The Somatosensory System
|
|
|
- Roland Bailey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com
2 Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body conditions Touch Pain Temperature Muscles Joints Balance
3 Touch Mechanoreceptors of the Skin Skin can be vibrated, pressed, pricked and stroked, and its hairs can be bent or pulled. Accordingly, there are many kinds of cutaneous receptors scattered about the body (providing an explicit map of space). Among these receptors are neuronal ( long ) touch receptors with specialized endings including: Meissner s corpuscles Merkel s disks Ruffini endings Pacinian corpuscles
4 Properties of Touch Receptors Touch mechanoreceptors vary in receptive fields sizes, preferred stimulus frequencies, and pressures. The identification of objects by touch is called stereognosis. Field Diameter Frequency Range Adaptation (pressure) Quality Meissner 3-4 mm Hz Rapid Light touch, stroke Merkel 3-4 mm DC-30 Hz Slow Touch, fine spatial details Ruffini > 10 mm DC-15 Hz Slow Stretch, finger position Pacinian > 20 mm Hz Rapid Vibration, strong pressure Meissner s corpuscle Merkel cells Ruffini endings Pacinian corpuscle
5 Transduction in Touch Receptors Stimuli applied to the skin deform, bend or stretch the membrane of the receptor, and this in turn changes directly its permeability to ions.
6 Pain and Temperature Receptors The transduction of painful and thermal stimuli occurs at free nerve endings. Pain receptors (nociceptors) may respond selectively to strong mechanical, thermal or chemical stimuli, or respond to all three kinds (polymodal). Thermoreceptors are highly sensitive to temperature in the innocuous range. There are distinct warm and cold types. Cold Mechanical Acid Heat Ad C Transmission is via myelinated Ad fibers (rapid adapting/rapid transmission) or unmyelinated C fibers (slow/slow). Ca ++ or Na + Rapid Slow Adapting
7 Distribution of Exteroceptors Exteroceptors are not uniformly distributed across the body Finger tips are enriched in mechanoreceptors with small receptive fields. (mm) There is a high density of nociceptors in palms and soles. There are more cold than warm thermoreceptors in the body, with the highest density of receptors on the face and ears.
8 Fibers from cutaneous receptors gather together in nerves and enter the spinal cord via the dorsal roots. Dermatome: area of the body that is innervated by the left and right dorsal roots of a given segment of the spinal cord. Dermatomes
9 Two Major Exteroceptor Pathways Dorsal-Column Medial Lemniscus Anterolateral System Periaqueductal gray (PAG) Interneurons enkephalins (endogeneous opioids) dorsolateral tract pain fibers glutamate substance P Mainly touch and muscles/joints First synapse in the dorsal column nuclei of the medulla Mainly pain and temperature First synapse in the spinal cord Three tracts
10 Proprioception from Muscles Muscle have two types of proprioceptors. Muscle spindles are in parallel with muscle fibers; they signal muscle length. Golgi tendon organs are in series with muscle fibers; they signal muscle tension.
11 Proprioception from Joints There are four types of mechanosensitive proprioceptors in joints. They respond to changes in angle, direction and velocity of the joint. joint capsule link.springer.com
12 Balance: The Vestibular System The vestibular system monitors the movement and position of the head, giving us our sense of balance or equilibrium. The system includes two structures: the semicircular canals and the otolith organs. what-when-how.com
13 The semicircular canals detect turning movements of the head, in particular angular accelerations (rapid adaptation). The Semicircular Canals austincc.edu Semicircular canals are paired with another on the opposite side of the head. Rotation in one axis excites the hair cells of one canal, and inhibits the other canal: push-pull. mjc.edu
14 The Otolith Organs The otolith organs sense changes of head angle (position of head); they are sensitive to gravity and linear acceleration. what-whenhow.com
15 Central Proprioceptive Pathways Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus SI (face area) Neck motor neurons Limb motor neurons Touch and muscles/joints
16 Primary Somatosensory Cortex Primary somatosensory cortex (SI) is located in the postcentral gyrus. Input is largely contralateral. It is organized according to a map of the body (i.e., it is somatotopic). The somatosensory map or homunculus is distorted; body areas with more sensitive tactile/position discrimination have more cortical representation.
17 Columnar Organization of SI Primary somatosensory is composed of four strips. Each strip is most sensitive to a different kind of somatosensory input skin muscles/joints
18 Two Streams from SI Dorsal stream from SI to posterior parietal cortex: direct attention Ventral stream through SII (bilateral) to prefrontal: perception of object shape
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Chapter 15! Chapter 15 Sensory Pathways, Somatic Nervous System! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System!
 Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? What must sensory systems encode? 9/8/2010. Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience. November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM. Ralph Adolphs
 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM Ralph Adolphs 1 Menu for today Touch -peripheral -central -plasticity Pain 2 Sherrington (1948): senses classified as --teloreceptive
Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience November 11, 2015 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM Ralph Adolphs 1 Menu for today Touch -peripheral -central -plasticity Pain 2 Sherrington (1948): senses classified as --teloreceptive
Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand)
 Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Lecture 19 revised 03/10 The Somatic Sensory System Skin- the largest sensory organ we have Also protects from evaporation, infection. Skin types: hairy and glabrous (e.g. back vs. palm of hand) 2 major
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems
 mm? Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems Recommended literature 1. Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessel TM (2000) Principles of Neural Science, McGraw-Hill, Ch. xx. 2. Berne EM, Levy MN, Koeppen
mm? Sensory information processing, somato-sensory systems Recommended literature 1. Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessel TM (2000) Principles of Neural Science, McGraw-Hill, Ch. xx. 2. Berne EM, Levy MN, Koeppen
Mechanosensation. Central Representation of Touch. Wilder Penfield. Somatotopic Organization
 Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements?
 Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
Section: Chapter 10: Multiple Choice 1. Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements? p.358 frontal lobe hippocampus basal ganglia cerebellum 2. The prefrontal cortex is
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
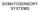 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS Schematic diagram illustrating the neural pathways that convey somatosensory information to the cortex and, subsequently, to the motor system. Double arrows show reciprocal connections.
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS Schematic diagram illustrating the neural pathways that convey somatosensory information to the cortex and, subsequently, to the motor system. Double arrows show reciprocal connections.
1. Somatosensory Pathways
 1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile
 Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
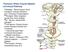 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway
 Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Coding of Sensory Information
 Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
Collin County Community College. BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves,
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 : Anatomy/ Physiology PNS Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord Includes sensory receptors, peripheral nerves,
III: To define the mechanoreceptive and thermoreceptive sensations.
 Somatic Sensations I: To explain the proper way of sensory testing. II: To describe the somatic sensations. III: To define the mechanoreceptive and thermoreceptive sensations. SOMATIC SENSATIONS Somatic
Somatic Sensations I: To explain the proper way of sensory testing. II: To describe the somatic sensations. III: To define the mechanoreceptive and thermoreceptive sensations. SOMATIC SENSATIONS Somatic
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
Overview of Questions
 Overview of Questions What are the sensors in the skin, what do they respond to and how is this transmitted to the brain? How does the brain represent touch information? What is the system for sensing
Overview of Questions What are the sensors in the skin, what do they respond to and how is this transmitted to the brain? How does the brain represent touch information? What is the system for sensing
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
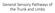 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
OVERVIEW. Today. Sensory and Motor Neurons. Thursday. Parkinsons Disease. Administra7on. Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online
 OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
COGS 107B Week 2. Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm
 COGS 107B Week 2 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Lecture 3: Proprioception Principles: The Neuron Doctrine and The Law of Dynamic Polarization Proprioception Joint-protecting reflexes (ex. Knee jerk reflex)
COGS 107B Week 2 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Lecture 3: Proprioception Principles: The Neuron Doctrine and The Law of Dynamic Polarization Proprioception Joint-protecting reflexes (ex. Knee jerk reflex)
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Sensation Chapter 46
 Sensation Chapter 46 Natasha McDougal and Kaleb Hood Background and Purpose Nerve impulses occur because of a change in action potential Graded potentials in the dendrites and cell body can have either
Sensation Chapter 46 Natasha McDougal and Kaleb Hood Background and Purpose Nerve impulses occur because of a change in action potential Graded potentials in the dendrites and cell body can have either
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools
 Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
Physiology of Tactile Sensation
 Physiology of Tactile Sensation Objectives: 1. Describe the general structural features of tactile sensory receptors how are first order nerve fibers specialized to receive tactile stimuli? 2. Understand
Physiology of Tactile Sensation Objectives: 1. Describe the general structural features of tactile sensory receptors how are first order nerve fibers specialized to receive tactile stimuli? 2. Understand
COGS 107B Week 1. Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm
 COGS 107B Week 1 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Before We Begin... Hyun Ji 4th year Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience Email: hji@ucsd.edu In subject, always add [COGS107B] Office hours: Wednesdays, 3-4pm in
COGS 107B Week 1 Hyun Ji Friday 4:00-4:50pm Before We Begin... Hyun Ji 4th year Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience Email: hji@ucsd.edu In subject, always add [COGS107B] Office hours: Wednesdays, 3-4pm in
The How of Tactile Sensation
 The How of Tactile Sensation http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter02.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives 1. Understand how sensory stimuli are encoded
The How of Tactile Sensation http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter02.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives 1. Understand how sensory stimuli are encoded
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
راما ندى أسامة الخضر. Faisal Muhammad
 22 راما ندى أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad Revision Last time we started talking about sensory receptors, we defined them and talked about the mechanism of their reaction. Now we will talk about sensory receptors,
22 راما ندى أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad Revision Last time we started talking about sensory receptors, we defined them and talked about the mechanism of their reaction. Now we will talk about sensory receptors,
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Cogs 107B A01: Monday 2pm. Ricardo Trujillo
 Cogs 107B A01: Monday 2pm Ricardo Trujillo ratrujil@ucsd.edu The Basics Email: ratrujil@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Thursdays 11am-12pm, Mandeville Coffee Cart Sections are not mandatory, but strongly recommended
Cogs 107B A01: Monday 2pm Ricardo Trujillo ratrujil@ucsd.edu The Basics Email: ratrujil@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Thursdays 11am-12pm, Mandeville Coffee Cart Sections are not mandatory, but strongly recommended
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 33. Touch perception
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Touch perception Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light,
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Touch perception Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light,
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions
 Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light, air pressure)
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light, air pressure)
4. Sensory Systems. 4.1 Receptors. - cutaneous receptors: on the body surface and accessible mucous membranes
 4. Sensory Systems The term 'sensory systems' applies to those parts of the nervous system concerned with the detection, transmission and analysis of information about stimuli from the internal and external
4. Sensory Systems The term 'sensory systems' applies to those parts of the nervous system concerned with the detection, transmission and analysis of information about stimuli from the internal and external
Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo , ( ), , M4.1, M6.2
 Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo 4.1 4.8, (4.9 4.23), 6.22 6.24, M4.1, M6.2 I. Transduction The role of sensory systems is to convert external energy into electrical signals
Neurobiology Biomed 509 Sensory transduction References: Luo 4.1 4.8, (4.9 4.23), 6.22 6.24, M4.1, M6.2 I. Transduction The role of sensory systems is to convert external energy into electrical signals
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
Chapter 6. Gathering information; the sensory systems
 Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
Somatosensory modalities!
 Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Chap Senses. 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Chap. 17 - Senses Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect. 2. Classification of Sensory Receptors a. mechanoreceptors b. thermoreceptors
Carl Christensen, PhD Chap. 17 - Senses Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect. 2. Classification of Sensory Receptors a. mechanoreceptors b. thermoreceptors
*Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord.
 *somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
*somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Lecture VIII. The Spinal Cord, Reflexes and Brain Pathways!
 Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
Reflexes and Brain Bio 3411! Monday!! 1! Readings! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed: Review Chapter 1 pp. 11-21;!!Read Chapter 9 pp. 189-194, 198! THE BRAIN ATLAS 3 rd ed:! Read pp. 4-17 on class web site! Look at
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Chapter 18 Senses SENSORY RECEPTION 10/21/2011. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations
 SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
Class 11: Touch, Smell and Taste PSY 302 Lecture Notes October 3, 2017
 Katie Cutaneous (skin) Senses: Somatosenses: Class 11: Touch, Smell and Taste PSY 302 Lecture Notes October 3, 2017 Cutaneous senses (touch) Kinesthesia, proprioception: joint and muscle stretch information,
Katie Cutaneous (skin) Senses: Somatosenses: Class 11: Touch, Smell and Taste PSY 302 Lecture Notes October 3, 2017 Cutaneous senses (touch) Kinesthesia, proprioception: joint and muscle stretch information,
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System. Chapter 15
 Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS. Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil
 SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil Sensory Deprivation Tank Is the world really as we perceive it? Is the world really as we perceive it? NO. The world
SENSORY NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSORY RECEPTORS Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil Sensory Deprivation Tank Is the world really as we perceive it? Is the world really as we perceive it? NO. The world
Introduction. Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups. General senses Special senses
 Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
There Are 5 Different Types Of Sensory Receptors* *Note: Not all are touch (somatic) receptors.
 1 First, a bit of information relating to receptors: From sensory organ to sensory organ, receptors work in fundamentally the same way A receptor is always the dendrite of a sensory neuron or a specialized
1 First, a bit of information relating to receptors: From sensory organ to sensory organ, receptors work in fundamentally the same way A receptor is always the dendrite of a sensory neuron or a specialized
Touch. Lecture Notes 10/3 -Brenna
 Lecture Notes 10/3 -Brenna Touch Cutaneous Sense Somatosenses o Cutaneous sense (touch) o Kinesthesia, proprioception: joint and muscle stretch information, giving body position (proprioception) and dynamics
Lecture Notes 10/3 -Brenna Touch Cutaneous Sense Somatosenses o Cutaneous sense (touch) o Kinesthesia, proprioception: joint and muscle stretch information, giving body position (proprioception) and dynamics
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Baraa Ayed. Salsabeel Fleifel. Faisal Muhammad
 23 Baraa Ayed Salsabeel Fleifel Faisal Muhammad Review for the previous lecture: - Last time, we talked about receptors and the objectives to define receptors. We define receptors as transducers that convert
23 Baraa Ayed Salsabeel Fleifel Faisal Muhammad Review for the previous lecture: - Last time, we talked about receptors and the objectives to define receptors. We define receptors as transducers that convert
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Somatosensation. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44757 1 Somatosensation OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m44757 1 Somatosensation OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Active sensing. Ehud Ahissar 1
 Active sensing Ehud Ahissar 1 Active sensing Passive vs active touch Comparison across senses Basic coding principles -------- Perceptual loops Sensation-targeted motor control Proprioception Controlled
Active sensing Ehud Ahissar 1 Active sensing Passive vs active touch Comparison across senses Basic coding principles -------- Perceptual loops Sensation-targeted motor control Proprioception Controlled
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM DR. WELCH
 BIOL 2401 DR. WELCH CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM I. Sensation conscious or subconscious awareness of internal & external changes. Define perception. Primary function of. Why isn t blood
BIOL 2401 DR. WELCH CHAPTER 16: SENSORY, MOTOR, & INTEGRATIVE SYSTEM I. Sensation conscious or subconscious awareness of internal & external changes. Define perception. Primary function of. Why isn t blood
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 1 1 2 2 Touch: Subtopics The stimuli of touch Anatomy of the skin Types of mechanoreceptors
The Somatosensory System General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 1 1 2 2 Touch: Subtopics The stimuli of touch Anatomy of the skin Types of mechanoreceptors
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System 1 1 General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 2 Touch: Subtopics The stimuli of touch Anatomy of the skin Types of mechanoreceptors
The Somatosensory System 1 1 General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 2 Touch: Subtopics The stimuli of touch Anatomy of the skin Types of mechanoreceptors
Sensory system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
Human sense organs. Five Senses Icons. Sense organs. five senses: specialized cells receptors for specific stimuli: touch taste smell sight hearing
 Sense Organs 1. classification 2. Sensory receptors: unencapsulated free nerve endings encapsulated 3. Gustatory apparatus 4. Olfactory apparatus five senses: touch taste smell sight hearing Human sense
Sense Organs 1. classification 2. Sensory receptors: unencapsulated free nerve endings encapsulated 3. Gustatory apparatus 4. Olfactory apparatus five senses: touch taste smell sight hearing Human sense
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System 1 General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 2 Touch Teaches Us About Other Senses Multimodality Transduction Parallel vs. Serial
The Somatosensory System 1 General Topics Chapter 3 in text Touch Thermal sensations Proprioception & Kinesthesis Pain 2 Touch Teaches Us About Other Senses Multimodality Transduction Parallel vs. Serial
My green thumb came only as a result of the mistakes I made while learning to see things from the plant s point of view. -H. Fred Ale Nervous System 1
 My green thumb came only as a result of the mistakes I made while learning to see things from the plant s point of view. -H. Fred Ale Nervous System 1 Classroom Rules You'll get one warning, then you'll
My green thumb came only as a result of the mistakes I made while learning to see things from the plant s point of view. -H. Fred Ale Nervous System 1 Classroom Rules You'll get one warning, then you'll
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Chapter 16. Sense of Pain
 Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
