Histological Observations on the Infundibulum of Kuttanad Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestics) during Postnatal Period
|
|
|
- Britton Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Histological Observations on the Infundibulum of Kuttanad Duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestics) during Postnatal Period Patki H. S *, Lucy K. M **, Chungath J. J ** * Part of MVSc Thesis submitted to Kerala Agricultural University, Thrissur, Kerala ** Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Mannuthy, Thrissur , Kerala. Abstract- Postnatal histological development of infundibulum of the oviduct in the Kuttanad duck (Anas Platyrhynchos domesticus) was studied using 78 ducks in different stages of development from day-old to 24th week of age. In the day-old ducklings, the cranial end of the undifferentiated oviduct corresponded to the infundibulum with no distinct differentiation into different tunics. At 12th week of age, tubular glands first appeared in the lamina propria of the neck region which was accompanied by ciliogenesis. Goblet cells increased in number in the lining epithelium of the caudal most region of the neck of the infundibulum, at 24th week of age. At this age, the proprial glands in the neck of the infundibulum were large in diameter, which increased in number as well as width gradually and attained maximum width. In all the age groups, lamina propria of the funnel region of the infundibulum was devoid of any glands and the mucosal folds in the funnel were shorter than that of neck region. Tunica mucosa occupied the maximum thickness followed by the tunica muscularis and tunica serosa respectively. Index Terms- Postnatal development, Histology, Infundibulum, Oviduct and Kuttanad duck K I. INTRODUCTION erala is the home tract for Kuttanad breed of ducks which are well known for their attractive egg size and high disease resistance (Jalaludeen et al., 2004). In order to ensure persistent and maximum production and to evolve better managemental practices, it is essential to have in depth knowledge on the developmental aspects of the reproductive tract. In birds, infundibulum plays key functional role in capture and transfer of ovum as well as in formation of chalazae. In general it consisted of two regions viz., a wide slit like funnel region cranially which continues as tubular neck region caudally. Although investigations encompassing gross as well as histological aspects have been conducted on the infundibulum of the oviduct in wide variety of birds including domestic fowl (Aitken and Johnston, 1963; Hodges, 1974; King, 1975 and Nickel et al., 1977), Japanese quail (Lucy and Harshan, 1999) and turkey and pigeon (Mohammadpour and Keshtmandi, 2008), information regarding the developmental changes in the histomorphology of the infundibulum in Kuttanad duck is scanty. Hence, the present work was undertaken to envisage the age related changes in the infundibulum with respect to its histoarchitecture during postnatal period in Kuttanad ducks. II. MATERIALS AND METHODS In all, 78 Kuttanad ducks were used for the present study. The birds were selected randomly from a single hatch and reared at the University Poultry Farm, Mannuthy under semi- intensive system of management. Feed and water were provided ad lib. The study was carried out in birds of different age groups, ranging from day-old to 24 weeks. The material was collected from six birds in each group at fortnightly intervals. After recoding the gross features, the material was fixed in neutral buffered formalin. Different segments of the oviduct were processed and paraffin sections of 5 m thickness were taken for histological studies. Routine staining technique such as Haematoxylin and Eosin staining method as described by Luna (1968) was followed. Micrometric observations were done by using ocular micrometer. III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In the day-old ducklings, the cranial end of the undifferentiated oviduct corresponded to the infundibulum and consisted of the innermost epithelium and subepithelial tissue (Fig. 1). The oviduct wall was not differentiated into different tunics distinctly. The lumen was flanked by characteristic low mucosal folds which were lined by simple columnar epithelium. The total number of mucosal folds was in the range of 10 to12. Caudally number of folds increased upto 16 to 18. The subepithelial connective tissue was made up of densely packed cells with fine collagen fibres and was rich in capillaries. Both dorsal as well as ventral ligaments were attached to the oviduct and were abundantly supplied by blood vessels. Ventral ligament showed the presence of smooth muscle fibres (Fig. 2). These observations are in accordance with the observations made by Lucy and Harshan (1999) in Japanese quail. At two weeks of age, the secondary mucosal folds started appearing in the cranial end of the undifferentiated oviduct corresponding to the infundibulum. By 6 th week, a very thin tunica muscularis appeared as a single layer. At 12 th week of age, tubular glands first appeared in the lamina propria of the neck region (Fig.3). In Japanese quail, glands could be first located at the age of 40 days (Lucy and Harshan, 1999).
2 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Ciliogenesis in the infundibulum began at this age and the lining epithelium also showed presence of few non-ciliated glandular cells and occasional vacuolation. Such extensive ciliation was also noticed by Mohammadpour and Keshtmandi (2008) who speculated that, the rhythmic beating of these cilia and the gross oblique arrangement of the mucosal folds created a vortex to pull and transport the egg. At 14 th week, neck region of the infundibulum showed rapid development of the mucosal folds into primary, secondary and tertiary folds with consequent increase in their height and width. Total number of mucosal folds was about 15 to 16. At this stage funnel region also showed development of secondary folds (Fig. 4). However, the mucosal folds in the funnel were shorter than that of neck region. Tunica muscularis of infundibulum was thinner than more caudal segments of the oviduct. In the adult Kuttanad duck (20 weeks of age), there were four types of epithelial cells in the mucosa of infundibulum namely predominant non-secretory ciliated cells; non-ciliated mucous-secreting goblet cells found in between the ciliated cells; secretory cells other than goblet cells which were located in the glandular grooves and lining cells of the tubular glands of the caudal region of the infundibulum (Figs. 5 and 6). These results are in total agreement with those of Aitken and Johnston (1963) in domestic fowl. Lamina propria of the funnel region of the infundibulum was devoid of any glands and contained collagen fibres along with fine reticular and a few elastic fibres as reported by Lucy and Harshan (1999) in Japanese quail. In differentiated oviduct, the lining epithelium at the opening of the lips of the funnel was low columnar ciliated type which rapidly changed into tall ciliated columnar in the distal funnel and neck of the infundibulum. Similar observations were also made in pigeon by Dominic (1960) and Hodges (1974) in domestic fowl. Ciliated cells possessed oval nuclei lying at or above the centre of the cell. Goblet cells showed a basal nucleus and apical granular cytoplasm. Similar findings were also documented by Hodges (1974) and Naragude et al. (1999) in domestic fowl, Lucy and Harshan (1999) in Japanese quail and Moraes et al. (2007) in nothura spotted quail and Das and Biswal (1968), Rao (1994) and Ozen et al. (2009) in duck. The formation of tubular glands was in accordance with observations made by Bradley and Grahame (1960) in domestic fowl. In the neck of the infundibulum the more complex mucosal folds with deeper glandular grooves eventually gave rise to small tubular glands from their corners (Fig. 6). The deeper regions of the mucosal folds where the transformation of glandular grooves into tubular glands occurred, the lining cells lacked cilia and were cuboidal with eosinophilic supranuclear cytoplasm. The proprial glands were lined by cuboidal to columnar cells with indistinct boundaries, basally located light stained round nuclei, eosinophilic supranuclear cytoplasm and enclosed a large lumen. The proprial glands in the neck of the infundibulum were large in diameter, which increased in number as well as width gradually and attained maximum width at 24 th week of age (Fig. 7). In the caudal most region of the neck of the infundibulum, goblet cells increased in number in the lining epithelium (Fig. 8). The funnel region showed mainly primary mucosal folds with some secondary folds. The depth of longitudinally oriented low mucosal folds appeared to increase as the funnel approached the neck region whereas within the neck of the infundibulum, the spirally oriented longitudinal folds increased in depth and gave rise to numerous secondary and tertiary folds. Among different segments of the oviduct, the infundibulum showed the least height and width of mucosal folds throughout the postnatal period. Similar observations were also made by Khokhlov and Kuznetcov (2007) in the domestic fowl. Different micrometric parameters of the Infundibulum of the oviduct in Kuttanad Duck at 12 th, 18 th and 24 th week of age are as shown in table1. The mucosal folds in the funnel were shorter than that of neck region. The muscular tunic of the neck region was thicker than that of the funnel and was differentiated into ill defined inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle bundles (Fig. 9). At the infundibulum-magnum junction, both the mucosal and muscular layers increased in thickness and structural complexity. These results are in total agreement with those of Hodges (1974) and Gilbert (1979) in domestic fowl and Lucy and Harshan (1999) in Japanese quail. The collagenous serosal tunic was found to be thin with folds, blood vessels and nervous plexuses. Distinct serosal tunic was visible only in adult birds (Fig. 9). In adult birds, analysis of the wall of the infundibulum revealed that tunica mucosa occupied the maximum thickness (81%) followed by the tunica muscularis (16%) and tunica serosa (3%). In domestic fowl, as reported by Khokhlov (2008), similar relationship between percentage contribution of different tunics was observed except the fact that tunica mucosa was comparatively thinner (64%). REFERENCES [1] Aitken, R. N. C. and Johnston, H. S Observations on the fine structure of the infundibulum of the avian oviduct. J. Anat. 97: [2] Bradley, O. C. and Grahame, T The Structure of the Fowl. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh, 155p. [3] Das, L. N. and Biswal, G Microanatomy of the reproductive tract of domestic duck (Anas boschas). Indian Vet. J. 45: [4] Dominic, C. J The secretory activity of the funnel of the avian oviduct. Current Sci. 29: [5] Gilbert, A. B Female Genital Organs. In: Form and Function in Birds. A. S. King and J. Mc Lelland (Eds.). Academic Press, New York, pp [6] Hodges, R. D The Histology of the Fowl. Academic Press, London, 648p. [7] Jalaludeen, A., Peethambaran, P. A., Leo, J. and Manomohan, C. B Duck Production in Kerala. NATP on Ducks, COVAS, KAU, Mannuthy. 44p. [8] Khokhlov, R. YU Morphology of an Infundibulum of the oviduct of the sexually mature hens. Int. J. Morphol. 26(4): [9] Khokhlov, R. YU. and Kuznetcov, S. I Morphogenesis of a tunica mucosa of oviduct of the hens. Int. J. Morphol. 25 (2): [10] King, A. S Aves - Urogenital system. In: Sisson and Grossman s the Anatomy of the Domestic Animals. Getty, R. (ed.). Vol. 2. Fifth edition. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia pp [11] Lucy, K. M. and Harshan, K. R Structure and development of infundibulum in Japanese quail. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 34 (2): [12] Luna, L. G Manual of Histological Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Third edition. Mc Graw-Hill Book Company, New York, 258p. [13] Mohammadpour, A. A. and Keshtmandi, M Histomorphological study on infundibulum and magnum in turkey and pigeon. World J. Zool. 3 (2):
3 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January [14] Moraes, C., Artoni, S. M. B., Oliveira, D. Pacheco, M. R., Amoroso, L. and Franzo, V. S Morphology and morphometry of Nothura maculosa quail oviduct. Ciência Rural, Santa Maria. 37 (1): [15] Naragude, H. B., Mugale, R. R., Bhosale, N. S. and Gayake, H. P Age related changes in the morphology and morphometry of avian oviduct. Indian J. Vet. 76: [16] Nickel, R., Schummer, A. and Sieferle, E Anatomy of the Domestic Birds. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin, 202p. [17] Ozen, A., Ergun, E. and Kurum, A Light and electron microscopic studies on the oviduct epithelium of the Pekin duck (Anas platyrhynchos). Ankara Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg., 56: [18] Rao, T. S. C Microanatomical studies on the reproductive system of the Domestic Duck (Anas boschas domesticus). Doctor of Philosophy in Anatomy. Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Madras. 145p. AUTHORS First Author Patki, H. S., PhD Scholar, Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Mannuthy, Thrissur , Kerala. author hpatki@gmail.com Second Author Lucy, K.M., Associate Professor, Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Mannuthy, Thrissur , Kerala. author drlucykm@yahoo.co.in Third Author Chungath, J. J., Professor, Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Mannuthy, Thrissur , Kerala. author jjchungath55@gmail.com Correspondence Author Patki, H. S., PhD Scholar, Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Mannuthy, Thrissur , Kerala. *Corresponding author hpatki@gmail.com Table 1. Different micrometric parameters of the Infundibulum of the oviduct in Kuttanad Duck at 12 th, 18 th and 24 th week of age (In µm as Mean ± S.E.) Sr. Region of the At 12 th week At 18 th week At 24 th week No. Infundibulum 1 Funnel (In µm) Mean ± S.E. Ciliated Epithelium ± ± ± 0.87 Goblet cell ± ± ± 1.11 Height of mucosal fold ± ± ± 5.69 Width of mucosal fold ± ± ± 2.85 Tunica muscularis ± ± ± Neck (In µm) Mean ± S.E. Ciliated Epithelium ± ± ± 0.74 Goblet cell ± ± ± 0.00 Diameter of gland ± ± ± 0.03 Lumen of gland ± ± ± 0.10 Gland cells ± ± ± 0.10 Height of mucosal fold ± ± ± Width of mucosal fold ± ± ± 2.85 Tunica Muscularis ± ± ± 2.85 Legend to figures Fig. 1 C. S. of cranial region of the oviduct (day-old). H & E. x Epithelium 2. Sub-epithelial connective tissue 3. Mucosal fold Fig. 2 C. S. of oviduct with ventral ligament (day-old). H & E. x Wall of oviduct 2. Ventral ligament with smooth muscles Fig. 3 C. S. of funnel of infundibulum showing low mucosal folds (12 weeks). H & E. x Lamina epithelialis 2. Lamina propria without glands 3. Vessels 4. Tunica muscularis Fig. 4 C. S. of funnel of infundibulum showing mucosal folds (14 weeks). H & E. x Lamina epithelialis 2. Cilia 3. Lamina propria 4. Lymphocytes Fig. 5 C. S. of infundibular neck (20 weeks). H & E. x100
4 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Lamina epithelialis 2. Lamina propria 3. Tunica muscularis 4. Serosa Fig. 6 C. S. of infundibular neck showing glandular groove (20 weeks). H & E. x Lamina epithelialis 2. Glandular groove 3. Lamina propria 4. Tunica muscularis Fig. 7 C. S. of infundibular neck with tubular glands (24 weeks). H & E. x Lamina epithelialis with ciliated cells 2. Lamina propria 3. Gland 4. Tunica muscularis Fig. 8 C. S. of caudal most region of infundibular neck showing goblet cells (24 weeks). H & E. x Lamina epithelialis 2. Tubular glands in lamina propria 3. Goblet cells Fig. 9 C. S. of infundibular neck showing outer layers (24 weeks). H & E. x Tunica muscularis 2. Serosa Fig.1
5 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Fig.2 Fig.3
6 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Fig. 4 Fig. 5
7 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Fig. 6 Fig. 7
8 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 1, January Fig. 8 Fig. 9
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS)
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS) A.D.Firdous and K.M. Lucy Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE THYROID GLAND IN FEMALE KUTTANAD DUCK (ANAS PLATYRHYNCHOS DOMESTICUS) A.D.Firdous and K.M. Lucy Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology, College of Veterinary and
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep
 DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
DOI: 10.30954/2277-940X.2018.00150.20 Journal of Animal Research: v.8 n.1, p. 125-129. February 2018 Biometrical, Histological and Histochemical Studies on Omasum of Gaddi Sheep Shabir Ahmad Malik 1*,
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Behzad Mobini* Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran. Received: 25 October 2010, Accepted: 4 January 2011
 Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
SUMMARY. Keywords: quail, Coturnix japonica, morphology, ovary, oviduct, neurotrophins, immunohistochemistry
 SUMMARY Keywords: quail, Coturnix japonica, morphology, ovary, oviduct, neurotrophins, immunohistochemistry Studies on the development of biological systems have expanded using animal models, always to
SUMMARY Keywords: quail, Coturnix japonica, morphology, ovary, oviduct, neurotrophins, immunohistochemistry Studies on the development of biological systems have expanded using animal models, always to
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Geese ovary and oviduct from an Anatomical and Histological point of view. Hanaa Kareem Ali Alshammary*, Ammar Ismail Jabar, and Rabab
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Geese ovary and oviduct from an Anatomical and Histological point of view. Hanaa Kareem Ali Alshammary*, Ammar Ismail Jabar, and Rabab
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE FEMUR, TIBIOTARSUS AND FIBULA OF PEAHEN (Pavo cristatus)
 MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE FEMUR, TIBIOTARSUS AND FIBULA OF PEAHEN (Pavo cristatus) A.R. Sreeranjini 1, N. Ashok, V. R. Indu, K. M. Lucy, S. Maya and K.V. Syam Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE FEMUR, TIBIOTARSUS AND FIBULA OF PEAHEN (Pavo cristatus) A.R. Sreeranjini 1, N. Ashok, V. R. Indu, K. M. Lucy, S. Maya and K.V. Syam Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE LYMPHOID TISSUES OF BROILER CHICKENS. S. H. Akter*, M. Z. I. Khan, M. R. Jahan, M. R. Karim and M. R.
 Bangl. J. Vet. Med. (2006). 4 (2): 87 92 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE LYMPHOID TISSUES OF BROILER CHICKENS S. H. Akter*, M. Z. I. Khan, M. R. Jahan, M. R. Karim and M. R. Islam Department of Anatomy
Bangl. J. Vet. Med. (2006). 4 (2): 87 92 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE LYMPHOID TISSUES OF BROILER CHICKENS S. H. Akter*, M. Z. I. Khan, M. R. Jahan, M. R. Karim and M. R. Islam Department of Anatomy
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS *
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 42 (1) : 23-28, 2008 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS * K. M. Lucy, K.R. Harshan 1, J.J. Chungath and N. Ashok 2 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
Indian J. Anim. Res., 42 (1) : 23-28, 2008 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE CRANIAL MENINGES IN GOATS * K. M. Lucy, K.R. Harshan 1, J.J. Chungath and N. Ashok 2 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE MAJOR LYMPHOID TISSUES IN INDIGENOUS DUCKLINGS OF BANGLADESH
 Bangl. J. Vet. Med. (2011). 9(1): 53 58 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE MAJOR LYMPHOID TISSUES IN INDIGENOUS DUCKLINGS OF BANGLADESH N. Sultana*, M. Z. I. Khan, M.A. Wares and M.A. Masum Department of
Bangl. J. Vet. Med. (2011). 9(1): 53 58 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE MAJOR LYMPHOID TISSUES IN INDIGENOUS DUCKLINGS OF BANGLADESH N. Sultana*, M. Z. I. Khan, M.A. Wares and M.A. Masum Department of
Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research, Shiraz University, Vol. 13, No. 1, Ser. No. 38, 2012
 Histological and histomorphometrical changes of different regions of oviduct during follicular and luteal phases of estrus cycle in adult Azarbaijan buffalo Ayen, E. 1* ; Shahrooz, R. 2 and Kazemie, S.
Histological and histomorphometrical changes of different regions of oviduct during follicular and luteal phases of estrus cycle in adult Azarbaijan buffalo Ayen, E. 1* ; Shahrooz, R. 2 and Kazemie, S.
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS)
 Indian J. Anim. Res., 38 (2): 102-106, 2004 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS) H.C. Kalita and P.C. Kalita Department
Indian J. Anim. Res., 38 (2): 102-106, 2004 COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE VOMERO-NASAL ORGAN IN MITHUN (BOS FRONTAUS), YAK (BOS GRUNNIENS) AND ZEBU (BOS INDICUS) H.C. Kalita and P.C. Kalita Department
MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE GALL BLADDER OF THE CHUKAR PARTRIDGE (ALECTORIS CHUKAR)
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 2, 73 78 MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF TH GALL BLADDR OF TH CHUKAR PARTRIDG (ALCTORIS CHUKAR) Summary B. MOBINI Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Islamic Azad
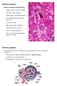
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface
 Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Epithelium Characteristics cont. 2. Apical Surface always has one exposed (apical) surface Some surfaces are smooth & slick, others may have: microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane; increase
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 4, 2017, 2706 2711 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE MICROANATOMICAL FEATURES OF THE RENAL CORTEX IN EMU (Dromaius novaehollandiae)
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Anatomy PHL 212. Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan. -
 Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN:
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues
 Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
The Tissue Level of Organization Study of this lecture is to be accomplished in conjunction with the Histology Module on the Web!! 1. Introduction Cell Tissue Histology A. General Tissue Types i. Epithelial
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
abstract Key words: Hard palate, Tongue, Buccal floor, Sambar deer, Gross anatomy
 Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
Gross anatomical studies on the hard palate, tongue and buccal floor in sambar deer (Cervus unicolor) a.r sreeranjini 1, c.v rajani 2 and n. ashok 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology College
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY
 Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space
 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB
 PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES ON THE ADRENAL GLAND OF HORSE
 Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Indo-Am. J. Agric. & Vet. Sci., 2016 ISSN Prasanth 2321 9602 Babu www.iajavs.com A et al., 2016 Vol. 4, No. 1, February 2016 2016 Meghana Publications. All Rights Reserved Research Paper HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
GROSS ANATOMY OF THE THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS IN INDIAN GRAY MONGOOSE (HERPESTES EDWARDSII)
 GROSS ANATOMY OF THE THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS IN INDIAN GRAY MONGOOSE (HERPESTES EDWARDSII) *Mina Tadjalli M 1 and Abbas Faramarzi 2 1 Department of Anatomical Science, School of Veterinary Medicine,
GROSS ANATOMY OF THE THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS IN INDIAN GRAY MONGOOSE (HERPESTES EDWARDSII) *Mina Tadjalli M 1 and Abbas Faramarzi 2 1 Department of Anatomical Science, School of Veterinary Medicine,
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Ductus Deferens-a Comparative Histology in Mammals
 163 J Anat. Soc. India 52(2) 163-165 (2003) -a Comparative Histology in Mammals Khan, Aijaz, A., Zaidi, M.T; Faruqi, N.A. Department of Anatomy,J.N. Medical College,A.M.U. Aligarh, INDIA. Abstract. The
163 J Anat. Soc. India 52(2) 163-165 (2003) -a Comparative Histology in Mammals Khan, Aijaz, A., Zaidi, M.T; Faruqi, N.A. Department of Anatomy,J.N. Medical College,A.M.U. Aligarh, INDIA. Abstract. The
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Histological and histochemical studies on the reproductive tract of Kashmir faverolla chicken
 2017; 5(6): 2256-2262 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(6): 2256-2262 2017 JEZS Received: 18-09-2017 Accepted: 21-10-2017 Henna Wani Mohammad Maqbool Darzi Shayaib Ahmad Kamil Shakil Ahmad
2017; 5(6): 2256-2262 E-ISSN: 2320-7078 P-ISSN: 2349-6800 JEZS 2017; 5(6): 2256-2262 2017 JEZS Received: 18-09-2017 Accepted: 21-10-2017 Henna Wani Mohammad Maqbool Darzi Shayaib Ahmad Kamil Shakil Ahmad
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas in mature pigeon (Columba Livia)
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development
 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED
 RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED Abstract Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LIX () ISSN 065-95, ISSN Online 067-66, ISSN-L
RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED Abstract Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LIX () ISSN 065-95, ISSN Online 067-66, ISSN-L
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
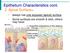
Upper Respiratory Histology
 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis
 DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2017.00167.X Journal of Animal Research: v.7 n.6, p. 1115-1121. December 2017 Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis Arup Kalita 1 *, Kabita Sarma 2, M.
DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2017.00167.X Journal of Animal Research: v.7 n.6, p. 1115-1121. December 2017 Gut Integrity of Neonatal Piglets: A Histomorphological Analysis Arup Kalita 1 *, Kabita Sarma 2, M.
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
Basic histology 5/4/2015
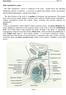 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Histology. Marcello Malpighi ( ) is regarded as Father of Histology.
 Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Dana Alrafaiah. Dareen Abu Shalbak. Mohammad Almuhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
2 Dana Alrafaiah Dareen Abu Shalbak Mohammad Almuhtaseb 1 P a g e Esophagus: A muscular tube that is 25 cm long, but if measured from the incisors it would be 45cm long. Extends from C6 of cervical vertebra,
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues. How do cells form tissues?
 Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Histological and Immunohistochemistry Studies of Trachea Calcification in the Laying Hens (Gallus gallusdomesticus)
 Histological and Immunohistochemistry Studies of Trachea Calcification in the Laying Hens (Gallus gallusdomesticus) Ahmed Mahdi Al- badri *, Asawer Abdul- Jabbar Al-Salman* *Wasit University, College of
Histological and Immunohistochemistry Studies of Trachea Calcification in the Laying Hens (Gallus gallusdomesticus) Ahmed Mahdi Al- badri *, Asawer Abdul- Jabbar Al-Salman* *Wasit University, College of
Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
 VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
VETERINARY RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL Journal homepage: www.jakraya.com/journal/vri ORIGINAL ARTICLE Histology, Histochemistry and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Tonsil of the Soft Palate of the Young Pigs
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to: Learn about the various types of tissues and their origins
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 4 The Tissue Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to: Learn about the various types of tissues and their origins
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
