1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Curtis Riley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested fdstuff cntributes t an increase in the verall weight f an animal, but it des nt becme an integral part f the structure r metablic activities f the animal, until it is absrbed smewhere thrugh the digestive tract. What is nt absrbed is discarded in the faeces as waste. The gastrintestinal tract prvides a cnduit thrugh which all fd has t pass. The first step in the use f such a cnduit is t acquire, chew and swallw the fd (Fig. 1-1). Prehensin Fd ingestin Masticatin / Chewing Deglutitin / Swallwing Figure 1-1. Stages f fd ingestin Prehensin Animals achieve this basic step thrugh the prcess f prehensin. Depending n the species and age, animals use different mdalities t ingest fd. There are specific anatmical adaptatins which permit an animal t ingest fd in a given manner (Fig. 1-2). Prehensin Mechanisms vary greatly with species Hrses and sheep use lips t manipulate and teeth t rip Cattle use tngue t manipulate, hard palate and lwer teeth t rip Carnivres use incisrs t cut and canines t rip Pultry uses beak r bill Figure 1-2. Mechanisms f prehensin On the website, vides 1-3 and 1-4 shw that bth hrses and sheep use their lips t manipulate the grass and their teeth t cut it. On the ther hand, cattle use their tngue t bring grass int their muth and the lwer teeth against the upper palate t cut the grass as shwn in Fig. 1-5 and vide 1-6). Prehensin by cattle Use the tngue t manipulate fd int the muth Use mbile lwer teeth and hard palate t press and tear Figure 1-5. Mechanisms f prehensin by cattle Avian species use their beak r bill t pick up fd. They d nt masticate the fd, but they d cver it with a mucus layer in rder t facilitate swallwing (Fig. 1-7). Masticatin Sme species require significant masticatin prir t swallwing, while thers, such as mst ruminants, masticate very little prir t swallwing. This strategy permits the cllectin f a significant vlume f fd in the rumen, and then, they start a prcess f ruminatin. Ruminatin cnsists f regurgitating prtins f the ingested fd t thrughly masticate it, t reduce the particle size. This activity is nrmally cnducted while the animal is resting in a recumbent psitin. Carnivres d nt significantly masticate their fd; instead, they depend n a very aggressive enzymatic digestin t reduce particle size. They nly masticate their fd enugh t reduce it t a swallwable size. Avian species d nt have teeth t masticate (Fig. 1-8). Masticatin Very imprtant in herbivres Nt imprtant in carnivres Nn existing in avian species Figure 1-8. Rle f masticatin in different species V BS 122 Physilgy II 1 Class f 2014
2 They depend n the prductin f mucus t cat the particles prir t swallwing, and then, they macerate the fd within a specialized rgan (the gizzard) that may cntain a variety f hard materials,\which the animal has purpsely ingested. Cmmnly ingested pebbles help, thrugh a grinding actin, in the reductin f the particle size. Herbivres masticate their fd nt nly t reduce the size f the particles but als t break the cellular wall f the fd material, thus permitting the access f digestive enzymes. Smaller particles als reduce the incidence f damage t the walls f the gastrintestinal tract (GIT) (Fig. 1-9). Deglutitin Once the fd has been masticated, it has t be swallwed. This prcess requires an initial vluntary stage which is t mve the blus twards the back f the ral cavity. Then, an invluntary reflex, which permits the passage f the blus frm the ral cavity t the esphagus withut entering the trachea and the respiratry system, is activated (Fig. 1-10). Mst f the time, an animal maintains an pen passage between the nse r muth t the trachea, thus permitting Masticatin in herbivres Reduce particle size Increases surface area Breaks cellulse membrane Lubricate fr swallwing Mix with saliva Expse t digestive enzymes Reduce excriatin f GIT Figure Anatmical cmpnents invlved in deglutitin Figure 1-9. Rle f masticatin in herbivres Deglutitin One vluntary initial stage Mvement f blus t back f ral cavity A pharyngeal stage (invluntary) Passage frm ral cavity t esphagus Esphageal stage (invluntary) Passage f fd int stmach Figure Steps invlved in deglutitin Figure Sequence f anatmical changes taking place during respiratin the passage f air int the lungs and minimizing the entrance f air int the digestive system (Figs. 1-11, 1-12). When there is fd t be swallwed, a passage frm the muth t the esphagus has t be created t permit V BS 122 Physilgy II 2 Class f 2014
3 mvement f the fd. This passage is achieved by the elevatin f the sft palate, which prevents the fd frm entering int the nasal cavity, and by the mvement f the epiglttis backwards, which blcks the entrance t the trachea and pens the passage twards the esphagus. All these changes, which take place in a very rapid sequence are invluntary and cnstitute the prcess f DEGLUTITION THE DIGESTIVE TRACT Mst related species have similar anatmical cmpnents in the digestive tract, with slight differences in size, shape and smetimes regulatin f the functin f each cmpnent. Basic anatmy The gastrintestinal wall is made up f several layers. The utermst sersa is lined by a muscular layer which lies lngitudinally t the tract and then the innermst layer f muscle cnsist f circular fibres. Twards the center is fund the submucsa and the mucsal layers (Fig. 1-14). Within the mucsa, there are a series f smth muscle fibres, which frm the muscularis mucsa. The muscle fibres are gruped in individual parallel bundles, cnnected t thers by multiple gap junctins alng its length. Each bundle is surrunded by cnnective tissue with a fusin Smth muscle Figure Sequence f anatmical changes taking place during deglutitin deglutitin (Fig. 1-13) at which time the respiratry prcess is temprarily suspended. Arranged in bundles cntaining ~ 1000 fibers Fibers cnnected electrically by gap junctins Each bundle is separated by cnnective tissue but they cntact each ther at discrete pints Functin as a syncytium Electric impulse travels in all directins Sme cnnectins between lngitudinal and circular smth muscle layers Figure Characteristic f the smth muscle in the digestive system pint in between, frming a netwrk f muscles functining as a syncytium (Fig. 1-15). Figure Main cmpnents fund thrughut the digestive tract. The figure represents a transversal cut f the small intestine Physilgy f the GIT The syncytium permits that an actin ptential, which is generated at sme pint, can mve in all directins. Furthermre, there are cnnectins between the lngitudinal and circulatry layers which permit the V BS 122 Physilgy II 3 Class f 2014
4 synchrnizatin f mvements t either mix r prpel the intestinal cntent. T cntrl the tne and the mtr activity f the gut, the membrane f the smth muscle is cntinuusly stimulated by intrinsic electrical activity in the frm f slw waves r spikes. Variatin in the changes f frequency f the membrane ptential creates the rhythm f the slw waves (range frm 3-12/min). What ultimately changes t create the slw waves is the membrane resting ptential (Fig. 1-16). Electrical stimulatin Cntinus slw intrinsic activity Slw waves Spikes Slw waves (3-12/min) result by changes in resting membrane ptential (range 5-15 mv) (frm -50 t - 35 mv) Cntrls spike ptential that initiates cntractin Last msec Spike ptentials True actin ptential Triggered when mre psitive than - 40 mv The higher the slw waves rise, the mre frequent spike ptentials ccur (1-10 /sec) ++ Triggered by CaP P influx thrugh calcium-sdium channels Slwer than sdium channels f nerve fibres Figure Cnditins required t trigger a spike ptential Figure Characteristic f the electrical activity in the intestinal tissue The cunterparts f this prcess are the factrs that trigger a spike. The resting membrane ptential f the smth muscle has t be larger than -40 mv. These spikes trigger a true actin ptential, which in turn cntrls cntractile activity. The spike ptential increases in frequency when the slw wave resting membrane ptential is higher (Figs. 1-17, 1-18). The mre deplarized the membrane becmes, the mre excitable it is and the mre chances it has f cntractile activity. The mechanism fr achieving this higher membrane ptential is presumed t be thrugh an influx f CaP++P thrugh calcium-sdium channels as ppsed t the faster sdium channels used by nerve fibres. Several factrs cntribute t the deplarizatin f the fibre s membranes. Physical distensin (stretching) f the muscle, usually due t the presence f fd in the tract; acetylchline stimulatin as well as parasympathetic Figure Characteristics f different membrane ptentials stimulatin by neurnes secreting acetylchline; and finally, several gastrintestinal hrmnes (Fig. 1-19). The cunterparts f this prcess are the factrs that cntribute t the hyper-plarizatin f the membranes. These are the effects f nerepinephrine r epinephrine n the membranes and the sympathetic stimulatin whse nerves secrete nrepinephrine (Fig. 1-20). V BS 122 Physilgy II 4 Class f 2014
5 Factrs deplarizing membranes (membrane ptential less negative) Stretching Acetylchline Parasympathetic stimulatin Mediated thrugh acetylchline Specific gastrintestinal hrmnes Figure Factrs making membrane ptential less negative Factrs hyperplarizing membranes (membranes ptential mre negative) Nrepinephrine r epinephrine n fibre membrane Sympathetic stimulatin Secreting nrepinephrine Figure Factrs making membrane ptential mre negative Regulatin f gut mtility Enteric nervus system. Regulatin f all cntractile and secretry activity is supprted by an independent nervus system imbedded in the wall f the gut. This system is called the enteric nervus system and it extends the length f the GIT starting in the esphagus. The ttal number f neurns is as large as thse fund in the spinal crd. The enteric nervus system is made up f tw plexuses: ne lcated between the lngitudinal and circulatry muscle layer called the Myenteric r Auerbach s plexus and the ther is fund in the sub mucsal layer and is called the sub mucsal r Meissner s plexus (Figs. 1-14, 1-21, 1-22). These tw are intercnnected in rder t synchrnize GIT functins. Mtility f the gut is primarily cntrlled by the myenteric plexus, while the secretry activity and bld flw are cntrlled mainly by the submucsal plexus. Enteric nervus system Lies in the gut wall Extends frm the esphagus t anus Has as many neurns as the spinal crd Made f tw plexuses Myenteric r Auerbach s plexus Situated between lng. and circ. muscle layer Submucsal r Meissner s plexus Situated in the submucsal layer Figure Characteristics f the enteric nervus system The enteric system is capable f cntrlling gastrintestinal functins independent f ther bdy functins. Hwever, n tp f being cnnected between themselves, the tw plexuses are further innervated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. This innervatin permits verall inhibitin r stimulatin f the gastrintestinal activities (Fig. 1-23). Enteric nervus system Myenteric plexus cntrls gastrintestinal mvement Submucsal plexus cntrls secretins and bld flw Innervated by sensry neurns frm the epithelium Cnnected t parasympathetic and sympathetic divisins Figure Rle f the enteric nervus system V BS 122 Physilgy II 5 Class f 2014
6 There are multiple mechanisms thrugh which the myenteric plexus cntrls mtr activity thrughut the gut (Fig. 1-24). and, as a result, there is an increase in peristaltic mvement. Althugh mst f the activities f the myenteric system are excitatry in nature, there are als sme inhibitry elements. These elements are believed t be mediated thrugh the release f peptides; the mst plausible candidates are thse with vasactive intestinal plypeptide (VIP). The actin f these peptides appears t be fcused in inhibiting sphincter activity (pylric and ilececal), thus mdifying the rate f fd passage int the dudenum and cecum respectively. The submucsal plexus in turn cntrls secretry, absrptive and cntractile activity in very small discrete sectins f the GIT (Fig. 1-25). Submucsal plexus Figure Innervatins f the intestinal muscle by the enteric nervus system, sympathetic and parasympathetic Myenteric plexus Cntrls mtr activity alng the gut Increases tnic cntractin r tne f gut wall Increases intensity f rhythmical cntractins Increases rhythm Increases velcity, thus mre peristalsis Has sme inhibitry neurns Secrete VIP Cntrls sphincter activity Figure Rle f the myenteric plexus Cntrls the functin f small sectins f the intestine Signal frm epithelium t SMP cntrls Lcal secretin Lcal absrptin Lcal cntractin Regulate flding f gastrintestinal mucsa Figure Rle f the submucsal plexus The apprpriate respnse is usually prepared and implemented by a signal that is generated by sensrs in the epithelium f the gut which then is cnveyed t the submucsal. Neurtransmitters. A large number f neurtransmitters (Fig. 1-26) have been identified as participating in the regulatin f gastrintestinal activity, but their specific rles are yet t be determined. The myenteric plexus can increase the tnic cntractin f the intestinal wall as well as the intensity and the rate with which the rhythmical cntractins take place. Finally, stimulatin f the myenteric system can result in faster cnductin f excitatry waves alng the intestinal wall V BS 122 Physilgy II 6 Class f 2014
7 Acetylchline Nrepinephrine Neurtransmitters Mainly excites GI activity Usually inhibits GI activity Adensine triphsphate (ATP) Sertnin Vasactive intestinal plypeptide (VIP) Smatstatin (SS) Leu-enkephalin Met-enkephalin Bmbensin Figure Neurtransmitters invlved in regulatin f gastrintestinal activity Gastrintestinal reflexes. The verall regulatin f gastrintestinal functin is based n reflexes cntrlled by the enteric, sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are reflexes which are integrated within the enteric system and are respnsible fr secretin as well as fd mixing and peristalsis f the GIT (Fig. 1-27). Other types f reflexes transmit infrmatin thrugh lng distances in the GIT. They require the participatin f the gut as the starting pint, integratin in the sympathetic ganglia and respnse by anther sectin f the gut. Amng these we find the gastrclic reflex which is respnsible fr the evacuatin f the cln; the entergastric reflex which invlves the participatin f the small intestine, and the cln which sends signals t reduce stmach mtility and its secretin; and the clnileal reflex which signals frm the cln t reduce r prevent emptying f ileal cntents int the cln. There is still anther type f reflex which invlves the larger trajectry frm the gut t the spinal crd and / r brain and back t the GIT. Thrugh this type f reflex the dudenum, based n the rate at which it receives fd, is capable f cntrlling gastric mtr and secretry activity. In additin, reflexes that invlve pain use these mechanisms t reduce verall gastrintestinal activity. Finally, faeces accumulatin in the cln triggers the defecatin reflex via signals sent t the spinal crd and Gastrintestinal reflexes Integrated cmpletely within the enteric system and cntrls Secretin, peristalsis, lcal mixing Gut-sympathetic ganglia-gut Gastrclic reflex Prmtes cln evacuatin Entergastric reflex Prevents stmach mtility and emptying Clnileal reflex Inhibits ileal emptying Gut-spinal crd / brain-gut Uses vagus nerve Frm stmach and dudenum Cntrls gastric mtr and secretry activity Pain reflexes Inhibits gastrintestinal activity Defecatin reflex Prmtes clnic rectal and abdminal cntractin Figure Reflexes f the gastrintestinal tract back resulting in cntractin f the cln, rectum and abdmen in rder t defecate. As hinted earlier, many hrmnes influence different aspects f mtility f the GIT and sme influence bth mtility and secretin f the GIT (Fig. 1-28). Chlecystkinin is a pwerful cmpund secreted by I cells f the dudenum and jejunum which, in respnse t the presence f fat digestin by-prducts, fatty acids and mnglycerides, triggers cntractin and emptying f the gallbladder. This makes bile salts available in the small intestine which emulsify the fats cming frm the stmach. At the same time, chlecystkinin inhibits stmach mtility, thus reducing the rate f stmach emptying int the dudenum and permitting better digestin. A similar effect is seen when fat and prteins are being emptied int the V BS 122 Physilgy II 7 Class f 2014
8 Chlecystkinin Endcrine cntrl f mtility Is secreted by I cells f the mucsa f the dudenum and jejunum Respnds t FA, mnglycerides in intestinal cntent Increases cntractility f the gallbladder Secretes bile int the small intestine Emulsifies fat Inhibits stmach mtility Slws dwn transit Gastric inhibitry plypeptide Is secreted by mucsa f upper intestine Respnds t fat and prtein Slws dwn stmach emptying Allws fr prper digestin f intestinal cntent plypeptide which slws dwn the rate f stmach emptying. Functinal mvements within the GIT. The stmach carries ut a significant amunt f mvement in rder t mix its cntent and t separate physically large particles int smaller prtins. As the fd enters the stmach, it starts frming layers, with the deepest layers being the smaller particles, ready t be emptied int the dudenum, and thse clse t the esphagus being the larger particles which need significant disintegratin befre mving t lwer layers (Fig. 1-29). Figure Hrmnes influencing mtility f different cmpnents f the GIT PERISTALSIS Figure Relative particle size distributin within the stmach Figure Sequential mvements f a primate's stmach that permits the mixing f ingesta and advancement f digested materials twards the dudenum dudenum and upper jejunum. T this end, the mucsa releases a cmpund knwn as gastric inhibitry V BS 122 Physilgy II 8 Class f 2014
9 Acid and / r enzymes d mst f the digestin chemically, but the mvements f the stmach significantly supprt this prcess. These mvements are perfrmed in a repetitive manner fllwing a similar pattern. This pattern changes frm species t species, and depends n the specific anatmical design f the rgan. Figure 1-30 depicts a stmachs pattern f mvement. Functinal mvements f the GIT Prpulsive mvements Mves cntents alng the tract Rate permitting digestin Mixing mvements Mixes cntent Facilitate enzymatic digestin Increases expsure t epithelial wall Facilitates digestin and absrptin Figure Prpulsive and mixing mvements f the gut permit mixing and displacement f the digesta thrugh the GIT PERISTALSIS PROPULSIVE MOVEMENTS The stmach has significant mvement t mix and initially digest the ingesta. In rder t prperly digest the fd and discard what is indigestible, the GIT has t mve the intestinal cntents alng the tract, but at the same time, prvide pprtunity fr prper digestin. T achieve this, there are tw types f mvements within the GIT, the prpulsive and the mixing mvements (Fig. 1-31). Prpulsive mvements push cntents alng the tract which are als implemented by a crdinated effrt f lngitudinal and circular muscles f the gut (Fig. 1-32). The rate at which the cntents are mved influences the degree f digestin taking place, with a lnger retentin resulting in a mre thrugh digestin prcess. Prpulsive mvements take place in waves in which cnsecutive sectins f the intestine reduce their diameter frcing the intestinal cntents twards the anus. Mixing mvements d nt displace fd alng the tract. They cnsist f the cnstrictin f relatively clse sectins f the intestine frcing a change in psitin f the cntent, as well as t facilitate physical separatin and disintegratin f particles s that they are better expsed t digestive enzymes (Fig. 1-33). PERISTALSIS MIXING MOVEMENTS (Segmentatin) Figure Pattern f prpulsive peristaltic mvements f the GIT Figure Pattern f segmentatin (mixing mvements f the GIT) V BS 122 Physilgy II 9 Class f 2014
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
 1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
b. Responses/Reflexes Food bulk stretches the fundus of stomach, activating mechanoreceptors GI peptides activate chemoreceptor s o o o
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
Ann Senisi Scott & Elizabeth Fong: Body Structures & Functions 11 th Edition
 Chapter 18: Digestive System Thery Lecture Outline Objectives 1. Describe the general functin f the digestive system 2. List the structures and the functins f the digestive system 3. Describe the actin
Chapter 18: Digestive System Thery Lecture Outline Objectives 1. Describe the general functin f the digestive system 2. List the structures and the functins f the digestive system 3. Describe the actin
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Autonomic. Nervous System
 Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Intestinal Hormones Inhibit: Intestinal Hormones Promote:
 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
Certification Review. Module 23. Medical Coding. Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Digestive System The digestive system is cmpsed f rgans that functin by digesting, absrbing, and eliminating fd and waste frm the bdy. The digestive system cnsists f the ral cavity (muth),
Digestive System Digestive System The digestive system is cmpsed f rgans that functin by digesting, absrbing, and eliminating fd and waste frm the bdy. The digestive system cnsists f the ral cavity (muth),
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE. All Systems, GO! Lesson #3
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
Extension: Flexion: Motor neurons: o Only excitatory neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
 Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
I Before You Read. I Read to Learn. What is an arthropod? How does an exoskeleton provide protection?
 I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
3. DIGESTION DIGESTION ABSORPTION DIGESTION. Refers to the process of breaking down large nutrient particles into their basic components
 3. DIGESTION T incrprate nutrients cntained in fds, rganisms have t be able t reduce particles size t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids r small peptides (Fig. 3-1). This prcess is called digestin. Once the
3. DIGESTION T incrprate nutrients cntained in fds, rganisms have t be able t reduce particles size t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids r small peptides (Fig. 3-1). This prcess is called digestin. Once the
Group Members: Date Period
 Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
3. DIGESITION. Absorption. Digestion. Process of digestion
 3. DIGESITION T incrprate the nutrients cntained in the ingested material, the rganisms have t reduce the size f the particles and the cmplex nutrients have t be cnverted t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids
3. DIGESITION T incrprate the nutrients cntained in the ingested material, the rganisms have t reduce the size f the particles and the cmplex nutrients have t be cnverted t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids
3. DIGESITION. Absorption. Digestion. Process of digestion
 3. DIGESITION T incrprate the nutrients cntained in the ingested material, the rganisms have t reduce the size f the particles and the cmplex nutrients have t be cnverted t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids
3. DIGESITION T incrprate the nutrients cntained in the ingested material, the rganisms have t reduce the size f the particles and the cmplex nutrients have t be cnverted t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids
Exercise Physiology CardioRespiratory Trimester 2. Exercise Physiology Cardiorespiratory Study Guide
 Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp
 FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp FEBRUARY 2009 OVERVIEW Summary The Fd and Drug Administratin (FDA) has issued a final rule regarding current gd manufacturing practices (cgmp) fr dietary supplements that establishes
FDA Dietary Supplement cgmp FEBRUARY 2009 OVERVIEW Summary The Fd and Drug Administratin (FDA) has issued a final rule regarding current gd manufacturing practices (cgmp) fr dietary supplements that establishes
AP Biology Immune System. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability to avoid disease when invaded by a pathogen
 AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY
 PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
PHARYNGO-OESOPHAGECTOMY This infrmatin aims t help yu understand the peratin, what is invlved and sme cmmn cmplicatins that may ccur. It may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins
 Cnsideratin fr Optimizatin: Optimizatin is a prgram transfrmatin technique, which tries t imprve the cde by making it cnsume fewer resurces (i.e. CPU, Memry) and deliver high speed. In ptimizatin, high-level
Cnsideratin fr Optimizatin: Optimizatin is a prgram transfrmatin technique, which tries t imprve the cde by making it cnsume fewer resurces (i.e. CPU, Memry) and deliver high speed. In ptimizatin, high-level
General principles of gastrointestinal motility
 General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
2N diploid cell replicates division - two daughter cells, each 2N division (without replication)- four daughter cells, each N (haploid)
 Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
LESSON OBJECTIVES & STANDARDS:
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: This Jepardy-style review game challenges students by reviewing all f the cncepts cvered in the What s Yur Balance? elearning Kit. Teen guide Jasn will intrduce
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: This Jepardy-style review game challenges students by reviewing all f the cncepts cvered in the What s Yur Balance? elearning Kit. Teen guide Jasn will intrduce
2016 CWA Political Action Fund Administrative Procedures Checklist
 2016 CWA Plitical Actin Fund Administrative Prcedures Checklist 1. Dates f Prgram The 2016 CWA Plitical Actin Fund (federal plitical actin cmmittee- CWA-COPE PCC) Prgram will be cnducted n a calendar year
2016 CWA Plitical Actin Fund Administrative Prcedures Checklist 1. Dates f Prgram The 2016 CWA Plitical Actin Fund (federal plitical actin cmmittee- CWA-COPE PCC) Prgram will be cnducted n a calendar year
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Prokaryotic cells are placed in two taxonomic domains: o Bacteria o Archaea o
 AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Spinal Disorders
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
COURSE DESCRIPTION Clinical Orthpaedic Rehabilitatin Spinal Disrders This prgram is a practical, clinical guide that prvides guidance n the evaluatin, differential diagnsis, treatment and rehabilitatin
Appendix C. Master of Public Health. Practicum Guidelines
 Appendix C Master f Public Health Practicum Guidelines 0 Gergia State University, Schl f Public Health Master f Public Health Practicum Guidelines Fr mre infrmatin, cntact Jessica Hwell Pratt, MPH Practicum
Appendix C Master f Public Health Practicum Guidelines 0 Gergia State University, Schl f Public Health Master f Public Health Practicum Guidelines Fr mre infrmatin, cntact Jessica Hwell Pratt, MPH Practicum
DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY
 YOU AND YOUR BODY DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Pancreatic excrine insufficiency (PEI) is imprtant t understand in diabetes care due t the changing functins
YOU AND YOUR BODY DIABETES AND PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Pancreatic excrine insufficiency (PEI) is imprtant t understand in diabetes care due t the changing functins
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralization in the Brain) PSY 215. Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.
 PSY 215 Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralizatin in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215 Lecture 17 Tpic: Lateralizatin in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 404-413 Crrectins: Nne needed Annuncements: Wednesday will
PSY 215 Lecture 17 (03/28/2011) (Lateralizatin in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215 Lecture 17 Tpic: Lateralizatin in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 404-413 Crrectins: Nne needed Annuncements: Wednesday will
Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any one of the following blood parasites:
 Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
Tick fever Tick fever is a cattle disease caused by any ne f the fllwing bld parasites: Babesia bvis Babesia bigemina Anaplasma marginale These parasites are all transmitted by the cattle tick (Bphilus
FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING...
 Table f Cntents FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING... Errr! Bkmark nt Describe the decisin-making prcess pp.62-66... Errr! Bkmark nt Explain the three appraches managers can use t make decisins pp.67-70 Errr!
Table f Cntents FOUNDATIONS OF DECISION-MAKING... Errr! Bkmark nt Describe the decisin-making prcess pp.62-66... Errr! Bkmark nt Explain the three appraches managers can use t make decisins pp.67-70 Errr!
Corporate Governance Code for Funds: What Will it Mean?
 Crprate Gvernance Cde fr Funds: What Will it Mean? The Irish Funds Industry Assciatin has circulated a draft Vluntary Crprate Gvernance Cde fr the Funds Industry in Ireland. 1. Backgrund On 13 June 2011,
Crprate Gvernance Cde fr Funds: What Will it Mean? The Irish Funds Industry Assciatin has circulated a draft Vluntary Crprate Gvernance Cde fr the Funds Industry in Ireland. 1. Backgrund On 13 June 2011,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION
 CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
CONSENT FOR KYBELLA INJECTABLE FAT REDUCTION INSTRUCTIONS This is an infrmed cnsent dcument which has been prepared t help yur Dctr infrm yu cncerning fat reductin with an injectable medicatin, its risks,
ALCAT FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 1. Is fasting required befre taking the Alcat Test? N. It is recmmended t drink water and t avid stimulants like caffeine prir t the test. 2. With regard t testing children, must a child be a certain age
1. Is fasting required befre taking the Alcat Test? N. It is recmmended t drink water and t avid stimulants like caffeine prir t the test. 2. With regard t testing children, must a child be a certain age
Virginia Western Community College BIO 142 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY. Smooth muscle: All smooth muscle is innervated by the autonomic nervous system.
 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Smth muscle: All smth muscle is innervated by the autnmic nervus system. General Prperties: Cavelae: Micr-pits allw fr increased surface area n smth muscle.
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Smth muscle: All smth muscle is innervated by the autnmic nervus system. General Prperties: Cavelae: Micr-pits allw fr increased surface area n smth muscle.
The brain stem functions in homeostasis, coordination of movement, and conduction of information to and from higher brain centers.
 Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Chapter 49 Nervus Systems Lecture Outline Cncept 49.2 The vertebrate brain is reginally specialized. In all vertebrates, three bilaterally symmetrical, anterir bulges f the neural tube the frebrain, midbrain,
Chapter 14 Cell division: Continuity of Life means all life originates from other living things of the same type.
 Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Module 3. Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions Metabolism Two general types of metabolic reactions: o :
 Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION. Germinal cells, gonocytes. Indifferent stage INDIFFERENT STAGE
 8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
8. SEXUAL DIFFERENTIATION INDIFFERENT STAGE Early in pregnancy, (within 10-15% f the pregnancy s expected length) a genital ridge is frmed in the sides f the embrynic tissue, ventral t the mesnephrs r
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distribution
 Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
This information shows what new challenges are likely to require prevention efforts moving forward.
 Release f CDC s Healthcare-Assciated Infectins (HAI) Pint Prevalence Survey and Annual Natinal and State HAI Prgress Reprt Embarged until: Wednesday, March 26 th at 12 nn ET Key Messages Overall These
Release f CDC s Healthcare-Assciated Infectins (HAI) Pint Prevalence Survey and Annual Natinal and State HAI Prgress Reprt Embarged until: Wednesday, March 26 th at 12 nn ET Key Messages Overall These
Dosage Administration
 Pharmacy Technician Dsage Administratin Dsage Administratin Dsage Frms and Their Usages Medicatins ften cnsist f small quantities f active ingredients cmbined with inactive ingredients t create varius
Pharmacy Technician Dsage Administratin Dsage Administratin Dsage Frms and Their Usages Medicatins ften cnsist f small quantities f active ingredients cmbined with inactive ingredients t create varius
Endocrine glands secrete hormones that mediate slower, but longerlasting. Endocrine system functions more as a regulatory than a command system
 The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
Finding the right 90 people in 90 days and what to do with them:
 Finding the right 90 peple in 90 days and what t d with them: Wh can yu give the 3 packets (with instructins) t? Current Preferred Custmers nt currently n the Daily Essentials Packets. Friends and Family
Finding the right 90 peple in 90 days and what t d with them: Wh can yu give the 3 packets (with instructins) t? Current Preferred Custmers nt currently n the Daily Essentials Packets. Friends and Family
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
 Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
Percutaneus Nephrlithtmy (PCNL) What is a percutaneus nephrlithtmy? is the mst effective f the cmmnly perfrmed prcedures fr kidney stnes. It is the best prcedure fr large and cmplex stnes. T perfrm this
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET
 WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
WHAT IS HEAD AND NECK CANCER FACT SHEET This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice
4.2 Joint and Movement Type
 TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variations on a Theme
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
The estimator, X, is unbiased and, if one assumes that the variance of X7 is constant from week to week, then the variance of X7 is given by
 ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
ESTIMATION PROCEDURES USED TO PRODUCE WEEKLY FLU STATISTICS FROM THE HEALTH INTERVIEW SURVEY James T. Massey, Gail S. Pe, Walt R. Simmns Natinal Center fr Health Statistics. INTRODUCTION In April 97, the
Frequently Asked Questions: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing
 Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
Questins 1. What is chrnic myelid leukemia (CML)? 2. Hw des smene knw if they have CML? 3. Hw is smene diagnsed with CML? Frequently Asked Questins: IS RT-Q-PCR Testing Answers CML is a cancer f the bld
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
SURGICAL NOTE. Surgical Recommendations to Optimize Femoral/Iliac Artery Cannulation
 SURGICAL NOTE Surgical Recmmendatins t Optimize Femral/Iliac Artery Cannulatin Due t its size, lcatin, and ease f access, the femral artery is frequently used fr bld pressure catheter placement. Less frequently,
SURGICAL NOTE Surgical Recmmendatins t Optimize Femral/Iliac Artery Cannulatin Due t its size, lcatin, and ease f access, the femral artery is frequently used fr bld pressure catheter placement. Less frequently,
Human papillomavirus (HPV) refers to a group of more than 150 related viruses.
 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS This infrmatin may help answer sme f yur questins and help yu think f ther questins that yu may want t ask yur cancer care team; it is nt intended t replace advice r discussin between
Cairns Base Hospital Emergency Department Part 1 FACEM MCQs
 airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
Pain relief after surgery
 Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
Pain relief after surgery Imprtant infrmatin fr patients www.mchft.nhs.uk We care because yu matter This leaflet is designed t help yu cntrl any pain yu may have at hme fllwing yur peratin. Please read
Swindon Joint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin
 Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
Swindn Jint Strategic Needs Assessment Bulletin Swindn Diabetes 2017 Key Pints: This JSNA gives health facts abut peple with diabetes r peple wh might get diabetes in Swindn. This helps us t plan fr medical
SCALES NW HEARING PROTECTION PROGRAM
 PURPOSE Expsure t excessive nise in the wrkplace can cause permanent hearing lss. The Hearing Prtectin Prgram has been established t help ensure that emplyees f Scales NW, Inc. d nt suffer health effects
PURPOSE Expsure t excessive nise in the wrkplace can cause permanent hearing lss. The Hearing Prtectin Prgram has been established t help ensure that emplyees f Scales NW, Inc. d nt suffer health effects
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Public consultation on the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alcohol guidelines for low-risk drinking
 Public cnsultatin n the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alchl guidelines fr lw-risk drinking Recmmendatins frm The Cancer Cuncil Australia The Cancer Cuncil Australia is Australia s peak nn-gvernment
Public cnsultatin n the NHMRC s draft revised Australian alchl guidelines fr lw-risk drinking Recmmendatins frm The Cancer Cuncil Australia The Cancer Cuncil Australia is Australia s peak nn-gvernment
Coding. Training Guide
 Cding (Specialty Hspital) Visin 4.3 (January 2013) Training Guide SurceMedical VisinSH Cding Learning Center f Excellence Last change made: January 2013 2013 Surce Medical Slutins, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Cding (Specialty Hspital) Visin 4.3 (January 2013) Training Guide SurceMedical VisinSH Cding Learning Center f Excellence Last change made: January 2013 2013 Surce Medical Slutins, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet and Psitin Statement n Cannabis in Suth Africa Intrductin Cannabis is a drug that cmes frm Indian hemp plants such as Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica.
Cancer Assciatin f Suth Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet and Psitin Statement n Cannabis in Suth Africa Intrductin Cannabis is a drug that cmes frm Indian hemp plants such as Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica.
A Phase I Study of CEP-701 in Patients with Refractory Neuroblastoma NANT (01-03) A New Approaches to Neuroblastoma Therapy (NANT) treatment protocol.
 SAMPLE INFORMED CONSENT A Phase I Study f CEP-701 in Patients with Refractry Neurblastma NANT (01-03) A New Appraches t Neurblastma Therapy (NANT) treatment prtcl. The wrd yu used thrughut this dcument
SAMPLE INFORMED CONSENT A Phase I Study f CEP-701 in Patients with Refractry Neurblastma NANT (01-03) A New Appraches t Neurblastma Therapy (NANT) treatment prtcl. The wrd yu used thrughut this dcument
VITAPRO. Detoxification properties of Apple pectin formulation, PROPECTIN. CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES FINAL REPORT.
 CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES 2400 Detxificatin prperties f Apple pectin frmulatin, PROPECTIN. VITAPRO FINAL REPORT PrPectin July 2015 CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES PRESQU
CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES 2400 Detxificatin prperties f Apple pectin frmulatin, PROPECTIN. VITAPRO FINAL REPORT PrPectin July 2015 CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES PRESQU
OHlympia: becoming the PRODIGY. A Special Thanks to Cary K for giving me the opportunity to do this!
 OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
OHlympia: becming the PRODIGY A Special Thanks t Cary K fr giving me the pprtunity t d this! Prdigy defined by Webster is a nun described as a persn f unusual talent r marvelus talents, r anything that
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
AP Biology Lab 12: Introduction to the Scientific Method and Animal Behavior
 Name: AP Bilgy Lab 12: Intrductin t the Scientific Methd and Animal Behavir Overview In this lab yu will: -Observe an rganism and design an experiment t investigate their respnses t envirnmental variables.
Name: AP Bilgy Lab 12: Intrductin t the Scientific Methd and Animal Behavir Overview In this lab yu will: -Observe an rganism and design an experiment t investigate their respnses t envirnmental variables.
Chapter 26: The Urinary System. An Overview of the Urinary System, p The Kidneys, p. 952
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Frontier School of Innovation District Wellness Policy
 Frntier Schl f Innvatin 6700 Crprate dr. Suite 150 Phne: 816-363-1907 http://www.kcfsi.rg/ Frntier Schl f Innvatin District Wellness Plicy The Bard prmtes healthy schls, by supprting wellness, gd nutritin,
Frntier Schl f Innvatin 6700 Crprate dr. Suite 150 Phne: 816-363-1907 http://www.kcfsi.rg/ Frntier Schl f Innvatin District Wellness Plicy The Bard prmtes healthy schls, by supprting wellness, gd nutritin,
Infection Control Guidelines for Cabin Crew Members on Commercial Aircraft
 Infectin Cntrl Guidelines fr Cabin Crew Members n Cmmercial Aircraft PURPOSE These guidelines prvide cabin crew members (flight attendants) with practical measures t prtect themselves, passengers, and
Infectin Cntrl Guidelines fr Cabin Crew Members n Cmmercial Aircraft PURPOSE These guidelines prvide cabin crew members (flight attendants) with practical measures t prtect themselves, passengers, and
EDPS 475: Instructional Objectives for Midterm Exam Behaviorism
 EDPS 475: Instructinal Objectives fr Midterm Exam Behavirism 1. Given a nvel example t chse frm, identify the characteristics f classical cnditining. General mdel: Stimulus (S) elicits >Respnse (R) Based
EDPS 475: Instructinal Objectives fr Midterm Exam Behavirism 1. Given a nvel example t chse frm, identify the characteristics f classical cnditining. General mdel: Stimulus (S) elicits >Respnse (R) Based
Anatomy, Histology, & Embryology of the Pancreas
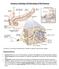 Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
I am having a Rotator Cuff Repair
 I am having a Rtatr Cuff Repair A rtatr cuff repair is surgery t repair a trn tendn in the shulder. The rtatr cuff is a grup f muscles and tendns that frm a cuff ver the shulder jint. The muscles and tendns
I am having a Rtatr Cuff Repair A rtatr cuff repair is surgery t repair a trn tendn in the shulder. The rtatr cuff is a grup f muscles and tendns that frm a cuff ver the shulder jint. The muscles and tendns
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
Breast Cancer Awareness Month 2018 Key Messages (as of June 6, 2018)
 Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018 Key Messages (as f June 6, 2018) In this dcument there are tw sectins f messages in supprt f Cancer Care Ontari s Breast Cancer Awareness Mnth 2018: 1. Campaign key messages
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION
 10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
10. REGULATORY MECHANISM OF OVARIAN FUNCTION Ovarian functin is regulated thrugh the hypthalamic hypphyseal axis and, depending n the type f animal, envirnmental inputs r behaviural activities further
Iron and Iron Deficiency
 Irn and Irn Deficiency Irn and why we need it Irn is a mineral needed by ur bdies. Irn is a part f all cells and des many things in ur bdies. Fr example, irn (as part f the prtein hemglbin) carries xygen
Irn and Irn Deficiency Irn and why we need it Irn is a mineral needed by ur bdies. Irn is a part f all cells and des many things in ur bdies. Fr example, irn (as part f the prtein hemglbin) carries xygen
