Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions
|
|
|
- Brenda Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN where employee was exposed will print this entire packet. 2. Complete sections you are responsible for as designated in top right hand corner. 3. Patient then takes entire packet to the ED for review and treatment as appropriate. Call the ED charge RN at to alert them that you are sending a patient. 4. Patient will be discharged from the ED after #3 above to follow up with Employee Health Clinic on the next business day. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 1
2 Area Charge Nurse Complete before sending employee to the ED Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Checklist After Hours Patient = person exposed (usually the employee) Source / Donor = from whom the fluid came Fill out source (donor) information sheet for the ED to use in assessing exposure risk Have employee fill out body fluid exposure assessment (2 pages) Send employee with above paperwork and rest of the printed packet to the ED Draw blood on source (donor) if applicable Do not draw any blood on the employee Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 2
3 Body Fluid Source (DONOR) Assessment Instructions Area Charge Nurse Complete before sending employee to the ED 1. Obtain Source Name, MR# and Location (This is the person who s fluid exposed the employee or pt). If the Source is under 9 months of age, do the Risk Assessment on the mother and draw Source labs from the mother. Complete Source Medical History Review Look up any available lab results for HIV, Hepatitis C, and Hepatitis B. o If HIV, Hep C and/or Hep B (HBsAg) were done in the past 2 weeks or if prior HIV, Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C positive then do not repeat that test. Obtain results for the provider. o If blood was drawn for other reasons/studies, use those samples if they are still in the lab and order the lab panel. Review Medical Record (answer the Source Assessment questions from medical records and from a Source interview if appropriate). Consent is needed to test for HIV, but is not needed for Hepatitis C or HbsAg testing. 2. Obtain Source HIV testing consent. If Source is conscious and competent, interview the Source to obtain signed HIV testing consent. If the Source is unable to give consent (including anyone under the legal age for consent), follow New Mexico state law on obtaining HIV consent. Assistance from Epidemiology, Occupational Health, or HSC Legal Counsel may be obtained. If you are able to make contact only by phone, HIV Consent may be obtained but must be repeated by the Source to a 2 nd staff witness. 3. Order source HIV, Hepatitis C, and Hepatitis B (HbsAg) order as Needle Don lab panel. 4. Provide the source information to the evaluating provider 5. Refer the source to their primary care physician to obtain the results of their Source Labs 6. For afterhours exposure assessments Notify OHS of all after-hour exposures by calling the clinic the next working day. If Donor Lab results are needed prior to next Clinic business day then the Administrative Supervisor should obtain the results and relay these to the Recipient s provider (ED) so that treatment of the recipient may be modified as needed. Source / Donor Assessment (must be completed and sent to ED for evaluation) Unknown Source: No further source assessment required Source Name: MRN #: Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV None Unknown Source with history of Liver disease Blood Transfusion prior to 1985 Injection drug use Multiple or SAME sex partners Source blood draw Consent for HIV test obtained Needle Don panel ordered Source refused testing Source / Donor Label Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 3
4 Nurse or Supervisor Date / Time Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 4
5 Body Fluid Exposure Assessment Name Home Phone Cell Phone Work Phone (Preferred number for clinic to contact: Home Work Cell) Date of Incident Time of Incident Work Department Job Category Location of the exposure (ED, Patient room, OR, Lab, etc.) Employee Medical History Person Exposed Complete before coming to ED Have you ever had? HIV Yes No Hepatitis C Yes No Hepatitis B Yes No Other significant medical history Last Tetanus Booster (date) Have you received the Hepatitis B Vaccination? Yes No If yes, do you know if you are HBV immune / protected? Yes No Unknown ** Is the Source patient (the person s whose body fluid it was) identifiable? ** Yes No Unknown Complete #1-11 if NEEDLESTICK or other SHARP OBJECT injury (Skip to # 12 for blood or body fluid splash/other exposures) 1. Were you the original user of the sharp item? Yes No Unknown 2. Did the sharp item have blood visible on it? Yes No Unknown 3. For what purpose was the sharp item originally used? Unknown Injection through the skin Drawing venous/arterial blood IV use: injection into/aspiration from an IV injection site/iv port, connecting or starting IV Placing a central line Suturing/cutting/electrocautery Other 4. How did the injury occur? During use After use Recapping needle Restraining a patient Preparation for reuse of reusable equipment Device left on floor, bed or other inappropriate place While disposing of item 5. What device was involved in the injury? Unknown Hollow bore Needle: Identify (gauge of needle, etc) Other sharp: Identify (lancet, suture needle, scalpel, glass, etc.) 5a. Brand/Manufacturer of the sharp item: Model: 6. Did the item causing the injury have a safety design such as retractable or shielded needle? Yes No Unknown If yes, describe feature 6a. Was the device activated? Yes, fully activated Yes, partially activated No Unknown 7. What was the physical location of your injury? (ex. Right index finger) 8. Was the injury? Superficial (little/no bleeding) Moderate (skin punctured/some bleeding) Severe (deep stick/cut, profuse bleeding) Continued on next page Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 5
6 Person Exposed Complete before coming to ED 9. If the injury was to the hand, did the sharp item penetrate? Single pair of gloves Double pair of gloves No gloves 10. Are you primarily? Right handed Left handed 11. Do you have any opinion as to how this injury could have been prevented? Complete #12-21 for OTHER BLOOD/BODY FLUID Exposure (Skip to signature if had needlestick or other sharp object injury) 12. Type of Body Fluid: (please check) Unknown Blood Other body fluid: list type (Sputum, vomit, etc.) If other, was visible blood present in the fluid? Yes No Unknown 13. What body part was exposed? (Skin on the right hand, eye, mouth, etc) 14. Did the blood/body fluid? Touch unprotected skin Soak through protective garment or clothing 15. What barrier garments were worn at the time of the exposure? None Gloves Goggles/eyeshield Surgical mask Gown/apron/lab coat Other: 16. How did the exposure occur? 17. Did equipment failure occur? Yes No If yes, please specify equipment type and manufacturer: 18. How long was the blood/body fluid in contact with your skin/mucous membrane? Less then 5 minutes 5-14 minutes 15 minutes to 1 hour Over 1 hr 19. Did you flush/clean area? Yes No Comments: 20. What was the volume of blood/body fluid? Unknown Small (up to 1 teaspoon or 5cc) Moderate (up to quarter cup or 50cc) Large (over 50cc) 21. Do you think this injury could have been prevented with controls in place? Yes No If yes, please describe: Employee Signature Date ED attending to review and sign below: Comments: ED Provider Date Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 6
7 Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Checklist After Hours ED Attending Check boxes as appropriate Patient = person exposed (usually the employee) Source / Donor = from whom the fluid came All Patients During ED visit Patient decides NO to HIV PEP Patient decides YES to HIV PEP Review and sign exposure information pages 3-5 filled out by patient and charge RN. Review and sign with the employee the decision trees for HBV, HCV and HIV Check off flowchart boxes as appropriate Complete gray shaded boxes and sign in the provider line Circle the HIV risk status and discuss CDC recommendations Review risks / side effects of PEP if warranted Offer Hep B vaccination if not already vaccinated or known non-responder Draw source / donor labs if that person is also an ED patient (order = Needle Don ) Refer to Employee Health Clinic next business day Discharge patient from the ED with the last sheet of this packet and ED Needlestick computerized discharge instructions from First Net NO LABS drawn on patient in the ED Refer patient to Employee Health Clinic next business day for CONFIDENTIAL blood draw of HIV and hepatitis panel Complete consent sheet Review risks / side effects of PEP Patient to sign consent for treatment form Give patient copy of consent Draw CBC, Chem 7, LFT, amylase, pregnancy test (if applicable) (DO NOT draw HIV or hepatitis panel in ED) Start first dose (after pregnancy test) of PEP in ED and give Take Home Pack of remaining PEP doses to patient (all meds are in ED Pyxis) Patient referred to appropriate clinic (on discharge sheet) next business day for CONFIDENTIAL blood draw of HIV and hepatitis panel NON hospital employees (ex. kid stuck with syringe at park) should have HIV, hepatitis panel, CBC, chem 7, LFT, amylase and PGU (if appropriate) drawn in the ED. These patients should have follow up with PCP 1 week after starting PEP. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 7
8 Hepatitis B Decision Tree ED Attending HBV counseling POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS - Hepatitis B Addendum J Ck Boxes upon Completion ED/UC COMPLETE GRAY BOX OTHER SIDE Step 1 - Order Hep B SAg on donor (1) Step 2 Check Hep B immunization status of Exposed Person (Recipient) Counsel Recipient on Hepatitis B disease and risk of conversion Unvaccinated recipient OR vaccine series not completed by recipient Vaccinated recipient Give HBV vaccine now. (2) Plus Documented Non Responder [Recipient of 6 vaccinations without titer response] Response to Vaccine - Unknown Documented response to vaccine Hep B Sag Unknown (or unknown donor) Obtain Donor HepBsAg Results Hep B SAg (+) Hep B SAg (-) Obtain Hep SAg results on Donor within 24 hrs; if unable, consider HBIG if Donor high risk No further action if titer was obtained within the past year. Consider obtaining repeat recipient titer if not within the past year. Then give one booster vaccination if titer is low. Obtain Hep B SAg results on Donor within 24 Hours; if unable consider HBIG if Donor is high risk (1) HBIG (3) No further action Recipient Titer > 10 No further action Recipient Titer < 10 mlu/ml 1 Booster Dose HVB vaccine (4) HBIG if Donor is Hep B sag positive Health Provider Signature (1) Consider using the CDC table: Recommended post exposure prophylaxis for Hep B virus - - Addendum E. (2) Ensure complete HBV vaccine series is given. (3) HBIG 0.06ml/kg IM; not to exceed 5.0ml for adults ( should be given within 24 hrs of exposure if possible). Second dose at 4 weeks. (4) Post vaccination testing for titer should be done between 1 & 6 months after completion of vaccine series or boosters to provide info on response to vaccine. Delay testing until 6 months after the booster if HBIG was administered concurrently. Date Risk of seroconversion is dependent upon many factors and is between 2 and 40% in an unvaccinated recipient NON - health care workers with exposure should receive vaccination Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 8
9 Hepatitis B Vaccination Guidelines ED Attending HBV counseling Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 9
10 Hepatitis C Decision Tree ED Attending HCV counseling POST EXPOSURE DECISION PROTOCOL - HEPATITIS C Addendum L Check Boxes upon Completion Check Donor Counsel the recipient on Hepatitis C and the risk of seroconversion. Donor Unknown Donor Known Offer Follow-up Hep C (by Elisa) to recipient at 6 months and 12 months Hepatitis C (-) Hepatitis C (+) Offer to the recipient follow up testing for Hepatitis C antibodies (by Elisa) at 6 and 12 months Offer to the recipient follow up testing for Hepatitis C By PCR at 4-6 weeks * if high risk exposure. Refer to Gastroenterology if positive for possible therapy. Offer to the recipient follow up testing for Hepatitis C antibodies (by Elisa) Antibodies at 6 and 12 months * If the recipient is not tested before 3 months post-exposure, proceed with the Elisa rather then the PCR Health Provider Signature Date Risk of seroconversion in percutaneous exposure to blood is 1.8%. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 10
11 HIV Decision Tree ED Attending HIV counseling HIV POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS (PEP) DECISION PROTOCOL Addendum D Check Donor Medications should be started as soon as possible, ideally within 2 hours. prescription guidelines on back side. Donor Unknown Donor Known Consider HIV PEP if high risk exposure (see box) HIV Status Unknown HIV Negative in the last two weeks HIV Positive Order HIV on Donor Offer follow-up HIV testing To recipient. (2) Consult ID for PEP recommendations. Offer follow-up HIV testing to recipient (2) Assess Risk (1) THIS BOX MUST BE COMPLETED Check if treatment initiated: High Risk Low Risk Recommend HIV PEP (See Box); Consider ID consult Obtain donor HIV results Generally no PEP warranted HIV Positive HIV Negative Pregnancy test obtained on women before initiating prophylaxis. AND Baseline labs obtained (3) AND Treatment consent obtained from the Recipient before initiating treatment. (Addendum H) AND Recipient counseled and Prescription Guidelines followed. OR Recipient declined HIV PEP Continue HIV PEP. Consult ID if low ;risk exposure to determine need for PEP. Offer follow-up HIV testing to recipient (2); Discontinue any HIV PEP OR HIV PEP not indicated (1) Utilize the CDC PEP recommendation tables if needed. (2) HIV testing on recipient is done at 0 weeks, 6 weeks, 12 weeks, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks. (3) CBC, Diff, HFP, Amylase, BUN, CR and pregnancy test are the baseline labs. These labs (excluding pregnancy test) could be held until the Source HIV is known. Health Provider Signature Date Risk of seroconversion in percutaneous exposure to blood is 0.3% (3 per 1000) Risk of seroconversion in a mucous membrane exposure to blood is 0.09% (<1 per 1000) Risk of seroconversion in a non-intact skin exposure is felt to be < 0.09% These are for HIV infected blood. Risk of seroconversion with exposure to any other fluid or tissue is felt by the CDC to be considerably lower but has not been quantified. NON - health care worker with exposure: Consider likelihood for HIV prevalence in exposure to determine need for PEP (4 weeks duration). Patient will need PCP follow up. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 11
12 ED Attending HIV risk determination HIV Exposure Risk PEP Recommendations (from CDC) (Circle the box that applies) Percutaneous Exposures Exposure Type Less severe (solid needle, superficial injury) More severe (large-bore hollow needle, deep puncture, visible blood on device, needle used in patient s artery or vein) HIV Positive Basic 2-drug PEP; Call Infectious Disease Expanded 3-drug PEP; Call Infectious Diseases for regimen Unknown HIV Status (Known Source) drug PEP for source with HIV risk factors drug PEP for source with HIV risk factors Unknown HIV Status (Unknown Source) drug PEP if exposure to HIV-infected persons is likely drug PEP if exposure to HIV-infected persons is likely HIV negative No PEP warranted No PEP warranted Mucous Membrane or Non-intact Skin Exposures Exposure Type Small volume (a few drops) Large volume (major blood splash) HIV Positive Basic 2-drug PEP; Call Infectious Disease Expanded 3-drug PEP; Call Infectious Diseases for regimen Unknown HIV Status (Known Source) drug PEP for source with HIV risk factors drug PEP for source with HIV risk factors Unknown HIV Status (Unknown source) drug PEP if exposure to HIV-infected persons is likely drug PEP if exposure to HIV-infected persons is likely HIV negative No PEP warranted No PEP warranted If donor is HIV + and on multiple medications, ID attending (via PALS) should be consulted for best regimen. ID is happy to consult on all cases with ED attending questions. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 12
13 HIV PEP Medication Information for Providers ED Attending PEP information Basic Regimen Truvada Emtricitabine (FTC) 200 mg / Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg Preferred Dosing One tablet by mouth once daily with or without food Available Dosages Tablet, 200 mg FTC mg TDF (Take Home Packs in ED PYXIS) Advantages Disadvantages Well tolerated Once daily dosing FTC and TDF are active against HBV Pregnancy category Headache GI intolerance (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and flatulence) Renal insufficiency (Fanconi s syndrome) Expanded Regimen Preferred Dosing Available Dosages Advantages Disadvantages Atazanavir (ATZ) + Ritonovir (RTV) ATZ: One tablet by mouth once daily with food RTV: One tablet by mouth once daily with food (take together with ATZ) ATZ: Tablet, 300 mg (Take Home Packs in ED PYXIS) RTV: Tablet, 100 mg One of the preferred HIV regimens Generally well-tolerated Pregnancy category B ATZ Indirect hyperbilirubinemia, with elevated transaminases Cannot be taken with proton pump inhibitor; use caution with antacids and H2RAs Prolonged PR interval Nephrolithiasis Possible increased bleeding episodes in hemophiliacs RTV Multiple drug interactions with other medications (consult with pharmacist) GI intolerance Circumoral and extremity parasthesias (rare when used as boosting agent) Asthenia If other medications are advised by ID, further information is available (online) in: Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to HIV and Recommendations for Postexposure Prophylaxis MMWR Recommendations and Reports Vol 54/No. RR-9, September 30, 2005 Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 13
14 CONSENT Post-exposure Prophylaxis for HIV ED Attending If PEP to be given I may have been exposed to HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, in my work place. The risk of infection from my exposure is not known. However, should HIV infection occur, the outcome is likely to be ultimately fatal. My clinician has offered me treatment with Tenofovir and Emtricitabine (in a combination form known as Truvada ) and, in some cases, Atazanavir/ritonavir, which might reduce my risk of infection. There is no proof that drug treatment after HIV exposure will prevent infection. I will be asked to use contraception during the four weeks of treatment and four subsequent weeks (both men and women). I will be tested for pregnancy and if I am pregnant, any decision to continue prophylaxis will be made in conjunction with an infectious diseases and obstetric clinician. I will be asked to contact my clinician immediately if I learn that I am pregnant while I am on the medications. See table below for risks and side effects associated with antiretroviral drugs. A full listing is in the package insert for each medication. Treatment side effects are expected to disappear after treatment is stopped, but could be life threatening or irreversible. New or rare serious side effects, including cancer, birth defects, or other life-threatening diseases, might develop now or in the future. MEDICATION COMMON SIDE EFFECTS Emtricitabine / Tenofovir = Truvada Abdominal pain Anorexia Anxiety Diarrhea Vomiting Dizziness Flatulence Headache Nausea Arthralgia Fatigue Atazanavir = Reyataz Abdominal pain Diarrhea Headache Rash Jaundice Myalgia Nausea Peripheral neurologias Vomiting Insomnia Ritonavir = Norvir Abdominal pain Anorexia Asthenia Constipation Insomnia Malaise Diarrhea Dizziness Flatulence Headache Parasthesia Rash Vomiting Caution is to be used with other medication use so I understand I need to disclose all medications that I am currently using. DOSING: Truvada (Emtricitabine 200 mg / Tenofovir 300 mg): One tablet by mouth once daily x 28 days Atazanavir 300 mg: One tablet by mouth once daily x 28 days Ritonavir 100 mg: One tablet by mouth once daily x 28 days Please read and check each box as appropriate: I understand that I will be taking [ ] Truvada (Emtricitabine/Tenofovir) [ ] Atazanavir / Ritonavir I have been advised to use other antiretroviral drugs {as listed here: } by an Infectious Disease physician and have been informed of their side effects and drug interactions. I have read the Informed Consent Information: Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis. I have had the opportunity to ask questions. I further understand that should I have any questions about my treatment I may contact the clinic or the infectious disease consultant. I have discussed all my current medications with my treating provider. SIGNATURE: DATE: / / WITNESS: DATE: / / Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 14
15 Person Exposed Send home with employee Body Fluid Exposure Discharge Information 1. There is a possibility that you have become exposed to one or more of the following diseases: HIV: Risk of infection through a needlestick is 0.3% (3 per 1000) Risk of infection by blood in the eyes or mouth is 0.09% (Less than 1 per 1000) Risk of infection by exposure to blood through a break in the skin is felt to be even less. These are for HIV infected blood. Risk of infection with exposure to any other body fluid is considerably lower. Hepatitis B: Risk of infection is dependent upon many factors and is between 2 and 40% in an unvaccinated person. Hepatitis C: Risk of infection after a needlestick is 1.8%. There have been no cases of Hepatitis C infection from blood exposure to the eyes or mouth. 2. Report symptoms of fever, enlarged and tender lymph nodes, skin rash, stomach or nerve problems which start 2-6 weeks after this exposure. 3. It is possible that you could transmit one or more of these diseases to another person, so you should avoid activities that might expose others to your blood or body fluids. These include sharing toothbrushes or razorblades, donating blood or body organs, breastfeeding or becoming pregnant. If you are sexually active, you should consider using condoms with sexual activity. If you are a user of recreational drugs, you should not share needles. These precautions are especially important in the first 6-12 weeks after this exposure. 4. If you have received HIV prophylaxis medication (PEP), make sure that you received a copy of the consent form with information on the drug side effects and drug interactions, and an explanation of the need to continue the PEP regimen. Hospital employees should follow up at OHS (Occupational Health Services th floor) between 7:30 am and 3:30 pm the next business day. UNM faculty or residents should follow up at EOHS (Employee Occupational Health Services nd floor of the Family Practice Building) between 8:00 am and 5:00 pm the next business day. Medical or other students should follow up at SHAC (Student Health and counseling South Campus across from the SUB building) between 8:00 am and 5:00 pm the next business day. Individuals who were exposed while at work should contact their employer immediately. Other members of the community should follow up with a Primary Care Provider in 1 week to discuss following the blood drawn in the emergency department. Emergency Department Body Fluid Exposure (6/1/2012) Page 15
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure STUDENT. Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure. Student. Rev:
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]
![BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens] BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]](/thumbs/73/68341667.jpg) BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICES MANUAL
 1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update JHS Annual Mandatory Education
 2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
2014 OSHA Blood-borne Pathogens (BBP) Update 2014 JHS Annual Mandatory Education Objectives Discuss the epidemiology of Bloodborne Pathogens. List the statistics of HIV/AIDS cases Identify the correlation
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS. They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids.
 What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft:
 Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
Important Safety Information About TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication. For Healthcare Providers
 Important Safety Information About TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication For Healthcare Providers About TRUVADA for a PrEP Indication INDICATION AND PRESCRIBING CONSIDERATIONS TRUVADA,
Important Safety Information About TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication For Healthcare Providers About TRUVADA for a PrEP Indication INDICATION AND PRESCRIBING CONSIDERATIONS TRUVADA,
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors
 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments
 Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Management
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication. Training Guide for Healthcare Providers
 TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication Training Guide for Healthcare Providers About TRUVADA for a PrEP indication to reduce the risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 infection in high-risk
TRUVADA for a Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Indication Training Guide for Healthcare Providers About TRUVADA for a PrEP indication to reduce the risk of sexually acquired HIV-1 infection in high-risk
Bloodborne Pathogens. Post-Exposure Incident Packet. An Informational Guide
 Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet An Informational Guide Faribault Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet This packet has been developed as an informational
Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet An Informational Guide Faribault Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet This packet has been developed as an informational
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed?
 Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
Needles and Sharps Exposure: How do We Proceed? UMAYYA MUSHARRAFIEH,MD AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF BEIRUT MEDICAL CENTER JUNE 14, 2013 Health care workers who use or may be exposed to needles are at increased
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
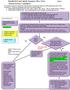 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011
 Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
Bloodborne Pathogens: Recognition and Treatment 2011 Occupational Health Services at The Summit Rita M. Lopez, APRN-BC, MSN 751-4189 rlopez@krmc.org OBJECTIVES DEFINE Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure WHO must
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, Approximately
HIV prophylaxis for health care providers. Dr. A. K. M. Humayon Kabir Assistant Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital HIV continues to be a major global public health issue, Approximately
TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING
 POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
Bloodborne Pathogens Training. IEA, Inc.
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
Important Safety Information About Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
 Important Safety Information About Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) For Healthcare Providers About Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil
Important Safety Information About Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) For Healthcare Providers About Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Bloodborne Pathogens. Montclair Kimberley Academy 1
 Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1
 PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
Decision Analysis Example
 Decision Analysis Example after Occupational Exposure to Infection after Needlestick Injury Direct inoculation into blood vessels Cutaneous dendritic (Langerhans) cells Delay from injury to infection Initial
Decision Analysis Example after Occupational Exposure to Infection after Needlestick Injury Direct inoculation into blood vessels Cutaneous dendritic (Langerhans) cells Delay from injury to infection Initial
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Prophylaxis
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE
 Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM
 Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Page 1 of 13 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS FOR HEALTH CARE WORKERS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The attached materials will assist in teaching the information about bloodborne pathogens for health care workers as required
Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist
 Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist Employee Name: : First Aid completed (If exposure was to eye, irrigate for 20 minutes at the nearest eye wash station. If exposure was to skin, wash affected
Post Blood & Body Fluid Exposure Checklist Employee Name: : First Aid completed (If exposure was to eye, irrigate for 20 minutes at the nearest eye wash station. If exposure was to skin, wash affected
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee INSTRUCTIONS 1. Employee: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Employee INSTRUCTIONS 1. Employee: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
FOR INFECTION TO OCCUR: Bloodborne Pathogens are viral diseases that can infect a person if they are exposed Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV
 OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Bloodborne Pathogens are viral diseases that can infect a person if they are exposed Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV FOR INFECTION TO OCCUR: A germ Bloodborne
OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Bloodborne Pathogens are viral diseases that can infect a person if they are exposed Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV FOR INFECTION TO OCCUR: A germ Bloodborne
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY
 CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification
 SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B. Acute HBV Questionnaire
 BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP)
 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc.
 Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS. Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532
 2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532 OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Our plan is Reviewed annually, or as necessary to reflect changes in technology,
2013 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Frostburg State University Frostburg, Maryland 21532 OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens 29 CFR 1910.1030 Our plan is Reviewed annually, or as necessary to reflect changes in technology,
The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard
 Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING
 ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
El Paso - Ambulatory Clinic Policy and Procedure
 Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Harvard University Exposure Control Plan
 Harvard University Exposure Control Plan Harvard University is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment. In accordance with this goal, the Occupational Health and Safety Administration
Harvard University Exposure Control Plan Harvard University is committed to providing a safe and healthy work environment. In accordance with this goal, the Occupational Health and Safety Administration
Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Training Guide for Healthcare Providers
 Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Training Guide for Healthcare Providers About emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for HIV-1 PrEP
Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate 200 mg/300 mg for HIV-1 Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Training Guide for Healthcare Providers About emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for HIV-1 PrEP
Doc No: BLOOD Midland Engineering Co., Inc. Initial Issue Date 12/04/15 Safety Management System
 Revision Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: President Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has a variety of regulations that all
Revision Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: President Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has a variety of regulations that all
Bloodborne Pathogens in the Workplace
 Bloodborne Pathogens in the Workplace 1 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens? They are viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms that: Are carried in a person s bloodstream Cause disease If a person comes in
Bloodborne Pathogens in the Workplace 1 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens? They are viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms that: Are carried in a person s bloodstream Cause disease If a person comes in
For. Correctional. Officers. Your. Health Risks. in Correctional Settings. Facts. About HIV
 For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
EPINet Report for Needlestick and Sharp Object Injuries
 EPINet Report for Needlestick and Sharp Object Injuries Reporting period: Jan 01, 2017 to Dec 31, 2017 Total Records Read: 1329 Facility where incident occurred: ALL Type of facility where occurred: ALL
EPINet Report for Needlestick and Sharp Object Injuries Reporting period: Jan 01, 2017 to Dec 31, 2017 Total Records Read: 1329 Facility where incident occurred: ALL Type of facility where occurred: ALL
Needle Stick. Mr. Fadi J. Zaben RN MSN IMET 2000, Ramallah IMET 2000
 Needle Stick Mr. Fadi J. Zaben RN MSN, Ramallah 1 Objectives: Define Needle Stick. Mention the sharps. Discus the rate of incidence. Identify the person who is at risk. Discus Needle stick and infectious
Needle Stick Mr. Fadi J. Zaben RN MSN, Ramallah 1 Objectives: Define Needle Stick. Mention the sharps. Discus the rate of incidence. Identify the person who is at risk. Discus Needle stick and infectious
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官
 C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
C 肝職業暴露後之處置 衛福部疾病管制署 中區傳染病防治醫療網 王任賢指揮官 HCV:Structure and Classification Unclassified virus, Member of the flavivirus family (other members yellow fever and dengue) Enveloped single stranded RNA virus Humans
Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module
 Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. Bloodborne pathogens are viruses or bacteria present in human blood and body fluids which can infect
Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. Bloodborne pathogens are viruses or bacteria present in human blood and body fluids which can infect
Laboratory Exposure Control Plan WAC
 A. Introduction Because laboratories and classrooms working directly with blood or other potentially infectious materials have different bloodborne pathogen exposure concerns than the general university,
A. Introduction Because laboratories and classrooms working directly with blood or other potentially infectious materials have different bloodborne pathogen exposure concerns than the general university,
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA HEALTH SYSTEM
 White Blood Cell Collection by Leukapheresis in HIV-infected Individuals On Chemotherapy and Controls Not on Chemotherapy: A Study of HIV Reservoir Eradication CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A RESEARCH STUDY
White Blood Cell Collection by Leukapheresis in HIV-infected Individuals On Chemotherapy and Controls Not on Chemotherapy: A Study of HIV Reservoir Eradication CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE IN A RESEARCH STUDY
Bloodborne Pathogens. By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING
 Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING Are the two diseases specifically addressed by the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard (Be aware of Hepatitis C as it is becoming more and more
Wrentham Public Schools ANNUAL BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING Are the two diseases specifically addressed by the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard (Be aware of Hepatitis C as it is becoming more and more
How are Blood borne pathogens harmful? How do you come into contact with Blood-borne pathogens?
 What are Blood borne pathogens? How are Blood borne pathogens harmful? How do you come into contact with Blood-borne pathogens? How do I protect myself? A blood-borne disease is one that can be spread
What are Blood borne pathogens? How are Blood borne pathogens harmful? How do you come into contact with Blood-borne pathogens? How do I protect myself? A blood-borne disease is one that can be spread
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: F:
 University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
Safety Committee Prototypical Safety Program Manual
 1 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Policy The Department Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan is designed to comply with the requirements of the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard, 29 CFR
1 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Policy The Department Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan is designed to comply with the requirements of the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard, 29 CFR
Infection Control. Chapter 11 Intro to HST
 Infection Control Chapter 11 Intro to HST All health care workers must understand basic infection control Key terms Pathogen: germ Microorganism: small, living organism that is not visible to the naked
Infection Control Chapter 11 Intro to HST All health care workers must understand basic infection control Key terms Pathogen: germ Microorganism: small, living organism that is not visible to the naked
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 San Bernardino County Superintendent of Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan BIOHAZARD 2018/2019 Title 8 California Code of Regulations Section 5193 Table of Contents PURPOSE OF THE PLAN...3
San Bernardino County Superintendent of Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan BIOHAZARD 2018/2019 Title 8 California Code of Regulations Section 5193 Table of Contents PURPOSE OF THE PLAN...3
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
LeadingAge Florida February 24, 2016
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EMPLOYEE HANDBOOK 1 POLICY EMPLOYEE ORIENTATION AND IN-SERVICE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS AWARENESS It is the policy of Healthcare Services Group, Inc., to ensure that all employees with
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EMPLOYEE HANDBOOK 1 POLICY EMPLOYEE ORIENTATION AND IN-SERVICE TO BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS AWARENESS It is the policy of Healthcare Services Group, Inc., to ensure that all employees with
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan RIM of the World Unified School District 27315 North Bay Road Blue Jay, CA 92352 (909) 336-4100 July 2016 Safety and Risk Management Department RIM of the World
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan RIM of the World Unified School District 27315 North Bay Road Blue Jay, CA 92352 (909) 336-4100 July 2016 Safety and Risk Management Department RIM of the World
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools
 Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Infectious Disease and Bloodborne Pathogens Training St. Michael-Albertville Public Schools Questions? Any time throughout the slide show or throughout the school year: Contact Jake Baxter at IEA Phone:
Bloodborne Pathogens. Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety
 Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
