Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
|
|
|
- June Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following parts: - Forebrain (prosencephalon) which is subdivided into: 1- Telencephalon: it is represented by the cerebral hemispheres. 2- Diencephalon: it is composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and subthalamus.
2 - Midbrain (mesencephalon). - Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) which is subdivided into: 1- Myelencephalon (medulla oblongata). 2- Metencephalon which is composed of pons and cerebellum. General facts: glial cells are ten times more than neurons in the mammalian brain. there is no connective tissue in the CNS. The mid brain, pons and medulla oblongata will form the brain stem. There are no two identical brains. Cortex = grey matter = gyri and sulci. Medulla =White matter, it contains group of nuclei (grey matter) inside it. Topography of the telencephalon: There are right and left cerebral hemispheres, they form the largest part of the brain. They are incompletely separated by the longitudinal cerebral fissure that contains the falx cerebri of the dura mater extend to corpus callosum, each cerebral hemisphere possesses a central cavity called the lateral ventricle.
3
4 Each cerebral hemisphere has three surfaces; each surface has gyri (convolutions) and sulci (fissures): - Superolateral surface has the main following gyri and sulci (main landmarks):
5 The central sulcus: just behind the midpoint of the superior border of the hemisphere, the fissure of Rolando (central sulcus) is start. The frontal gyrus in front of this sulcus is the precentral (motor cortex), while the parietal gyrus behind the sulcus is the postcentral gyrus (somatosensory cortex). The central sulcus extends to medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere. It separates on superolateral surface between the frontal and parietal lobes. The lateral sulcus: (fissure of Sylvius) it is composed of anterior and posterior rami or parts. At the junction of the two parts, there are two ascending rami (V- shaped rami) arise toward the inferior frontal gyrus, and so this gyrus is further divided by the V- shaped ascending rami into pars orbitalis, pars triangularis and pars opercularis.
6 Insula (island of Reil): is situated deep in the floor of the lateral sulcus and is almost surrounded by a circular sulcus, and can only be seen when the lips of the lateral sulcus are widely separated. It involves parts from frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The insula is composed of long and short gyri that almost completely surrounded by the circular sulcus. The insula is divided into two regions by a central sulcus, several short gyri lie in front of the central sulcus and one or two long gyri lie behind it. The gustatory and olfaction areas are related to insula.
7 Note: looks for other main sulci and gyri of the Superolateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere such as angular and supramarginal gyri. Lobes of the cerebral hemisphere: 1- Frontal lobe: it is situated in front of the central sulcus and above lateral sulcus. 2- Parietal lobe: it lies behind central sulcus and above the lateral sulcus. 3- Temporal lobe: it is below the lateral sulcus. 4- Occipital lobe: it is situated below and behind the parieto-occipital sulcus. Pre-occipital notch is the land mark that delineates the occipital lobe from the temporal lobe.
8
9 - Medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere has the main following features: The corpus callosum: the two cerebral hemispheres are joined by the corpus callosum which formed from rostrum anteriorly, genu, body and splenium posteriorly. The calcarine sulcus: in which the visual cortex is around this sulcus. Cuneus, parieto-occipital sulcus, precuneus, lingual gyrus, collateral sulcus, isthmus, parahippocampal gyrus, cingulate gyrus and sulcus and looks for other main features of the medial surface. Isthmus is continuous with the cingulate gyrus. Subparietal sulcus is continuous with the cingulate sulcus. Paracentral lobule is between paracentral sulcus and marginal sulcus. Uncus is the extension of the parahippocampal gyrus.
10
11
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of:
 The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
The Nervous system is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System (CNS): found within bones & consists of: - The Brain: within the skull, composed of cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem.
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (NS) It is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (NS) It is divided into 2 major divisions: 1) Central Nervous System
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions
 Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Gross Morphology of the Brain
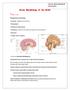 Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Human Anatomy. Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM..
 Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM.. (CNS Block, Radiology) Dr. Hamdy Hassan Ass.Prof. Consultant Radiology Department KKHU King Saud University Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord Cephalization Evolutionary development of rostral (anterior) portion of CNS Increased number of neurons in head Highest level reached in human brain 1 Mostly to orient
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Gives few collaterals, it is mainly a single process surrounded by a myelin sheath
 Lecture 1 - Nerve fiber refers to both axons and dendrites, the dendrites are the afferent fibers (sensory); they receive impulses from neighbouring neurons, and the axon is the efferent fiber (motor);
Lecture 1 - Nerve fiber refers to both axons and dendrites, the dendrites are the afferent fibers (sensory); they receive impulses from neighbouring neurons, and the axon is the efferent fiber (motor);
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
FRONTAL LOBE. Central Sulcus. Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Sulcus. Cingulate Sulcus. Lateral Sulcus
 FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Embryonic Brain Development
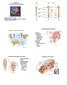 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
A few notions of brain anatomy
 A few notions of brain anatomy Christophe Pallier CNRS, INSERM 562, Orsay, France Note some slides were taken from lectures available from the excellent web site 'fmri for dummies' by Jody Culham. Drawing
A few notions of brain anatomy Christophe Pallier CNRS, INSERM 562, Orsay, France Note some slides were taken from lectures available from the excellent web site 'fmri for dummies' by Jody Culham. Drawing
A Dozen Neuroanatomical Landmarks Every Radiologist Should Know
 A Dozen Neuroanatomical Landmarks Every Radiologist Should Know Poster No.: R-0037 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Gan, B. Di Muzio, F. Gaillard; Melbourne/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
A Dozen Neuroanatomical Landmarks Every Radiologist Should Know Poster No.: R-0037 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Gan, B. Di Muzio, F. Gaillard; Melbourne/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
The human brain weighs roughly 1.5 kg and has an average volume of 1130 cm 3. A sheep s brain weighs in however at kg.
 Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Lecture title: cerebral cortex Lecture number: 4 Doctor: Eizz Elden meqdadi
 Nervous system Lecture title: cerebral cortex Lecture number: 4 Doctor: Eizz Elden meqdadi Raghad ibrahim فقل لمرج معال االمور بغ ر اجتهاد: رجوت لمحاال *slides included in the sheet Cerebral Hemispheres
Nervous system Lecture title: cerebral cortex Lecture number: 4 Doctor: Eizz Elden meqdadi Raghad ibrahim فقل لمرج معال االمور بغ ر اجتهاد: رجوت لمحاال *slides included in the sheet Cerebral Hemispheres
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory.
 Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Telencephalon. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Telencephalon Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Telencephalon Gray matter Cortex Basilar nuclei White matter-medulla Lateral ventricles General introduction
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Telencephalon Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Telencephalon Gray matter Cortex Basilar nuclei White matter-medulla Lateral ventricles General introduction
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
DIENCEPHALON. ..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures
 DIENCEPHALON..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures ---------- --thalamus, --------hypothalamus, -------epithalamus..encloses the third ventricle Diencephalon between cerebral
DIENCEPHALON..Central core of the forebrain..consists of three paired structures ---------- --thalamus, --------hypothalamus, -------epithalamus..encloses the third ventricle Diencephalon between cerebral
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
BASIC ANATOMICAL STRUCTURES. The Cerebrum
 BASIC ANATOMICAL STRUCTURES The Cerebrum Development of the Cerebral Vesicles Primary Vesicle secondary Vesicles CNS structures Ventricle telencephalon Cerebral Hemispheres Lateral Ventricles Prosencephalon
BASIC ANATOMICAL STRUCTURES The Cerebrum Development of the Cerebral Vesicles Primary Vesicle secondary Vesicles CNS structures Ventricle telencephalon Cerebral Hemispheres Lateral Ventricles Prosencephalon
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES NERVOUS SYSTEM TISSUES: HISTOLOGY SLIDES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Lateral Surface of the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Lateral Surface of the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Stanley Pruisinger 1980's
 Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally
 KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
Chapter 1 Introduction and overview
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction and overview Components and organisation of the nervous system 1 Neurones and neuroglia 1 Central and peripheral nervous systems 2 Autonomic nervous system 2 Afferent neurones,
1 Chapter 1 Introduction and overview Components and organisation of the nervous system 1 Neurones and neuroglia 1 Central and peripheral nervous systems 2 Autonomic nervous system 2 Afferent neurones,
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Note to Self. The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Organization of the Brain
 Note to Self Despite what you think you can get through this chapter in 1 class period, or one with only a few slides left over The Brain and Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Organization of the Brain The brain
Note to Self Despite what you think you can get through this chapter in 1 class period, or one with only a few slides left over The Brain and Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Organization of the Brain The brain
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
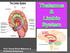 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
PARIETAL LOBE. Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS
 PARIETAL LOBE Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS Diplomate of the American Board of Neurological Surgery Fellow of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons Professor of Neurosurgery, European
PARIETAL LOBE Vasilios A. Zerris MD, MPH, MSc, FAANS Diplomate of the American Board of Neurological Surgery Fellow of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons Professor of Neurosurgery, European
Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition
 Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition Q: In what way has paedomorphosis been important in human evolution? Brain Architecture F F F F H H 3 Q. How d we get to this point? Evolutionary
Brain Architecture and Function Parts Size and Cognition Q: In what way has paedomorphosis been important in human evolution? Brain Architecture F F F F H H 3 Q. How d we get to this point? Evolutionary
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Cerebral Cortex. Gross Divisions of the Brain. Cerebrum. Diencephalon. Cerebellum. Brainstem. (cerebral hemisphere)
 Cerebral Cortex Gross Divisions of the Brain Cerebrum (cerebral hemisphere) Diencephalon Cerebellum Brainstem 1 2 Embryonic (developmental) divisions of the Brain Primary vesicle Secondary vesicle Derivatives
Cerebral Cortex Gross Divisions of the Brain Cerebrum (cerebral hemisphere) Diencephalon Cerebellum Brainstem 1 2 Embryonic (developmental) divisions of the Brain Primary vesicle Secondary vesicle Derivatives
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Neurology. Dr. Mohd. Zahirul Islam Khan DVM, MS, Ph.D, Postdoc.
 Neurology By, 1. Central Nervous System: a) Brain of different animals. b) Spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): a) Cranial Nerves b) Spinal Nerves and ganglia 3. Autonomic Nervous System (PNS)
Neurology By, 1. Central Nervous System: a) Brain of different animals. b) Spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): a) Cranial Nerves b) Spinal Nerves and ganglia 3. Autonomic Nervous System (PNS)
