A Abortion: The spontaneous or medically induced ending of a pregnancy.
|
|
|
- Marjorie Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Health Education Appendix D: Glossary A Abortion: The spontaneous or medically induced ending of a pregnancy. Abstinence: Deliberate or voluntary decision to refrain from behaviors such as sexual activity or the use of alcohol, tobacco and other drugs. Abuse: Physical, emotional or sexual harm on one individual by another. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS): An incurable communicable disease in which the immune system of the body becomes progressively weaker. Addiction: A physiological dependence on a drug. Aerobic activity: Rhythmic, steady exercise that requires more oxygen than sedentary behavior and promotes a healthy heart, lungs, and circulatory system. Examples of aerobic activities include jumping rope, cycling, long-distance swimming or running, and soccer. Agility: The ability to change the position of the entire body in space quickly and accurately. Adolescence: The segment of life between childhood and adulthood. Anaerobic activity: Exercises of short duration, using explosive strength that deplete the energy sources of the body in the absence of oxygen. Examples of anaerobic activities are sprinting and other speed activities, weightlifting, and shot-putting. Anal Sex: Penis to anus contact. Anxiety: Feelings of worry or uneasiness. Arrhythmia: Irregular heartbeats. Assertiveness: Being firm in positive ways to justify personal beliefs. Assessment: Using a number of different measures and observations to evaluate a student s performance, knowledge or achievement. Atods: Alcohol, tobacco and other drugs 26
2 B Bacteria: A single-celled micro-organism. Benign: Noncancerous. Binge Drinking: Consumption of five or more alcoholic drinks in one drinking episode. Binge Eating Disorder: Compulsive overeating. Bisexual: A person who feels sexual attraction to or has sexual contact with both sexes Blood Alcohol Concentration: The percentage of alcohol in a person s blood used to define legal intoxication. Body composition: A health-related component of physical fitness that relates to the percentage of fat and lean tissue in the body. Body Image: The way a person sees his/her body. Body Mass Index (BMI): A body measurement expressing ideal weight according to the ratio of a person s height and weight. Bulimia: An eating disorder characterized by overeating followed by forced vomiting. Bullying: Taking pleasure from inflicting physical, emotional, or psychological pain on another person. C Caloric content: The amount of energy supplied by food. Calories in/calories out: Balance of daily calories consumed with the daily calories burned through activity. Cancer: Disease in which abnormal cells grow in an uncontrollable manner. Carbohydrates: Energy-rich substances found in foods like bread, potatoes, pasta, etc. Carcinogen: Cancer-causing substance. Carbon Monoxide: A poisonous gas that is colorless and odorless. 27
3 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): A first aid procedure combining chest compressions and rescue breathing to supply oxygen to the brain of a person who cannot breathe on his/her own. Cardiovascular Disease: A disease that impacts the heart and blood vessels Cardiovascular endurance: A physical fitness component that relates to the heart, lungs, and circulatory system as they supply oxygen to the body during sustained physical activity. Cervix: The opening to the uterus. Chain of Survival: A sequence of first aid actions that increase a victim s chances for survival. Chlamydia: A sexually transmitted infection that attacks male and female reproductive organs. Circuit training: Exercise program similar to an obstacle course, in which a person goes from station to station doing a different exercise at each station. Clitoris: A highly sensitive structure of the female external genitals. Club Drugs: Drugs associated with use at social events such as concerts, and all night parties. Communicable Diseases: Disease spread from person to person or through the environment. Community: A group of people whose members are connected to one another through a common identity, set of experiences, or a common place. Conflict Resolution: A strategy to end conflict through cooperation, communication, and problem solving. Contraception: Techniques, drugs or devices to prevent conception. Coping: Ability to successfully deal with life s changes and challenges. Culture: A group of people sharing a common belief, experience, identity, history, language, tradition, religion, etc. D Date Rape: One person forcing another to have sexual intercourse in a dating relationship. Decision-Making Skills: Skills that help protect an individual in risky situations. Defibrillator: A device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to restore normal rhythm. Depressants: Drugs that slow down the central nervous system. 28
4 Depression: Long term feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, and sadness. Developmentally appropriate: Teaching and learning that meet the needs of students as their abilities change with age, experience, and maturity. Diabetes: Chronic illness that affects the way carbohydrates are metabolized leading to blindness, amputations and organ failure. Dietary Supplement: A nonfood item containing one or more nutrients. E Eating Disorder: Harmful eating behavior/habit that can cause illness or death. Ectopic Pregnancy: A fertilized ovum that implants in a location other than the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes. EIA: A screening test that detects HIV antibodies in the blood. Ejaculation: The process whereby semen is expelled out of the body through the penis. Embryo: A cluster of cells that develops between the third and eighth weeks of pregnancy. Emotional Abuse: A behavioral pattern that attacks the emotional development and self-worth of an individual. Emotional Maturity: The stage of life when the mental and emotional abilities of a person are fully developed. Endurance: Stamina; the ability to exercise for long periods of time to develop cardiovascular and muscular endurance. Empathy: The ability to understand the feelings that another person experiences. Erection: The process of the penis and clitoris engorging with blood and increasing in size. Estrogen: Sex hormone produced primarily in the female. Euphoria: An intense feeling of well-being. 29
5 F Fad Diet: A weight loss plan that is popular with people for only a short period of time. Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts): Two tubes that extend from near each ovary and connect to the uterus allowing eggs to travel to the uterus for fertilization. Fats: Energy-rich substances such as butter and oils. Fertilization: The joining of the male sperm cell and the female egg cell. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS): Physical and mental birth defects caused by alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Fetus: The developing embryo in the uterus. First Aid: Care given to an ill or injured individual until professional medical assistance arrives. FITT principle: Frequency (exercise must be regular to be effective) Intensity (to produce fitness gains, exertion must be beyond daily exertion requirements), Time (duration of activity must be sufficient to improve fitness), Type (aerobic or anaerobic exercise). Flexibility: The range of motion available at a given joint of the body. Food guide pyramid: A visual, online tool used to assist children and adults to plan healthy eating habits based on the Dietary Guidelines for America. Foster Care: A method of child care in which a child is placed with a family or an adult who is not related to the child by birth. G Gametes: Reproductive cells. Gateway Drug: First drugs of use such as tobacco, alcohol and marijuana that may lead to the transition of use to more dangerous drugs. Genes: Basic units of heredity. Gender Identity: The way one psychologically perceives himself/herself as either male or female. Genitals: The sexual organs of males and females. Genital Herpes: A sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by a virus. 30
6 Gonads: the ovaries in females and the testes in males. Gonorrhea: A bacterial sexually transmitted disease that affects mucous membranes in males and females. Group Therapy: A form or treatment where people with similar problems meat regularly with a trained counselor to discuss their issues. Gynecology: The medical practice specializing in women s health and diseases of the reproductive and sexual organs. H Hallucinogens: Drugs that alter moods and senses perceptions including hearing, sight, smell, and touch. Harassment: The act of continually annoying others. Health Literacy: The ability to obtain, interpret, and understand basic health information, and to apply it in ways to enhance health throughout one s life. Health Scam: The promotion and/or sale of worthless items claimed to prevent diseases or cure other health problems. Herbal Supplement: A substance from plants that may be sold and used as a dietary supplement. Heredity: Traits that are biologically passed from parents to children. Heterosexual: A person whose primary social, emotional, and sexual orientation is towards members of the opposite sex. Homosexual: A person whose primary social, emotional, and sexual orientation is towards members of the same sex. Hormones: Chemical substances produced by endocrine glands that affect the functioning of body organs. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): A virus that attacks the immune system. Human Papillomavirus (HPV): A sexually transmitted virus that affects the genitals of men and women that can lead to cervical cancer in women. Hymen: Tissue that partially covers the vaginal opening. 31
7 Hypertension: High blood pressure. I Illicit Drugs: Chemical substances (drugs) that are illegal to manufacture or use. Immune System: A defense system in the body that prevents and fights disease. Immunity: Being protected from specific diseases. Incest: Sexual interaction between close relatives other than husband and wife. Inhalants: Substance or chemicals that inhaled to achieve a mind-altering state. Intentional Violence: Homicide, suicide or other acts of violence. Intoxication: Poisoning of the body by alcohol or other substances significantly reducing physical and emotional control. L Labia Majora: The outer skin folds of the vulva on both sides of the vaginal opening. Labia Minora: The inner folds of the vaginal opening. Labor: The final stage of pregnancy in which the uterus contracts and pushes the baby through the birth canal. Lesbian: A woman whose primary social, emotional, and sexual attraction is towards members of the same sex. Lymph: A clear liquid in the body containing specialized white blood cells that provide the body with protection against disease. M Malignant: Cancerous growth. Maximum Heart Rate: Highest heart rate attainable when exercising in an all-out effort to the point of exhaustion (general formula: age). Marijuana: A plant whose leaves, buds and flowers are used to produce intoxicating effects. Media: Radio, television, newspapers and magazines, the Internet, and other methods of communicating information. 32
8 Melanoma: The most serious form of skin cancer. Menarche: The initial onset of menstrual cycles in women. Menopause: The stage of life ending the reproductive years for women. Menstruation: Shedding of the uterine lining through the vaginal opening. Mental Disorder: An illness of the mind that can affect the body mentally, emotionally, and physically preventing a person from living a happy and healthful life. Mental and Emotional Health: The ability of a person to accept his/her strengths and weaknesses, adapt to change, and to respond positively to challenges of life. Metabolism: The process of breaking down and converting foods to energy. Metastasis: The spreading of cancer from an original site to other sites in the body. Miscarriage: The spontaneous premature ending of a pregnancy also known as a spontaneous abortion. Moderate physical activity: Sustained, repetitive, large-muscle activities (e.g., walking, running, cycling) done at less than 60 percent of maximum heart range for age. The maximum heart rate is 220 beats/minute minus the participant s age. Muscular endurance: The ability of the muscles to perform without fatigue for an extended period of time. Muscular strength: The amount of force that is produced by muscles contracting, as measured by one maximum attempt in an activity. My Pyramid: The government s guide for healthful eating N Narcotics: Prescription drugs used to relieve pain. Nocturnal Emission: Involuntary ejaculation in males during sleep; also known as a wet dream. Non-communicable Disease: A disease that is not transmitted from person to person or through the environment. Nutrient: A basic component of food that nourishes the body. 33
9 O Obesity: An excess amount of body fat expressed through BMI or other method. Osteoarthritis: A joint disease in which the cartilage weakens and breaks down. Osteoporosis: Progressive loss of bone tissue as the body ages. Oral Sex: Mouth to genital or anus contact. Ova: Female reproductive cells. Ovaries: Two female sex glands that produce ova and sex hormones. Overdose: A reaction to taking a large amount of a drug sometimes resulting in death. Ovulation: The release of a mature ovum from the ovary. Ovum: Female reproductive cell. P Pandemic: A worldwide outbreak of infectious disease. Peer pressure: Influence that friends or acquaintances may exert on an individual. Penis: Male sexual organ including the internal root, external shaft and glans. Physical activity: Any fitness, sports, or recreational activity involving movement of the body that is produced through muscle contraction that increases energy expenditure. Physical education: A planned, sequential curriculum to develop strategies for students to develop and maintain a healthy lifestyle. It includes cognitive and physical aspects of sport and activity, goal setting, proper nutrition, and formal assessment. Physiological Dependence: A condition where a drug user has a physical need for a drug. Placenta: A disc-shaped organ that lines the uterus during pregnancy and provides nourishment to the embryo. Pornography: Visual and written materials of a sexual nature for purpose of sexual arousal. Premarital Sex: Sexual intercourse that occurs before marriage. Proteins: Substances that build and repair the body, especially muscle tissue. Protein-rich foods include meat, eggs, cheese, nuts, soybeans, etc. 34
10 Psychological Dependence: A condition where a person believes a drug is necessary for normal daily functions. Puberty: The stage of life between childhood and adulthood during which the reproductive organs mature. Pulse: The rhythmic beat of the blood pumped by the heart through the arteries that can be felt on the wrist and at the side of the neck R Rape: Sexual intercourse that occurs without consent under actual or threatened force. Rape Trauma Syndrome: The emotional difficulties women may experience after they have been raped. Refusal Skills: Strategies that can help individuals say no when they are urged to take part in activities that go against their beliefs and values. Remission: A period in time when symptoms of a disease disappear. Repetitive Motion Injury: Injury to muscle and connective tissue caused by repeated movements over a prolonged period of time. Resiliency: The ability to positively adapt and recover from disappointment, difficulty or loss. Resting Heart Rate: The heart rate at rest, generally beats/minute. Road Rage: Losing emotional control while driving a car endangering the safety of self and others. Rubric: A set of scoring guidelines for assessing student skills and knowledge. S Scrotum: The pouch of skin of the external male genitals that encloses the testicles. Secondary Sex Characteristics: The physical characteristics other than genitals that indicate sexual maturity, such as, body hair, breast development, and deepened voice. Sedentary Lifestyle: A lifestyle characterized by a lack of physical activity. Self-Actualization: A person s quest to become the best he/she can become. 35
11 Semen: The fluid ejaculated through the penis that contains sperm and fluids from the male sexual glands. Sexual Abuse: Any sexual contact that is forced upon a person without his/her consent. Sexual Harassment: Uninvited sexual conduct, including comments, directed at another person. Sexual Intercourse: Erect penis of the male entering the vagina of the female. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): Contagious diseases spread from person to person through sexual behaviors. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): See Sexually Transmitted Diseases Side Effects: Physical and psychological reactions to medicines other than those intended. Sperm: Male reproductive cells. Statutory Rape: Sexual intercourse with a person under the legal age of consent. Sterility: The inability for a person to reproduce. Stimulant: A drug that speeds up the central nervous system. Stroke: A blockage to artery that interrupts blood flow to the brain. Stress: The body s positive or negative physical and mental reactions to everyday challenges in life. Stressor: Anything in life that causes stress. Stress-Management Skills: Strategies to address stress in a healthy and effective manner. Syphilis: A sexually transmitted bacterial disease that attacks many parts of the body including the brain. T Target heart rate: Maintaining an exercise rate between 60 and 80 percent of the maximum heart rate. Testes: Two small glands in the male that produce sperm. Testosterone: Sex hormone produced primarily in the male. Toxin: A substance that may kill cells or interfere with their functions. 36
12 Tumor: An abnormal mass of tissue in the body that may or may not be malignant. U Unconditional Love: Love without qualifications or restrictions by one individual to another. Universal Precautions: Measures taken to prevent the spread of communicable diseases by treating all blood and other body fluids as if they contaminated. Urethra: The tube that leads from the bladder to the outside of the body. Uterus: A hollow, pear-shaped female reproductive organ. V Vaccine: A mixture of dead or weakened cells introduced cells introduced into the body to produce an immune response to diseases. Vagina: A muscular, stretchable canal that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body. Values: Personal ideas, attitudes and beliefs that guide individuals in decisions they make throughout their lives. Verbal Abuse: Using words to harm or injure another person. Virgin: Male or female who has never engaged in sexual intercourse. Vulva: The female external genitals. W Warm-up: Activity that involves a gradual increase in the heart and breathing rates, and a slight rise in body temperature, and prepares the mind and body for activity. Withdrawal: The physical/psychological reaction that takes place when a person stops using a drug to which that he or she is chemically dependent. 37
Study Guide: Final Exam Health AC
 Study Guide: Final Exam Health AC Chapter 1 Understanding Health and Wellness Your Health Triangle: Wellness What effects your health? Heredity/genetics Environment a. b. c. d. Attitude/Behavior Media/Technology
Study Guide: Final Exam Health AC Chapter 1 Understanding Health and Wellness Your Health Triangle: Wellness What effects your health? Heredity/genetics Environment a. b. c. d. Attitude/Behavior Media/Technology
Health Final Exam Study Guide
 Health Final Exam Study Guide 1. The providing of accurate health information to help people make healthy choices is called. (Chp.1) 2. Refusal skills are. (Chp. 2) 3. The three categories of total health
Health Final Exam Study Guide 1. The providing of accurate health information to help people make healthy choices is called. (Chp.1) 2. Refusal skills are. (Chp. 2) 3. The three categories of total health
HEALTH GRADE 11. THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618
 HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
HEALTH GRADE 11 THE EWING PUBLIC SCHOOLS 2099 Pennington Road Ewing, NJ 08618 Board Approval Date: August 29, 2016 Michael Nitti Written by: Bud Kowal and EHS Staff Superintendent In accordance with The
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Prentice Hall Health: Skills for Wellness '2001 Correlated to: Tennessee Lifetime Wellness Curriculum Standards (Grades 9-12)
 Tennessee Lifetime Wellness Curriculum Standards (Grades 9-12) STANDARD NUMBER 1.0: DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL Standard: The student will recognize behavioral factors leading to communicable and non-communicable
Tennessee Lifetime Wellness Curriculum Standards (Grades 9-12) STANDARD NUMBER 1.0: DISEASE PREVENTION AND CONTROL Standard: The student will recognize behavioral factors leading to communicable and non-communicable
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness.
 Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness. Power Benchmark 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention. Code B Grade Level Benchmark Vocabulary Skills
Standard: To promote lifelong health and wellness. Power Benchmark 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention. Code B Grade Level Benchmark Vocabulary Skills
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE 10 HEALTH
 UNIT: Mental and Emotional Health/Importance of Adequate Sleep NO. OF : 13 KEY LEARNING(S): To know what it means to be emotionally and mentally healthy. To know why adequate sleep is so important for
UNIT: Mental and Emotional Health/Importance of Adequate Sleep NO. OF : 13 KEY LEARNING(S): To know what it means to be emotionally and mentally healthy. To know why adequate sleep is so important for
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY
 HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
HEALTHY GROWTH & SEXUALITY Y T LI X E S A U SEX GEND ER https://youtu.be/df2yow4xad4 First, egg cells are produced in two almond shaped organs known as the ovaries. During the process of ovulation,
Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key
 Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions
Pre/Post-Summative Assessment Answer Key Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions
Male and Female Reproduction
 Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Male and Female Reproduction Similarities / Differences Develop very similar structures of sex glands Two genital tubes Manufacture the hormones of the other sex. Hormones of one sex are often used to
Grade 10 Comprehensive Health Education Indicators and Objectives
 Grade 10 Comprehensive Health Education Indicators and Objectives Mental and Emotional Health III. Community Resources Accessing Information 1. Demonstrate the ability to access valid information, products,
Grade 10 Comprehensive Health Education Indicators and Objectives Mental and Emotional Health III. Community Resources Accessing Information 1. Demonstrate the ability to access valid information, products,
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Decision-Making Skills (These objectives can be incorporated into all areas of health throughout the course.)
 HEALTH-8 This is a list all the information we may cover throughout the semester. Quarter 1/3 Decision-Making Skills (These objectives can be incorporated into all areas of health throughout the course.)
HEALTH-8 This is a list all the information we may cover throughout the semester. Quarter 1/3 Decision-Making Skills (These objectives can be incorporated into all areas of health throughout the course.)
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Post-Summative Assessment
 Post-Summative Assessment Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions by circling the
Post-Summative Assessment Directions: The following questions will ask you about your knowledge of life skills, human reproduction and making healthy choices. Please answer the questions by circling the
Foundations of Personal Wellness - EL2082
 Unit 1: Health and Wellness Basics Your Health and Wellness Your Fitness Log Health and Wellness Describe the six dimensions of health Differentiate between health and wellness Analyze how influences such
Unit 1: Health and Wellness Basics Your Health and Wellness Your Fitness Log Health and Wellness Describe the six dimensions of health Differentiate between health and wellness Analyze how influences such
MONITORING RESPONSIBILITY: Site administrators or Designees
 TITLE: 5232R Sex Education Instruction PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: To provide guidelines for instruction on acquired immune deficiency syndrome, human reproductive system, related communicable diseases and
TITLE: 5232R Sex Education Instruction PURPOSE AND BACKGROUND: To provide guidelines for instruction on acquired immune deficiency syndrome, human reproductive system, related communicable diseases and
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
10 th Grade Health. Concepts/Content Vocabulary
 1 st or 3 rd Quarter 10 th Grade Health : Definition of Health Definition of Wellness Lifestyle Factors Life Expectancy Healthy People 2012 goals Behavior change What is Health Identifying Health Risks
1 st or 3 rd Quarter 10 th Grade Health : Definition of Health Definition of Wellness Lifestyle Factors Life Expectancy Healthy People 2012 goals Behavior change What is Health Identifying Health Risks
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Unit 1: Health Literacy/Communicable & Non Communicable Diseases Approximate Time Frame: 3 Weeks Standards Essential Questions Enduring
 Course: 10 th Grade Health Sophomore Health is a broad overview of health concepts. Year: 2014 Teacher: Nicole Esposito Lacroix Unit 1: Health Literacy/Communicable & Non Communicable Diseases Approximate
Course: 10 th Grade Health Sophomore Health is a broad overview of health concepts. Year: 2014 Teacher: Nicole Esposito Lacroix Unit 1: Health Literacy/Communicable & Non Communicable Diseases Approximate
Overview of Health Curriculum:
 USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden Health Curriculum Map Welcome to the curriculum design maps for Manhattan-Ogden USD 383, striving to produce learners who are: Effective Communicators who clearly express ideas
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Wellness Final Exam Study Guide
 Wellness Final Exam Study Guide Wellness Final Exam Study Guide ***Highlight Three Keywords for each section Wellness Social Wellness-- Encourages participation in ones community, campus, and environment.
Wellness Final Exam Study Guide Wellness Final Exam Study Guide ***Highlight Three Keywords for each section Wellness Social Wellness-- Encourages participation in ones community, campus, and environment.
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
How to Prevent Sexually Transmitted Diseases
 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright owner. This includes
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Chapter 115. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Health Education. Subchapter B. Middle School
 Middle School 115.B. Chapter 115. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Health Education Subchapter B. Middle School Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter B issued under the Texas Education
Middle School 115.B. Chapter 115. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Health Education Subchapter B. Middle School Statutory Authority: The provisions of this Subchapter B issued under the Texas Education
TExES Health EC 12 Curriculum Crosswalk
 TExES Health EC 12 Curriculum Crosswalk Domain I Personal Health Competency 001: The teacher understands human body systems and the processes of human growth and development. A. Demonstrates an understanding
TExES Health EC 12 Curriculum Crosswalk Domain I Personal Health Competency 001: The teacher understands human body systems and the processes of human growth and development. A. Demonstrates an understanding
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
SENECA HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT #160 Teacher: Baker Grade: 10 Subject: Health Year:
 A Healthy Foundation Nutrition Understanding Health and Wellness Building Health Skills Decision Making/Goal Setting Health Literate Consumerism Importance of Nutrition Healthy Eating Guidelines Nutrition
A Healthy Foundation Nutrition Understanding Health and Wellness Building Health Skills Decision Making/Goal Setting Health Literate Consumerism Importance of Nutrition Healthy Eating Guidelines Nutrition
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Model Curriculum Grade 6-8 Units
 Grade 6-8 Unit Overview Comprehensive Health Education Overview for the Model Curriculum Units The grades 6-8 Comprehensive Health Education Units are a cohesive set of four units that will scaffold instruction
Grade 6-8 Unit Overview Comprehensive Health Education Overview for the Model Curriculum Units The grades 6-8 Comprehensive Health Education Units are a cohesive set of four units that will scaffold instruction
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT. Course Description. Instructional Strategies, Learning Practices, Activities, and Experiences.
 SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Health Education Grade Level(s): 10 Units of Credit:.50 Classification: Required Length of Course: 15 cycles Periods Per Cycle: 6
SPRING GROVE AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT PLANNED COURSE OVERVIEW Course Title: Health Education Grade Level(s): 10 Units of Credit:.50 Classification: Required Length of Course: 15 cycles Periods Per Cycle: 6
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
Know, Understand, Do
 Know, Understand, Do Unit Topic: Health and your Wellness By completing this unit, students will Know Infectious Diseases Lifestyle Diseases Six Components of Health Technology s improvement on medical
Know, Understand, Do Unit Topic: Health and your Wellness By completing this unit, students will Know Infectious Diseases Lifestyle Diseases Six Components of Health Technology s improvement on medical
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc.
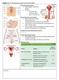 Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
Chapter 11: The Reproductive System and Sexual Health The Reproductive System Responsibility: Continue the species Structure: Pair of Gonads Accessory organs, ducts, hormones, etc. Sexual Autonomy and
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Topic: Effects Standard: Analyzes the impact of the use of alcohol, tobacco products, and other drugs on the individual, family, and community.
 Create Date: 5/26/2004 Copyright 2002 Georgia Department of Education Browse Quality Core Curriculum Standards by subject Subject: Health Grade: 6 Strand: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 1 2 3 4 Topic:
Create Date: 5/26/2004 Copyright 2002 Georgia Department of Education Browse Quality Core Curriculum Standards by subject Subject: Health Grade: 6 Strand: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 1 2 3 4 Topic:
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
The Female Reproductive System
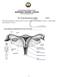 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Teen Health Vocabulary List
 Term health wellness emotions risk behavior self-assessment hygiene refusal skills nutrition calories diet anorexia nutrition food groups vitamins nutrients carbohydrates proteins minerals fats fiber saturated
Term health wellness emotions risk behavior self-assessment hygiene refusal skills nutrition calories diet anorexia nutrition food groups vitamins nutrients carbohydrates proteins minerals fats fiber saturated
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Twinsburg City Schools Standards-Based Health Course of Study. Health
 Course Name: () Rationale: The acquisition of basic health concepts and functional health knowledge provides a foundation for promoting health-enhancing behaviors among youth. This standard includes essential
Course Name: () Rationale: The acquisition of basic health concepts and functional health knowledge provides a foundation for promoting health-enhancing behaviors among youth. This standard includes essential
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Growth and Development 6 th Grade
 Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
Growth and Development 6 th Grade All living things reproduce. Our bodies change during puberty to make reproduction possible. This is not always fun But it is pretty amazing! PUBERTY is the process of
SAU #48 Health Curriculum Middle School Level Grades 6-8
 SAU #48 Health Curriculum Middle School Level Grades 6-8 EMOTIONAL HEALTH 1. Positive Self-Image Personal assets and strengths Characteristics of positive role models How to develop and demonstrate a sense
SAU #48 Health Curriculum Middle School Level Grades 6-8 EMOTIONAL HEALTH 1. Positive Self-Image Personal assets and strengths Characteristics of positive role models How to develop and demonstrate a sense
5th Grade Physical Education Pacing Guide
 5th Grade Pacing Guide Overarching PEL 1.5.1 Demonstrate and describe how the muscular and skeletal systems interact during movement activities (e.g., proper lifting techniques, throwing or catching activities)
5th Grade Pacing Guide Overarching PEL 1.5.1 Demonstrate and describe how the muscular and skeletal systems interact during movement activities (e.g., proper lifting techniques, throwing or catching activities)
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS 9 th Health Education Curriculum Pacing Guide Days SOL Objective Vocabulary 4 weeks 9.1 Essential Health Concepts: The student will apply health knowledge and skills to
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS 9 th Health Education Curriculum Pacing Guide Days SOL Objective Vocabulary 4 weeks 9.1 Essential Health Concepts: The student will apply health knowledge and skills to
Rockaway Township Public Schools Health Unit Plan Grade 7
 Unit Title: Time Frame: 21 st Century Theme: Family Life 7 5-6 days Health Literacy, critical thinking and problem solving, communication and collaboration, Information Literacy, Media Literacy, ITC Literacy
Unit Title: Time Frame: 21 st Century Theme: Family Life 7 5-6 days Health Literacy, critical thinking and problem solving, communication and collaboration, Information Literacy, Media Literacy, ITC Literacy
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS
 LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
LTASEX.INFO STI SUMMARY SHEETS FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY. COMMERCIAL USE RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 2013, JEROME STUART NICHOLS LTASEX.INFO! IN AIDS is a treatable complication of advanced HIV infection.
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education
 Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
Word list of symbols and signs in Sex Education Abbreviations Key: CV Core Vocabulary * Signs Only + Symbols Only Abortion / Termination Abuse, to (2) / Physical Abuse Abuse, to (3) / Verbal Abuse* Adolescence
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
Health Education Appendix F: Life Skills Connections
 Health Education Appendix F: Connections In 2006 The Utah State Office of Education produced a document that describes the attributes of a well-educated person. The seven domains reflect the thinking of
Health Education Appendix F: Connections In 2006 The Utah State Office of Education produced a document that describes the attributes of a well-educated person. The seven domains reflect the thinking of
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 6 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproduction Systems 1 Terms Alimentary canal Bladder Cervix Clitoris Cloaca Copulation Cowper s gland Epididymis Fallopian
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
4 CATEGORIES. Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs
 DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Comprehensive Health & Physical Education Colorado Sample Graduation Competencies and Evidence Outcomes
 Comprehensive Health & Physical Education Colorado Sample Graduation Competencies and Evidence Outcomes Physical Education Graduation Competency 1 Demonstrate competency in motor skills, movement concepts,
Comprehensive Health & Physical Education Colorado Sample Graduation Competencies and Evidence Outcomes Physical Education Graduation Competency 1 Demonstrate competency in motor skills, movement concepts,
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System. Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems
 Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Topic 18- Human Reproductive System Day 2-Female (and review of) Male Reproductive Systems Bell Ringer (5 minutes) Bioblitz WHAT ARE WE LEARNING TODAY? Date: 12/14-12/15 Topic: Human Reproductive System
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
CURRICULUM DOCUMENT GRADE: 6 th Grade SUBJECT: Physical Education
 1 st Quarter Enduring I can control my body movements. Standard 1: Motor Skills and Movement- demonstrate competency in motor skills and understanding of movement concepts, principles, strategies, and
1 st Quarter Enduring I can control my body movements. Standard 1: Motor Skills and Movement- demonstrate competency in motor skills and understanding of movement concepts, principles, strategies, and
Chapter 11 Gender and Sexuality
 Chapter 11 Gender and Sexuality Defining Some Terms Sex: Whether you are biologically male or female Gender: All the psychological and social characteristics associated with being male or female; defined
Chapter 11 Gender and Sexuality Defining Some Terms Sex: Whether you are biologically male or female Gender: All the psychological and social characteristics associated with being male or female; defined
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Sexually Transmitted Infections Introduction Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are some of the most common infectious diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases are also called sexually transmitted
Sexually Transmitted Infections Introduction Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are some of the most common infectious diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases are also called sexually transmitted
Content Map For Physical Education
 Content Map For Physical Education Content Strand: Physical Fitness 6-H/PE-1 Participates in fitness assessment (i.e., Fitness Gram) and developmentally appropriate health-related fitness activities for
Content Map For Physical Education Content Strand: Physical Fitness 6-H/PE-1 Participates in fitness assessment (i.e., Fitness Gram) and developmentally appropriate health-related fitness activities for
How Do You Catch An Infection?
 How Do You Catch An Infection? Animals Insects Water People Food Infectious Diseases Considerations for the 21 st Century Viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths Infectious diseases are the second
How Do You Catch An Infection? Animals Insects Water People Food Infectious Diseases Considerations for the 21 st Century Viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, helminths Infectious diseases are the second
Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity
 Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Unit 7 Lesson 7.1 Notes Introductory Video Video STIs: Running the Risk Chapter 20: Risks of Adolescent Sexual Activity Section 1: What Are the Risks? Key Terms: Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) an infectious
Calvert County Public Schools Health Education Curriculum High School
 Calvert County Public Schools Health Education Curriculum High School Introduction The high school health education curriculum was created using the Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool (HECAT) provided
Calvert County Public Schools Health Education Curriculum High School Introduction The high school health education curriculum was created using the Health Education Curriculum Analysis Tool (HECAT) provided
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview
 Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Overview Q: What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? A: It is an infection or disease passed from person to person through sexual contact. Q: How many people have STDs?
Shrewsbury Borough School Comprehensive Health and Physical Education in the 21 st Century 2012 Health: Grade 8
 Shrewsbury Borough School Comprehensive Health and Physical Education in the 21 st Century 2012 Health: Grade 8 Topic 1: Personal Growth and Development Discuss how heredity, physiological changes, environmental
Shrewsbury Borough School Comprehensive Health and Physical Education in the 21 st Century 2012 Health: Grade 8 Topic 1: Personal Growth and Development Discuss how heredity, physiological changes, environmental
11TH GRADE HEALTH #912
 11TH GRADE HEALTH #912 Health instruction includes family life and substance abuse education. Major areas of study include: love, male and female reproductive systems, human development, abstinence, pregnancy,
11TH GRADE HEALTH #912 Health instruction includes family life and substance abuse education. Major areas of study include: love, male and female reproductive systems, human development, abstinence, pregnancy,
High School Health Education Curriculum Guide
 High School Health Education Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 To align with the 2008 Virginia Health standards of Learning the 2009 adoption of the Holt: Lifetime Health textbook and the inclusion of Driver
High School Health Education Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 To align with the 2008 Virginia Health standards of Learning the 2009 adoption of the Holt: Lifetime Health textbook and the inclusion of Driver
Standard 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health.
 Grade 8 Standard 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health. Benchmark 1-M-1: Describe interrelationships among physical, intellectual, emotional
Grade 8 Standard 1: Students will comprehend concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health. Benchmark 1-M-1: Describe interrelationships among physical, intellectual, emotional
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1
 Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
