General Information Adult brain consists of ~100 billion neurons and 1 trillion neuroglia cells.
|
|
|
- Theodore Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Central Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe in general, the four major components of the brain. 2. Describe the functions of the components of the brain stem. 3. Explain the functions of the components of the diencephalon. 4. Describe the functions of the components of the cerebrum. 5. Explain the concept of cerebral lateralization. 6. Describe an EEG and the various wave patterns 7. Explain the functions of the limbic system. 8. Explain the functions of the reticular activating system. 9. Explain the protective coverings of the brain. 10. Describe the components and functions of the blood-brain barrier. 11. Describe the functions of cerebrospinal fluid. 12. Discuss the Clinical Applications from the study guide and be able to describe the disorders from the Applications to Health located at the end of this chapter. 1 General Information Adult brain consists of ~100 billion neurons and 1 trillion neuroglia cells. Receives ~20% of the total blood flow to the body per minute. High rate of blood flow/oxygen content is due to the high metabolic requirements. Brain: Divided into 4 Major Regions Brain stem, which consists of: Diencephalon, which consists of: Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus Cerebellum Cerebrum, which consists of: Right and left cerebral hemispheres Brain Stem Brain stem consists of: Medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. Medulla oblongata (medulla) Contains all ascending and descending fiber tracts that Most tracts cross over from one side of the spinal cord to the other side at an elevated structure in the medulla called the pyramids. Results in motor fibers originating in the left cerebral cortex activating muscle on the right side of the body and vice versa Results in the left side of the brain receiving sensory information from the
2 Contains centers that regulate autonomic functions such as: Centers that coordinate swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and hiccupping. Contains the origins (nuclei) of cranial nerves VIII, IX, X (Vagus), XI, and XII. 2 Pons Bridges the spinal cord to the brain and parts of the brain with each other. Together with the medulla oblongata help control breathing (respiratory rhythm). Contains the origins (cell bodies) of cranial nerves V, VI, VII, and VIII. Midbrain (Mesencephalon) Contains the cerebral peduncle and tectum. Origin of cranial nerves III and IV. Cerebral peduncle contains: Substantia nigra: Darkly pigmented nuclei whose neurons help coordinate skeletal muscle activity. Neurons release dopamine at the basal nuclei Loss of these neurons is associated with Tectum (corpora quadragemina): Dorsal portion that contains 4 rounded elevations called the superior and inferior colliculi. Two Superior colliculi: Reflex centers of movement of the eyes, head and neck in response to visual stimuli Two Inferior colliculi: Reflex centers for movements of the
3 Cerebellum Coordinates skeletal muscle contractions required for skilled movements and balance Refines learned movement patterns controlled at the 3 Compares motor commands with sensory info from muscles and joints and performs any adjustments to make the movement smooth. White fiber tracts form the arbor vitae or tree of life The cerebellum can be permanently damaged by trauma or stroke or temporarily affected by drugs such as alcohol. Damage produces ataxia lack of Diencephalon Diencephalon consists of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. Thalamus: Relay center through which all sensory information (except smell) passes on the way to the cerebrum for interpretation. Acts like a switchboard that receives sensory signals and sends them to the correct associated cortical areas. Acts as a filter along with the reticular activating system, passing on only a small portion of arriving sensory information. Hypothalamus: Control of ANS: Initiates the physical responses to emotions. When you think about a dangerous or stressful situation, your heart rate and respiratory rate go up and your body prepares for an emergency. These autonomic adjustments are made by the hypothalamus. Regulation of emotional and behavior patterns. Together with the limbic system participates in expressions of rage, aggression, loathing, fear, pleasure, and behavior pattern related to sexual arousal. Regulates Hypothalamic neurons monitor blood temperature and receive input from other thermoreceptors in the brain and body periphery. Will initiate cooling (sweating) or heat-generating actions (shivering) to maintain constant body temperature. Regulates Monitors changing blood levels of certain nutrients (glucose and amino acids) and regulates feelings of hunger and satiety). When body fluids become too concentrated, hypothalamic neurons called osmoreceptors become activated and trigger the release of antidiuretic
4 hormone (ADH) from the posterior pituitary that causes the kidneys to retain water. Also causes person to feel thirsty and drink more fluids. Regulates circadian rhythm (sleep/wake cycle) and states of consciousness. Works in conjunction with the 4 Production of hormones (ADH and oxytocin) and regulates the anterior pituitary gland via the release of regulatory factors. Epithalamus consists of: Pineal gland: Secretes melatonin Function: Promotes sleepiness and helps regulate circadian rhythm. Cerebrum
5 Cerebrum The cerebrum forms the largest portion of the brain (80% of its mass) and responsible for higher mental functions. 5 Has an outer cortex of gray matter surrounding an interior that is mostly white matter, except for a few small portions. Cortex contains folds called gyri that function to increase the surface area of the brain. Deep sulci divide each hemisphere into 5 lobes: Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, Occipital, and Insula Why/How are the 1st 4 named? What does insular mean? Lobes of Cerebrum Frontal Lobe Frontal lobe functions: Reasoning; higher intellectual processes (decision making, planning), Verbal communication. Broca s Area: Directs muscles of tongue, lips, and throat that are used in speech production and Involved in planning speech production. Located in the Broca s aphasias: Speech disorder caused by damage to area due to trauma or stroke. Person s speech is slow and poorly articulated (non-fluent) but they can understand speech. Can understand a sentence but have difficulty repeating it. Voluntary control of skeletal muscles and The entire body is represented spatially in the primary motor cortex, i.e., in one region we have neurons controlling hand movements and in another region leg movements, etc. Determined by the number of effectors in an area Frontal Lobotomy Frontal Lobotomy: Surgical procedure severing the connection between the Reasoning for procedure was that this area was somehow malformed or damaged, and if the nerves were severed they might regenerate into new, healthy connections. The main indications for a frontal lobotomy included severe chronic anxiety, depression with risk of suicide, incapacitating obsessive-compulsive disorder and high levels of aggression. Thousands were performed between By the 1960s, the number of operations was in decline as the procedure became much less fashionable. Transorbital lobotomy (icepick lobotomy) Improvements in psychopharmacology and behavior therapy gave the opportunity for more effective and less-invasive treatment.
6 Parietal Lobe Parietal lobe functions: Somatosensory interpretation (cutaneous and muscular sensations) Interpretation of 6 Temporal Lobe Temporal Lobe functions: Interpretation of auditory sensations Memory storage of auditory and visual experiences Associations are made between Understanding speech. Wernicke s area: In both the left temporal and parietal lobes is involved in understanding written and oral words. Wernicke s aphasia: Difficult form person to understand either spoken or written language. Speech is rapid and fluid but without meaning. Form real words but they are Occipital Lobe Occipital Lobe functions: Vision Integration of movements for Interpretation of visual images and correlating visual images with previous visual experiences and other sensory stimuli. Insula Insula functions: Involved with Include upset stomach, full bladder, and the feeling that your lungs will burst when you hold your breath too long Role in pain experience and the experience of a number of basic emotions, including anger, fear, disgust, happiness and sadness. Cerebral Lateralization Specialization of function in one hemisphere or the other. The two hemispheres communicate with each other via the corpus callosum. Left hemisphere: specialized for language, analytic ability and logic. Right hemisphere: Geared towards musical, artistic and other creative endeavors. Most individuals with
7 Basal Nuclei Set of nuclei deep within the white matter. Provides subconscious control of skeletal muscle tone and coordinates learned movement patterns and other somatic motor activities. Allows intended movements to occur while inhibiting unintended movements. Doesn t initiate movements but once voluntary movement is underway, they assist in the pattern and rhythm (especially for trunk and proximal limb muscles Parkinson s disease Each side of the midbrain contains a nucleus called the substantia nigra (SN). Neurons in the substantia nigra inhibit the activity of Degeneration of dopaminergic neurons produces the symptoms of Parkinson s. 7 Damage to SN neurons Decrease in dopamine secretion Appearance of symptoms of Parkinson s disease: tremor, slow movement, inability to move, rigid gait, reduced facial expression Increased activity of basal nuclei Gradual increase in muscle tone Electroencephalogram Electroencephalogram (EEG): A record to the electrical currents that occur among the neurons of the cerebral cortex. Four type so EEG patterns: Alpha waves (10-12 cycles/second): Produced when person is awake and relaxed with the eyes are closed. Beta waves (13-25 cycles/second): Theta waves (5-8 cycles/second): Produced in newborn infant In adults may indicate severe emotional stress and possible nervous breakdown. Delta waves (1-5 cycles/second): Common during sleep and in awake infant.
8 Limbic System Limbic system: Includes nuclei and tracts along the border between the cerebrum and the diencephalon. Prominent structures include the hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and fornix. More of a functional grouping rather than anatomical structure. Functions: Center for basic emotional drives called the emotional brain Motivation; goal directed behavior; 8 Processes memory storage and retrieval particularly the hippocampus and amygdala The Reticular Activating System (RAS) Functions of RAS: Maintains cerebral cortical alertness. Sends impulses to the cerebral cortex keeping the cortex alert. Filters out repetitive stimuli from sensory inputs such as pressure from your watch, clothes, etc. Works to help person fall asleep by decreasing sensory stimuli. RAS is depressed by RAS Extends through the central core medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain with connections to the thalamus to relay sensory information. Sedatives and the RAS A common over-the-counter sedative is a H1 antihistamine (H1-receptor antagonist) and includes diphenhydramine (Benadryl). For Sedation: The exact mechanism is unclear. It reduces the arousal component of the RAS. The RAS includes a group of cholinergic neurons (neurons that release acetylcholine) in the brain stem that project to the thalamus; these neurons enhance the transmission of sensory information from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex. Diphenhydramine may block the action of acetylcholine (anticholinergic effect similar to atropine) on muscarinic receptors and causes drowsiness by decreasing the activity of the RAS. Benadryl can cross the blood-brain barrier and cause drowsiness. The antihistamines that don t cause drowsiness, such as Claritin, cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. Drowsiness caused by benzodiaszpines (such as Valium), barbiturates, alcohol, and most anesthetic gases is due to the ability of these agents to enhance the activity of GABA receptors. Increased ability of GABA to inhibit the RAS then reduces arousal and promotes sleepiness. GABA is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
9 Protection and Coverings The brain is protected by: Cranial bones Cranial meninges Dura mater Arachnoid Mater Subarachnoi d space contain CSF Pia mater Blood-Brain Barrier Cerebrospinal fluid Blood-Brain Barrier Blood-brain barrier: Regulates passage of substances from the blood into the brain tissue and formed by: Presents difficulties in chemotherapy of brain diseases because certain drugs cannot enter the brain. Ex: Parkinson s disease can be treated with increased levels of dopamine but dopamine cannot pass the BBB. Solution: levodopa (L-dopa) is used which crosses the BBB and is then converted to dopamine. Endothelial cells: Astrocyte processes that press up against capillaries and help maintain the permeability characteristics. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) CSF consists of: Clear fluid with Glucose, proteins, lactic acid, urea, electrolytes, and lymphocytes Has three major functions: Mechanical protection: Shockabsorber and buoys the brain so that it floats in the cranial cavity. Chemical protection: Maintains optimal chemical environment of neuronal signaling CSF Formation takes place at the choroid plexuses located in the ventricular walls. CSF is produced at a rate of ~500 ml/day Total volume of CSF at 9
10 CSF circulates from the choroid plexus thru the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord. CSF is reabsorbed at the sagittal sinus into the venous blood at the same rate it is formed. If its drainage is blocked, a condition called hydrocephalus occurs. Results in increased pressure on the A shunt can be inserted to drain excess CSF 10 Spinal Cord and Reflexes Reflex: Involuntary action that occurs in response to a stimulus. Reflex arc: Pathway followed by nerve impulses that produce a reflex. Reflex arc components: Sensory receptor: Respond to a stimulus by generating nerve impulses. Sensory neuron: Carry nerve impulses toward the CNS. Integrating Center: Determines the response to the stimulus Motor neuron: Carry nerve impulses away from the CNS to an effector. Effector: Responds to the motor nerve impulse. Somatic reflex involves skeletal muscle Autonomic (Visceral) reflex involves smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or a gland
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory.
 Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
2/22/2012. Cerebrum CNS
 Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Chapter 8 outline CNS: Consists of???? Structural organization of the brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain and hindbrain Spinal cord tracts Cranial and spinal nerves Receives input from???? neurons Directs
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum
 4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum White Matter = myelinated tracts or nerves Gray Matter = unmyelinated tracts or nerves Brain: gray matter on outside, white matter inside
4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum White Matter = myelinated tracts or nerves Gray Matter = unmyelinated tracts or nerves Brain: gray matter on outside, white matter inside
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 1B Medulla Oblongata Cardiovascular Center: Regulates the rate and force of the heartbeat and the diameter of blood vessels Medullary Rhythmicity Area: adjusts the basic rhythm of
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
The Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Cauda Equina
 The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain
 Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
Introduction to the Organization of the Brain 98% of the body s neural tissue is in the brain An avg. human brain weighs 1.4 kg (3lbs.) and has a volume of 1200 cc brains average about 10% bigger than
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424. By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi
 Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
Anatomy of the Human Brain
 Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13. The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2. PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM
 BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
BIO 210 CHAPTER 13 The Central Nervous System SUPPLEMENT 2 PowerPoint by John McGill Supplemental Notes by Beth Wyatt CEREBELLUM Second Largest Division of the Brain Lies Below the Posterior Portion of
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Embryonic Brain Development
 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Protection of the Brain. Overview of the Brain. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober. Chapter 13. Lecture 20
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Neurotransmitter: dopamine. Physiology of additive drugs. Dopamine and reward. Neurotransmitter: dopamine
 Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
Physiology of additive drugs Cocaine, methamphetamine, marijuana, and opiates influence the neurotransmitter dopamine. Neurotransmitter: dopamine Dopamine - a neurotransmitter associated with several functions,
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline *
 Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
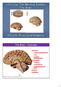 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 12.1 Overview of the Central Nervous System (Figures 12.1, 12.2, 12.3) A. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the and, and is involved
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU
 If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
The brain: Diencephalon
 The brain: Diencephalon Hypothalamus helps maintain homeostasis (hunger, sleep, thirst, body temperature and water balance) and controls pituitary gland Thalamus 2 masses of gray matter that receive all
The brain: Diencephalon Hypothalamus helps maintain homeostasis (hunger, sleep, thirst, body temperature and water balance) and controls pituitary gland Thalamus 2 masses of gray matter that receive all
Nervous System. Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson
 Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
