NECK SUPERFICIAL STRUCTURES OF THE NECK Compartments: SCM, Posterior, Lateral, Anterior
|
|
|
- Ambrose Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NECK SUPERFICIAL STRUCTURES OF THE NECK Compartments: SCM, Posterior, Lateral, Anterior BONES Cervical Vertebrae SCM Mastoid process of temp bone & Sup Nuchal line of occiput Manubrium & medial 1/3 1 clavicle XI Platysma Inf border mandible, VII Trapezius Med 1/3 sup nuchal line, ext occipital protuberance, C7-12 SP Deep fascia deltoid & pec major Lateral 1/3 clavicle, acromion, spine scapula Type Typical C3-6 Atypical C1 C2 C7 Body small and wide Vertebral foramen large & triangular TP incl foramina transversaria for vert vessels Sup facets sup/post vs Inf facets inf/post Bifid spin process no spine process or body, articulates with occiput dens projects and articulates with C1 long non-bifid SP, large TP with small foramina transversaria Hyoid Level C3 Attached to styloid via Stylohyoid ligament Attached to thyroid cartilage 1 XI Lateral flexion/rotation atlanto-occipital Flex (chin to chest) Ext sup & flex inf vert Elevate manubrium Tenses skin superficial vein release pressure, Depress mandible &angles of mouth Scapula: elevate, retract, rotate Superior fibres: elevate pec girdle Middle fibres: retract scapula Inferior fibres: depress shoulder Fixed shoulders: extend neck or flex to either side Forms lesser supraclavicular fossa when splits FASCIA SUPERFICIAL FASCIA Cutaneous nerves, bloods, lymphatics, nodes, fat Platysma From 2nd pharyngeal arch Deep fascia of deltoid & pec major inf border mandible Innervated by VII Deep to incl EJV DEEP CERVICAL FASCIA Investing, Pretracheal, Prevertebral Carotid sheath & pretracheal fascia communicate with cranial vault and mediastinum Investing Most superficial, surrounding entire neck At margins splits into deep/superficial and invest trapezius & SCM (supplied by XI) Investment of SCM also includes suprasternal space enclosing ant jugular veins, jugular arch, fat, deep nodes Superior Attachments Sup nuchal line of occipital Mastoid process of temp Zygomatic arch Inf border mandible (split to enclose submandibular, parotid gland) Hyoid SP of C-vert (A) Sternocleidomastoid Region Overlies SCM Anterior region in front / Lateral Region behind Inferior Attachments Manubrium, clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula (C) Lateral Cervical Region aka Posterior Triangle (B) Posterior Cervical Region Post to ant border of Trapezius (NB Sub occipital region (E) deep to superior part) Pretracheal Hyoid pericardium Muscular part: thin, encloses Infrahyoid Visceral part: thyroid, trachea, oesophagus, cont post/sup with buccopharyngeal fascia Superior: intermediate tendon of digastric passes up then loops down to suspend hyoid Prevertebral Around vert column and ass muscles (ant: longus colli & capitis, lat: scalenes, post: deep cervical) Cranial base Endothoracic fascia & ant longitudinal T3 & axillary sheath (encloses plexus, vessels) Carotid sheath Condense around Common carotid, IJV & X, carotid sinus nerve, carotid periarterial plexus All 3 contribute to sheath Artery medial, IJV lateral, X posterior Retropharyngeal space Between prevertebral layer and buccopharyngeal fascia/pretracheal fascia (cont) Alar fascia: midline buccopharyngeal fascia (Cranium C7) to carotid sheath Border Ant Post Inf Apex Roof Floor Post border of SCM Ant border trapezium Middle 1/3 clavicle SCM + Trap Investing layer of deep fascia Prevertebral muscles Sup to Inf: Splenius capitis Levator scapulae Middle scalenes Posterior scalenes Subdivisions Occipital Triangle (2) Omoclavicular Triangle (3) supraclavicular fossa Divided by inferior belly of Omohyoid Occipital artery in apex XI crosses EJV crosses Subclavian a. deep to rd Lateral branches of Thyrocervical trunk or 3 part of Subclavian a. & occipital a. Artery Origin Suprascapular Cervicodorsal trunk Thyrocervical trunk (branch of Subclavian) Occipital rd Subclavian (3 part) ECA Brachiocephalic trunk Course Inferolateral across ant scalene & phrenic n., Subclavian a, brachial plexus then post to clavicle to supply muscles on post scapula Laterally ant to phrenic n., ant scalene through brachial plexus to supply them terminates deep to levator scapulae and rhomboids and supply them Ascends to head to supply post scalp Cont from alt border of ant scalene post sup to vein and ant to st plexus deep to clavicle and on 1 rib EJV retromandibular + posterior auricular EJV near angle of mandible Desc over SCM Pierces investing layer & lateral SCM to Subclavian XI runs deep to SCM and emerges in sup 1/3 Descends in lateral region and exits under trapezius Tranatomy: Neck 2012 Page 1 of 5
2 FASCIA Brachial Plexus C5-T1 Roots: btwn ant/mid scalenes Trunks: pass through cervicoaxillary canal (1 st rib, clavicle, scapula) Suprascapular n. from superior trunk Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus & jt Cervical Plexus C1-4 Btwn levator scapulae & middle scalenes (deep to SCM) Ansa cervicalis Superior Root: C1,2, joins XII briefly as it descends then splits away at level C3 Inferior Root: C2,3 Both combine to form secondary loop to supply Infrahyoid muscles (not Thyrohyoid-C1) Branches of C2-3 loop Lesser Occipital: C2 neck, post scalp Great Auricular: C2,3 over SCM to parotid supply skin on parotid, mastoid, auricle Transverse cervical: C2,3 skin over anterior cervical region Branches of C3-4 loop Supraclavicular nerve: emerges beaneath SCM to supply clavicle and shoulder skin Phrenic Nerve C3,4,5 Motor, sensory, sympth Diaphragm, mediastinal pleura, pericardium Forms at lateral border of ant scalenes (sup border of thyroid cart) Descends deep to Prevertebral layer Left crosses ant to 1 st part Subclavian a. Right crosses ant to 2 nd part Both desc post to Subclavian vein/ant to internal thoracic artery Superficial cervical along EJV deep cervical (D) Anterior Cervical Region Border Ant Post Sup Apex Roof Floor Subdivisions 1 Submental (5)(unpaired) Submandibular (4) Carotid (6) Muscular (7) Median line of neck Ant border SCM Inf border mandible Jug notch Platysma and subcut tissue Pharynx, larynx, thyroid 1 By Omohyoid & digastric Hyoid/mandible/digastric/mandibular symphysis Floor: Mylohyoid Contains nodes and ant jugular vein Mandible/ant/post bellies of digastric Floor: Mylohyoid & hyoglossus, middle pharyngeal constrictor Submandibular gland fills most of triangle, Submandibular nodes, XII and branch of V3 Superior belly Omohyoid, posterior belly of digastric, ant border SCM Contains common carotid dividing at level of thyroid cartilage Other contents: Carotid sinus ( IX, X) Carotid body ( IX, X) Superior belly Omohyoid, ant border scm, median plane of neck Infrahyoid muscles Brachiocephalic branches into r Subclavian & r carotid vs L carotid from Ao arch Both bifurcate at level of thyroid cartilage Internal carotid has no branches in neck, enters cranium via carotid canal (in petrous temp) Sigmoid sinus in post cranial fossa jugular foramen IJV Descends in carotid sheath Cervical sympathetic trunk post to sheath Exits anterior region through supraclavicular fossa Tributaries Inferior petrosal sinus (from cranium via jug foramen and into IJV) Facial vein enters near hyoid Lingual enters IJV near artery Pharyngeal veins at level of angle of mandible Thyroid veins (superior/middle) Transverse cervical (C2-3) XII IX X DEEP STRUCTURES OF THE NECK Prevertebral Muscle Anterior Vertebral Muscle 1 Longus Colli C1 ant tubercle C1-3 body C3-6 TP C5-T3 body C3-5 TP Ant Rami C2-6 Longus Capitis Basilar occipital C3-6 TP (ant Ant rami C1-3 tubercle) Rectus capitis ant Base of cranium 2 Ant lat arch C1 C1-2 loop branches Anterior Scalenes C3-6 TP 1 st rib C4-6 Flex neck with rotation Flex head Lateral Vertebral Muscles Rectus capitis Jugular process C1 TP C1-2 loop lateralis occipital bone Flex head, stabilise Splenius capitis Lateral aspect of Inf ½ nuchal Post rami C3-5 mastoid process ligament, SP of T1-6 Flex/rotate or extend Levator scapulae C2-6 TP Sup-Med scapula C5 dorsal scapular, C3-4 spinal nerves Down rotate scapula Glenoid tilt inf Middle scalenes Sup surface 1 st rib Ant rami c-spine C5-7 TP post to Subclavian Flex, elevate rib 1 groove Posterior scalenes External border C2 Ant rami C7,8 Flex, elevate 2 nd rib 1 post to retropharyngeal space & medial to cervical/brachial plexus and Subclavian a 2 ant to occipital condyle External carotid Supplies outside of cranium except scalp and orbits (supraorbital artery) Terminates as maxillary and superficial temporal artery after traversing parotid gland 6 main branches arise (1-2-3 = 1 medial, 2 posterior, 3 anterior) Branch Arise Notes Ascending Medial Only medial branch pharyngeal Asc on parynx medial to IC Dsit: pharynx, pervert muscles, middle ear, cranial meninges Occipital Posterior Begins on post side IC (and superior to facial artery) Parallels post belly digastric Branches and supplies posterior scalp Superficial to IX-XI Posterior Posterior Asc btwn EAC & mastoid to supply parotid, VII, temporal bone, auricle, scalp auricular Superior Anterior Deep to Infrahyoid to thyroid gland thyroid Branches to Infrahyoid muscls and scm Branches to superior laryngeal a. Lingual Anterior Lies on middle pharyngeal constrictor Deep to XII, Stylohyoid, post belly digastric Facial Anterior Anterior branch with or above lingual Ascends under digastric, Stylohyoid and abgle Submandibular gland, subemtnal branch Tranatomy: Neck 2012 Page 2 of 5
3 ROOT OF NECK Brachiocephalic trunk branches post to SCJ on right Subclavian on both sides begin at SCJ and reach highest point behind ant scalenes 3 parts based on location to scalenes Part Location Branches 1 Medial Vertebral, Internal Thoracic, Thyrocervical trunk 2 Posterior Costocervical trunk 3 Lateral Dorsal Scapular Vertebral Artery Cervical (branch of vertebral) ascends btwn scalenes and longus, passes deep through foramen transversaria of C1-6 Sub occipital part ascends in groove on post arch C1 through foramen magnum Cranial part supplies medulla, cord, cerebellum, dura Joins to form basilar artery Thyrocervical trunk Branches from Subclavian near medial border of ant scalenes 4 branches Inferior thyroid Asc cervical artery Suprascapular Cervicodorsal trunk Costocervical trunk Branches into sup intercostal and deep cervical Prelaryngeal Pretracheal Paratracheal Lateral Drainage Superior deep cervical Paratracheal Inferior deep cervical VISCERA OF THE NECK 1. Endocrine (thyroid/parathyroid) 2. Respiratory (larynx/trachea) 3. Alimentary (pharynx/oesophagus) 1. ENDOCRINE LAYER Thyroid Deep to Sternothyroid and Sternohyoid C5-T1 or tracheal ring 2-3 Anterolateral to larynx Artery Origin Course Superior Thyroid 1 st branch of ext carotid Pierces fascia and branches into ant/post Dist: anterosuperior thyroid Inferior Thyroid Branch of Thyrocervical trunk (from Subclavian) Ascends post to carotid sheath, Inserts post before branching Dist: inferoposterior thyroid, all parathyroid Thyroid Ima Brachiocephalic 10% of people Dist: isthmus NB heavy anastomoses between sup/inf thyroid arteries Axillary a. forms when SC a. passes 1 st rib Vein Drainage of Drainage to Orientation Superior Superior lobes IJV With sup a. Middle Middle area Parallel to inf a. Inferior Inferior lobes Brachiocephalic Indep Innervation Superior middle inferior nerves From cardiac and superior/inferior thyroid periarterial plexus Vasomotor (secretion is hormonally regulated) EJV (scalp and skin of face) & AJV AJV drains into EJV at root Suprasternal, AJV combine to form jugular venous arch Subclavian vein begins at lateral border 1 st rib IJV (NB EJV joins near insertion to IJV) NERVES Vagus Exits through Jugular foramen & travels post in carotid sheath Right: ant to 1 st part of SCA/post to brachiocephalic vein and SCJ Left: btwn L Common carotid/subclavian and post to SCJ Recurrent Laryngeal Right: loops under R SCA at T1-2 Left: loops under Arch Ao at T4-5 Both asc in trachea-oesophageal groove Phrenic Descends ant to ant scalene under IJV & SCM Sympathetic Trunk Cervical portion: anterolateral to vert column No white rami Efferent to cervical spinal nerves via grey rami communicantes Thoracic viscera via cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves Head and neck viscera via cephalic arterial branches Parathyroid x2 superior x2 inferior (superior less variable) Superior located at inferior border of cricoid cartilage Without capsule but within sheath Vessels Inferior thyroid a. Parathyroid vein thyroid plexus Paratracheal or deep cervical nodes Innervation Thyroid branches of cervical sympth ganglia Vasomotor not vasosecretory 2. RESPIRATORY LAYER Laryngeal Skeleton 9 cartilages: unpaired x3 (thyroid, cricoid, epiglottic) & 3 paired (arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform) Thyroid cartilage Aspect Anterior Fuse to form laryngeal prominence with sup thyroid notch Posterior Open, greater horn and lesser horns Superior Thyrohyoid membrane attaches sup horn and sup border to hyoid (greater horn and body) Sup C4 Inferior Cricothyroid joint: inf horn post cricoid (movt incl rotation & gliding VC length) Remainder attaches via median cricothyroid ligament Cricoid Only complete ring Arch anterior, lamina posterior Cricotracheal ligament to 1 st tracheal ring Tranatomy: Neck 2012 Page 3 of 5
4 Arytenoid Position Corniculate cart (1) Sup/Med Sits on apex Apex (2) Sup/Med Attachment for ary-epiglottic fold/ligament 1 Vocal process (4) Inf/Med/Ant Post attachment for vocal ligament Muscular process (5) Inf/Lat attaches posterior and lateral crico-arytenoid muscles Crico-arytenoid jt (9) Inf/Mid/Post Movt: slide together, tilt ant/post or rotate Oblong fovea (6) Inf/Lat Thyro-arytenoid attaches 1 Forms lateral border of inlet, attaches to quadrangular membrane to lat/inf edge of epiglottis Branches of superior & inferior thyroid Artery Origin Course Superior Laryngeal Superior Thyroid With sup laryngeal nerve Thyrohyoid membrane Dist: internal larynx Cricothyroid Superior thyroid Cricothyroid muscle Inferior Laryngeal Inferior thyroid With inf laryngeal nerve mucous membrane/muscles of inf larynx Superior and inferior follow arteries and nerves Superior sup thyroid IJV Inferior venous plexus on trachea L brachiocephalic trunk Superior to vocal folds sup deep cervical nodes Inferior to vocal folds pre & paratracheal nodes inferior deep cervical nodes Epiglottic Cartilage Elastic cartilage covered with mucous membrane Posterior to root of tongue but anterior border of laryngeal inlet Free edge superiorly with tapered end inferiorly as stalk of epiglottis attached to thyroid lamina via thyro-epiglottic ligament Hyo-epiglottic ligament attaches to hyoid Quadrangular membrane attaches inferior edge of epiglottis to arytenoid Conus Elasticus Made up of vocal ligament, lateral cricothyroid ligament and rima glottis Vocal Ligament From internal laryngeal prominence of thyroid cartilage vocal process of arytenoid cartilage Lateral Cricothyroid Ligament Membrane from vocal ligament to cricothyroid Superior Laryngeal Inlet Lateral epiglottic border Ary epiglottic fold Cuneiform tubercle Corniculate tubercle Superior thyroid horn Interior Larynx Laryngeal vestibule (parts above vestibular folds) Middle part (btwn vestibular and vocal folds) Laryngeal ventricle (btwn vestibular & vocal folds) Infraglottic cavity Laryngeal Muscles Extrinsic Move larynx as a whole Include Infrahyoid & Suprahyoid Intrinsic Move individual components All supplied by X (recurrent laryngeal) except cricothyroid (external laryngeal from sup laryngeal) Branch Course Supply Superior laryngeal form inferior vagal ganglion Internal Pierces Thyrohyoid membrane with sup Sensory to superior surface of vocal folds and above laryngeal artery External Pierces inf pharyngeal constrictor follows superior thyroid artery Pharyngeal plexus as well as cricothyroid Inferior laryngeal follow inf laryngeal artery Motor to all laryngeal muscles (except cricothyroid) Sensory to Infraglottic larynx Anterior lateral cricothyroid, thyro-arytenoid, vocalis, ary-epiglottis, thyro-epiglottis Posterior posterior crico-arytenoids, transverse/oblique arytenoids TRACHEA Incomplete tracheal rings (post) with Trachealis muscle overlies incomplete areas 2.5cm diameter C6 T4/5 Aspect Lateral Inferior Right Surrounding Common carotids, thyroid Jugular venous arch, inferior thyroid veins Brachiocephalic trunk 3. ALIMENTARY LAYERS Pharynx Cranial base inf border of cricoid cartilage & C6 Widest opp hyoid vs Narrowest at inferior end Piriform fossa (around larynx) houses internal & recurrent laryngeal nerves Interior Nasopharynx: post nose soft palate Oropharynx: posterior to mouth Laryngopharynx: posterior to larynx Tonsils Lymphoid aggregates Palatine: Roof/post wall of nasopharynx Pharyngeal: post to nasal cavity Tubal: sup to entry of pharyngotympanic tube Lingual: post tongue Cricothyroid Ant cricoid car Inf margin/horn thyroid cart Thyroarytenoid Post aspect of thyroid Ant surface lamina arytenoid Post cricoarytenoid Post cricoid lamina Lateral cricoarytenoid Arch of cricoid Vocal process Transverse & One arytenoid cartilage Contralateral Oblique arytenoid cartilage arytenoids Pivots thyroid post on inf horn stretch cord Pulls arytenoid towards thyroid lamina relax cord Pivots arytenoids outwards abduct cords Pivots arytenoids inwards adduct cords Adducts arytenoids closing rima glottides Vocalis Vocal process Ipsilateral VC Same as thyro-aretynoid Tranatomy: Neck 2012 Page 4 of 5
5 External Layer: Pharyngeal constrictors Pterygoid hamulus, Pterygomandibular raphe, Occipital bone Pharyngeal branch of Superior Post Mylohyoid line of mandible, (pharyngeal tubercle) X & plexus 1 Lateral tongue Hyoid: <, > horns and Middle Pharyngeal raphe + branches of Stylohyoid ligament ext/recurrent Pharyngo-oesopahgeal Inferior Thyroid and cricoid cartilage laryngeal junction Internal Hard palate & palatine Palatopharyngeus Thyroid lamina aponeurosis Pharyngeal branch of Pharyngotympanic Salpingopharyngeus X tube Palatopharyngeus Stylopharyngeus Styloid 1 Located on lateral wall of pharynx mostly on middle constrictor Constrict Elevate Passage 1 Sup & Cranium Sup & Mid Mid & Inf Inf to Inf const. 1 Made byy gaps in muscles Contents Levator veli palatine, pharyngotympanic tube, asc palatine artery Pharyngobasiliar fascia (ant) and buccopharyngeal fascia (post) blend = pharyngeal recess Stylopharyngeus, glossopharyngeal nerve, Stylohyoidd ligament Internal laryngeal nerve, sup laryngeal a. v. Recurrent laryngeal, inferior laryngeal Vessels Tonsillar artery (branch of facial) pierces superior constrictor External palatine vein pharyngeal venous plexus jugulodigastric nodes Pharyngeal plexus Motor: X to all but Stylopharyngeus ( IX) and tensor veli palatine ( V3) Sensory: XII OESOPHAGUS Cervical oesophagus starts at C6 also the narrowest part of oesophagus Supplied by inferior thyroid arteries Drained by inferior thyroid veins Paratracheal or inf deep cervical nodes Innervated by recurrent laryngeal (somatic) and cervical sympathetic trunk (motor) Tranatomy: Neck 2012 Page 5 of 5
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream
 1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Upper Respiratory Tract
 Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Upper Respiratory Tract Lectures Objectives Describe the structure of nasal cavity including nasal septum. Describe the structure of lateral wall of nasal cavity including conchae and meatuses. Locate
Respiratory System. Cambridge University Press Concise Anatomy for Anaesthesia Andreas G. Erdmann Excerpt More information
 Respiratory System 1 The mouth DESCRIPTION The mouth extends from the lips (anterior) to the isthmus of the fauces (posterior). There are two sections: Vestibule slit-like cavity between the cheeks/lips
Respiratory System 1 The mouth DESCRIPTION The mouth extends from the lips (anterior) to the isthmus of the fauces (posterior). There are two sections: Vestibule slit-like cavity between the cheeks/lips
The Larynx. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Larynx Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb The Larynx Extends from the middle of C3 vertebra till the level of the lower border of C6 Continue as Trachea Above it opens into the laryngo-pharynx Suspended
The Larynx Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb The Larynx Extends from the middle of C3 vertebra till the level of the lower border of C6 Continue as Trachea Above it opens into the laryngo-pharynx Suspended
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Chapter 28: The neck. Fascia of the neck
 Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
Chapter 28: The neck Fascia of the neck The superficial fascia is a fatty areolar layer between the skin and the more obvious deep fascia. It contains the platysma muscles and the external jugular veins
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
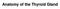 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
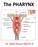 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA
 THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA THE NECK THE NECK The neck has four major compartments, which are enclosed
THE NECK PART I BONES AND JOINTS OF THE NECK MUSCLES OF THE NECK SCM CAROTID TRIANGLE ENDOCRINE LAYER OF THE CERVICAL VISCERA THE NECK THE NECK The neck has four major compartments, which are enclosed
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
CHAPTER 9. The Neck THE "CERVICAL CAVITY" TRACHEA ESOPHAGUS THYROID GLAND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
281 CHAPTER 9 The Neck CERVICAL VERTEBRAE POSTERIOR TRIANGLE OF NECK Trapezius and Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS REGARDING TRAPEZIUS Sternocleidomastoid CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Respiratory System. Ling Shucai
 Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Respiratory System Ling Shucai General Description Ⅰ. Constituents: Respiratory tract Lungs Pleura and plural cavity Ⅱ. Function: exchange O 2 and CO 2 mainly Mediastinum Respiratory tract Upper respiratory
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory fibers to the skin of the clavicular area
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes
 Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Anatomy 2. Parotid bed (V.imp): meaning that gland is sleeping on structures and they are:
 Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
Anatomy 2 Parotid Gland: "refer to previous sheet for extra details." Its pyramidal in shape, apex is toward pharynx. Its Medial surface is divided into Anterio-medial and posterio-medial and its posterio-medial
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
NECK (pp.1000~1022) Fascia. 1. Investing layer. 2. Prevertebral layer. 3. Pretracheal layer
 NECK (pp.1000~1022) Head Neck Trunk Anterior: lower border of mandible > upper surface of manubrium Posterior: superior nuchal line > intervertebral disc between CVII and TI Four compartments separated
NECK (pp.1000~1022) Head Neck Trunk Anterior: lower border of mandible > upper surface of manubrium Posterior: superior nuchal line > intervertebral disc between CVII and TI Four compartments separated
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
CHAPTER 7. The Neck RETROMANDIBULAR REGION
 205 CHAPTER 7 The Neck BODY WALL OF THE NECK Skeletal Components Cervical Vertebrae The Hyoid Bone and the Styloid Process of the Skull Thyroid Cartilage Cricoid Cartilage Muscular Components Cervical
205 CHAPTER 7 The Neck BODY WALL OF THE NECK Skeletal Components Cervical Vertebrae The Hyoid Bone and the Styloid Process of the Skull Thyroid Cartilage Cricoid Cartilage Muscular Components Cervical
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
General Anatomic Layout
 General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage.
 [ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
[ANATOMY #3] 1 بسم رلاهللا Please refer back to the slides as these are extra notes only. Slide 2 -The Larynx is a Box of cartilage. -The lower border of c6 is the lower border of cricoid cartilage. -The
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
LARYNX ANATOMY. Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE
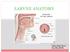 LARYNX ANATOMY Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE INTRODUCTION v Odd and median organ v Infrahyoid region v Phonation, swallowing and breathing v Triangular pyramid v Postero- superior base à pharynx and hyoid
LARYNX ANATOMY Elena Rizzo Riera R1 ORL HUSE INTRODUCTION v Odd and median organ v Infrahyoid region v Phonation, swallowing and breathing v Triangular pyramid v Postero- superior base à pharynx and hyoid
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 10 The Muscular System Axial Musculature Introduction The skeletal muscle of the body can be subdivided into: Axial musculature Muscles that position
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX. By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Digestive System in the Head and Neck
 The Digestive System in the Head and Neck The Mouth The Lips The lips are two fleshy folds that surround the oral orifice They are covered on the outside by skin and are lined on the inside by mucous membrane
The Digestive System in the Head and Neck The Mouth The Lips The lips are two fleshy folds that surround the oral orifice They are covered on the outside by skin and are lined on the inside by mucous membrane
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Chapter 26: The temporomandibular joint, pharynx and larynx. The Temporomandibular Joint. Ligaments. (a) Capsular
 Chapter 26: The temporomandibular joint, pharynx and larynx The Temporomandibular Joint This is a synovial joint of a condyloid (modified hinge) variety between the condyle of the mandible and the mandibular
Chapter 26: The temporomandibular joint, pharynx and larynx The Temporomandibular Joint This is a synovial joint of a condyloid (modified hinge) variety between the condyle of the mandible and the mandibular
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
