CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (118)
|
|
|
- Oswin Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
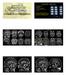
1 Medical Education Singapore Med , 48 (9) : 869 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (118) Subramanian S, Hari S, Santosh Kumar S Fig. I Axial TI -W image of the brain taken at the level of the cerebellar peduncle. Fig. 2 Parasagittal TI -W image of the brain. /7' Fig. 3 Mid -sagittal TI -W image of the brain. Fig. 4 Axial T I of the fourth ventricle. l -W axial image taken at the level Department of Radiodiagnosis, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi , India Subramanian S, MD Senior Resident Han S, MD Assistant Professor CASE PRESENTATION An 18 -month -old boy presented to the paediatric outpatient clinic with delayed milestones and a recent episode of seizure. There was no history of birth asphyxia. On examination, the child had strabismus in his right eye. The head circumference was normal. The muscle tone was reduced. There was delay in speech and language development; however, the child could localise auditory stimuli. He could stand with support but he had difficulty in walking. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of brain was done (Figs. 1-4). What is your diagnosis? Santosh Kumar S, MD Senior Resident Correspondence to: Dr Subramanian Subramanian Tel: (91) Fax: (91) drsubbusmc@ yahoo.co.in
2 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 870 IMAGE INTERPRETATION Axial MR image revealed the molar tooth sign (Fig. 1) due to an abnormally -oriented and thickened superior cerebellar peduncle. Sagittal MR image showed a thickened cerebellar peduncle lying perpendicular to the brain stem (Fig. 2). MR image also showed thinning of isthmus with a widened interpeduncular cistern (Fig. 3) and hypoplastic cerebellar vermis. The fourth ventricle was enlarged with a bat -wing configuration on the axial MR image (Fig. 4). The posterior fossa was mildly enlarged. The clinical and MR imaging features were diagnostic of Joubert syndrome. DIAGNOSIS Joubert syndrome CLINICAL COURSE The child was started on physiotherapy for the strengthening of his muscles. Antiepileptic drugs were prescribed. Renal function tests and renal ultrasonography are being performed at regular intervals as these patients may have cysts in the kidneys and suffer from poor renal function. Routine ocular examination has also been advised because retinal dystrophy may be associated with this syndrome. The prognosis has been explained to the parents. The risk of recurrence and the need for prenatal counselling in future pregnancies were also explained. DISCUSSION Marie Joubert, a French neurologist, first reported this syndrome in five children who had episodes of abnormal breathing and eye movements, ataxia, mental retardation in association with vermian agenesis.(1 This syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder, with characteristic abnormalities in the cerebellar vermis and pontomesencephalic junction.(') Affected children have facial dysmorphism with mild epicanthus, high rounded eyebrows, broad nasal bridge, low set ears and triangular - shaped open mouth. They have developmental delay and decreased muscle tone. Other associated features are coloboma of retina and retinal dystrophy in 50%, renal cystic disease in 30% and polydactyly in 15% of the patients.(2) Presence of retinal dystrophy in these patients is associated with increased prevalence of multicystic kidney disease and they have decreased survival rates.(3) The molecular and biochemical abnormalities in these patients have not been established and no specific chromosomal locus has been identified. (4) Maria et al proposed revised diagnostic criteria for the diagnosis of Joubert syndrome.(5) These include hypotonia, ataxia, global developmental delay and molar tooth sign on imaging. Other associated abnormalities which have been included in their diagnostic criteria are facial dysmorphism, breathing abnormalities, ocular abnormalities (such as retinal dysplasia, coloboma, nystagmus, strabismus and ptosis), oculomotor apraxia and renal microcystic disease. Seizure is not a part of this syndrome, though it was seen in the present patient. Pathological studies in these patients have shown abnormalities in the cerebellar vermis and pontomesencephalic junction.(6) The cerebellar vermis is hypoplastic and the dentate nucleus is fragmented. The pontomesencephalic junction is dysplastic, with abnormal decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle and elongation of rostral fourth ventricle. There is a reduction in neurons of the basis pontis and reticular formation. In the medulla, the inferior olivary nucleus, tractus solitorius, the nucleus and spinal tracts of trigeminal nerves are hypoplastic. The posterior median sulcus and pyramidal decussation are absent. In addition, there is neuronal swelling seen in the nucleus gracilius and cuneatus. Quisling et al studied the MR imaging features in 44 patients with Joubert syndromes') They reported various morphological abnormalities in the isthmus and rostral brain stem. The characteristic MR imaging features seen in these patients were: (1) thinning of the isthmus with widened interpeduncular fossa; (2) thickened superior cerebellar peduncles lying perpendicular to the dorsal pons; (3) hypoplasia of the vermis with enlargement of the fourth ventricle and rostral shift of the fastigium; and (4) sagittal vermian cleft due to incomplete fusion of the two halves of vermis. These patients had normal cerebellar hemisphere volume suggesting a normal neocerebellar formation. The characteristic MR imaging findings were present in 35 patients in their study. In the other nine patients, there was either tecto-cerebellar dysplasia or the Dandy -Walker malformation, in addition to the characteristic MR imaging features of Joubert syndrome. They classified these patients as having the Joubert plus syndrome. Supratentorial abnormalities were uncommon and two-thirds of the patients in their study had normal cerebral hemispheres. Prominent subarachnoid spaces and ventriculomegaly were seen in one third of patients. Delayed myelination was noted in ten patients. The molar tooth sign is seen on the axial MR images, due to thickened and abnormally -oriented superior cerebellar peduncles, isthmic dysgenesis and vermian hypoplasia. It was first described by Maria et a1.(8) This sign is not specific for Joubert syndrome. It may be seen in other syndromes, such as the Dekaban-Arima, Senior-Loken, COACH, Varadi-Papp, Joubert with polymicrogyria, and Malta syndromes.(9) Although the molar tooth sign and other key clinical features of the Joubert syndrome, such as neonatal respiratory abnormality, hypotonia, developmental delay, ataxia and ocular motor apraxia, may be seen in these syndromes, they usually have additional striking features. The Dekeban Arima syndrome is associated Leber
3 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 871 5b 5c. - Fig. 5 Dandy -Walker malformation. MR imaging appearances. (a) The vermis is hypoplastic. However, the fourth ventricle is enlarged and communicates with a cyst in the posterior fossa. In addition, there is hydrocephalus. (b) The pontomesencephalic junction (arrow) and interpeduncular fossa (arrowhead) are normal. (c) The superior cerebellar peduncle is normal in thickness (arrowheads). congenital amarousis and cystic dysplastic kidneys,(9) whereas the Senior-Loken syndrome is associated with Leber congenital amarousis, retinitis pigmentosa and juvenile nephronophthisis. Patients with COACH syndrome have hepatic fibrosis, bilateral coloboma and renal calcification, and in the Varadi papp syndrome there is mesaxial polydactyly, Y-shaped metacarpal, cleft lip or cleft palate, lingual hamartomas and vermian hypoplasia(9) In the Malta syndrome, the affected patients have the molar tooth sign, occipital encephalocoele, hydrocephalus, cortical renal cysts with or without coloboma, and Leber congenital amarousis.(9) Some patients may have features of Joubert syndrome and polymicrogyria. None of the additional features were seen in the present patient Cerebellar vermian abnormality may be seen in other conditions such as the Dandy Walker malformation and rhomboncephalosynapsis.(3) In Dandy Walker malformation, the inferior part of the vermis is hypoplastic. However, the fourth ventricle is enlarged and communicates with a cyst in the posterior fossa (Fig. 5a). In addition, the ponto- mesencephalic junction, interpeduncular fossa (Fig. Sb) and superior cerebellar peduncle (Fig. 5c) are normal. In rhomboncephalosynapsis, the cerebellar hemispheres are fused, whereas in Joubert syndrome, there is clefting of vermis.(3) The prognosis of these patients is poor, with a five-year survival rate of only 50%.(2) Renal and retinal dysfunction can be progressive. In patients with retinal anomalies, the renal function should be monitored regularly and ultrasonography should be done to detect cystic renal disease." Genetic counselling is required in these patients. As the recurrence rate is 25%, prenatal counselling and screening with ultrasonography are required. These patients are also sensitive to respiratory depressant effects of anaesthetic agents, like opiates and nitrous oxide.(11) Hence, the use of these anaesthetic agents should be avoided in these patients. ABSTRACT An I8 -month -old boy presented with delayed milestones, hypotonia, strabismus and an episode of seizure. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of the brain revealed abnormally - oriented and thickened superior cerebellar peduncle, giving rise to the characteristic molar tooth sign on axial images. The isthmus was thinned out, with widened interpeduncular cistern and hypoplastic vermis. The clinical and MR imaging features were diagnostic of Joubert syndrome. Keywords: congenital brain abnormalities, hypoplastic cerebellar vermis, Joubert
4 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 872 syndrome, magnetic resonance molar tooth sign Singapore Med J 2007; 48(9): REFERENCES imaging, 1. Joubert M, Eisenring JJ, Robb W, Andermann F. Familial agenesis of the cerebellar vermis. A syndrome of episodic hyperpnea, abnormal eye movements, ataxia and retardation. Neurology 1969; 19: Alorainy IA, Sabir S, Seidahmed MZ, Farooqu HA, Salih MA. Brain stem and cerebellar findings in Joubert syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2006; 30: McGraw P. The molar tooth sign. Radiology 2003; 229: Chance PF, Cavalier L, Safran D, et al. Clinical nosologic and genetic aspects of Joubert and related syndromes. J Child Neurol 1999; 14: Maria BL, BoltshauserE, Palmer SC, TranTX. Clinical features and revised diagnostic criteria in Joubert syndrome. J Child Neurol 1999; 14: Yachnis AT, Rorke LB. Neuropathology of Joubert syndrome. J Child Neurol 1999; 14: Quisling RG, Barkovich AJ, Maria BL. Magnetic resonance imaging features and classification of central nervous system malformations in Joubert syndrome. J Child Neurol 1999; 14: Maria BL, Hoang KB, Tusa RJ, et al. "Joubert syndrome" revisited: key ocular motor signs with magnetic resonance imaging correlation. J Child Neurol 1997; 12: Gleeson JG, Keeler LC, Parisi MA, et al. Molar tooth sign of the midbrain-hindbrain junction: occurrence in multiple distinct syndromes. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 125: van Beek EJ, Majoie CB. Case 25: Joubert syndrome. Radiology 2000; 216: Habre W, Sims C, D' Souza M. Anaesthetic management of children with Joubert syndrome. Paediatr Anaesth 1997; 7:251-3.
5 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 873 SINGAPORE MEDICAL COUNCIL CATEGORY 3B CME PROGRAMME Multiple Choice Questions (Code SMJ B) Question 1. Regarding the clinical features of Joubert Syndrome: (a) Affected children have breathing abnormalities, ataxia, mental retardation and oculomotor apraxia. (b) It is an autosomal dominant disorder. (c) Retinal dystrophy and renal cystic disease may be seen in these patients. (d) The specific chromosomal abnormality has been identified. True False Question 2. Regarding the pathological findings in Joubert Syndrome: (a) The cerebellar vermis is hypoplastic and pontomesencephalic junction is abnormal. (b) There is reduction in neurons of basis pontis and reticular formation. (c) The superior cerebellar peduncle and fourth ventricle are normal. (d) In the medulla, pyramidal decussation and posterior median sulcus are normal. Question 3. Regarding the MR imaging findings in Joubert Syndrome: (a) Characteristic MR imaging findings are thinning of isthmus with widened interpeduncular fossa, thickened superior cerebellar peduncles, vermian hypoplasia, and vermian cleft. (b) The cerebellar hemispheres are hypoplastic. (c) Supratentorial abnormalities are common. (d) Tectocerebellar dysplasia and Dandy walker malformation is seen in all patients. Question 4. Regarding the molar tooth sign on MR imaging: (a) It is seen in coronal MR image due to thickened and abnormally oriented superior cerebellar peduncle, isthmic dysgenesis and vermian hypoplasia. (b) It is specific for Joubert Syndrome. (c) It is seen in COACH syndrome, which is associated with hepatic fibrosis, bilateral coloboma and renal calcification. (d) Occipital encephalocoele, hydrocephalus, cortical renal cysts are seen in addition to this sign in Malta Syndrome. Question 5. Regarding the clinical outcome of these patients: (a) These patients have good prognoses. (b) Renal and retinal dysfunction can be progressive. (c) They are sensitive to respiratory depressant effect of anaesthetic agents, like opiates and nitrous oxide. (d) In patients with retinal anomalies, the renal function should be monitored regularly and an ultrasonogram should be done to detect cystic renal disease. Doctor's particulars: Name in full: MCR number: address: Specialty: SUBMISSION INSTRUCTIONS: (1) Log on at the SMJ website: and select the appropriate set of questions. (2) Select your answers and provide your name, address and MCR number. Click on "Submit answers" to submit. RESULTS: (1) Answers will be published in the SMJ November 2007 issue. (2) The MCR numbers of successful candidates will be posted online at by 15 November (3) All online submissions will receive an automatic acknowledgment (4) Passing mark is 60%. No mark will be deducted for incorrect answers. (5) The SMJ editorial office will submit the list of successful candidates to the Singapore Medical Council. Deadline for submission: (September 2007 SMJ 3B CME programme): 12 noon, 25 October 2007
Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2012; 54: 605-611 Original Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases Faruk İncecik 1, M. Özlem Hergüner 1, Şakir Altunbaşak 1, Joseph G. Gleeson 2 1 Department of Pediatric
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2012; 54: 605-611 Original Joubert syndrome: report of 11 cases Faruk İncecik 1, M. Özlem Hergüner 1, Şakir Altunbaşak 1, Joseph G. Gleeson 2 1 Department of Pediatric
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Posterior fossa malformations
 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Case Report Joubert syndrome in a neonate: case report with literature review
 Case Report Joubert syndrome in a neonate: case report with literature review Haifa A Bin Dahman (1), Abdul-Hakeem M Bin Mubaireek (2), Zain H Alhaddad (3) (1) Hadhramout University College of Medicine,
Case Report Joubert syndrome in a neonate: case report with literature review Haifa A Bin Dahman (1), Abdul-Hakeem M Bin Mubaireek (2), Zain H Alhaddad (3) (1) Hadhramout University College of Medicine,
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa Bosemani, Thangamadhan;
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Congenital abnormalities of the posterior fossa Bosemani, Thangamadhan;
MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations.
 MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations. Poster No.: C-0814 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cabaj, M. Bekiesinska-Figatowska, A. Duczkowska, M. Duczkowski;
MRI characteristics of posterior cranial fossa malformations. Poster No.: C-0814 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cabaj, M. Bekiesinska-Figatowska, A. Duczkowska, M. Duczkowski;
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Journal of Child Neurology
 Journal of Child Neurology http://jcn.sagepub.com/ Molar Tooth Sign in Joubert Syndrome: Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Significance Bernard L. Maria, Ronald G. Quisling, Louis C. Rosainz, Anthony
Journal of Child Neurology http://jcn.sagepub.com/ Molar Tooth Sign in Joubert Syndrome: Clinical, Radiologic, and Pathologic Significance Bernard L. Maria, Ronald G. Quisling, Louis C. Rosainz, Anthony
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain
 The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
Molar Tooth Sign of the Midbrain Hindbrain Junction: Occurrence in Multiple Distinct Syndromes
 American Journal of Medical Genetics 125A:125 134 (2004) Molar Tooth Sign of the Midbrain Hindbrain Junction: Occurrence in Multiple Distinct Syndromes Joseph G. Gleeson, 1 * Lesley C. Keeler, 1 Melissa
American Journal of Medical Genetics 125A:125 134 (2004) Molar Tooth Sign of the Midbrain Hindbrain Junction: Occurrence in Multiple Distinct Syndromes Joseph G. Gleeson, 1 * Lesley C. Keeler, 1 Melissa
A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4
 A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Ningappa, Vaishali D. M, Vijayaraghavachari
A STUDY OF POSTERIOR FOSSA MALFORMATIONS: MR IMAGING Ravi Ningappa 1, Vaishali D. M 2, Vijayaraghavachari T. V 3, Manjappa B. H 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Ningappa, Vaishali D. M, Vijayaraghavachari
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Lecture X. Brain Pathways: Movement!
 Bio 3411 Readings (background only) Bio 3411 Monday Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord The Brain Atlas 3 rd ed Page(s) Feature 198-199 Vestibular
Bio 3411 Readings (background only) Bio 3411 Monday Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord The Brain Atlas 3 rd ed Page(s) Feature 198-199 Vestibular
Lecture X. Brain Pathways: Movement!
 Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings (background only) Neuroscience 5 th ed Page(s) Feature 353-398Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control
Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings (background only) Neuroscience 5 th ed Page(s) Feature 353-398Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Central nervous system malformations in
 Case reports 659 Central nervous system malformations in Mohr's syndrome W REARDON*, M G HARBORDt, M A HALL-CRAGGSt, B KENDALLt, E M BRETTt, AND M BARAITSER *Mothercare Department of Paediatric Genetics,
Case reports 659 Central nervous system malformations in Mohr's syndrome W REARDON*, M G HARBORDt, M A HALL-CRAGGSt, B KENDALLt, E M BRETTt, AND M BARAITSER *Mothercare Department of Paediatric Genetics,
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Joubert syndrome
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Joubert syndrome Disease name: Joubert syndrome ICD 10: Q04.3 Synonyms: CPD IV, Cerebelloparenchymal disorder IV, Classic Joubert
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Joubert syndrome Disease name: Joubert syndrome ICD 10: Q04.3 Synonyms: CPD IV, Cerebelloparenchymal disorder IV, Classic Joubert
Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia
 Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2011, Article ID 262641, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/262641 Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia Harjinder Gill, 1 Brinda Muthusamy,
Case Reports in Pediatrics Volume 2011, Article ID 262641, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/262641 Case Report Joubert Syndrome Presenting with Motor Delay and Oculomotor Apraxia Harjinder Gill, 1 Brinda Muthusamy,
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye. Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine
 Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM..
 Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 02 Page February 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.65 Septo-Optic Dysplasia: A Case Report Authors
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Chiari Malformations. Google. Objectives Seventh Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/22/13. Kerry R. Crone, M.D.
 Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Brainstem and Cerebellum
 Brainstem and Cerebellum Lecture two Objectives: 1. Identify radiological anatomy of brain stem and cerebellum. 2. Compares CT and MRI imaging of brain stem and cerebellum. 3. Recognize the imaging findings
Brainstem and Cerebellum Lecture two Objectives: 1. Identify radiological anatomy of brain stem and cerebellum. 2. Compares CT and MRI imaging of brain stem and cerebellum. 3. Recognize the imaging findings
REVIEW ARTICLE INHERITED NEURODEVELOPMENTAL BRAIN DISEASES: APPLICATIONS OF HOMOZYGOSITY MAPPING TO IDENTIFY NEW GENETIC CAUSES OF DISEASE.
 REVIEW ARTICLE INHERITED NEURODEVELOPMENTAL BRAIN DISEASES: APPLICATIONS OF HOMOZYGOSITY MAPPING TO IDENTIFY NEW GENETIC CAUSES OF DISEASE. Joseph G. Gleeson, MD Abstract Objective The last two decades
REVIEW ARTICLE INHERITED NEURODEVELOPMENTAL BRAIN DISEASES: APPLICATIONS OF HOMOZYGOSITY MAPPING TO IDENTIFY NEW GENETIC CAUSES OF DISEASE. Joseph G. Gleeson, MD Abstract Objective The last two decades
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov Dandy-Walker Malformation
 REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic Cleft
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 An Unusual Kind Of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage: Post Traumatic Bleed Into The Schizencephalic J T, V Rajendran, E Devarajan Citation
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
Chiari III Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 07/02/2010 History Newborn with suboccipital mass. Diagnosis Chiari III Additional Clinical Surgery-Skin covered suboccipital cystic mass confined by the dura. Pathology-Leptomeningeal
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of congenital brain malformations at a referral hospital in Saudi Arabia: An MRI study Ibrahim A. Alorainy BACKGROUND: More than 2000 different congenital cerebral malformations
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pattern of congenital brain malformations at a referral hospital in Saudi Arabia: An MRI study Ibrahim A. Alorainy BACKGROUND: More than 2000 different congenital cerebral malformations
CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135)
 Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Medical Education Singapore Med J 2011; 52(5) : 384 CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (135) Pojchamarnwiputh S, Muttarak M, Sriplakich S H 1a 1b 1c 1d Fig. 1 (a) Axial unenhanced; (b & c) delayed
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Mystery Case - Answers Due September 17, Neurology Resident & Fellow Mystery Case. A 2-month old girl with difficulty swallowing
 Mystery Case - Answers Due September 17, 2018 Neurology Resident & Fellow Mystery Case Page description: August 27, 2018 New Mystery Case! A 2-month old girl with difficulty swallowing Adapted from a NeuroImage
Mystery Case - Answers Due September 17, 2018 Neurology Resident & Fellow Mystery Case Page description: August 27, 2018 New Mystery Case! A 2-month old girl with difficulty swallowing Adapted from a NeuroImage
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Fig. 1.4 (A B). The brain stem. Anterior view. Bar: 5 mm.
 Section I A Fig. 1.4 (A B). The brain stem. Anterior view. Bar: 5 mm. Medulla The boundaries between the spinal cord and medulla are noted on Fig. 1.30. The pontomedullary sulcus (1) separates the medulla
Section I A Fig. 1.4 (A B). The brain stem. Anterior view. Bar: 5 mm. Medulla The boundaries between the spinal cord and medulla are noted on Fig. 1.30. The pontomedullary sulcus (1) separates the medulla
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus. Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto
 Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
Fetal obstructive hydrocephalus Charles Raybaud Hospital for Sick Children, University of Toronto charles.raybaud@sickkids.ca Extensive definition No mention of aqueductal stenosis Purpose Working definition
DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL
 Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 23 `28, 1998 23 DIRECT SURGERY FOR INTRA-AXIAL BRAINSTEM LESIONS Kazuhiko Kyoshima, Susumu Oikawa, Shigeaki Kobayashi Department of Neurosurgery, Shinshu University School of Medicine,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42 cases
 Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Non-cranial nerve nuclei
 Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Chapter 2. Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord
 Chapter 2 Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord CNS 1. Topography; - what are the main components of the brain - how do you recognize them? 2. The location of the major functional areas of
Chapter 2 Central Nervous System; the brain and spinal cord CNS 1. Topography; - what are the main components of the brain - how do you recognize them? 2. The location of the major functional areas of
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA
 LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS APPROACH and DIAGNOSIS 2 Cochlea and Auditory nerve Pons (superior olive) lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Thalamus
LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS APPROACH and DIAGNOSIS 2 Cochlea and Auditory nerve Pons (superior olive) lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Thalamus
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
