Neuroanatomy. Cerebral Cortex: Movement and Speech
|
|
|
- Jacob Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuroanatomy Cerebral Cortex: Movement and Speech
2 Functional Neuroanatomy Phrenology: Pseudoscience Functional neuroanatomy is the study of how different parts of the brain control different aspects of behavior. It s only in the last couple hundred years that people have really begun to appreciate that behaviors are localized to different parts of the brain. One of the earliest ways of studying brain function was quackery called phrenology. According to phrenology, different parts of the brain controlled different aspects of behavior and personality (this part is true) and our abilities and behaviors are determined by how developed those areas are. Phrenologists would feel the heads of patients in order to see what brain areas were most developed, figuring that well-developed brain areas would be associated with bumps on the head and underdeveloped areas would be associated with dents. While phrenology is baloney, it was important because it got science thinking about the idea of localizing functions in the brain.
3 Functional Neuroanatomy Another historically important event for functional neuroanatomy is the story of Phineas Gage. Phineas Gage was a foreman on a railroad construction crew in the mid-19 th century. As part of their duties, the crew had to clear the way for the railroad with explosives. This involved drilling a hole, pouring in blasting powder, covering the powder with sand or other wadding, then firmly tamping the explosives with a long steel rod before igniting the mixture. Obviously a hazardous job! Unfortunately, Gage somehow forgot to put the sand in on one fateful day. When he went to tamp the explosives, they ignited, turning his tamping rod into a projectile. It went right through his head, entering just under his left eye and coming out the top of his head. He went into convulsions but somehow survived the accident. He was able to walk and talk normally shortly after the accident. Despite severe brain damage, he seemed behaviorally normal at first (except, of course, for the physical damage to his head and face he was blinded in the left eye, for example). As the story goes, though, Gage s personality was dramatically changed by the accident. While he was previously a respectable, well-liked, hard-working man, afterwards he was said to be rude, violent, and unemployable. Clearly, the damage to his brain had altered his very personality! It turns out that while his personality probably was changed for a little while, he probably recovered his social abilities and became more-or-less normal. Despite being more of a fairy tale than a true story, the story of Phineas Gage is still very important in the history of neurology because it launched a lot of interest in localizing brain function.
4 Functional Neuroanatomy The Brain Brainstem Diencephalon Cerebral cortex Cerebellum Very generally speaking, we can divide the brain into four general parts : The brainstem: This is the stalk that the rest of the brain sits on top of. It controls our most basic vegetative life-support functions: heart rate, breathing, alertness, digestion, vomiting, etc. It also has a lot of tracts carrying impulses to and from the higher brain centers. The diencephalon: Sitting on top of the brainstem, the diencephalon is responsible for more complex life-support functions such as motivational behaviors (hunger, thirst, sex drive, etc.) and hormone control. It also routes sensory signals to the correct nuclei in the cortex. The cerebral cortex (or cerebrum): The highly-folded part of the brain that wraps around the diencephalon and brainstem ( cortex means covering ). This is where all of our thinking, memory, and conscious awareness, and voluntary behaviors happen. The rest of this lecture covers the cortex in more detail. The cerebellum ( little brain ): The cerebellum is a separate structure attached to the rest of the brain on the posterior-inferior side. It is involved in coordinating and controlling movements, timing of muscle voluntary movements, and well-learned motor behaviors.
5 Features Cerebral hemispheres Corpus callosum The word cortex means covering, an appropriate name considering the cortex covers the diencephalon and brainstem. (That s not it s job; that s just where it s located). The cortex includes neurons that handle voluntary movement, thinking, planning, reasoning, personality, emotion, associations, and other higher-order cognitive functions. Structurally, the cortex is divided into two hemispheres: a left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. The two hemispheres are separated by a deep rift called the longitudinal fissure and communicate with one another across a huge slugshaped band of axons called the corpus callosum. 5
6 Features Gyri, sulci, & fissures Major landmarks When you look at the cortex, you ll noticed that it s not a smooth surface: it has lots of folds, hills, and wrinkles. The raised parts of the cortex (the hills) are called gyri (singular: gyrus). The folds between gyri are called sulci (singular: sulcus). A verydeep sulcus is sometimes called a fissure.every gyrus and sulcus has a name, but you re only responsible for memorizing a few. As already mentioned, the deep fissure that separates the right and left hemispheres is called the longitudinal fissure. The long sulcus that separates the frontal from the parietal lobe is the central sulcus and it is bordered by the precentral gyrus on the anterior side and the postcentral gyrus on the posterior side. The horizontal sulcus that divides the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes is the longitudinal sulcus (or longitudinal fissure). 6
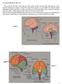
7 Features Major landmarks Central Sulcus, Lateral sulcus Precentral gyrus, postcentral gyrus Longitudinal Fissure See if you can identify all of the major landmarks in these pictures. In the numbered picture, precentral gyrus is number 12, postcentral gyrus is number 13, and the central sulcus separates them. The lateral fissure is the sulcus between numbers 13 and 18. 7
8 Features Cortical Lobes (insula underneath) The major sulci of the cortex visually divide the brain into 5 different regions that we call lobes. The frontal lobe consists of all the cortex anterior to the central sulcus. It is involved in voluntary motor control, planning and learning movements, learning skills, personality, emotions, social behavior, planning, reasoning, judgement, etc. Posterior to central sulcus is parietal lobe. The parietal lobe is involved in perception of the general senses, identifying things by touch, and recognizing objects visually. Inferior to the lateral fissure is the temporal lobe, which is involved in perception of smell and hearing, understanding speech, forming new memories, and emotion. The most posterior part of the cortex is the occipital lobe, which is involved in visual perception and processing visual associations. Finally, the more-basic insula is a lobe of the brain not visible from the outside. It s involved in more basic associations, strong emotions (fear, rage, etc.), and perception of balance and taste. 8
9 Features Cortical Lobes Try to identify each lobe of the brain in this picture. 9
10 Cortical Functions To some extent, different regions of the cortex are responsible for different behavioral functions. 10
11 Cortical Functions Motor, sensory, and association areas Mostly contralateral Lateralization Generally speaking, we can categorize each functional area of the cortex as motor (plans or initiates voluntary movement), sensory (involved in perception or processing of sensory information), or association (connects sensory information to previous memories recognizing things, for example). For the most part, motor and sensory pathways show contralateral organization. This means that the skin and muscles on the left side of the body are handled by the right hemisphere of the brain and vice-versa. Olfaction is an exception to this rule. It shows ipsilateral organization. Many behavior functions show lateralization. This means that they are represented completely or mostly in just one hemisphere of the cortex. For example, speech production is lateralized in most people in the left hemisphere. The analogous region of the brain in the right hemisphere is involved in adding inflection and emotion to the voice. 11
12 Cortical Functions Somatic sensory area Parietal lobe/postcentral gyrus General senses Sensory homunculus Somatosensory association area Let s examine a few functional areas of the brain. The somatic sensory area (also called somatosensory cortex) covers the entire postcentral gyrus. It is involved in perception of the general senses (pressure, pain and temperature). Since different regions of somatosensory cortex correspond to sensory receptors from specific parts of the body, we can make a sort of map of the body on the brain. We call this a corticotropic map. However, some regions of the skin are more sensitive than other regions of the skin some regions are lots of brain dedicated to them (such as the lips and the fingers) while others have less (such as the back and the legs). A model of how much brain is dedicated to each region of the skin is called a sensory homunculus (see the next slide). Posterior to somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe, we have the somatosensory association areas. This part of the brain is responsible for connecting our current touch sensations with our memories. It s what allows us to recognize an object based on how it feels. 12
13 Cortical Functions This is a sculpture of a sensory homunculus. Which regions have very sensitive touch? Which have less sensitive touch? 13
14 Cortical Functions Primary motor area Frontal lobe/ precentral gyrus Corticospinal tracts/ pyramids Motor homunculus Premotor area Just anterior to somatosensory cortex, covering the precentral gyrus in the frontal lobe, is the primary motor area. This is where all of the body s voluntary movements are initiated. Like the somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex has different areas that control muscles from specific muscles and, like somatosensory cortex, the top of the body is represented on the inferior and lateral parts of the cortex while the lower parts of the body are represented on the superior and medial parts of the cortex. Primary motor cortex has a homunculus similar to that of somatosensory cortex: the parts of the body where we have very good dexterity (lots of neurons, each controlling very small motor units) have a lot of brain dedicated to them while parts where we have poor dexterity (few large motor units) have less brain dedicated. Anterior to primary motor cortex, we have the premotor area. This is the region of the brain that plans out movements and learns motor skills. If premotor area becomes damaged, we may lose motor skills such as typing, driving a car, etc., but the skills can be relearned. 14
15 Cortical Functions This a motor homunculus. 15
16 Cortical Functions Identify all the brain regions discussed so far. 16
17 Cortical Functions Language & Speech areas Broca s area (Frontal lobe) Wernicke s area (Temporal lobe) Arcuate fasciculus (Connection) Aphasias Speech and language are processed and produced in some very specific parts of the cortex. A part of the brain called Broca s area is responsible for producing speech. It s found in the frontal lobe near the part of primary motor cortex that controls the muscles of the tongue, mouth and throat. The part of the brain responsible for speech comprehension is called Wernicke s area. It s found in the temporal lobe, very near the part of the brain that perceives sound. Wernicke s area is connected to Broca s area by a band of fibers called the arculate fasciculus. In most people, speech production and comprehension are highly lateralized. We call the hemisphere of the brain where Broca s and Wernicke s areas are found the dominant hemisphere. In most people, this is the left hemisphere. In the nondominant hemisphere, the analogs of Broca s and Wernicke s areas are involved in producing or understanding the tone of speech (inflections, sarcasm, etc.) A deficit in speech production or comprehension as a result of brain damage is called an aphasia. There are several types of aphasias, but here are the three most straightforward: Broca s aphasia: Caused by damage to Broca s area. Speech production is very difficult (non-fluent), but understanding of speech is preserved. Sometimes patients are still able to write, sometimes not. Speech is telegraphic (very short), but it does make sense. Wernicke s aphasia: Caused by damage to Wernicke s area. Characterized by an inability to understand language or read as well as an inability to produce meaningful speech. Speech is fluent, but nonsensical. Conduction aphasia: Caused by damage to the arcuate fasciculus. Speech production and comprehension are normal, but patients are unable to repeat spoken language or read aloud. 17
18 Cortical Functions To look for aphasias and determine the extent of damage, patients are presented with pictures such as this one and asked to describe what s going on. 18
19 Broca s Aphasia Examiner: Describe this picture. Patient: kid kk can cookie caandy well I don t t know but it s s writ easy does it slam early fall men many no girl. Dishes soap water water falling pah that s s all dish that s s all. Cookies can candy cookies cookies he down That s s all. Girl slipping water water and it hurts much to do. Her clean up. Dishes up there I think that s doing it Examiner: What is she doing with the dishes? Patient: discharge no I forgot dirtying clothes [?] dish {?} water Examiner: What about it? Patient: slippery water [?] scolded slipped
20 Broca s Aphasia Examiner: Describe this picture. Patient: uh mother and dad no mother dishes uh runnin[g] ] over water and floor and they uh wipin[g] dis[h]es and uh two kids uh stool and cookie cookie jar uh cabinet and stool uh tippin[g] ] over and uh bad and somebody gonna get hurt.
21 Wernicke s Aphasia Clinician: Tell me where you live. Patient: Well, it s s a meender place and it has two two of them. For dreaming and pinding after supper. And up and down. Four of down and three of up (Brookshire 2003:155) Clinician: What s s the weather like today? Patient: Fully under the jimjam and on the altigrabber. (Brookshire 2003:155)
22 Wernicke s Aphasia Patient is asked what brought him to the hospital. Is this some of the work that we work as we did before? All right From when wine [why] I m I m here. What s s wrong with me because I was myself until the taenz took something about the time between me and my regular time in that time and they took the time in that time here and that s s when the the time took around here and saw me around in it s s started with me no time and I bekan [began] work of nothing else that s s the way the doctor find me that way (Obler & Gjerlow 1999:43)
23 Cortical Functions Identify all the major cortical areas discussed. 23
24 Cortical Functions Special Sensory Areas Visual cortex (occipital lobe) Auditory cortex (temporal lobe) Olfactory cortex (temporal lobe) Gustatory cortex (insula) Equilibrium cortex (insula) All of the special senses have cortical regions involved in perception. Visual cortex is located in the occipital lobe. Auditory (hearing) and olfactory (smelling) cortices are located in the temoporal lobe. Gustatory (taste) and equilibrium (balance) cortices are located in the insula. 24
Neocortex. Hemispheres 9/22/2010. Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs. Structures are divided into several section or lobes.
 Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
-Zeina Assaf. -Omar Odeh. - Maha Beltagy
 -3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
-3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Seventh Edition. The Nervous System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
PsychoBrain. 31 st January Dr Christos Pliatsikas. Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading
 PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain
 XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain Studies by Bell and Magendie initiated an extremely important scientific procedure,, where a specific part of the nervous system
XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain Studies by Bell and Magendie initiated an extremely important scientific procedure,, where a specific part of the nervous system
Human Brain. Lateralization of Function. Cortex. Cerebral Hemispheres. An extension of the spinal cord. Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD
 Lateralization of Function Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Cerebral Hemispheres Two millimeters thick and has area of 1.5 square meters Corpus
Lateralization of Function Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Cerebral Hemispheres Two millimeters thick and has area of 1.5 square meters Corpus
XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain
 XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain Studies by Bell and Magendie initiated an extremely important scientific procedure,, where a specific part of the nervous system
XIXth Century: Localization of Functions to Different Parts of the Brain Studies by Bell and Magendie initiated an extremely important scientific procedure,, where a specific part of the nervous system
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Human Brain. Lateralization of Function. An extension of the spinal cord. Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD
 Lateralization of Function Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Cerebral Hemispheres Corpus Callosum Cerebral Lobes Neurons Brain composed of neurons
Lateralization of Function Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Cerebral Hemispheres Corpus Callosum Cerebral Lobes Neurons Brain composed of neurons
Disorders affecting region: depression anxiety
 Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
Amygdala Involved in learning, and the processing of emotional memories. Measures sensory input for potential threat level, then hypothalamus Regulates volatile emotions like fear and anger. Disorders
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
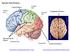
FRONTAL LOBE. Central Sulcus. Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Sulcus. Cingulate Sulcus. Lateral Sulcus
 FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
Hemispheric Specialization (lateralization) Each lobe of the brain has specialized functions (Have to be careful with this one.)
 Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
A recap of the Brain- Bio 230
 A recap of the Brain- Bio 230 This recap of the brain is to help you make sense of that 3 pound tofu blob that you carry around everyday. My hope is that if you get these basics, you can build and add
A recap of the Brain- Bio 230 This recap of the brain is to help you make sense of that 3 pound tofu blob that you carry around everyday. My hope is that if you get these basics, you can build and add
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU
 If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Lateral Surface of the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Lateral Surface of the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology. Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm
 Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm Lecture 2. Functional Organisation of the Nervous System Lecture Outline 1.1 Introduction
Introduction to the Nervous System. Code: HMP 100/ UPC 103/ VNP 100. Course: Medical Physiology Level 1 MBChB/BDS/BPharm Lecture 2. Functional Organisation of the Nervous System Lecture Outline 1.1 Introduction
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Central Nervous System. January 7, 2016
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System
 Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Specific Sulci/Fissures:
 Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure http://www.bioon.com/book/biology/whole/image/1/1-8.tif.jpg http://www.dalbsoutss.eq.edu.au/sheepbrains_me/human_brain.gif
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Central Nervous System
 Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Anatomy of a neuron Cell Body (soma) Receives information from the soma s extensions (dendrites) Central Nervous System January 7, 2016 Passes on information away from the soma towards extensions (axons)
Lateralization of Function. Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD
 Lateralization of Function Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Cortex Two millimeters thick and has area of 1.5 square meters Cerebral Hemispheres
Lateralization of Function Dr. Coulson Cognitive Science Department UCSD Human Brain An extension of the spinal cord Cortex Two millimeters thick and has area of 1.5 square meters Cerebral Hemispheres
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
The One Who Falls And Gets Up Is So Much Stronger Than The One Who Never Fell
 Text Important Formulas Numbers Doctor notes Notes and explanation Lecture No.19 The One Who Falls And Gets Up Is So Much Stronger Than The One Who Never Fell 1 Function of Cerebral hemisphere Objectives:
Text Important Formulas Numbers Doctor notes Notes and explanation Lecture No.19 The One Who Falls And Gets Up Is So Much Stronger Than The One Who Never Fell 1 Function of Cerebral hemisphere Objectives:
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Clinical Learning Exercise #1
 Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Psy /16 Human Communication. By Joseline
 Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Brain anatomy tutorial. Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics
 Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
2Lesson. Outline 1.5. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 1.5: How do the parts of my brain work together? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to emphasize the need of the structures of the brain to work together to create and control behaviors, like the creation and comprehension
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to emphasize the need of the structures of the brain to work together to create and control behaviors, like the creation and comprehension
PSY 215 Lecture 17 (3/28/2010) (Lateralization in the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215
 PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
PSY 215 Lecture 17 Topic: Lateralization in the Brain Chapter 14.1, pages 403-414 Corrections: Lecture 16 (page 4) Broca s Area: trouble producing language, comprehension is okay. Announcements: Review
Gross Morphology of the Brain
 Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
The human brain weighs roughly 1.5 kg and has an average volume of 1130 cm 3. A sheep s brain weighs in however at kg.
 Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key
 Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) D AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters 6) E AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters
Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) D AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters 6) E AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters
Brain II: Physiology and Senses Special vs Somatic Senses Olfaction
 Brain II: Physiology and Senses Special vs Somatic Senses Olfaction Topology of cerebral function Forebrain Frontal lobes Motor functions or movements (posterior) Memory/recognition Emotional regulation
Brain II: Physiology and Senses Special vs Somatic Senses Olfaction Topology of cerebral function Forebrain Frontal lobes Motor functions or movements (posterior) Memory/recognition Emotional regulation
 BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 1 Brain and Its Vital Functions Student s Name Institution Name Professor s Name Course Title BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 2 The brain is the integral organism and all its
BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 1 Brain and Its Vital Functions Student s Name Institution Name Professor s Name Course Title BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 2 The brain is the integral organism and all its
Test Bank. Multiple Choice
 Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language
 Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Gives few collaterals, it is mainly a single process surrounded by a myelin sheath
 Lecture 1 - Nerve fiber refers to both axons and dendrites, the dendrites are the afferent fibers (sensory); they receive impulses from neighbouring neurons, and the axon is the efferent fiber (motor);
Lecture 1 - Nerve fiber refers to both axons and dendrites, the dendrites are the afferent fibers (sensory); they receive impulses from neighbouring neurons, and the axon is the efferent fiber (motor);
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally
 KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images
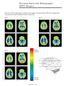 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images Each set of PET images below contains four images of a human brain. The four images show cross-sections taken at different levels of the brain. Set 1 Set 2 a b
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Images Each set of PET images below contains four images of a human brain. The four images show cross-sections taken at different levels of the brain. Set 1 Set 2 a b
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Anatomy of the Human Brain
 Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Bob Jacobs, Ph.D., Colorado College First Grade Lesson Plan Example. Introduction Who are we? Where are we from? What are we doing/ Why are we here?
 Introduction Who are we? Where are we from? What are we doing/ Why are we here? Brainstorming Where is your brain? What does your brain do? What does it look like? What do you want to learn?/ What questions
Introduction Who are we? Where are we from? What are we doing/ Why are we here? Brainstorming Where is your brain? What does your brain do? What does it look like? What do you want to learn?/ What questions
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture. Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D.
 Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
Cerebral Cortex Structure, Function, Dysfunction Reading Ch 10 Waxman Dental Neuroanatomy Lecture Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. March 7, 2012 Anatomy Review Lobes and layers Brodmann s areas Vascular Supply
