Neuroscience. Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
|
|
|
- Abel Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biological psychology: a branch of psych concerned with the links between biology and behavior. The Nervous System: Nervous system: the body s speedy electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous system. Central nervous system (CNS): the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS): connects CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a communication relay going back and forth between the brain and the extremities. Somatic nervous system: the division of the PNS that controls the body s skeletal muscles. Also known as the skeletal nervous system. Autonomic nervous system: the part of the PNS that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs. Controls the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Sympathetic nervous system: the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Flight or flight Parasympathetic nervous system: the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy. Rest and disgest Reflex: a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response. Neuroscience
2 The Neuron: Neuron: a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands. Soma (cell body): the neuron s life support center that also produces neurotransmitters. Dendrite: the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands. Myelin sheath: a layer of fatty tissue that covers the axon which aides in the speed of neural impulses; the thicker the myelin sheath, the faster the impulse. If the myelin sheath degenerates, it could lead to multiple sclerosis (communication to muscles slows, with eventual loss of muscle control). Nodes of Ranvier: spaces between the myelin. Schwann cell: produces myelin. Action potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
3 Ions: electrically charged atoms. Resting potential: the fluid interior of a resting axon has an excess of negatively charged ions, while the fluid outside the axon membrane has more positively charged ions. (Positive-outside/ negative-inside state). Selectively permeable: the axon s surface is very selective about what it allows in. Polarized: during the resting state of a neuron when the outside is positively charged and the inside is negatively charged. Depolarized: axon is no longer at resting potential; outside is now negatively charged and inside is now positively charged. Refractory period: resting state after firing in which the neuron goes back to its polarized resting state. Excitatory: accelerates neuron s firing speed. Inhibitory: slows neuron s firing speed.
4 Threshold: the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. Synapse: the junction between the terminal branch of the synaptic gap. Synaptic gap/synaptic cleft: the tiny gap at the synapse in which neurotransmitters cross. Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse. Reuptake: a neurotransmitter s reabsorption by the sending neuron. Endorphins: natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
5 Agonist: a molecule that may be similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor and mimic its effects (blocks the original neurotransmitter). Ex. The body thinks morphine is close enough to the naturally made endorphins so it binds to the endorphin receptors to block pain. Antagonist: a molecule that binds to receptors but blocks a neurotransmitter s functioning. Ex. Botulin, a poison that can form in improperly canned food, causes paralysis by blocking Ach release for muscle movement. Neurotransmitter Agonist The Endocrine System: Antagonist Endocrine system: the body s slow chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues. Adrenal glands: a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinphrine/adrenaline and norepinephrine/noradrenaline) that help arouse the body in times of stress. Pituitary gland: the endocrine system s most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
6 The Brain: Lesion: tissue destruction that is naturally or experimentally caused to help study regions and functions of the brain. Plasticity: the brain s ability to modify itself after tissue damage. EEG (electroencephalogram): an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain s surface. CT/CAT (computed tomography): a series of x-ray photographs of the brain taken from different angles and combined by computer to create an image that represents a slice through the brain. PET (positron emission tomography): different levels of activity in the brain by detecting radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain is performing a MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): uses and radio waves to produce computerimages of different structures within the brain. measures the where a given task. magnetic fields generated fmri (functional MRI): a technique for revealing bloodflow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. fmri scans show brain function. Brainstem: the oldest and innermost region of the brain that is responsible for automatic survival functions. It begins where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. Thalamus: the brain s sensory switchboard located on the top of the brainstem. It directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex. It also transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla. The sense of smell (olfaction) does not go through the thalamus. Medulla: part of the brainstem that controls heartbeat and breathing. *Remember the 2 Ls: life and love for heartbeat and breathing. Reticular Formation: a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal. *Remember: say the name and function together reticularousal. Cerebellum: the little brain attached to the rear of the brainstem that assists in balance and voluntary
7 movements. Limbic System: the doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres that is associated with emotions (such as fear and aggression) and drives (such as those for food and sex). Amygdala: two almond-shaped the limbic system that are linked especially fear, rage, and *Remember: Amy grrrrrrrr Hypothalamus: located in the lies below (hypo) the thalamus. the regulation of body as eating, drinking, and body *Remember: if your body you get hypothermia. neural clusters in to emotions, aggression. limbic system that It is responsible for maintenance such temperature. temperature drops, Hippocampus: the part of the limbic system responsible for memory and learning. *Remember you do a lot of learning and memorization at a college CAMPUS. Pituitary gland: master endocrine gland located in the limbic system. Cerebral cortex/cerebrum: the thin layer of interconnected neural cells that forms a surface layer on the cerebral hemispheres (like bark on a tree). It is the body s ultimate control and information processing center. It is what makes humans upper-level thinking beings as opposed to animals. Glial cells: glue cells in the cortex that guide neural connections, provide nutrients and insulating myelin, and mop up ions and neurotransmitters. Frontal lobes: the portion of the cerebral cortex that lies just behind the forehead that is involved in speaking, muscle movements, and in making plans and judgments. It also includes the motor cortex. *Remember: when you misspeak or do something wrong, you hit your forehead doh! Motor cortex: the area at the back of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Parietal lobes: the portion of the cerebral cortex between the frontal
8 and occipital lobes that is deals with body sensations. It includes the (somato)sensory cortex. (Somato)sensory cortex: the area at the front of the parietal lobe that registers and processes body sensations. Occipital lobes: the portion of the cerebral cortex at the back of the brain that includes the visual cortex for vision. Visual cortex: the area of the occipital lobe that receives visual information from the eyes. Temporal lobes: the portion of the cerebral cortex that lies roughly above the ears that includes the auditory cortex for hearing (audition). *Remember: the temporal lobes are near the temples. Auditory cortex: the area of the temporal lobe that receives auditory information from the ears. Association areas: the areas of the cerebral cortex involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking. *Remember: the association areas let people make associations between things. Ex. my stomach is growling, I must be hungry. Broca s Area: an area of the left frontal lobe that controls the muscle movements involved in speech. Damage to this area impairs speaking. Wernicke s Area: an area of the left temporal lobe that is involved in language comprehension. Damage to this area impairs understanding. Angular gyrus: an area of the left occipital lobe that transforms visual representation into an auditory code. Aphasia: impairment of language usually caused by damage to the Broca s Area or the Wernicke s Area. Neurogenesis: the formation of new neurons.
9 Corpus callosum: the large band of neural fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres to carry messages between them. If the corpus callosum is severed, the two hemispheres cannot communicate. Split brain: a condition in which the two hemispheres of the brain cannot communicate. This is caused by the severing of the corpus callosum. Alien Hand Syndrome: a rare neurological disorder that causes hand movement without the person being aware of what is happening or having control over the action. This usually occurs after a person has had the two hemispheres of the brain surgically separated, as in splitbrain surgery. Cognitive neuroscience: the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory and language). Dual processing: the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks. Neuroscience Key People: Franz Gall: invented phrenology, an ill-fated theory that claimed bumps on the skull could reveal our mental abilities and our character traits. Phineas Gage: 1800s railroad worker who had a tamping iron shoot through his left cheek and out the top of his skull. He miraculously lived but massively damaged his frontal lobes. The once calm and rational Gage became irritable and dishonest. This paved the way for research on the functions of the frontal lobes. Roger Sperry, Ronald Myers, and Michael Gazzaniga: divided the brains of cats and monkeys with no serious ill effects. Set the stage to study split brain in people. Philip Vogel and Joseph Bogen: tried to alleviate seizures in epileptic patients by severing the corpus callosum and causing split brain patients.
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Biological Psychology
 Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Unit 3a Defini,ons Biological Psychology = a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior. Some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Structure of the Cortex
 Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
Structure of the Cortex Introduction Cerebrum Cerebral cortex Structure of the Cortex Glial cells ( glue cells ) Lobes Frontal lobes Parietal lobes Occipital lobes Temporal lobes Structure of the Cortex
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Neural and Hormonal Systems
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Neural and Hormonal Systems Module 4 2 Neural and Hormonal Systems Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Unit III. Biological Bases of Behavior
 Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Unit III Biological Bases of Behavior Module 9: Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Module 10: The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Module 11: Studying the Brain, and Other Structures Module 12: The
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System
 AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
AP PSYCH Unit 3A Biological Basis Of Behavior Neural Processing & The Endocrine System 1. Everything psychological is simultaneously biological 2. What are neurons and how do they communicate? 3. How do
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission
 I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
I. Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission Objectives: Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology. Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. Describe
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain
 Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
Welcome it is a great day to learn about the Brain What does the Brain do? Stand up Walk around every person you pass tell them a different function the brain performs Do this until you are told to stop
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
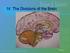 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Biopsychology. Biological Bases of Behaviour. Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017
 Biopsychology Biological Bases of Behaviour Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017 http://fundersandfounders.com/9-types-of-intelligence/#naturalist How does your brain process information? Naturalist Intelligence
Biopsychology Biological Bases of Behaviour Miss. Paslawski Psychology 40S 2017 http://fundersandfounders.com/9-types-of-intelligence/#naturalist How does your brain process information? Naturalist Intelligence
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Unit 3 Biology of the Brain
 Unit 3 Biology of the Brain Module 9 Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission To think, feel or act without a body would be like running without legs Biological Psychologists Scientific study the links
Unit 3 Biology of the Brain Module 9 Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission To think, feel or act without a body would be like running without legs Biological Psychologists Scientific study the links
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
The Nervous System II Neurons
 The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
PSYCHOLOGY. (8th Edition) David Myers. PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University. Worth Publishers,
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Neuroscience and Behavior Chapter 2 2 Neuroscience and Behavior Neural Communication
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Neuroscience and Behavior Chapter 2 2 Neuroscience and Behavior Neural Communication
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems. Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers
 Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems Worth/Palgrave/Macmillan Publishers Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
AP Psychology Ch. 02 The Brain Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
THE BRAIN! UNIT 3B: BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR
 THE BRAIN! UNIT 3B: BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR THE BRAIN! ENABLES THE MIND THINK ABOUT IT. IF YOU WERE TO TRANSPLANT ALL OF YOUR ORGANS, EXCEPT FOR YOUR BRAIN, YOU WOULD STILL BE MUCH THE SAME PERSON.
THE BRAIN! UNIT 3B: BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR THE BRAIN! ENABLES THE MIND THINK ABOUT IT. IF YOU WERE TO TRANSPLANT ALL OF YOUR ORGANS, EXCEPT FOR YOUR BRAIN, YOU WOULD STILL BE MUCH THE SAME PERSON.
Chapter 2 The Biology of Mind
 Chapter 2 The Biology of Mind PowerPoint Presentation by Jim Foley 2013 Worth Publishers Surveying the Chapter: Overview What We Have in Mind Building blocks of the mind: neurons and how they communicate
Chapter 2 The Biology of Mind PowerPoint Presentation by Jim Foley 2013 Worth Publishers Surveying the Chapter: Overview What We Have in Mind Building blocks of the mind: neurons and how they communicate
Biological Psychology. Phrenology (Franz Gall) branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior
 Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Neural Communication Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists,
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Unit 2 Multiple Choice test
 Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Name: Date: 1. Resting potential is to action potential as is to. A) adrenal gland; pituitary gland B) sensory neuron; motor neuron C) temporal lobe; occipital lobe D) polarization; depolarization E) dendrite;
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Nervous System (cont)
 Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
Nervous System (cont) Dopamine Deals with motor movement and alertness. Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson s disease. Too much has been linked to schizophrenia. Endorphins Involved in pain control.
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Nervous System Review
 Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Nervous System Review Name: Block: 1. Which processes are involved in the movement of molecule Y from point X to point Z? A. exocytosis and diffusion B. endocytosis and diffusion C. exocytosis and facilitated
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How Do Genetic Factors Affect Behavior? II. Does Our Evolutionary Heritage Influence Current Behavior? III. How is the Nervous
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Copyright 2017 Pearson Education. All rights reserved. 1
 1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
1 Learning Objectives LO 2.13 Name the parts of the cortex that are responsible for higher forms of thought, such as language. LO 2.14 Explain how some brain functions differ between the left and right
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: :: Slide 3 :: :: Slide 4 :: :: Slide 5 :: :: Slide 6 ::
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 2 :: Left blank Your nervous system is a complex communication network in which signals are constantly being received, integrated, and transmitted. The nervous system handles information,
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology
 PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 221 Introduction to General Psychology Session 2 Biological foundations of behaviour Lecturer: Dr. Joana Salifu Yendork, Psychology Department Contact Information: jyendork@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 12 Nervous System Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which part of a neuron receives an impulse
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
