in the corpus cavernosum penis (CCP) can be 200-400 lbs/sq in. at
Diseases of the Reproductive Tract of the Male Penis and Prepuce Bulls Hematoma of the Penis (Broken Penis) Pertinent Anatomy Pressure in the corpus cavernosum penis (CCP) can be 200-400 lbs/sq in. at
FIGURE The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis.
 Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
Testicular Histology (see p. 1034 in text) FIGURE 28.3 1. The tunica albuginea is a connective tissue capsule forming the outer part of each testis. 2. Septa are extensions of the tunica albuginea that
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Bull BreedingSoundness Evaluation
 Bull BreedingSoundness Evaluation Scott Norman (BVSc, PhD, DipACT, GCEd) Registered Specialist in Veterinary Reproduction Associate Professor in Theriogenology, School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences
Bull BreedingSoundness Evaluation Scott Norman (BVSc, PhD, DipACT, GCEd) Registered Specialist in Veterinary Reproduction Associate Professor in Theriogenology, School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls
 Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls A herd bull that will serve a higher percentage of cows during a limited breeding season is essential to a successful cow-calf operation. In many of these operations,
Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls A herd bull that will serve a higher percentage of cows during a limited breeding season is essential to a successful cow-calf operation. In many of these operations,
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND
 VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND VENEREAL DISEASES IN BULLS Bret McNabb, DVM, MPVM, DACT University of California, Davis School of Veterinary Medicine Physical Examination A
VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND VENEREAL DISEASES IN BULLS Bret McNabb, DVM, MPVM, DACT University of California, Davis School of Veterinary Medicine Physical Examination A
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
Lecture 28, The Reproductive System
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Semen collection in domestic animals
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I Semen collection in domestic animals Prof. Alberto Contri Aims Technological aim Diagnostic aim Methods for semen collection Indirect collection post-coital method
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I Semen collection in domestic animals Prof. Alberto Contri Aims Technological aim Diagnostic aim Methods for semen collection Indirect collection post-coital method
Domestic Animal Behavior ANSC 3318 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR. Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library
 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O.
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Basic Reproduction & Genetics. Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties
 Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
Animal Science 434. Sperm Head. Sperm From Different Species. Sperm Structure. Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen. Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece
 Sperm Structure Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece Animal Science 434 Annulus Principal Piece Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen End Piece Sperm From Different Species Sperm Head (Equatorial Segment) Nucleus
Sperm Structure Head Acrosome Neck Middle Piece Animal Science 434 Annulus Principal Piece Epididymis, Ejaculation and Semen End Piece Sperm From Different Species Sperm Head (Equatorial Segment) Nucleus
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Handling Semen and Breeding the Pig
 Handling Semen and Breeding the Pig Dr. Tim Safranski University of Missouri-Columbia SafranskiT@Missouri.edu Presented Ohio Show Pig Producer Symposium August 25, 2018 Plain City, OH Outline Semen storage
Handling Semen and Breeding the Pig Dr. Tim Safranski University of Missouri-Columbia SafranskiT@Missouri.edu Presented Ohio Show Pig Producer Symposium August 25, 2018 Plain City, OH Outline Semen storage
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems!
 Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
Dr. Chris Doumen! Female Reproductive Anatomy BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems! Establishing the Ovarian Cycle During childhood, until puberty Ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens Estrogen
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Male Reproductive System. Anatomy
 Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
Male Reproductive System Medical Terminology Chapter Seven HIT # 141 Anatomy Testis or testicle = main male sex organs, paired, oval shaped, enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. Seminiferous tubules =
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems
 Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
Collin College Dr. Chris Doumen BIOL 2402 Reproductive Systems 1 Reproductive System Most systems between males and females in the human body are similar in structure. The exception of course are the organs
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
