Fertilization: Beginning a New New Organism Or
|
|
|
- Daniel Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fertilization: Beginning a New Organism
2 1. Contact and recognition between sperm and egg. In most cases, this ensures that the sperm and egg are of the same species. 2. Regulation of sperm entry into the egg. Only one sperm can ultimately fertilize the egg. This is usually accomplished by allowing only one sperm to enter the egg and inhibiting any others from entering. 3. Fusion of the genetic material of sperm and egg. 4. Activation of egg metabolism to start development.
3 Initial observations of sperm and views of germ cells function (17C) Sperm had been accepted as one of the parasites (Spermatozoa) Sperm acts like a seed that t contain all vital information, while egg provides nutrients grow sperm s vital information. Homunculus (Figure 7.1) Revisiting the function of sperm in reproduction (19C) Spallanzani suggested that sperm itself is not enough, while egg contains all information that can be activated by sperm. Prevost and Dumas found sperm enters into egg and contribute materially to the next generation. In late 1800 s, Hertwig and Fol observed the union between sperm and egg s nuclei. The human infant preformed in the sperm, as depicted d by Nicolas Hartsoeker (1694).
4 The statue to Spallanzani has him examining a frog through a magnifying g glass.
5
6 The modification of a germ cell to form a mammalian sperm (Part 1)
7 The modification of a germ cell to form a mammalian sperm (Part 2)
8 The modification of a germ cell to form a mammalian sperm (Part 3)
9 The modification of a germ cell to form a mammalian sperm (Part 4) Acrosome (Proacrosin-GFP) Nucleus/mitochondria/mictotubule
10 The motile apparatus of the sperm 9+2 structure
11 The motile apparatus of the sperm (Part 2) The movements of cilia and flagella result from the sliding of outer microtubule doublets relative to one another, powered by the motor activity it of the axonemal dyneins. Dyneins provide driving force for microtubules and vend the flagella with their ATPase activity.
12 Movement of microtubules in cilia and flagella Kartagener triad
13 Proteins Ribosomes and trna Messenger RNA Morphogenetic p g factors Protective chemicals. Structure of the sea urchin egg during fertilization. The drawing also shows the relative sizes of egg and sperm. (After Epel 1977.)
14
15 The sea urchin egg cell surface.
16 Hamster eggs immediately before fertilization.
17 1. The chemoattraction of the sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg 2. The exocytosis of the acrosomal vesicle to release its enzymes 3. The binding of the sperm to the extracellular l envelope (vitelline layer or zona pellucida) of the egg 4. The passing of the sperm through this extracellular envelope 5. Fusion of egg and sperm cell plasma membranes
18 External Fertilization in Sea Urchins How can sperm and eggs meet in such a dilute concentration? ---species-specific attraction of sperm How can sperm be prevented from trying to fertilize eggs of p p y g gg another species? ---species-specific sperm activation
19 20 s 40 s Figure Sperm chemotaxis in Arbacia. 60 s 70 s 90 s Effect of 10 nm resact on A. punctulata tlt spermatozoa
20 Comparison of the effects of (a)100 nm resact and (b)10 m speract on A. punctulata p ( ) ( ) p p spermatozoa.
21 Model for chemotactic peptides in sea urchin sperm
22
23 Fusion Extension Acrosomal reaction in sea urchin sperm.
24 Species-specific binding of acrosomal process to egg cell surface in sea urchins.
25 Localization of bindin on the acrosomal process.
26 Bindin receptors on the egg.
27 Bindin receptors on the egg (Part 2)
28 Scanning electron micrographs of the entry of sperm into sea urchin eggs.
29 Aberrant development in a dispermic sea urchin egg (Part 1) Why can only one sperm enter into the egg? To prevent improper numbers of chromosomes in daughter cells.
30 Aberrant development in a dispermic sea urchin egg (Part 2)
31 Membrane potential of sea urchin eggs before and after fertilization
32 Membrane potential of sea urchin eggs before and after fertilization 490 mm Na mm Na+
33 Formation of the fertilization envelope and removal of excess sperm
34 Cortical granule exocytosis (Part 1)
35 Cortical granule exocytosis (Part 2)
36 Cortical granule exocytosis (Part 3)
37 Wave of calcium release across sea urchin eggs during fertilization.
38 Endoplasmic reticulum surrounding cortical granules in sea urchin eggs.
39
40
41 Model of possible pathway of egg activation in the sea urchin.
42 The roles of inositol phosphates in releasing calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum and the initiation of development
43 A burst of protein synthesis at fertilization uses mrnas stored in the oocyte cytoplasm.
44 Fusion of genetic material Sperm s nucleus and centriole separate from the mitochondria and dflagellum. ll The sperm nucleus undergoes dramatic decondensation to form pronucleus. Nuclear envelope vesiculates into small packets, and the sperm s s proteins associated with condensed chromosomes are exchanged by egg s to decondensate chromosomes. Phosphorylation of lamin and histones by PKA after the binding to glycoprotein in the egg jelly. Rotation of male pronucleus results in the localization of centriole between male and female nuclei
45 Nuclear events in the fertilization of the sea urchin (Part 1)
46 Nuclear events in the fertilization of the sea urchin (Part 2)
47 Nuclear events in the fertilization of the sea urchin (Part 3)
48
49
50 1. The sperm cell membrane is altered by the removal of cholesterol l byalbumin proteins ti in the female reproductive tract. 2. Particular proteins or carbohydrates on the sperm surface are lost during capacitation. 3. The membrane potential of the sperm cell membrane becomes more negative as potassium ions leave the sperm. 4. Protein phosphorylation h occurs. 5. The outer acrosomal membrane changes and comes into contact with sperm cell membrane in a way that prepares it for fusion.
51
52 Mouse ZP3 as the zona protein that binds sperm.
53 Acrosomal reaction in hamster sperm.
54 Entry of sperm into golden hamster egg.
55 Nature 434, (10 March 2005)
56 Fusion of genetic materials Sperm pronucleus migrate tangentially to the surface of the egg Glutathione in the egg cytoplasm reduces disulfide bonds among protamines to uncoil sperm chromosome. Proteolysis of cyclin B and securin, with the subsequent degradation of cohesin holding metaphase chromosomes, is induced by Ca2+ release. The rest of sperm components in fertilized egg cytoplasm, such as mitochondria and other trace cytoplasmic content, except centromere is degraded d d
57 Pronuclear movements during human fertilization
58 Summary of events leading to fusion of egg & sperm plasma membranes
Developmental Biology Biology Fertilization. October 19, 2006
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Fertilization October 19, 2006 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Fertilization October 19, 2006 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology. Fertilization. June 24, 2009
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Fertilization June 24, 2009 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg cytoplasm
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Fertilization June 24, 2009 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg cytoplasm
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology. Fertilization. October 18, 2007
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Fertilization October 18, 2007 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Fertilization October 18, 2007 Fertilization Fertilization accomplishes two things: Sex (combining genes from two genomes) Reproduction (initiates reactions in the egg
Development: is the growth of an individual organism from a simple to a more complex or mature level. A slow process of progressive change
 1. Define the following terms (use your own words): development, growth, differentiation, histogenesis, organogenesis, morphogenesis, reproduction, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism. Development:
1. Define the following terms (use your own words): development, growth, differentiation, histogenesis, organogenesis, morphogenesis, reproduction, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism. Development:
Definition of Fertilization
 Fertilization Definition of Fertilization is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which eventually
Fertilization Definition of Fertilization is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which eventually
Bi-potent Gonads. Sex Determination
 יצירת הגונדות Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) Somatic cells Genital ridge Bi-potent Gonads Sex Determination Testis and Sperm Ovary and Oocyte Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in the Chick Embryo The
יצירת הגונדות Primordial Germ Cells (PGCs) Somatic cells Genital ridge Bi-potent Gonads Sex Determination Testis and Sperm Ovary and Oocyte Migration of Primordial Germ Cells in the Chick Embryo The
Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species.
 Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species. www.uchsc.edu/ltc/fertilization.html Fertilization union of sperm and egg Is a chain of events. Interruption of any step
Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species. www.uchsc.edu/ltc/fertilization.html Fertilization union of sperm and egg Is a chain of events. Interruption of any step
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology. October 11, Multiple choice (one point each)
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Name: Key Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005 Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Primordial germ cells a. are immortal b. produce polar bodies c. are haploid d. are somatic
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Name: Key Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005 Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Primordial germ cells a. are immortal b. produce polar bodies c. are haploid d. are somatic
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Animal Development. Lecture 3. Germ Cells and Sex
 Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
ECOL /14/2016. Evolution of Animal Form & Function. Dr Alex Badyaev. Lecture The interaction of egg and sperm:
 Evolution of Animal Form & Function Dr Alex Badyaev Lecture 18 2016 ECOL 330 The interaction of egg and sperm: 1. Chemo attraction of the sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg The interaction
Evolution of Animal Form & Function Dr Alex Badyaev Lecture 18 2016 ECOL 330 The interaction of egg and sperm: 1. Chemo attraction of the sperm to the egg by soluble molecules secreted by the egg The interaction
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Internal Fertilization
 Internal Fertilization Fertilization which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilization(the union of the gametes within the female body after insemination) Occurs in the widest part
Internal Fertilization Fertilization which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilization(the union of the gametes within the female body after insemination) Occurs in the widest part
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Derived copy of Fertilization *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56433 1 Derived copy of Fertilization * Stephanie Fretham Based on Fertilization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m56433 1 Derived copy of Fertilization * Stephanie Fretham Based on Fertilization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology
 3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
Biology Developmental Biology Spring Quarter Midterm 1 Version A
 Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Spring Quarter 2013 Midterm 1 Version A 75 Total Points Open Book Choose 15 out the 20 questions to answer (5 pts each). Only the first 15 questions that are answered
Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Spring Quarter 2013 Midterm 1 Version A 75 Total Points Open Book Choose 15 out the 20 questions to answer (5 pts each). Only the first 15 questions that are answered
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Molecular BASIS OF FERTILIZATION
 COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY PRESENTATION ON: Molecular BASIS OF FERTILIZATION By TEKETEL ERISTU Kediso 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Fertilization Types of Fertilization Cellular
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY PRESENTATION ON: Molecular BASIS OF FERTILIZATION By TEKETEL ERISTU Kediso 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Fertilization Types of Fertilization Cellular
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
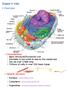 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 3
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 3 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Chapter 2: The Cell. Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College
 Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy
 7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
7.4 - Translation 7.4.1 - Explain that each trna molecule is recognised by a trna-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the trna, using ATP for energy Each amino acid has a specific trna-activating
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. RPTSE Biology Fall 2015, Dr. Jong B. Lee 1. Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Biology and Society: Antibiotics: Drugs that Target Bacterial Cells Antibiotics were first isolated from mold in 1928. The widespread use of antibiotics drastically decreased
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
