Health Sciences 1111 Module 17 Skeletal System Lab 17. View the Video Reconstructive Hand Surgery and answer the questions on your worksheet.
|
|
|
- Leo Long
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Health Sciences 1111 Module 17 Skeletal System Lab 17 View the Video Reconstructive Hand Surgery and answer the questions on your worksheet. Anatlab o On campus students: Double-click on the Anatlab icon o Online/Ind Study Students: Insert the Anatlab CD o Click on the upper limb o View the Axial Skeleton and Muscles o Answer the questions on the computer as they appear in the material. o Answer the quiz questions at the end of the material. o View the Bones of the Upper Limb o Answer the questions on the computer as they appear in the material Stop at screen # 40. o Answer the quiz questions at the end of the material. o Click on the Head and Neck button o View the Skull o Answer the questions on the computer as they appear in the material. o Answer the quiz questions at the end of the material. o Exit Anatlab Webpath o Go to the Health Sciences Website o Click on Webpath o Click on Systemic System Pathology o Click on Bone and Joint Pathology
2 o As you view the following images, be sure to click on the x-ray box and the highlighted words o Regarding normal and reactive condition o 11 - Femur, osteosarcoma, gross o 12 - Tibia, osteosarcoma, gross o 13 - Osteosarcoma o 14 Osteosarcoma o 16 - Pelvis, chondrosarcoma, gross o 25 - Metastic carcinoms o 27 - osteochondroma, gross and radiograph o 28 - Osteochondroma, gross o 32 - Giant cell tumor of bone o 63 - Vertebrae, degenerative osteoarithitis, gross o 67 - Rheumatoid arthritis, pannus in joint o 72 - Foot, gout, gross o 73 - Gouty arthritis, radiograph o 75 - Gouty arthritis, joint fluid o 80 - Short-limbed dwarfism
3 As you view the film Reconstructive Hand Surgery be sure to answer the following questions. 1. What was Maria s diagnosis? 2. Where are they getting another bone to enhance her finger? 3. Will the surgery affect her walking? 4. What does MRA stand for? 5. What is used to limit blood loss? 6. What is the white strand called? 7. What is the purple structure behind it? 8. What is used to retract the flesh? 9. What instrument spreads the structures apart? 10. Is the Second Digital Nerve located near the pinky or the thumb? 11. Why wouldn t you want a straight line scar across the joint? 12. What is used to force blood out of Maria s leg and foot? 13. What is used as a cutting board for an artery? 14. How long will Maria have the cast on her hand?
4 WebPath Questions: Image 4 1. In this image you see a bone end sticking through a laceration; it is located on the anterior portion of the upper right arm equidistant from the axilla and the antecubitals. This can be considered a definitive sign of a a. fracture of the distal radius of the right arm b. compound fracture of the distal radius of the left arm c. fracture of the mid-humerus d. compound fracture in the mid-humerus of the right arm 2. What is commonly used to fixate an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of a fracture to the humeral neck? a. The ORIF is an accepted procedure in this area. b. A stainless steel hammer and surgical nails. c. The fixation is accomplished with a rod and screws. d. Pins held in place by stainless steel wire. Image 5 (x-ray) 3. The x-rays in this image show a fracture of the a. fifth metatarsal of the right hand b. fifth metacarpal of the left hand c. fifth phalanges of the left hand. d. fifth phalanges of the right hand. 4. What type of new bone growth would you expect to find in the region of a healing fracture? a. irregular new bone or woven bone b. smooth almost undetectable new bone growth c. no new bone growth, the old bone will eventually heal d. the new bone growth will be the result of osteoclastic bone building activity. Image 6
5 5. In what area of this fracture will the new bone growth occur? a. only in the outer edges of the fracture b. only in the inner edges of the fracture c. in the disrupted trabeculae d. in the non-disrupted trabeculae. Image 6 (x-ray) 6. In these radiographs, what is the clue in the bottom panel that indicates there is healing to the tibial and fibular fractures? a. there is no healing the fracture is still visible in the bottom panel b. the muscle tissue is more visible in the lower panel indicating healing c. there is callus formation in the fracture areas. d. the entire Tibia and Fibula in the lower panel is obviously a brighter white. Image 7 7. Where will the callus be seen to form in this region of a recent fracture? a. in every empty area b. only in the irregular empty areas c. at the broken ends of the bony trabeculae d. at the stable unbroken end of the bony trabeculae. Image 7 (X-ray) 8. This radiograph demonstrates two pathologic fractures in the superior and inferior pubic rami that have occurred. What is more likely to have caused them? a. major trauma from a high fall impacting the inferior pubic rami b. any major trauma to the pelvis c. a consequence of weakening by metastatic melanoma d. there is not enough information to make a reasonable diagnosis Image 8
6 9. An infection that becomes established in bone is difficult to treat, since one is relatively avascular. If this process occurs over years, the bone becomes markedly remodeled. What is this established infection in the bone called? a. osteoinfectitis b. osteogenicities c. myorotinitis d. osteomyelitis Image Note the fibrosis of the marrow space accompanied by chronic inflammatory cells. This is a chronic osteomyelitis. What is the consequence of this condition? a. there can be bone destruction with remodeling b. chronic softening of the surrounding cartilage c. a very putrid smell coming from the surrounding muscle tissue d. the fibrosis will make the bone much stronger Image This femur has a large eccentric tumor mass arising in the metaphyseal region. Since the epiphysis seen at the right is still present, what should this tell us about this type of tumor? a. This patient has very little chance of survival. b. These tumors most often occur in young persons. c. These tumors most often occur in middle age persons. d. These tumors most often occur in geriatric patients. Image 12
7 12. This osteosarcoma arising in the metaphysis at the upper tibia of a teenage boy breaks through the bone cortex and extends into soft tissue. What other general medical terminology can you use instead of osteosarcoma? a. osteomyelitis b. osteo cancerous c. neoplasm d. benign bone fracturation Image 12 (X-ray) 13. In this AP radiograph of the distal femur, an osteosarcoma involves the metaphyseal region. Generally speaking where is it located? a. just above the knee b. just below the knee c. just above the hip d. just below the hip Image The microscopic appearance of an osteosarcoma is shown here. Sarcomas have very pleomorphic cells; often what shape will they take? a. spindle shape b. rectangle shape c. shape of a small boat d. honeycomb shape Image 13 (X-ray) 15. This radiograph demonstrates a consequence of weakening of the lower tibial metaphysis by a lytic osteosarcoma. How can you correctly describe this fracture? a. a pathologic fracture
8 b. an open hole fracture c. a fracture from tumor pressure d. a physiologic fracture Image The neoplastic spindle cells are seen to be making pink osteoid here. Osteoid production by a sarcoma is diagnostic of a. osteosarcoma b. osteomyelitis c. osteonotsureus d. normal osteoblastic function Image 14 (PX) 17. Positive staining in the cytoplasm of these neoplastic cells at high magnification with antibody to vimentin suggests that this is a a. sarcoma b. carcinoma c. canceremia d. osteoma 18. What is a chondrosarcoma? a. cancer of the bone b. neoplasm of the cartilage c. infection of the chondro d. an indicator of good health Image 16 (CT)
9 19. This pelvic CT scan demonstrates a large chondrosarcoma involving the left pelvic sing. What other tissue does it appear to involve? a. the adjacent soft tissue b. only the pelvic wing c. the pubic bone d. distant soft tissue Image Here is a microscopic view of metastases to bone. Why is a pathologic fracture possible, in this case? a. patients with this condition are much more likely to stumble and fall b. chemotherapy can cause these fractures c. if the bone is markedly weakened by the metastasis, then a pathologic fracture is possible d. pathologic fractures only occur in pathophysiology Image 25 (NM) 21. This nuclear medicine bone scan reveals multiple areas of increase uptake, which are the darker foci, such as in the vertebral column. What does this represent? a. calcium deficiency b. calcium and postassium deficiency c. increased uptake representing metastases d. nothing significant, everyone has areas of increased uptake Image 27
10 22. This is an osteochondroma of bone. This lesion appears as a bony projection (exostosis). What is the common treatment for this condition? a. immediate amputation b. aggressive chemotherapy and radiation therapy c. physical therapy is very successful for removing the growth d. most are solitary, incidental lesion that my be excised if they cause local pain Image 28 (X-ray) 23. This radiograph demonstrated a lateral projection from the metaphyseal region of the distal femur. This is an osteochondroma. What type of symptoms would you expect? a. local discomfort then the patient s knee is bumped or rubbed against another object. b. no symptoms at all, the patient will only have symptoms if it is malignant c. severe discomfort when the patient s knee is bumped or rubbed against another object d. itching and a crushing pain to the lower extremity Image This is an osteochondroma cut into three sections. A bluish-white cartilaginous cap overlies the bony cortex. These are probably not true neoplasms, but they are a mass lesion that extends outward from the metaphyseal region of a long bone. How many metaphyseal regions are there of the femur? a. one b. the entire femur is metaphyseal c. two d. four
11 Image Histologically, giant cell tumors of bone as seen here are composed of osteoclast-like multinucleated giant cells in a sea of round to oval mononuclear stromal cells. There may also be foamy macrophages and hemosiderin deposition in the stroma. These tumors are biologically benign so, are they a problem? a. No, they are benign b. Yes, they can expand and cause pain, deformity, or fracture c. No, the patient has not developed the tell-tale histologic signs that indicate a problem. d. There is not enough information to discern a problem in this case. Image 32 (CT) 26. This is a CT scan of a giant cell tumor involving the left ischial ramus. The tumor is an eccentric, expansile, lytic mass with extension into soft tissue along with overlying reactive new bone formation. Generally, what area of the body does this scan refer to? a. chest b. abdomen c. pelvis d. middle section including the diaphragm Image Here is another example of degenerative osteoarthritis in which there is prominent lipping of the vertebrae. Osteoarthritis increases with age beyond 50. Generally, a few large joints are involved, such as hip or knee. Note also that there is a curve to the right indicating a minor degree of scoliosis. What causes this condition? a. osteoarthritis due to wear and tear with loss of articular cartilage b. osteoarthritis caused by poor nutrition and lifestyle choices
12 c. osteoarthritis is idiopathic d. osteoarthritis has a genetic predisposition and has the tendency to appear near the age of 50 Image This is the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. There is chronic inflammation with lymphocytes and plasma cells that produce the blue areas beneath the nodular proliferations. This pannus is destructive and produces erosion of the articular cartilage. What does this type of arthritis eventually lead to? a. destruction of the bone due to lytic enzymes b. osteosarcoma c. osteomyelitis d. destroy the affected joint Image This is gout. The joint most often affected is the first MP joint (big toe) as seen here. Acute attacks are characterized by severe pain, swelling and erythema of the joint. What causes gout? a. stubbing of the toe usually after getting up in the middle of the night b. stubbing of the toe from any traumatic cause c. gouty arthritis results from deposition of sodium urate crystals in joints d. gouty arthritis results from deposition of calcium silicate crystals in joints Image 72 (X-ray) 30. Chronic gout leads to deposition of urates into a chalky mass known as a tophus. The first metatarsophalangeal joint is a common location. Such tophi can appear around a joint and adjacent bone as seen her radiographically. Tophaceous
13 deposits consist of sodium urate crystals, and there is a surrounding destructive inflammatory response. What is the common name for the toe affected? a. fifth little piggy b. great toe c. grand toe d. the first metacarpal phalanges Image Chronic gout leads to deposition of urates into chalky mass know as tophus. Seen here radiographically in sequential radiographs of the same foot is a tophaceous deposit that has destroyed the 1st MP joint and adjacent bone. In most, but not all, cases the patient could have a. hypocalcemia b. hyperuricemia c. septicemia d. bacterium in the first metacarpal Image If synovial fluid is aspirated from a patient with gout, the fluid can be examined for the presence of the causative agent, which is seen here to be needle shaped. If they are observed under polarized light with a red compensator, they appear yellow (negatively birefringent) in the main axis of the compensator and blue in the opposite perpendicular direction. In this case what is the causative agent? a. sodium urate citrals b. calcium silicate crystals
14 c. sodium chloride crystals d. sodium bicarbonate crystals Image Ultrasound may reveal long bones that are shortened. There are several possibilities, including short-limbed dwarfism. Seen here is a radiograph demonstrating short, curved femora and humeri, along with prominent platyspondyly of the vertebrae. This is thanatophoric dysplasia. What type of condition is this? a. a lethal condition b. a survivable condition c. short term and will resolve d. a tragic condition that causes the patient to be confined to wheelchair Graphics for Module 17 Exam Applications Manual Page
15 Hthsci 1111 Lab 17 Skeletal System As you view the film Reconstructive Hand Surgery be sure to answer the following questions. 1. What was Maria s diagnosis? AMNIOTIC BAND SYNDROME 2. Where are they getting another bone to enhance her finger? TOE 3. Will the surgery affect her walking? NO 4. What does MRA stand for? MAGNETIC RESONANCE ANGIOGRAM 5. What is used to limit blood loss? TOURNIQUET 6. What is the white strand called? DIGITAL NERVE 7. What is the purple structure behind it? COMMON DISTAL ARTERY 8. What is used to retract the flesh? SUTURES 9. What instrument spreads the structures apart? RETRACTOR-MOSQUITO 10. Is the Second Digital Nerve located near the pinky or the thumb? PINKY 11. Why wouldn t you want a straight line scar across the joint? RESTRICT MOTION 12. What is used to force blood out of Maria s leg and foot? RUBBER BANDAGE 13. What is used as a cutting board for an artery? TONGUE DEPRESSOR 14. How long will Maria have the cast on her hand? 4 WEEKS WebPath Questions: Image 4 1. In this image you see a bone end sticking through a laceration; it is located on the anterior portion of the upper right arm equidistant from the axilla and the antecubitals. This can be considered a definitive sign of a a. fracture of the distal radius of the right arm b. compound fracture of the distal radius of the left arm c. fracture of the mid-humerus d. compound fracture in the mid-humerus of the right arm ANS: D 2. What is commonly used to fixate an open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of a fracture to the humeral neck? a. The ORIF is an accepted procedure in this area. b. A stainless steel hammer and surgical nails. c. The fixation is accomplished with a rod and screws. d. Pins held in place by stainless steel wire. ANS: C
16 Image 5 (x-ray) 3. The x-rays in this image show a fracture of the a. fifth metatarsal of the right hand b. fifth metacarpal of the left hand c. fifth phalanges of the left hand. d. fifth phalanges of the right hand. ANS: B 4. What type of new bone growth would you expect to find in the region of a healing fracture? a. irregular new bone or woven bone b. smooth almost undetectable new bone growth c. no new bone growth, the old bone will eventually heal d. the new bone growth will be the result of osteoclastic bone building activity. ANS: A Image 6 5. In what area of this fracture will the new bone growth occur? a. only in the outer edges of the fracture b. only in the inner edges of the fracture c. in the disrupted trabeculae d. in the non-disrupted trabeculae. ANS: C Image 6 (x-ray) 6. In these radiographs, what is the clue in the bottom panel that indicates there is healing to the tibial and fibular fractures? a. there is no healing the fracture is still visible in the bottom panel b. the muscle tissue is more visible in the lower panel indicating healing c. there is callus formation in the fracture areas. d. the entire Tibia and Fibula in the lower panel is obviously a brighter white. ANS: C
17 Image 7 7. Where will the callus be seen to form in this region of a recent fracture? a. in every empty area b. only in the irregular empty areas c. at the broken ends of the bony trabeculae d. at the stable unbroken end of the bony trabeculae. ANS: C Image 7 (X-ray) 8. This radiograph demonstrates two pathologic fractures in the superior and inferior pubic rami that have occurred. What is more likely to have caused them? a. major trauma from a high fall impacting the inferior pubic rami b. any major trauma to the pelvis c. a consequence of weakening by metastatic melanoma d. there is not enough information to make a reasonable diagnosis ANS: C Image 8 9. An infection that becomes established in bone is difficult to treat, since one is relatively avascular. If this process occurs over years, the bone becomes markedly remodeled. What is this established infection in the bone called? a. osteoinfectitis b. osteogenicities c. myorotinitis d. osteomyelitis ANS: D Image Note the fibrosis of the marrow space accompanied by chronic inflammatory cells. This is a chronic osteomyelitis. What is the consequence of this condition? a. there can be bone destruction with remodeling b. chronic softening of the surrounding cartilage c. a very putrid smell coming from the surrounding muscle tissue
18 d. the fibrosis will make the bone much stronger ANS: A Image This femur has a large eccentric tumor mass arising in the metaphyseal region. Since the epiphysis seen at the right is still present, what should this tell us about this type of tumor? a. This patient has very little chance of survival. b. These tumors most often occur in young persons. c. These tumors most often occur in middle age persons. d. These tumors most often occur in geriatric patients. ANS: B Image This osteosarcoma arising in the metaphysis at the upper tibia of a teenage boy breaks through the bone cortex and extends into soft tissue. What other general medical terminology can you use instead of osteosarcoma? a. osteomyelitis b. osteo cancerous c. neoplasm d. benign bone fracturation ANS: C Image 12 (X-ray) 13. In this AP radiograph of the distal femur, an osteosarcoma involves the metaphyseal region. Generally speaking where is it located? a. just above the knee b. just below the knee c. just above the hip d. just below the hip ANS: A
19 Image The microscopic appearance of an osteosarcoma is shown here. Sarcomas have very pleomorphic cells; often what shape will they take? a. spindle shape b. rectangle shape c. shape of a small boat d. honeycomb shape ANS: A Image 13 (X-ray) 15. This radiograph demonstrates a consequence of weakening of the lower tibial metaphysis by a lytic osteosarcoma. How can you correctly describe this fracture? a. a pathologic fracture b. an open hole fracture c. a fracture from tumor pressure d. a physiologic fracture ANS: A Image The neoplastic spindle cells are seen to be making pink osteoid here. Osteoid production by a sarcoma is diagnostic of a. osteosarcoma b. osteomyelitis c. osteonotsureus d. normal osteoblastic function ANS: A Image 14 (PX) 17. Positive staining in the cytoplasm of these neoplastic cells at high magnification with antibody to vimentin suggests that this is a a. sarcoma b. carcinoma c. canceremia d. osteoma ANS: A 18. What is a chondrosarcoma? a. cancer of the bone
20 b. neoplasm of the cartilage c. infection of the chondro d. an indicator of good health ANS: B Image 16 (CT) 19. This pelvic CT scan demonstrates a large chondrosarcoma involving the left pelvic sing. What other tissue does it appear to involve? a. the adjacent soft tissue b. only the pelvic wing c. the pubic bone d. distant soft tissue ANS: A Image Here is a microscopic view of metastases to bone. Why is a pathologic fracture possible, in this case? a. patients with this condition are much more likely to stumble and fall b. chemotherapy can cause these fractures c. if the bone is markedly weakened by the metastasis, then a pathologic fracture is possible d. pathologic fractures only occur in pathophysiology ANS: C Image 25 (NM) 21. This nuclear medicine bone scan reveals multiple areas of increase uptake, which are the darker foci, such as in the vertebral column. What does this represent? a. calcium deficiency b. calcium and postassium deficiency c. increased uptake representing metastases d. nothing significant, everyone has areas of increased uptake ANS: C Image This is an osteochondroma of bone. This lesion appears as a bony projection (exostosis). What is the common treatment for this condition? a. immediate amputation
21 b. aggressive chemotherapy and radiation therapy c. physical therapy is very successful for removing the growth d. most are solitary, incidental lesion that my be excised if they cause local pain ANS: D Image 28 (X-ray) 23. This radiograph demonstrated a lateral projection from the metaphyseal region of the distal femur. This is an osteochondroma. What type of symptoms would you expect? a. local discomfort then the patient s knee is bumped or rubbed against another object. b. no symptoms at all, the patient will only have symptoms if it is malignant c. severe discomfort when the patient s knee is bumped or rubbed against another object d. itching and a crushing pain to the lower extremity ANS: A Image This is an osteochondroma cut into three sections. A bluish-white cartilaginous cap overlies the bony cortex. These are probably not true neoplasms, but they are a mass lesion that extends outward from the metaphyseal region of a long bone. How many metaphyseal regions are there of the femur? a. one b. the entire femur is metaphyseal c. two d. four ANS: C Image Histologically, giant cell tumors of bone as seen here are composed of osteoclastlike multinucleated giant cells in a sea of round to oval mononuclear stromal cells. There may also be foamy macrophages and hemosiderin deposition in the stroma. These tumors are biologically benign so, are they a problem? a. No, they are benign b. Yes, they can expand and cause pain, deformity, or fracture c. No, the patient has not developed the tell-tale histologic signs that indicate a problem. d. There is not enough information to discern a problem in this case. ANS: B
22 Image 32 (CT) 26. This is a CT scan of a giant cell tumor involving the left ischial ramus. The tumor is an eccentric, expansile, lytic mass with extension into soft tissue along with overlying reactive new bone formation. Generally, what area of the body does this scan refer to? a. chest b. abdomen c. pelvis d. middle section including the diaphragm ANS: C Image Here is another example of degenerative osteoarthritis in which there is prominent lipping of the vertebrae. Osteoarthritis increases with age beyond 50. Generally, a few large joints are involved, such as hip or knee. Note also that there is a curve to the right indicating a minor degree of scoliosis. What causes this condition? a. osteoarthritis due to wear and tear with loss of articular cartilage b. osteoarthritis caused by poor nutrition and lifestyle choices c. osteoarthritis is idiopathic d. osteoarthritis has a genetic predisposition and has the tendency to appear near the age of 50 ANS: A Image This is the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. There is chronic inflammation with lymphocytes and plasma cells that produce the blue areas beneath the nodular proliferations. This pannus is destructive and produces erosion of the articular cartilage. What does this type of arthritis eventually lead to? a. destruction of the bone due to lytic enzymes b. osteosarcoma c. osteomyelitis d. destroy the affected joint ANS: D Image 72
23 29. This is gout. The joint most often affected is the first MP joint (big toe) as seen here. Acute attacks are characterized by severe pain, swelling and erythema of the joint. What causes gout? a. stubbing of the toe usually after getting up in the middle of the night b. stubbing of the toe from any traumatic cause c. gouty arthritis results from deposition of sodium urate crystals in joints d. gouty arthritis results from deposition of calcium silicate crystals in joints ANS: C Image 72 (X-ray) 30. Chronic gout leads to deposition of urates into a chalky mass known as a tophus. The first metatarsophalangeal joint is a common location. Such tophi can appear around a joint and adjacent bone as seen her radiographically. Tophaceous deposits consist of sodium urate crystals, and there is a surrounding destructive inflammatory response. What is the common name for the toe affected? a. fifth little piggy b. great toe c. grand toe d. the first metacarpal phalanges ANS: B Image Chronic gout leads to deposition of urates into chalky mass know as tophus. Seen here radiographically in sequential radiographs of the same foot is a tophaceous deposit that has destroyed the 1st MP joint and adjacent bone. In most, but not all, cases the patient could have a. hypocalcemia b. hyperuricemia c. septicemia d. bacterium in the first metacarpal ANS: B Image 75
24 32. If synovial fluid is aspirated from a patient with gout, the fluid can be examined for the presence of the causative agent, which is seen here to be needle shaped. If they are observed under polarized light with a red compensator, they appear yellow (negatively birefringent) in the main axis of the compensator and blue in the opposite perpendicular direction. In this case what is the causative agent? a. sodium urate citrals b. calcium silicate crystals c. sodium chloride crystals d. sodium bicarbonate crystals ANS: A Image Ultrasound may reveal long bones that are shortened. There are several possibilities, including short-limbed dwarfism. Seen here is a radiograph demonstrating short, curved femora and humeri, along with prominent platyspondyly of the vertebrae. This is thanatophoric dysplasia. What type of condition is this? a. a lethal condition b. a survivable condition c. short term and will resolve d. a tragic condition that causes the patient to be confined to wheelchair ANS: A
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Notes: The Skeletal System
 Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
Date: Notes: The Skeletal System Humans have an endoskeleton that develops from of the mesoderm. Composed of o o o : connects bone-to-bone o : connects muscle-to-bone Functions: o o o o Divided into two
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System. Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
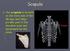 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend
 Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
Health Sciences 1110 Module 10 Endocrine System LAB 10
 Health Sciences 1110 Module 10 Endocrine System LAB 10 View the Film on Pituitary Tumor Surgery and answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. Anatlab o On campus students: Double-click on the
Health Sciences 1110 Module 10 Endocrine System LAB 10 View the Film on Pituitary Tumor Surgery and answer the questions on your laboratory worksheet. Anatlab o On campus students: Double-click on the
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP
 Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP I. Introduction The purpose of this material is to provide information that may be useful in the identification of tumors
Cytology of Neoplasms that Occur on the Limbs Rick Alleman, DVM, PhD, DABVP, DACVP I. Introduction The purpose of this material is to provide information that may be useful in the identification of tumors
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Why do we need the skeletal system?
 EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Advertisement. Osteochondroma
 Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/17/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 99 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/17/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 99 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Osteosarcoma (Canine)
 Osteosarcoma (Canine) Answering Your Questions About Osteosarcoma In Dogs What Is Osteosarcoma? Usual Sites for Osteosarcoma Development Osteosarcoma is by far the most common bone tumor of the dog, usually
Osteosarcoma (Canine) Answering Your Questions About Osteosarcoma In Dogs What Is Osteosarcoma? Usual Sites for Osteosarcoma Development Osteosarcoma is by far the most common bone tumor of the dog, usually
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Anesthesia Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes
 Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Bone tumors. RMG: jan
 Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Bone Tumors Clues and Cues
 William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
William Herring, M.D. 2002 Bone Tumors Clues and Cues In Slide Show mode, advance the slides by pressing the spacebar All Photos Retain the Copyright of their Authors Clues by Appearance of Lesion Patterns
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The Skeletal System. Support Systems Unit 2
 The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 The Basic Functions of the Skeletal System Hematopoiesis Structure Support Muscle Attachment and Movement Mineral Storage Axial vs. Appendicular The Axial Skeleton
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW
 Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
CONSULTATION DURING SURGERY / NOT A FINAL DIAGNOSIS. FROZEN SECTION DIAGNOSIS: - A. High grade sarcoma. Wait for paraffin sections results.
 Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Functions of Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Protruding wrist and ankle bones
 Protruding wrist and ankle bones The Borg System is 100 % Protruding wrist and ankle bones You're talking about the medial (on the inside) and lateral (on the outside) malleolus (mah-lee-o-lus). The medial
Protruding wrist and ankle bones The Borg System is 100 % Protruding wrist and ankle bones You're talking about the medial (on the inside) and lateral (on the outside) malleolus (mah-lee-o-lus). The medial
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Chapter 6
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
Radiology Reference Guide
 Radiology Reference Guide Your skeleton gives your body structure and support. It is made of living bone cells, living tissues, blood vessels, mineral deposits and water. Your skeleton also protects delicate
Radiology Reference Guide Your skeleton gives your body structure and support. It is made of living bone cells, living tissues, blood vessels, mineral deposits and water. Your skeleton also protects delicate
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Understanding Osteoporosis
 Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Cluster - 26 ORTHOPEDICS. X Ray of Affected Limb, MIR of Shoulder
 Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Brain Atrophy. Brain Atrophy
 Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
Aging Central Nervous System Processes Age related brain atrophy Non-age related brain atrophy Cerebrovascular disease Cerebral infarction Hypertensive hemorrhage Carotid artery stenosis and occlusion
3 section of the Foot
 TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
