Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities
|
|
|
- Kellie Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page1 Lab #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms and Body Cavities Objectives Understand the purpose of the scientific method and describe the six steps involved List and describe the sections of a scientific laboratory report Name the base units, abbreviations, and prefixes used in the metric system Apply significant figure rules to mathematical calculations Recognize and describe anatomical position Define and learn to properly use directional terms and planes of section Identify major body cavities Identify abdominal quadrants and abdominopelvic regions I. Scientific Method Scientists are interested in understanding how the natural world works. For this purpose, scientists typically follow an orderly sequence of steps called the scientific method. This process allows scientists to make measurements and collect data to solve a problem and discover new information. The scientific method can be broken down into the following six major steps: 1. Observation. Make observations regarding an environment, condition or situation. 2. Gather Information. Gather and analyze information about topics directly related to your observations. 3. Propose a Hypothesis. An hypothesis is an educated guess specifically developed to explain your observations. 4. Test the Hypothesis. Perform an experiment and collect data to test the hypothesis. 5. Present and Analyze Results. Results data can be presented in many formats, including tables, figures, and graphs. 6. Conclusion. Explain whether the data supports or rejects the hypothesis. The scientific method is cyclical, meaning that after a conclusion is reached, new questions are often asked.
2 Page2 II. Scientific Laboratory Report The process of the scientific method is often documented by a scientific lab report containing the following sections: Introduction: The general topics of the experiment are presented. The introduction section of the lab report should answer the following questions: What was/were the topic/s of the laboratory? What was the experimenter trying to study/discover in this laboratory? What was the hypothesis? What is currently known about the topic? Materials and Methods: In this section, the materials that were used in the experiment are presented and the procedures (how the experiment was performed) are described in detail. A person reading the laboratory report should be able to replicate the study exactly using the information provided in this section. Results: In this section, the data is presented as clearly as possible. Usually, this section includes tables, figures, and/or graphs. Discussion: The discussion section of the laboratory report should explain the data from the results section with respect to supporting or refuting the experiment s hypothesis. The discussion should also explain if the data supports what is currently known about the concept that was tested. If it does not, this is the section where you would identify possible errors in the experiment or suggestions for improvement if the experiment was replicated. Conclusion: This section is used to summarize the information that was presented in the laboratory report. The conclusion should provide the reader with a take home message. Conclusions are usually brief, approximately two to three sentences. In a future laboratory exercise, you will have an opportunity to use the scientific method and write a scientific lab report. III. Metric System A. MAKING MEASUREMENTS Scientific experiments usually involve collecting data by making measurements. By convention the metric system is always used for scientific measurements. The table below shows the base units for the metric system. Mass is measured in grams (g), volume in liters (L), linear measurements in meters (m) and time in seconds (s). Prefixes are used to denote larger and
3 Page3 smaller numbers (Table 1). For example, 1 kilometer (km) is 1000 meters (m), and 1 millimeter (mm) is meters (m), or 1/1000 of a meter. Table 1. The Metric system prefixes Giga G 1,000,000,000 Mega M 1,000,000 kilo k 1,000 hecto h 100 deca dk or da 10 Base unit : Gram (g) Meter (m) Liter (L) Second (s) deci d 0.1 centi c 0.01 milli m micro µ 0.000,001 nano n 0.000,000,001 B. Practice measuring using the instruments provided. Record the mass (in grams), volume (in milliliters) and length (in centimeters) of the items provided to you by your instructor, in your lab report. IV. Significant Figures Every measurement has some degree of uncertainty. Significant figures are used as a way to express the degree of uncertainty associated with a particular measurement. A. Significant Figure Rules Many of the quantities that we measure in the lab are often used for some type of mathematical calculation. The accuracy of these mathematical calculations is limited by the accuracy of the original measurements. Follow the rules below for using significant figures: a. All non-zero numbers are significant. Example: 145 has 3 significant figures b. All zeros between non-zero numbers are significant. Example: 1001 has 4 significant figures
4 Page4 c. All zeros to right of the decimal point AND at the end of the number are significant. Example: has 4 significant figures d. All zeros before a non-zero digit are NOT significant they are placeholders only. Example: has 2 significant figures e. Zeros after a non-zero number with no decimal point are NOT significant. Example: 5000 has 1 significant figure f. Exact numbers have an unlimited number of significant digits. Exact numbers are counted numbers or ones that are created by definition. They have no uncertainty. Examples: 10 heart beats, 12 inches in a foot B. Math with Significant Figures a) Addition / Subtraction round off the answer to the same number of decimal places as the lowest in the calculation. Example: = 6.8 (you must round the answer off to 1 decimal place) b) Multiplication / Division round off the answer to the lowest number of significant digits in the calculation. Example: 4.3 x = 11 (you must round off answer to 2 significant figures) C. Rounding Off Rules When rounding to the correct number of significant digits, use the following rules: a) If the digit being rounded is 5 or greater, round up. Example: 4.56 rounds to 4.6 b) If Less than 5, round down. Example: 4.54 rounds to 4.5 D. Mean (Average) A data set is a collection of numbers. Below is an example of a data set containing 3 values: Example: The mean is the average value for a data set. To calculate the mean, add all the numbers together and divide by the number of values in the data set. Example: = 10.3 then 10.3 divided by 3 = 3.4
5 Page5 E. Answer the following questions using the math rules provided and put the answers in your laboratory report. 1. Indicate the number of significant figures in the following numbers: a b c Round the following numbers to 2 significant digits. a. 113 b c Perform the calculation and use the rounding rules to use the correct number of significant figures. a b x c Calculate the mean of the following data set: (12, 14, 13, 12, 17, 10). V. Anatomical Position & Directional Terms A. Introduction The study of any discipline begins with learning the proper terminology. Anatomists and health care personnel must agree to a standardized language in order to communicate accurately. B. Anatomical Position In human anatomy, directional terms assume the subject is in the anatomical position. Note each of the following body positions on Figure 1 depicting a subject in anatomical position. a. Standing upright in front of the observer b. Head level with eyes forward c. Legs straight, feet flat, pointed forward d. Arms at sides, straight, palms facing forward, thumbs to the side e. Right and left refers to subject, not observer C. Directional Terms Words such as up, under, behind and beside have subjective meanings. For precision, directional terms are used to convey specific relationships allowing precise descriptions of location. Review the directional terms in table 2 and use the definitions to fill in the blanks in part IV of the lab. Note that terms in parentheses are used for animals that walk on four legs.
6 Page6 Table 2. Directional Terms. Definitions and Examples. Directional Term Definition Example of Use a. superior / cranial above or toward the head the nose is superior to the mouth, both are cranial b. inferior (caudal) Below or away from the head the chin is inferior to the mouth c. anterior / ventral* closer to the front of the body the sternum is anterior to the heart d. posterior / dorsal* closer to the back of the body the vertebral column is posterior to the heart e. midline an imaginary line down the center of the body dividing it into matching halves the umbilicus is on the midline. f. medial closer to midline of the body the eye is medial to the ear g. lateral farther from the midline of the body the shoulder is lateral to the sternum h. proximal closer to the point of attachment the elbow is proximal to the hand i. distal farther from the point of attachment the fingers are distal to the wrist j. superficial toward the surface of the body the skin is superficial to the rib cage k. deep toward the interior of the body the lungs are deep to the rib cage l. ipsilateral on the same side of the body all injuries were ipsilateral, on the right side m. contralateral on opposite sides of the body n. visceral pertaining to organs (viscera) o. parietal pertaining to cavity linings control of the right hand by the left motor cortex is contralateral the visceral layer of the pericardium is adjacent to the heart the parietal layer of the pericardium is adjacent to the pericardial cavity p. afferent to carry toward afferent neurons carry impulses toward the CNS q. efferent to carry away efferent neurons carry impulses away from the CNS * Note that these are synonymous for bipeds, but have different meanings for quadrupeds. (Caudal : toward or near the tail) VI. Planes of Section A. Introduction It is often necessary to view only a section or slice of the human body or organ. There are four basic cuts that can be made and these are referred to as body planes or planes of section. The view of the object after it has been cut is called a section.
7 Page7 1. Sagittal plane: A cut through the long axis of the body that results in right and left portions. Also referred to as a longitudinal cut, resulting in a longitudinal section. a. midsagittal plane: The cut is midline resulting in two equal halves. b. parasagittal plane: The cut results in unequal right and left portions. 2. Frontal (coronal) plane: A cut through the long axis of the body that results in anterior and posterior portions. 3. Transverse plane: A horizontal cut that divides the body into superior and inferior portions. Also called cross section. 4. Oblique plane: A cut performed an angle between the other planes. Use these terms to help answer the questions in part V of the lab report. B. Banana Dissection Procedure 1. Observe the shape of the banana. Orient the banana so that the stem is pointed upward. Observe how it is bilaterally symmetrical (a mirror image along the midline) similar to a human. 2. Do not peel the banana, face the stem forward and write a face on it to keep track of its orientation. 3. Perform a transverse section of the banana (using the plastic knife) roughly cutting it in half. Draw the resulting shape of the cut end in lab report part II. 4. Cut the bottom half in a midsagittal section. Draw the cut end. 5. Cut the top half in a frontal section. Draw the cut end. 6. Cut one of the remaining pieces in an oblique section. Draw the cut end. You should have four drawings in part II, one for each cut. VII. Body Cavities A. Introduction The body is divided into cavities. The cavities contain tissue coverings called membranes that will be discussed at a later time. The dorsal body cavity contains the cranial cavity and vertebral /spinal cavity /canal that house the brain and spinal cord, respectively. The ventral body cavity is composed of the superior thoracic cavity with the diaphragm at is inferior margin. This cavity contains the lungs, heart, and parts of the esophagus and trachea. Below the thoracic cavity is the abdominopelvic cavity which contains the abdominal and pelvic organs. This cavity is further subdivided into the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
8 Page8 B. Definitions 1. Dorsal Body Cavity: can be subdivided into the cranial and vertebral cavities although they are continuous with each other a. Cranial Cavity: contains the brain within the skull b. Vertebral Cavity: contains the spinal cord within the vertebral column 2. Ventral Body Cavity: is divided into superior and inferior sections by the diaphragm a. Thoracic Cavity: contains the heart and lungs protected by the rib cage i. Pleural Cavity: fluid-filled membrane-enclosed region that contains the lungs ii. Pericardial Cavity: fluid-filled membrane-enclosed region that contains the heart b. Abdominopelvic Cavity: although there are no physical divisions between these sections, it is easier to refer to the abdominal cavity separately from the pelvic cavity i. Abdominal Cavity: inferior to the diaphragm, the area contains the stomach, liver, intestines, and associated organs ii. Pelvic Cavity: region partially enclosed by the pelvic bones containing the reproductive organs, bladder and rectum C. Mapping the Abdominopelvis As you observed from the human torso, the abdominopelvic cavity contains many organs and structures. The abdominopelvic area can be divided into regions by two methods: the quadrant method and the regional method. 1. Quadrant method: divides the abdomen into four parts via two imaginary lines: one down the midline and the other horizontal through the umbilicus A. right upper quadrant (RUQ) B. left upper quadrant (LUQ) C. right lower quadrant (RLQ) D. left lower quadrant (LLQ) 2. Regional method: four imaginary lines in a tic-tac-toe formation separate the abdominopelvis into nine regions A. umbilical region F. left hypochondriac region B. right lumbar regions G. hypogastric (pubic) region C. left lumbar region H. right iliac (inguinal) region D. epigastric region I. left iliac (inguinal) region E. right hypochondriac region
9 Page9 Lab Report #2 Scientific Method, Metric System, Directional Terms & Body Cavities Name: I. Scientific Method Define hypothesis and explain its importance to the scientific method. II. Scientific Laboratory Report Write in the appropriate section of a scientific lab report into which each of the items below would properly fit. The statements are not necessarily in the correct order. See page Make a prediction that increased sugar consumption has a harmful effect on the body s ability to properly respond to insulin. 2. Set up an experiment to compare two populations of lab mice- one population with a high sugar diet and the other with a regular diet 3. Noticing that people with a higher sugar consumption have a greater risk of diabetes 4. Gather current research information about diabetes 5. Create a data table to present data collected 6. The data support the hypothesis that the lab mice consuming a sugar rich diet respond differently to insulin. III. Metric System Measure each of the specimens on display and record your measurements on the lines below (include the units of measurement) IV. Significant Figures 1. A. B. C. 2. A. B. C. 3. A. B. C. 4.
10 Page10 V. Anatomical Position & Directional terms A. Human Skeleton Model - Locate the labels (I-O) to answer the following questions. 1.Which is the most distal point I, J or K? 2.Which is more medial, L or M? 3.N is relative to O. 4.What is the most superior label? B. Cat Skeleton Model - Locate the labels (P-U) to answer the following questions. 1. Which is the most caudal point (closer to the tail)? P or Q? 2. Are R and S contralateral or ipsilateral? 3. T is _proximal / distal (circle one) relative to U. VI. Planes of Section A. Sectioned Models and Specimens Observe each of the structures on display and determine the body plane/section demonstrated. (Note the orientation of the organs within body using the torso models for reference.) B. Banana Dissection Draw each section as the cut end appears. Transverse Midsagittal
11 Page11 Frontal Oblique VII. Body Cavities A. Human Torso Model (with the exposed vertebral column) - Locate each of the cavities defined previously. The cavities have been labeled (A-F). Record the observed labels on the correct line below. pelvic cavity abdominal cavity cranial cavity vertebral cavity pleural cavity pericardial cavity B. Using the letters A-F above, complete these statements (more than one applies to each). a. The dorsal cavity includes b. The thoracic cavity includes c. The ventral cavity includes C. Human Torso Model - Mapping the abdominopelvis 1. On the human torso, observe the quadrant and regional method of dividing the abdominopelvis by placing the transparent grids in the marked locations. Refer to the torso model to help answer the questions below. 2. Using the quadrant method abbreviations, identify the quadrant that contains: a. the majority of the stomach b. the uterus (two answers) c. the majority of the liver 3. Using the regional method, identify the region(s) that contain(s): a. the spleen b. the right hip c. the center region named for the belly button d. upper right portion of the liver
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units
 hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
hapter 1: Introduction to the Structural Units TRUE/FLSE 1. The pelvic cavity contains the organs of the reproductive and excretory system. NS: T 2. The thoracic cavity protects the heart and lungs. NS:
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Dr.Susan Maskel. BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community College A&P I.
 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community
1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click to advance. Arrow keys etc.also work. Dr.Susan Maskel BIO 105 Western Connecticut State University A&P I BIO 211 Naugatuck Valley Community
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology
 Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
Unit 1: Intro to Physiology Anatomy The branch of science that studies body parts. Physiology! The branch of science that describes HOW the body works, or functions.! Example - how the heart pumps blood
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
3. A plane is an imaginary line dividing the body into.
 CHAPTER 2 Multiple Choice Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Knowing the exact body region where pain is located can help a physician determine the.
CHAPTER 2 Multiple Choice Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Knowing the exact body region where pain is located can help a physician determine the.
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Medical Terminology. Unit 2
 Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Medical Terminology Unit 2 Students will apply medical terminology. Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Body Planes & Positions
 Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Learning Objectives Objective 1: Identify and utilize anatomical positions, planes, and directional terms. Demonstrate what anatomical position is and how it is used to reference the body. Distinguish
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions
 Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Body Structure. Directional Terms
 Body Structure 6 Directional Terms In describing the location or direction of a given point in the body, it is always assumed that the subject is in the anatomical position, that is, upright, with face
Body Structure 6 Directional Terms In describing the location or direction of a given point in the body, it is always assumed that the subject is in the anatomical position, that is, upright, with face
the study of the body s physical structures
 Chapter 1: Page 10 anatomy anterior (ventral) coronal (frontal) plane distal the study of the body s physical structures directional term meaning "toward the front" plane of reference which divides the
Chapter 1: Page 10 anatomy anterior (ventral) coronal (frontal) plane distal the study of the body s physical structures directional term meaning "toward the front" plane of reference which divides the
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY. Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER. The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides
 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Complete! Second Edition CHAPTER 4 The Human Body in Health and Disease Content Review Slides Learning Objectives Define and spell the word parts used to create terms for the human
Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
2. Draw or define ANTERIOR/VENTRAL and POSTERIOR/DORSAL. Give an example.
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
Introduction to Human Anatomy. Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili
 Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
Introduction to Human Anatomy 1 Prepared by:- Mohammad Zmaili Definitions Anatomy: the science of the structure and shape of living organisms and their parts. Physiology: the science that deals with the
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
Review. Labeling Exercise. 80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology
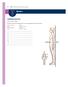 80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology Chapter Review Labeling Exercise Directional Terms Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer sheet. Anterior (ventral) Distal
80 Part I Introduction to Medical Terminology Chapter Review Labeling Exercise Directional Terms Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer sheet. Anterior (ventral) Distal
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM:
 ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM: OBJECTIVE: This dissection activity is designed to help you learn anatomical terms, and also to help you practice doing a dissection without the gross-out
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM: OBJECTIVE: This dissection activity is designed to help you learn anatomical terms, and also to help you practice doing a dissection without the gross-out
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
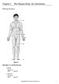 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass
 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Grade
7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass 7a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Body Compass! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Grade
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Link full download:
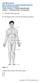 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-forhuman-anatomy-7th-edition/ Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
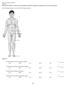 Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later)
 Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Welcome to BIOL 241! Tonight s handouts: Syllabus These slides (you will usually print these yourself) Worksheet (later) Tonight s agenda: Go over syllabus Peek at course website Chapter 1 of textbook
Directions: Read and annotate the passage below and be prepared to watch a short video. Glue this paper in a your science notebook!
 Directions: Read and annotate the passage below and be prepared to watch a short video. Glue this paper in a your science notebook! Anatomy uses a precise language to communicate specific areas and structures
Directions: Read and annotate the passage below and be prepared to watch a short video. Glue this paper in a your science notebook! Anatomy uses a precise language to communicate specific areas and structures
"Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
Levels of Organization. Anatomical Position
 Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
Levels of Organization Anatomical Position A stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor, arms at the sides, and the palms, face, and eyes facing forward. The body standing erect,
