Chapter: Control and Coordination
|
|
|
- Garry Knight
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Table of Contents Chapter: Control and Coordination Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Senses
3 1 The Nervous System How the Nervous System Works Responding to Stimuli Any internal or external change that brings about a response is called a stimulus (STIHM yuh lus). Noise, light, the smell of food, and the temperature of the air are all stimuli from outside your body. Chemical substances such as hormones are examples of stimuli from inside your body.
4 1 Homeostasis The Nervous System The regulation of steady, life-maintaining conditions inside an organism, despite changes in its environment, is called homeostasis. Your nervous system is one of several control systems used by your body to maintain homeostasis.
5 1 Nerve Cells The Nervous System The basic functioning units of the nervous system are nerve cells, or neurons (NOOR ahns).
6 1 Nerve Cells The Nervous System A neuron is made up of a cell body and branches called dendrites and axons.
7 1 Nerve Cells The Nervous System Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons and send them to the cell body.
8 1 Nerve Cells The Nervous System Axons (AK sahns) carry impulses away from the cell body.
9 1 The Nervous System Types of Nerve Cells Three types of neurons sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons transport impulses. Sensory neurons receive information and send impulses to the brain or spinal cord.
10 1 The Nervous System Types of Nerve Cells Interneurons relay these impulses to motor neurons. Motor neurons then conduct impulses from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands throughout your body.
11 1 Synapses The Nervous System To move from one neuron to the next, an impulse crosses a small space called a synapse (SIH naps).
12 1 Synapses The Nervous System When an impulse reaches the end of an axon, the axon releases a chemical. This chemical flows across the synapse and stimulates the impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron. Your neurons are adapted in such a way that impulses move in only one direction. Click image to view movie.
13 1 The Nervous System The Central Nervous System The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of all the nerves outside the CNS.
14 1 The Brain The Nervous System The brain coordinates all of your body activities. The brain is made up of approximately 100 billion neurons. Surrounding and protecting the brain are a bony skull, three membranes, and a layer of fluid.
15 1 The Brain The Nervous System The brain is divided into three major parts the brain stem, the cerebellum (ser uh BE lum), and the cerebrum (suh REE brum).
16 1 Cerebrum The Nervous System Thinking takes place in the cerebrum, which is the largest part of the brain. This also is where impulses from the senses are interpreted, memory is stored, and movements are controlled.
17 1 Cerebellum The Nervous System Stimuli from the eyes and ears and from muscles and tendons, which are the tissues that connect muscles to bones, are interpreted in the cerebellum.
18 1 Cerebellum The Nervous System With this information, the cerebellum is able to coordinate voluntary muscle movements, maintain muscle tone, and help maintain balance.
19 1 Brain Stem The Nervous System At the base of the brain is the brain stem. The brain stem is made up of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla (muh DUH luh).
20 1 Brain Stem The Nervous System The midbrain and pons act as pathways connecting various parts of the brain with each other. The medulla controls involuntary actions such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
21 1 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord Your spinal cord is made up of bundle of neurons that carry impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and from the brain to all parts of your body.
22 1 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord A column of vertebrae, or bones, protects the spinal cord.
23 1 The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The PNS is made up of 12 pairs of nerves from your brain called cranial nerves and 31 pairs from your spinal cord called spinal nerves. Some nerves contain only sensory neurons, and some contain only motor neurons, but most nerves contain both types of neurons.
24 1 The Nervous System Somatic and Autonomic Systems The somatic system controls voluntary actions. It is made up of the cranial and spinal nerves that go from the central nervous system to your skeletal muscles.
25 1 The Nervous System Somatic and Autonomic Systems The autonomic system controls involuntary actions those not under conscious control such as your heart rate, breathing, digestion, and glandular functions.
26 1 The Nervous System Safety and the Nervous System Any injury to the brain or the spinal cord can be serious. A severe blow to the head can bruise the brain and cause temporary or permanent loss of mental and physical abilities.
27 1 The Nervous System Safety and the Nervous System Spinal cord injuries can be just as dangerous as a brain injury. Injury to the spine can bring about damage to nerve pathways and result in paralysis (puh RA luh suhs), which is the loss of muscle movement.
28 1 The Nervous System Safety and the Nervous System
29 1 Reflexes The Nervous System A reflex is an involuntary, automatic response to a stimulus. You can t control reflexes because they occur before you know what has happened.
30 1 Reflexes The Nervous System A reflex involves a simple nerve pathway called a reflex arc.
31 1 Reflexes The Nervous System A reflex allows the body to respond without having to think about what action to take. Reflex responses are controlled in your spinal cord, not in your brain. Your brain acts after the reflex to help you figure out what to do to make the pain stop.
32 1 The Nervous System Drugs and the Nervous System Many drugs, such as alcohol and caffeine, directly affect your nervous system. When swallowed, alcohol passes directly through the walls of the stomach and small intestine into the circulatory system.
33 1 The Nervous System Drugs and the Nervous System This drug slows the activities of the central nervous system and is classified as a depressant. Heavy alcohol use destroys brain and liver cells.
34 1 The Nervous System Drugs and the Nervous System Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, cocoa, and many soft drinks.
35 1 The Nervous System Drugs and the Nervous System Too much caffeine can increase heart rate and aggravates restlessness, tremors, and insomnia in some people. It also can stimulate the kidneys to produce more urine.
36 1 Question 1 Section Check Explain what could happen if damage occurred to the spinal cord in the lower neck area. Answer An injury to the spinal cord is always serious. If damage occurs to the spinal cord in the lower neck area, the body can be paralyzed from the neck down.
37 1 Question 2 Section Check Which helps maintain balance? A. brain stem B. cerebellum C. cerebrum D. spinal cord
38 1 Answer Section Check The correct answer is B. The cerebellum also coordinates voluntary muscle movements and maintains muscle tone.
39 1 Question 3 Section Check Which is NOT part of a neuron? A. axon B. cell body C. dendrite D. sensory fibers
40 1 Answer Section Check The answer is D. A neuron is made up of a cell body, dendrites, and axons.
41 2 The Senses The Body s Alert System Light rays, sound waves, heat, chemicals, or pressure that comes into your personal territory will stimulate your sense organs.
42 2 The Senses The Body s Alert System Sense organs are adapted for intercepting these different stimuli. They are then converted into impulses by the nervous system.
43 2 Vision The Senses The eye is the vision sense organ. Your eyes have unique adaptations that usually enable you to see shapes of objects, shadows, and color.
44 2 The Senses How do you see? Your eyes are equipped with structures that refract light.
45 2 The Senses How do you see? As light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea the transparent section at the front of the eye and is refracted.
46 2 The Senses How do you see? Then light passes through a lens and is refracted again. The lens directs the light onto the retina (RET nuh). The retina is a tissue at the back of the eye that is sensitive to light energy.
47 2 The Senses How do you see? Two types of cells called rods and cones are found in the retina. They are used to help you detect shape and movement. The impulses pass to the optic nerve. This nerve carries the impulses to the vision area of the cortex, located on your brain s cerebrum.
48 2 The Senses How do you see? The image transmitted from the retina to the brain is upside down and reversed. The brain interprets the image correctly, and you see what you are looking at.
49 2 Lenses The Senses Light is refracted when it passes through a lens. The way it refracts depends on the type of lens it passes through. A lens that is thicker in the middle and thinner on the edges is called a convex lens.
50 The Senses 2 Lenses The lens in your eye refracts light so that it passes through a point, called a focal point.
51 The Senses 2 Lenses A lens that is thicker at its edges than in its middle is called a concave lens. Light that passes through a concave lens is refracted outward.
52 2 The Senses Correcting Vision Problems In an eye with normal vision, light rays are focused onto the retina by the coordinated actions of the eye muscles, the cornea, and the lens. The image formed on the retina is interpreted by the brain as being sharp and clear.
53 2 The Senses Correcting Vision Problems A nearsighted person cannot see distant objects because the image is focused in front of the retina. A concave lens corrects nearsightedness.
54 2 The Senses Correcting Vision Problems A farsighted person cannot see close objects because the image is focused behind the retina. A convex lens corrects farsightedness.
55 2 Hearing The Senses Sound waves are necessary for hearing sound. When an object vibrates, sound waves are produced. These waves can travel through solids, liquids, and gases.
56 2 Hearing The Senses When the waves reach your ear, they usually stimulate nerve cells deep within your ear. Impulses are sent to the brain. When the sound impulse reaches the hearing area of the cortex, it responds and you hear a sound.
57 2 The Senses The Outer Ear and Middle Ear Your outer ear intercepts sound waves and funnels them down the ear canal to the middle ear. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate.
58 2 The Senses The Outer Ear and Middle Ear These vibrations then move through three tiny bones called the hammer, anvil, and stirrup.
59 2 The Senses The Inner Ear The cochlea (KOH klee uh) is a fluidfilled structure shaped like a snail s shell. When the stirrup vibrates, fluids in the cochlea begin to vibrate.
60 2 The Inner Ear The Senses These vibrations bend hair cells in the cochlea, which causes electrical impulses to be sent to the brain by a nerve. Depending on how the nerve endings are stimulated, you hear a different type of sound.
61 2 Balance The Senses Structures in your inner ear also control your body s balance. Structures called the cristae ampullaris (KRIHS tee am pyew LEER his) and the maculae (MA kyah lee) sense different types of body movement.
62 2 Balance The Senses In your inner ear, the cristae ampullaris react to rotating movements of your body, and the maculae check the position of your head with respect to the ground.
63 2 Smell The Senses You smell food because it gives off molecules into the air. These molecules stimulate sensitive nerve cells, called olfactory (ohl FAK tree) cells, in your nasal passages. Olfactory cells are kept moist by mucus.
64 2 Smell The Senses When molecules in the air dissolve in this moisture, the cells become stimulated. If enough molecules are present, an impulse starts in these cells, then travels to the brain where the stimulus is interpreted.
65 The Senses 2 Taste Taste buds on your tongue are the major sensory receptors for taste. About 10,000 taste buds are found all over your tongue, enabling you to tell one taste from another.
66 2 Tasting Food The Senses Most taste buds respond to several taste sensations. The five taste sensations on the tongue are sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and the taste of MSG (monosodium glutamate).
67 2 Tasting Food The Senses In order to taste something, it has to be dissolved in water. Saliva begins this process. This solution of saliva and food washes over the taste buds, and impulses are sent to your brain. The brain interprets the impulses, and you identify tastes.
68 2 The Senses Smell and Taste Smell and taste are related. The sense of smell is needed to identify some foods such as chocolate. When saliva in your mouth mixes with the chocolate, odors travel up the nasal passage in the back of your throat. The olfactory cells are stimulated, and the taste and smell of chocolate are sensed.
69 2 The Senses Other Sensory Receptors in the Body Your internal organs have several kinds of sensory receptors. These receptors respond to touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. In turn, your body responds to this new information.
70 2 The Senses Other Sensory Receptors in the Body Sensory receptors also are located throughout your skin. Your fingertips have many different types of receptors for touch. As a result, you can tell whether an object is rough or smooth, hot or cold, and hard or soft.
71 2 Question 1 Section Check Which does light pass through first? A. cornea B. lens C. pupil D. retina
72 2 Answer Section Check The answer is A. As light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea.
73 2 Question 2 Section Check Which is used to correct nearsightedness? A. concave lens B. convex lens C. concave mirror D. convex mirror
74 2 Answer Section Check The correct answer is A. A nearsighted person cannot see distant objects because the image is focused in front of the retina.
75 2 Question 3 Section Check Which are the sensory receptors for taste? A. cochlea B. olfactory cells C. semicircular canals D. taste buds
76 Section Check 2 Answer The correct answer is D. About 10,000 taste buds are found all over your tongue, enabling you to tell one taste from another.
77 Help To advance to the next item or next page click on any of the following keys: mouse, space bar, enter, down or forward arrow. Click on this icon to return to the table of contents Click on this icon to return to the previous slide Click on this icon to move to the next slide Click on this icon to open the resources file. Click on this icon to go to the end of the presentation.
78 End of Chapter Summary File
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System
 Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Sensing the Environment
 2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS
 THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTROLS THE BODY S ACTIVITIES IT RECEIVES AND SENDS OUT INFORMATION ABOUT ACTIVITIES WITHIN THE BODY MONITORS AND RESPONDS TO CHANGES
THE NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTROLS THE BODY S ACTIVITIES IT RECEIVES AND SENDS OUT INFORMATION ABOUT ACTIVITIES WITHIN THE BODY MONITORS AND RESPONDS TO CHANGES
Chapter 20. The Nervous System
 Chapter 20 The Nervous System Overview: The Nervous System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8ntmdrb_qo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy9ntvh-awo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kr7dgpowzsa Section 1
Chapter 20 The Nervous System Overview: The Nervous System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q8ntmdrb_qo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qy9ntvh-awo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kr7dgpowzsa Section 1
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Challenge Question: What does the structure of the ear tell you about its function?
 Ear Activity Challenge Question: What does the structure of the ear tell you about its function? Initial Thoughts: Evidence: Go to www.nobelprize.org. Click Educational Games and then fine the Ear Page.
Ear Activity Challenge Question: What does the structure of the ear tell you about its function? Initial Thoughts: Evidence: Go to www.nobelprize.org. Click Educational Games and then fine the Ear Page.
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System
 Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
 Lesson 5 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the nervous and endocrine systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the nervous and endocrine
Lesson 5 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the nervous and endocrine systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the nervous and endocrine
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Control and Coordination
 Control and Coordination sections 1 The Nervous System Lab Improving Reaction Time 2 The Senses Lab Skin Sensitivity Virtual Lab How does human hearing compare with that of other organisms? Could you stop
Control and Coordination sections 1 The Nervous System Lab Improving Reaction Time 2 The Senses Lab Skin Sensitivity Virtual Lab How does human hearing compare with that of other organisms? Could you stop
Name Date Class. How the Nervous System Works (pages ) 2. Is the following sentence true or false? You can move without your
 CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
CHAPTER 15 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM SECTION 15 1 How the Nervous System Works (pages 486-490) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Functions
Objectives. ! Describe the major structures of the nervous system. ! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.
 Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
Objectives! Describe the major structures of the nervous system.! Explain how a nerve impulse is transmitted.! Distinguish between the functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.! Identify
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (CHAPTER 36)
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (CHAPTER 36) I) The Central Nervous System (DIVISION 1) A) A nerve impulse traveling in your body must first go to the brain (Control Center) for processing 1) Brain and spinal cord
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (CHAPTER 36) I) The Central Nervous System (DIVISION 1) A) A nerve impulse traveling in your body must first go to the brain (Control Center) for processing 1) Brain and spinal cord
Nervous System. Chapter Test A. Part A: Multiple Choice. Part B: Matching. Part C: Interpreting Drawings CHAPTER 33
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 33 Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or answers each question. 1. Neurons are specialized
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 33 Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or answers each question. 1. Neurons are specialized
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms may be used more than once.
 THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
How the Nervous System Works (pp )
 How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
Control and Coordination One second, the puck is
 5 Control and Coordination One second, the puck is halfway across the ice. In the next second you re trying to stop it from making a goal. For a hockey goalie, keen eyesight is not enough. He needs to
5 Control and Coordination One second, the puck is halfway across the ice. In the next second you re trying to stop it from making a goal. For a hockey goalie, keen eyesight is not enough. He needs to
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Chapter 18 Senses SENSORY RECEPTION 10/21/2011. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations
 SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Unit 3 Lesson 3 How Do Cells Work Together? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
The Nervous System. Chapter 35: Biology II
 The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism
 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems Five Levels of Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism ORGANS ORGAN SYSTEM ORGANISM 28.1 35.1 Levels Human of Body Organization Systems
15-2: Divisions of the Nervous System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
Special Senses. Accessory Structures of the Eye. The Eye and Vision. Accessory Structures of the Eye. Accessory Structures of the Eye
 8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
The Nervous System. Two Systems Within a System. 526 Chapter 17
 1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
Senses. hear. smell. see. taste. touch. Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things.
 Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
Human Body Senses 1 Senses Your senses gather information from the outside world. They help you see, hear, taste, smell and touch things. They also help you to detect pain, pressure, and temperature. All
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
TASTE: Taste buds are the sense organs that respond to gustatory stimuli. Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals broken down from food in the saliva
 UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
Chap Senses. 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Chap. 17 - Senses Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect. 2. Classification of Sensory Receptors a. mechanoreceptors b. thermoreceptors
Carl Christensen, PhD Chap. 17 - Senses Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Give an example of something a general sensory receptor would detect. 2. Classification of Sensory Receptors a. mechanoreceptors b. thermoreceptors
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Chapter 2. The Senses
 Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM The vertebrate nervous system includes sensation, integration, and motor output. Sensation includes specialized senses (vision, taste, hearing, etc.)
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM The vertebrate nervous system includes sensation, integration, and motor output. Sensation includes specialized senses (vision, taste, hearing, etc.)
Nervous System and Senses Objectives
 LEARNING TARGETS The nervous system maintains body homeostasis through sensation, interpretation, response and activity. Nerve cells send electrical signals for communication. Reflexes help protect our
LEARNING TARGETS The nervous system maintains body homeostasis through sensation, interpretation, response and activity. Nerve cells send electrical signals for communication. Reflexes help protect our
[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]
![[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY] [CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]](/thumbs/71/65616244.jpg) WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
The Nervous System. We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies.
 The Nervous System The Nervous System We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies. There is one master system which controls all of these other systems.
The Nervous System The Nervous System We have covered many different body systems which automatically control and regulate our bodies. There is one master system which controls all of these other systems.
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE
 THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE Introduction to nervous system There are 3 main parts to your Nervous System 1. Your Nerves 2. Your Brain 3. Your Spinal Cord Your Nerves Your nerves are made
THE CONTROL SYSTEMS NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE Introduction to nervous system There are 3 main parts to your Nervous System 1. Your Nerves 2. Your Brain 3. Your Spinal Cord Your Nerves Your nerves are made
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes
 Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Unit 4 - REGULATORY SYSTEMS Special Senses Lecture Notes 4.04 Describe the Special Senses A. Smell Smell occurs when specialized cells in the nose (chemoreceptors) detect certain chemicals resulting in
Chapter 35. Nervous System
 Chapter 35 Nervous System Objectives You will be able to describe the function of the nervous system, relate the structure of a neuron to its function and explain the changes that occur across a neuron
Chapter 35 Nervous System Objectives You will be able to describe the function of the nervous system, relate the structure of a neuron to its function and explain the changes that occur across a neuron
Senses- Ch. 12. Pain receptors- respond to tissue damage in all tissues except in the brain
 Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
The Senses. senses are almost impossible to describe, and yet we use them every moment of the day.
 The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
Nervous System. Part Two
 Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Nervous System Part Two CNS: Spinal Cord Protected by bone, fluid, & membranes Composed of gray and white matter Serves as conduction pathway btwn brain and peripheral nerves Extends from base of brain
Unit 22.1: The Nervous System
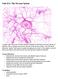 Unit 22.1: The Nervous System A spider web? Some sort of exotic bacteria? Maybe an illustration of a new species of jellyfish. This is actually a nerve cell, the cell of the nervous system. This cell sends
Unit 22.1: The Nervous System A spider web? Some sort of exotic bacteria? Maybe an illustration of a new species of jellyfish. This is actually a nerve cell, the cell of the nervous system. This cell sends
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT
 HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION. ü Excretory system
 NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Nervous System, the Brain, and the Sensory Organs
 Nervous System, the Brain, and the Sensory Organs Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input is the gathering information to monitor changes ( ) occurring inside and outside the body 2. Integration
Nervous System, the Brain, and the Sensory Organs Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input is the gathering information to monitor changes ( ) occurring inside and outside the body 2. Integration
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
H. composed of the brain and spinal cord.
 Mrs. Keadle H Science Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following vocabulary words to their definition. Please write a capital letter in the blank. 1. central nervous system 2.
Mrs. Keadle H Science Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following vocabulary words to their definition. Please write a capital letter in the blank. 1. central nervous system 2.
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri
 JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the:
 Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Lesson 18: The Senses
 Lesson 18: The Senses Lesson Objectives: Students will explore the senses of smell, hearing, sight, taste and touch. Student will learn the structures and functions of the eye. Student will learn the structures
Lesson 18: The Senses Lesson Objectives: Students will explore the senses of smell, hearing, sight, taste and touch. Student will learn the structures and functions of the eye. Student will learn the structures
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
35-2 The Nervous System
 1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
GRADE12. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 REVISION SHEET GRADE12 BIOLOGY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which system coordinates the body s response to changes in its internal
REVISION SHEET GRADE12 BIOLOGY Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which system coordinates the body s response to changes in its internal
The Special Senses. Chapter 17
 The Special Senses Chapter 17 Objective Describe the structure of vertebrate sensory organs and relate structure to function in vertebrate sensory systems. The 5 Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation
The Special Senses Chapter 17 Objective Describe the structure of vertebrate sensory organs and relate structure to function in vertebrate sensory systems. The 5 Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation
Sensory Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 9 Sensory Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 9 Sensory Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
1 ahmadanizahscienceteacher14
 CHAPTER 1: THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES 1.1 THE SENSOR ORGAN AND THEIR FUNCTION 8. The diagram below shows a girl watching a television show 1. Which of the following A,B,C or D is a sensory organ 2. Diagram
CHAPTER 1: THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES 1.1 THE SENSOR ORGAN AND THEIR FUNCTION 8. The diagram below shows a girl watching a television show 1. Which of the following A,B,C or D is a sensory organ 2. Diagram
Name Class Date. Read the words in the box. Read the sentences. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best completes the sentence.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: The Nervous System TWO SYSTEMS WITHIN A SYSTEM 1. What does the nervous system do? a. pump blood b. gather and interpret information c. digest food d. eliminate
15-1: How the Nervous System Works. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
7 th Grade Life Science Purpose Students will be able to: 1. Identify the functions of the nervous system. 2. Describe the structure of a neuron and the kinds of neurons found in the body. 3. Explain how
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, WORKBOOK - Biology WORKBOOK. Student:
 WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
WORKBOOK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Teacher: Student: Biology Iva Kubištová.. School year:../ This material was prepared with using http://biologygmh.com/ Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nervous system, Senses,
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Functions of the Nervous System
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy)
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy)
Notes: Nervous System
 Notes: Nervous System KEY CONCEPT #1 The and the provide the means by which organ systems. The body s communication systems help maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is. Responses. The nervous and endocrine
Notes: Nervous System KEY CONCEPT #1 The and the provide the means by which organ systems. The body s communication systems help maintain homeostasis. A stimulus is. Responses. The nervous and endocrine
