You will watch 6 tutorials on Anatomy Terminology then play 3 different interactives.
|
|
|
- Debra Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CCP Anatomy & Physiology Summer Work: You will be learning many new terms and concepts. To make the beginning of the year easier; I want you to learn some of the major regional, directional and plane terminology that we will be using this year. You will watch 6 tutorials on Anatomy Terminology then play 3 different interactives. 1. On the tutorials; take notes as you watch; and attach it to this document. 2. You will need to screen shot the results of each interactives and post them here. 3. There are follow up worksheets to complete and post. ***All due by first day of class. YouTube videos to watch: The following interactives are very helpful with understanding the terminology as well. Please go through each; snip and copy your results here. Also write a brief summary of what you learned drill/ch1.html Lastly: do the following worksheets that will cement your knowledge of the terms and concepts we will review the first week of class. See Schoology for Introduction and follow up worksheet.
2 1 Name: Introduction / Terminology Objectives : 1. Obtain an understanding of anatomy and the subdivisions which comprise the major disciplines in the study of the structure of the human body 2. Obtain an understanding of the generalized body structure 3. Mastery of Anatomical terms : Body Regions, Planes of section, Directional Terms, Body Cavities 4. Understanding of serous membranes and their significance I. Anatomy : Human Anatomy is the scientific discipline concerned with the organization and structure of the human body. The term anatomy originates from its Greek roots meaning literally to cut up. Anatomy was born from the discoveries of these early anatomists. Since their study was limited to observations made available through the dismemberment of unfortunate individuals, their study was confined to only those structures discernable with the naked eye; large, visible, dissectible, physical attributes. Today this aspect of anatomy is described as Macroscopic (large) or Gross Anatomy. As with all other scientific disciplines, the study of anatomy has paralleled technology. Unlike the early anatomists which were limited to structures they could see with the unaided eye, today anatomists go beyond elucidating just macroscopic structures and include the descriptions and understanding of structures visible through the use of technology. Anatomy today includes structures which are discernible through the use of highly advanced microscopic and computerized digital equipment, such as electron microscopes, CT scans (Computerized Tomography), and MRI s (Magnetic Resonance Imaging). We will begin our understanding of the structure of the human body with the smallest structural unit of life, the cell. This study of cell and cellular function is referred to as Cytology. It will serve the same purpose in our studies as it does in the body; it will form the framework onto which we will build our understanding of Anatomy. Anatomy is more than just observing the physical structure of the body and body parts. The goal of anatomy is to be able to discern the plausible function in the structure. The beauty and the challenge of anatomy is to be able to determine the functional significance for a specific structural design. Beneath every structural design in lies the function. It is through the understanding of anatomy that we will build the foundation for our understanding the function, or the Physiology, of the human body. II. Divisions of Anatomy : Anatomy is a broad field of study consisting of several divisions or subdisciplines. Each division of anatomy specializes on a specific aspect of the body s arrangement. These divisions are outlined below : 1. Macroscopic (Gross) Anatomy : Study of structures which can be seen with an unaided eye. a. Surface Anatomy : Study of the general form and superficial markings of the body. b. Systemic Anatomy : Study of 11 specific body systems (ie ; Digestive, Endocrine, Nervous Systems) c. Regional Anatomy : Study of specific regions of the body, including all tissues residing within the region (ie ; Upper extremity, head & neck, abdominal region). 2. Microscopic Anatomy : Study of structures which cannot be seen without the aide of magnifying equipment. a. Cytology : (Cyto = cell) Study of the internal structure of individual cells. b. Histology : (Histo = tissue) Study of the structure of groups of cells and how they interact to form functional tissues. 3. Specialized Anatomical Study : a. Developmental Anatomy : Study of the structural changes in the form of and individual from the fertilized egg to the mature adult. Embryology is a sub-branch of developmental anatomy. b. Medical / Radiological : Study of the characteristic changing in anatomy during disease. / Study of anatomical features visible which radiographic technology. 1
3 III. Generalized Body Structure : The human body is not a solid mass of cells, but rather one large hollow structure (trunk), subdivided into smaller spaces. Within these hollow spaces (cavities), specialized organs are contained. The extremities, while advantageous to have are not explicitly necessary, serving simply to move the body in its surrounding or the surrounding around the body. The head sits atop the trunk surveying the internal and external environments making the necessary adjustments to ensure continued body function. A. Body Divisions : On a very basic level, the body can be divided into three main divisions; 1. Body Wall : The structures forming the framework of the body, supporting and enclosing vital organs. The skin, skeleton, and skeletal muscles are all components of the body wall. The head, arms, and legs will be considered specialized modifications of the body wall. 2. Body Cavities : The internal spaces within the body wall are filled with the body s organs. The largest body cavity is the Ventral (abdominal side) Cavity. This cavity is further divided into the Thoracic Cavity, housing the heart and lungs, and the Abdominopelvic Cavity, housing the abdominal and pelvic organs (stomach, liver, intestines, bladder, reproductive structures). Body cavities are significant because they function to protect and house the internal organs, while still allowing them the freedom of movement. The heart would be very ineffective in pumping blood if it were housed in a solid tissue unable to move and beat. 3. Organs : Structures within the body capable of specific functions. Organs can be found 1) contained within the body cavities (heart, liver), 2) as a component of the body wall (skeletal muscle, bone), or 3) transiting between the two (blood vessels, nerves). B. Body Systems : Together, the body wall, cavities, and organs interact to form a beautifully constructed human structure. Body organs which function to perform a similar function are grouped together as a body systems, responsible for accomplishing specific essential tasks. There are eleven body systems which comprise the human body. 1. Integumentary System : Forms the outermost part of the body wall (the skin) parts: epidermis, dermis (accessory structures: hair, nails, glands, sensory endings) Function : Protection from the environment & temperature control. 2. Skeletal System : Component of the body wall. Consists of bones, ligaments, cartilage and connective tissue. Function : Support, protection, blood formation, mineral storage. 3. Muscular System : Component of body wall. Consists of skeletal muscles and tendons. Function : support, mobility, and heat production. 4. Nervous System : Central (brain & spinal cord) and peripheral (motor & sensory nerves) nervous systems. Function : controls body systems, perceiving internal and external environments. 5. Endocrine System : Glandular tissue throughout the body. Function : coordinates and controls body systems (use chemical signals - hormones). 6. Cardiovascular System : Heart and blood vessels throughout body. Function : Internal transport of dissolved materials : nutrients, gases, waste. 7. Lymphatic System : Structures throughout the body. Consists of lymph vessels, nodes and organs. Function : Internal defense and blood volume maintenance. Fig.1.1 Generalized diagram of interactions between the main human body systems 8. Respiratory System : Structures involved in the exchange of gases; lungs, nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi. Exchange of gases (O 2 &CO 2 ) with the body and the environment. 9. Digestive System : Primarily within the abdominal cavity. Function : processing of food and the absorption of nutrients, minerals, vitamins, & water and the elimination of waste. 10. Urinary System : Primarily within the pelvic cavity ; consists of the kidney, ureter, bladder & urethra. Function : regulation of blood chemistry via the elimination of excess water, salts, & waste products. 11. Reproductive System : Primarily within pelvic cavity. Consists of sex organs (ovaries / testis) and support structures. Function : production and support of sex cells and hormone production. 2
4 IV. Anatomical Terminology : Anatomy is the study of the body's internal and external structures and the physical relationships between them. In the study of Anatomy it is essential that you are able to express yourself correctly and without confusion. Anatomy uses an international language of terms which enables one to correctly convey information to health care professionals around the world, as well as scholars in basic and applied heath sciences. Your successful study of the body's structure will rely on your ability to not only communicate using the correct terminology and spelling, but to also understand the language of directionality and organization. A. Standard Anatomical Position : All descriptions of the human body are based on the assumption that the individual is standing what is known as the Standard Anatomical Position (SAP). Standard Anatomical Position: An individual in SAP will adhere to the following positions: (see fig. 1.2) Stand erect Upper limbs are at ones side Lower limbs are together Face, palms, and feet are directed forward B. Principle Body Regions : In your study and use of the following regional terminology, it is important to be able to communicate correctly to you peers as well as to the lay person. It is therefore important to learn both the anatomical term in conjunction with the common names. The anatomical terms and common names and used to describe the principle body regions are given below : You are responsible for knowing all anatomical names, regions and areas (common names) listed : Anatomical Name Anatomical Region Area indicated (common name) 1. Cephalon Cephalic Head a. Cranium Cranial Skull b. Nasus Nasal Nose c. Bucca Buccal Cheek d. Auris (Otic) Aurical Ear e. Oculus Ocular Eye f. Oris Oral Mouth 2. Cervicis Cervical Neck 3. Thoracis Thoracic Chest a. Mamma Mammary Breast 4. Axilla Axillary Armpit 5. Acromium Acromial Shoulder 6. Brachium Brachial Portion of upper limb closest to trunk(arm) 7. Antebrachium Antebrachial Forearm 8. Antecubitis Antecubital Front of elbow 9. Carpus Carpal Wrist 10. Manus Manual Hand a. Palma Palmar Palm b. Digits (phalanges) Digital (phalangeal) Fingers 11. Abdomen Abdominal Abdomen 12. Pelvis Pelvic Pelvis a. Coxa Coxal Hip b. Pubis Pubic Anterior Pelvis 13. Inguen Inguinal Groin 14. Lumbus Lumbar Lower Back 15. Gluteus Gluteal Buttock 16. Femur Femoral Thigh 17. Patella Patellar Knee a. Popliteus Popliteal Back of knee 18. Crus Crural Leg; from knee to ankle 19. Sura Sural Calf 20. Tarsus Tarsal Ankle 21. Pes Pedal Foot a. Planta Plantar Sole of foot b. Digits (phalanges) Digital (phalangeal) Toes 22. Calcaneus Calcaneal Heel 3
5 Cephalon - Cephalic Cranium - Cranial Nasus - Nasal Cervicis - Cervical Axilla - Axillary Brachium - Brachial Antebrachium - Antebrachial Carpus - Carpal Manus - Manual Palma - Palmar Digits - Digital Femur - Femoral Patella - Patellar Oculus - Ocular Bucca - Buccal Oris - Oral Thoracis - Thoracic Mamma - Mammary Antecubitis - Antecubital Abdomen - Abdominal Pelvis - Pelvic Coxa - Coxal Inguen - Inguinal Pubis - Pubic Crus - Crural Pes - Pedal Tarsus - Tarsal Digits (phalanges) Digital (phalangeal) Acromium - Acromial Lumbus - Lumbar Gluteus - Gluteal Popliteus - Popliteal Sura - Sural Fig. 1.2 Calcaneus - Calcaneal 4
6 C. Planes of Section : The human body can be dismantled (dissected) into pieces (sections) along imaginary planes (Imaginary flat surfaces that pass through the body). See figure Sagittal Plane : Divides the body or organ into Right & Left sections Midsagittal Plane : Passes through the mid-line & divides the body or organ into exactly EQUAL right and left halves Parasagittal Plane : Divides the body or organ into UNEQUAL right & left sections 2. Frontal (Coronal ) Plane : Divides the body or organ into Anterior (Front) & Posterior (Back) sections 3. Transverse (Cross-sectional or Horizontal) Plane : Divides the body or organ into Superior (top) & Inferior (Bottom) sections 4. Oblique Plane : Passes through the body or organ at an angle and divides the body into unequal sections. Figure 1.3 : Anatomical Body Planes of Section : D. Directional Terms : When expressing anatomical locations it is important to utilize correct directional terms. Various adjectives, arranged into antagonistic pairs, describe the relationship of body parts and compare the relationship of anatomical structures with each other. See figure 1.4 All directional terms express relative location : i.e. The cephalon is superior to the cevicis 1. a. Superior: Above ; at a higher level (in humans - toward the head) b. Inferior : Below; at a lower level (in humans - toward the feet) The cranial region is superior to the cervical region The patellar region is inferior to the inguinal region 2. a. Cephalic or Cranial : Toward the head The cranial border of the pelvis is the attachment site for many abdominal muscles 3. a. Anterior (Ventral) : Near the front of the body or structure (belly side). b. Posterior (Dorsal) : Near the back of the body or structure. The crus is anterior to the sura The tarsus is posterior to the phalanges 5
7 4. a. Medial : Toward the midline (longitudinal axis) of body or structure. b. Lateral : Away from the midline (longitudinal axis) of body or structure. The medial portions of the thighs may touch The lateral digit is the pollex (thumb) 5. a. Ipsilateral : On the same side of the body. b. Contralateral : On the opposite side of the body. The appendix and gall bladder are ipsilateral The Spleen and liver are contralateral 6. a. Proximal : Near to point of attachment (trunk) - Used to describe relative distance down a limb. b. Distal : Far from point of attachment (trunk) - Used to describe relative distance down limb. The femur is proximal to the crus The antebrachium is distal to the brachium 7. a. Superficial : Toward the surface of the body or organ. b. Intermediate : Between a superficial structure and a deep structure. c. Deep : Away from the surface of the body or organ (more internal) The skin is superficial to the muscle The muscle is intermediate between the skin and the bone The bone is deep to the muscle and the skin Figure 1.4 : Directional Terminology E. Body Cavities : When viewed in section one realizes that the human body is not a solid object. It has numerous spaces and internal chambers. These internal chambers, called cavities, house the body's organs. There are 2 major body cavities (Ventral & Dorsal Body Cavities) which are further subdivided into smaller cavities housing specific organs. 6
8 Functional significance : Body cavities have several functions : 1. They house & separate body organs 2. They protect & cushion organs from external impact 3. They allow considerable freedom for movement of internal organs without disrupting the functions of other organs The Heart, Lungs, & Small Intestine all require the relatively uninhibited ability to move 4. They enable different pressures to be developed within the body without disrupting other organs Lung Cavity : Breathing results from changes in pressures within the Thoracic cavity F. 2 Principal Body Cavities : With further subdivisions : 1. Dorsal Body Cavity : Cushions & protects the Central Nervous System (Brain & Spinal Cord) a. Cranial Cavity : Cavity formed by the bones of the Skull ; Houses the Brain b. Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity : Cavity formed by the vertebral column; Houses the Spinal Cord 2. Ventral Body Cavity (Coelom) : Enclosed by the ribs, abdominal and lumbar musculature. Surrounds organs of the Respiratory, Digestive, Cardiovascular, Urinary, & Reproductive systems Ventral Cavity is further divided into 2 cavities by the transversely oriented Diaphragm a. Thoracic Cavity : Enclosed by the rib cage & separated from the abdominopelvic cavity by the diaphragm. 1. Right & Left Pleural Cavities : House the right & left lungs 2. Pericardial Cavity : Houses the heart b. Abdominopelvic Cavity : Enclosed by the abdominal and lumbar muscles, inferior to the diaphragm. Houses abdominal Viscera (Organs) 1. Abdominal Cavity : Separated from inferior Pelvic cavity by an imaginary line at the pelvic brim. Houses Digestive Organs and Glands 2. Pelvic Cavity : Separated from superior Abdominopelvic cavity by an imaginary line at the pelvic brim. Houses Urinary, Reproductive, & distal portions of Digestive Systems. There is no definitive structure which separates Abdominal & Pelvic Cavities Figure 1.5 ; Body Cavities Lateral Figure 1.6 : Body Cavities Anterior 7
9 Figure 1.7 : Body Cavities Transverse V. Serous Membranes : All body cavities & organs are lined with a thin continuous layer of fluid secreting cells. These cells form a specialized membrane called a Serous Membrane. The serous membrane which lines all cavities and organs functions to secrete a slippery fluid called serous fluid or Transudate. Serous membranes are significant because they function to allow the frictionless movement of moist organs across one another. Serous Membrane Terminology : Serous Membranes are named according to their location. 1. Visceral Serous Membranes (Visceral Serosa) : Cover all body organs a. Visceral Pleura : Membrane covering the lungs b. Visceral Pericardium : Membrane covering the heart c. Visceral Peritoneum : Membrane covering all abdominal organs 2. Parietal Serous Membranes (Parietal Serosa) : Cover & line all body cavities a. Parietal Pleura : Membrane lining the Pleural Cavity b. Parietal Pericardium : Membrane lining the Pericardial Cavity c. Parietal Peritoneum : Membrane lining the Abdominopelvic Cavity The Serous membranes which line the Pleural cavities meet in the middle of the thoracic cavity. The space within the thoracic cavity which lies between the pleural cavities is called the MEDIASTINUM. The mediastinal space contains the pericardial cavity and portions of the trachea & esophagus, thymus, and major arteries & lymph vessels which pass through. (see fig. 1.7) Clinical Significance : Peritonitis is an inflammation of the Abdominal Peritoneum. Peritonitis can occur after an injury or infection to the abdominal peritoneal serous linings. The injuries or infection can cause an increase in the production and an accumulation of serous fluid (called ascites) resulting in abdominal swelling. Several symptoms can result : heart burn, indigestion, & lower back pain. 8
10 1 Name : Introduction / Terminology Define the following : 1. Anatomy : 2. Histology : 3. Body Cavity : 4. Standard Anatomical Position : 5. Midsagittal Plane : 6. Serous Membrane 7. Mediastinum : Matching 1.1 : Body Systems 1. Urinary System a. Structures involved in the exchange of gases; lungs, nose, larynx, trachea, bronchi. 2. Respiratory System b. Controls body systems, perceiving internal and external environments 3. Cardiovascular System c. Glandular tissue throughout the body. Coordinates and controls body systems 4. Muscular System d. Internal transport of dissolved materials : nutrients, gases, waste. 5. Endocrine System e. Internal defense and blood volume maintenance. 6. Nervous System f. Regulation of blood chemistry via the elimination of excess water, salts, & waste products. 7. Reproductive System g. Support, mobility, and heat production. 8. Skeletal System h. Forms the outermost part of the body wall (the skin) parts: epidermis, dermis 9. Digestive System i. Production and support of sex cells and hormone production. 10. Integumentary System j. Support, protection, blood formation, mineral storage. 11. Lymphatic System k. Processing of food & absorption of nutrients, minerals, vitamins, & water. Matching 1.2 : Body Regions (Anterior Surface) 1. Patella a. Armpit 2. Antebrachium b. Leg 3. Axilla c. Ankle 4. Brachium d. Groin 5. Pes e. Forearm 6. Thoracis f. Back of Knee 7. Cervicis g. Foot 8. Phalanges (digits) h. Buttock 9. Inguin i. Chest 10. Popliteus j. Arm 11. Gluteus k. Knee 12. Femur l. Neck 13. Tarsus m. Fingers 14. Crural n. Thigh 9
11 Labeling 1.1 : Body Regions Anterior : Label the figures below with all relevant anatomical terms Labeling 1.2 : Body Region - Posterior 10
12 Labeling 1.3 : Planes of Section : Label the specific planes of section identified Labeling 1.4 : Body Cavities
13 Labeling 1.5 : Transverse section through the Thoracic Cavity Fill ins 1.1 : Directional Terms : For each set of structures or regions, give the directional term that best describes the relationship 1. The Antebrachium is to brachium. 2. Cranial region is to cervical region. 3. Phalanges are to the Carpus. 4. Inguen is to the Coxa. 5. Crural region is to sural region. 6. is lateral to the thoracic region. 7. The axilla is proximal to the. 8. Patellar is anterior to the. 9. is inferior to the cervical region. 10. The antecubital region is to the phalanges. Fill ins 1.2 : Body Cavities & Membranes 1. The cavity contains the brain, and the cavity contains the spinal cord. Both cavities are a part of the larger cavity. 2. The abdominopelvic cavity is separated by the muscular from the cavity. 3. In the thoracic cavity, the esophagus, thoracic nerves, and pericardial cavity (with the heart) occupy an area called the. 4. The cavity includes the cavity which houses the heart and the cavity which houses the lungs. 5. The membrane functions to line the abdominal cavity. 6. The lines the heart, functioning to reduce friction by the secretion of transudate (serous fluid). 7. The lines the plueral cavity. 12
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Lab Activity 1. Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
NOSE GOES. What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent?
 1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
Figure 1.2. Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5) Umbilical region. Answer: C. 6) Right hypochondriac. Answer: B
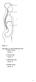 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Anatomy Physiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology
 Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Systemic The study of anatomy by body systems
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
8/27/2017. The Human Body: An Orientation. Homeostasis BODY SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER TO MAINTIN HOMEOSTASIS. Chapter 1 Part B
 Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Link full download:
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
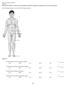 Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Station 2: Torso Model Practical
 Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
"Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
 Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body You must be
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology professor edit PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body You must be
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities
 Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
