17β-Estradiol Alters the Activity of Conventional and IFN-Producing Killer Dendritic Cells
|
|
|
- Shanon Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This informtion is current s of Septemer, 28. 7β-Estrdiol Alters the Activity of Conventionl nd IFN-Producing Killer Dendritic Cells Mrk C. Sircus, Michel G. Overstreet, Frnck Housseu, Aln L. Scott nd Sr L. Klein J Immunol 28; 8:423-43; ; doi:.449/jimmunol References Suscription Permissions Emil Alerts This rticle cites 5 rticles, 22 of which you cn ccess for free t: Why The JI? Sumit online. Rpid Reviews! 3 dys* from sumission to initil decision No Trige! Every sumission reviewed y prcticing scientists Fst Puliction! 4 weeks from cceptnce to puliction *verge Informtion out suscriing to The Journl of Immunology is online t: Sumit copyright permission requests t: Receive free emil-lerts when new rticles cite this rticle. Sign up t: Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28 The Journl of Immunology is pulished twice ech month y The Americn Assocition of Immunologists, Inc., 45 Rockville Pike, Suite 65, Rockville, MD 2852 Copyright 28 y The Americn Assocition of Immunologists All rights reserved. Print ISSN: Online ISSN:
2 The Journl of Immunology 7 -Estrdiol Alters the Activity of Conventionl nd IFN-Producing Killer Dendritic Cells Mrk C. Sircus,* Michel G. Overstreet,* Frnck Housseu, Aln L. Scott,* nd Sr L. Klein 2 * Estrogens increse spects of innte immunity nd contriute to sex differences in the prevlence of utoimmune diseses nd in response to infection. The gol of the present study ws to ssess whether exposure to 7 -estrdiol (E2) ffects the development nd function of one mrrow-derived dendritic cells nd to determine whether similr chnges re oserved in CDc splenocytes exposed to E2 in vivo. E2 fcilitted the differentition of BM precursor cells into functionl CDc CD MHC clss II dendritic cells (DCs) with incresed expression of the costimultory molecules CD4 nd CD86. Exposure of one mrrow-derived dendritic cells to E2 lso enhnced production of IL-2 in response to the TLR lignds, CpG nd LPS. In contrst, CDc cells isolted from the spleens of femle C57BL/6 mice tht were intct, ovriectomized, or ovriectomized with E2 replcement exhiited no differences in the numer or ctivity of CDc CD MHC clss II DCs. The presence of E2 in vivo, however, incresed the numer of CDc CD49 NK. low cells nd reduced numers of CDc CD49 NK. high cells, surfce phenotype for IFN-producing killer DCs (IKDCs). Ultrstructurl nlysis demonstrted tht CDc NK. popultions were comprised of cells tht hd the ppernce of oth DCs nd IKDCs. CDc splenocytes isolted from nimls with supplementl E2 produced more IFN- in response to IL-2 nd IL-8. These dt illustrte tht E2 hs differentil effects on the development nd function of DCs nd IKDCs nd provide evidence tht E2 my strengthen innte immunity y enhncing IFN- production y CDc cells. The Journl of Immunology, 28, 8: Sex-sed differences in susceptiility to oth utoimmune nd infectious diseses re widely reported (). Approximtely 8% of ll cses of utoimmunity in the U.S. re women, with differences etween the sexes eing most pronounced for Sjogren s syndrome, systemic lupus erythemtosus, thyroid disese (Hshimoto s thyroiditis nd Grves disese), scleroderm, nd mystheni grvis (2, 3). Although femles re more likely to develop utoimmune diseses, the prevlence nd intensity of virl, cteril, nd prsitic infections re typiclly reduced in femles compred with mles (4). Sex differences in susceptiility to utoimmune nd infectious diseses my reflect n immunologicl dimorphism, in which femles often mount more roust immune responses thn mles (4 6). The previling hypothesis for heightened immunologicl responsiveness in femles compred with mles is tht sex hormones, in prticulr testosterone nd 7 -estrdiol (E2), 3 directly influence immune function. *The W. Hrry Feinstone Deprtment of Moleculr Microiology nd Immunology, Johns Hopkins Bloomerg School of Pulic Helth nd Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cncer Center, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Bltimore, MD 223 Received for puliction June 6, 27. Accepted for puliction Novemer 2, 27. The costs of puliction of this rticle were defryed in prt y the pyment of pge chrges. This rticle must therefore e herey mrked dvertisement in ccordnce with 8 U.S.C. Section 734 solely to indicte this fct. This work ws supported y Ntionl Institutes of Helth Grnt R AI (to S.L.K.) nd grnt from The Johns Hopkins Mlri Reserch Institute (to S.L.K.). 2 Address correspondence nd reprint requests to Dr. Sr Klein, Deprtment of Moleculr Microiology nd Immunology, Johns Hopkins Bloomerg School of Pulic Helth, 65 North Wolfe Street, Bltimore, MD 225. E-mil ddress: sklein@jhsph.edu 3 Arevitions used in this pper: E2, 7 -estrdiol; ER, estrogen receptor; ERE, estrogen response element; DC, dendritic cell; BM, one mrrow; cdc, conventionl dendritic cell; pdc, plsmcytoid dendritic cell; IKDC, interferon-producing killer dendritic cell; ovx, ovriectomized; shm, shm surgery; WT, wild type; MHCII, MHC clss II; IMDM, Iscove s modified Dulecco s medium. Copyright 28 y The Americn Assocition of Immunologists, Inc /8/$2. Estrogens re lipophilic hormones tht exert their iologicl effects y inding to intrcellulr receptors, specificlly estrogen receptor (ER) nd ER. Both receptor sutypes re present in the thymus nd spleen s well s in circulting lymphocytes, dendritic cells (DCs), NK cells, nd mcrophges (7 ). The inding of E2 to the ER is sufficient to lter the effector functioning of immune cells. For exmple, exposure to E2 enhnces cytotoxicity nd production of IFN- y NK cells (, 2); process likely medited y the presence of estrogen response elements (ERE) in the promoter region of the ifng gene (3). E2 lso fcilittes the differentition of one mrrow (BM) progenitor cells into functionl CDc DCs in vitro (4); enhnces the synthesis of inducile NO synthse nd proinflmmtory cytokines, including IL-, IL-6, nd TNF, y mcrophges (5, 6); nd ugments the expnsion of CD4 CD25 T cells in mice (7). Although there re reports of E2 suppressing proinflmmtory responses, including production of IL-6 y mcrophges (8 2), generlly, estrogens enhnce oth cell-medited nd humorl immune responses (2, 22). These effects, however, cn e dependent on the dose of E2, the timing of estrogen tretment, nd the cell popultion exmined (9, 2). A wide rry of immune effector mechnisms medites dimorphic utoimmune nd infectious disese outcomes; thus, sex differences in disese susceptiility cnnot e ttriuted to one prticulr rm of the immune system tht my e differentilly regulted in femles thn in mles. Much of the work investigting sex-sed differences in utoimmune nd infectious diseses hs focused on end-point effector mechnisms of dptive immunity, such s A production, cell-medited cytotoxicity, nd cytokine production (23 26). Whether sex-ssocited susceptiility to utoimmune nd infectious diseses lso reflects differences in the ctivity of the innte immune system is less well chrcterized (27). DCs serve s criticl link etween innte nd dptive immunity nd re essentil for ctivtion nd regultion of immune responses ginst infection (28, 29). In mice, susets of splenic DCs Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
3 424 ESTROGEN AND INNATE IMMUNITY cn e differentited sed on surfce mrker expression nd cytokine production: ) conventionl DCs (cdcs) re CDc CD8 or CDc CD nd produce IL-2; 2) plsmcytoid DCs (pdcs) re CDc dull B22 Gr nd produce primrily type I IFNs following stimultion; nd 3) IFN-producing killer DCs (IKDCs) re CDc MHCII CD49 NK. high nd produce type I IFNs, IL-2, nd IFN-, depending on the stimulus (3). To dte, studies exmining the effects of E2 on DCs hve primrily een restricted to in vitro stimultion of BM-derived precursors, with focus on cdc popultions (4, 3). In the work presented in this study, we expnd these oservtions nd demonstrte tht E2 differentilly ffects the numer, phenotype, nd ctivity of cdcs nd IKDCs. Furthermore, we estlish tht E2 hs distinct effects on BMderived precursors stimulted with E2 in vitro s compred with CDc splenocytes exposed to E2 in vivo. Specificlly, we oserved tht E2 promotes the differentition nd ctivity of cdcs from BMderived precursors nd ugments the differentition of CDc splenocytes into n lterntive DC phenotype tht morphologiclly resemle IKDCs, express CD49 nd NK., nd synthesize high mounts of IFN-. These results suggest tht E2 plys significnt role in enhncing innte immune ctivtion nd my provide insight into the mechnism underlying sex-sed differences in disese outcomes. Mterils nd Methods Animls Adult ( 6 dys of ge) femle (n 4; 5 /group/repliction/experiment) C57BL/6 mice were purchsed from the Ntionl Cncer Institute (Bethesd, MD) nd Esr / femles on C57BL/6 ckground (n 5) were purchsed from Tconic Frms. All nimls were housed five per cge in microisoltor room nd mintined on constnt light:drk 6:8 cycle. Food nd sterile tp wter were ville d li. The Johns Hopkins Animl Cre nd Use Committee (protocol # MO4H532) pproved ll procedures descried. Ovriectomy nd hormone replcement Animls were ssigned to remin intct or e ilterlly ovriectomized (ovx). Mice were ilterlly ovx under ketmine (8 mg/kg ody mss) xylzine (8 mg/kg ody mss) nesthesi (Phoenix Phrmceuticl) nd given 2 wk to recover from surgery. Intct femles received shm surgeries (shm). After recovery, femles ssigned to hve E2 replced, were ech s.c. implnted with mm length Silstic cpsule (i.d..2 mm, o.d. 2.6 mm) filled with either 2.5 mm or 5 mm (5 mm of E2 ws used in ll experiments, except where noted; ovx E2) of E2 (Sigm-Aldrich) nd seled with Silstic dhesive to form controlled-relese cpsule s descried previously (32). The remining ovx femles s well s shm femles were ech implnted with n empty Silstic cpsule of equl length. The 5-mm dose of E2 ws sed on previous report tht this mount is sufficient to mintin physiologicl E2 concentrtions (i.e., 2 pg/ ml) in femle mice for 4 dys (33). Estrdiol-contining nd control Silstic cpsules were incuted in sterile sline (37 C) for 24 h efore s.c. implnttion in the midscpul region. All nimls were processed 2 wk fter implnting cpsules. Serum E2 concentrtions were ssyed using stndrd ether extrction nd rodent E2 EIA kit, optimized in our lortory (Cymn Chemicls). Uterine horns were removed nd weighed s n dditionl iossy for E2 concentrtions. Genertion of DCs from BM cells BM cells were isolted from the femurs nd tiie of dult femle C57BL/6 mice nd cultured in Iscove s modified Dulecco s medium (IMDM) supplemented with 2% culture superntnt from GM-CSF-producing J558 cells (4). Becuse phenol red is wekly estrogenic (34), we conducted preliminry experiments to compre the phenotype nd ctivity of BMDCs tht were incuted in stndrd culture medi tht contined phenol red IMDM (Invitrogen Life Technology) plus % filtered FBS (Sigm- Aldrich) with cells incuted in estrogen-deficient medi tht contined phenol red-free IMDM (Invitrogen Life Technology) supplemented with % chrcol-dextrn-treted FBS (HyClone). As reported previously (4), stndrd culture medi hd significnt effect on BMDCs (dt not shown); thus, ll in vitro experiments were conducted using estrogen-deficient medi only. Totl BM cells were suspended t 6 cells per ml in estrogen-deficient medium in 2-well pltes. Estrogen-deficient medium contined phenol red-free IMDM, % chrcol-dextrn-treted FCS, L- glutmine, penicillin/streptomycin, gentmicin, nd 2-ME (Invitrogen Life Technologies nd Sigm-Aldrich). On dys 3 nd 6, hlf of the culture medium ws removed nd replced with fresh estrogen-deficient medium contining GM-CSF. Estrdiol (Sterloids) nd/or ICI 82,78 (Tocris) were dded t the eginning of the culture nd were replenished with the medium on dys 3 nd 6. DCs were hrvested on dy 9. Cell isoltion nd flow cytometry Spleens were dissected nd splenocytes were isolted y mincing nd digesting whole tissue in 2 mg/ml collgense D (Roche). Tissues were homogenized, cells were filtered nd wshed severl times in PBS supplemented with 2 mm EDTA nd 2% FCS, nd mononucler cells were isolted y resuspending cells in ACK lysis uffer (Invitrogen Life Technologies). Nonspecific inding ws locked y stining with FcR. Cell smples were stined with CDc FITC, incuted with nti-fitc microeds, nd processed through LS columns using the qudromacs mgnet (Miltenyi Biotec). Retined cells were collected nd vile cells were counted using hemcytometer nd trypn lue exclusion. Cells were then stined for pproprite mouse DC, NK, nd IKDC mrkers. Cells were stined with the following mas: nti-mouse CD49-PE (clone DX5), NK.-APC (clone PK36), CD-PE (clone M/ 7), H2D -PE (clone KH95), CD8 -PE (Ly-2; clone ), CD45R-APC (B22; clone RA3 6B2), Ly-6G-PE (Gr; clone RB6 8C5), CD4-PE (clone IC), NKG2D-PE (clone C7), nd CD22-PE (clone 5H4) (BD Biosciences; ebiosciences). Cell ctivtion nd cytokine production Cells were stimulted with 5 ng/ml ril-2 (ebiosciences), 5 ng/ml ril-8 (MBL), g/ml LPS (Sigm-Aldrich), g/ml poly I:C (Invivogen), g/ml CpG (Integrted DNA Technologies), or g/ml control oligonucleotide (Integrted DNA Technologies) for 24 h. Cytokine concentrtions were ssyed y ELISA using the mnufcturer s protocols for IFN-, IL-2p4, IL-2p7 (BD Phrmingen), nd IFN- (PBL Biomedicl Lortories). NK cell lysis Vile CDc cells were djusted to 6 cells/ml nd incuted with 5 Cr-leled YAC- trget cells (Americn Type Culture Collection) for 4 h t 37 C t E:T rtios rnging from : to 2.5:. After the 4 h incution, 5 Cr relesed from trget cells ws counted using counter nd lysis ws clculted s: ((mesured 5 Cr relese spontneous 5 Cr relese)/(mximum 5 Cr relese spontneous 5 Cr relese)). Mximum relese ws determined sed on cid-lysed trget cells nd spontneous relese ws determined y incuting trget cells in the sence of effector cells. The verge percent cytotoxicity for ech set of duplictes ws used in sttisticl nlyses. Microscopy CDc splenocytes were isolted s descried ove nd sorted into CD49 NK. high nd CD49 NK. low popultions on FACS Ari (BD Biosciences). For microscopy, sorted cells were fixed with 2% glutrldehyde for2ht24 C followed y postfixtion with 2% osmonium tetroxide for2ht24 C. The cells were emedded in Epon 82, sectioned t 2 m, stined with toluidin lue, nd exmined y light microscopy using Nikon Eclipse E8 light microscope (Nikon). Imges were cquired t 6 using SPOT RT CCD imger nd softwre (Dignostic Instruments). Sttisticl nlyses The effects of E2 on ll dependent mesures were nlyzed using one- or two-wy ANOVAs with tretment group nd/or TLR lignd s the independent vrile(s). Significnt interctions were further nlyzed using the Tukey method for pirwise multiple comprisons. Comprisons etween Esr / nd wild-type (WT) femles were conducted using Student s t tests. If the dt sets violted the ssumptions of norml distriution, then nonprmetric sttistics were used. Men differences were considered sttisticlly significnt if p.5. Results 7 -estrdiol enhnces the differentition of nive BM-derived DCs In vitro exposure to physiologicl concentrtions of E2 fcilittes differentition of BM precursor cells into functionl CDc DCs with incresed levels of MHC clss II (MHCII), CD8, nd CD86 Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
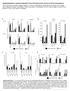
4 The Journl of Immunology 425 A MHCII E2(nmol)... B CD E2(nmol) ICI(nmol) on their surfce (4). Mny cells, however, express CDc, including cdcs, pdcs, IKDCs, nd NK cells (35, 36). We confirmed nd expnded previous findings y generting CDc cells from BM precursors, incuting cells with vrying concentrtions of E2 nd/or the ER ntgonist, ICI 82,78, nd ssessing cells for surfce mrkers chrcteristic of cdcs, pdcs, IKDCs, nd NK cells. Exogenous dministrtion of. nm of E2 (i.e., concentrtions within the rnge circulting in dult femle mice (37)) fcilitted differentition of BM precursor cells into functionl CDc DCs nd incresed the expression of MHCII (Fig. A), CD, CD4, nd CD86, ut not NK. or CD49 (dt not shown). The effect of E2 ws medited y the estrogen receptor ecuse locking ER nd ER with nm of ICI 82,78 significntly inhiited DC differentition ( p.5; Fig. B nd dt not shown). Neither E2 nor ICI 82,78 lone or in comintion ffected BMDC viility s tested y 7-AAD stining (dt not shown). ICI 82,78 lone lso did not significntly ffect differentition of BMDCs ( p.5; Fig. B nd dt not shown). These dt illustrte tht the in vitro effects of E2 on BM-derived CDc cells re limited to cdcs nd re medited y the ER. 7 -estrdiol is required for ctivtion of BMDCs y TLR lignds To determine the effect of E2 on the ility of DCs to initite n innte immune response, BM-derived cells differentited in the presence of either no E2 or nm of E2 (i.e., the medin dose from Experiment ) nd were exposed to the TLR lignds LPS, poly I:C, CpG, medi lone, or control ODN. Cells were ssessed for surfce mrkers chrcteristic of mture cdcs nd superntnts were collected to mesure cytokine concentrtions. E2 enhnced the expression of MHCII, CD4, nd CD86 on CDc BMDCs s compred with cells not treted with E2, regrdless of the TLR gonist used ( p.5; Figs. 2, A nd B). Strikingly, BM-derived DCs differentited in the sence of E2 showed no ctivtion in response to stimultion with ny of the TLR lignds. Among E2- treted BMDCs, exposure to CpG nd LPS, ut not poly I:C or the control ODN, further enhnced the expression of MHCII, CD4, nd CD86 s compred with exposure to medi lone ( p.5, Fig. 2B). Tretment of BMDCs with E2 incresed the production of IL-2p4 in response to CpG nd LPS, ut not poly I:C or the control ODN ( p.5; Fig. 2C). Exposure to E2 lso fcilitted... CD86+.. FIGURE. 7 -estrdiol (E2) fcilittes differentition of DCs from one mrrow (BM). Bone mrrow cells were cultured in estrogen-deficient medium with GM-CSF for 8 dys in the sence or presence of the indicted concentrtions of E2. Nondherent cells were hrvested nd ssessed for surfce mrkers chrcteristic of mture cdcs y FACS. Plots represent the expression of I-A on CDc cells. Vlues represent the percentge of MHCII (top) nd MHC II high (ottom) of the totl CDc cells (A). Bone mrrow cells were cultured in estrogen-deficient medium with GM-CSF, E2 ( nm), nd the indicted concentrtions of the ER ntgonist, ICI 82,78. On dy 8, cells were stined for FACS nlysis. Plots represent CD4 v. CD86 expression on CDc cells. Vlues represent the percentge of CD4 CD86 of the totl CDc cells (B). Results re representtive of three independent experiments. production of IL-2p7 y BMDCs in response to LPS (E2: 3..4 ng/ml vs medi:.54. ng/ml; p.5), ut not CpG, poly I:C, or the control ODN (dt not shown). E2 tretment tended to increse the synthesis of IFN- in response to CpG, ut this difference did not rech sttisticl significnce ( p.5; Fig. 2C). Previous studies illustrte tht BMDCs cn produce IFN- following stimultion with IL-2 nd IL-8 (38, 39). In ddition to eing responsive to clssic TLR lignds, we sought to determine whether differentited DCs from BM precursors were responsive to IL-2 nd IL-8 nd could produce IFN- in the presence of E2. BMDCs were differentited s descried ove, exposed to either E2 or medi lone, nd ctivted with ril-2 nd ril-8. BMDCs stimulted with IL-2 nd IL-8 exhiited no chnges in the expression of MHCII, CD4, nd CD86 or the synthesis of IFN-, regrdless of E2 exposure ( p.5; dt not shown). 7 -estrdiol increses numers of CDc CD49 NK. low cells in the spleen The dt presented in this study nd y others (4) illustrte tht E2 impcts the in vitro differentition of BM-derived precursors into functionl cdcs. The effect of E2 on the phenotype nd function of DCs in peripherl lymphoid orgns, however, hs not een ddressed. To test whether E2 lters the numer, surfce phenotype, or ctivity of splenic DCs, we conducted series of in vivo studies using intct/shm femles, ovx femles, nd ovx femles with E2 replcement (ovx E2). Serum levels of E2 were significntly different mong the three groups of femles, in which concentrtions were elevted in ovx E2 femles nd reduced in ovx femles reltive to shm femle mice ( p.5; Fig. 3A). Exogenous replcement of E2 resulted in circulting estrdiol concentrtions tht were within the physiologicl rnge ( 2 pg/ml) for femle mice in estrus (37). Uterine horn mss ws mesured s iossy nd ws consistent with E2 concentrtions, in which ovx E2 nd shm femles hd hevier uterine horns thn ovx femle mice ( p.5; Fig. 3B). CDc splenocytes from C57BL/6 mice re heterogeneous popultion of cells comprised of multiple susets of DCs, including cdcs, pdc, nd IKDCs, ll of which re clssified sed on their surfce mrker profiles (3, 36, 4). To exmine the effects of E2 on the solute numers nd percentges of DCs in the spleen, CDc splenocytes were isolted nd stined for MHCII, CD, Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
5 426 ESTROGEN AND INNATE IMMUNITY FIGURE 2. E2 enhnces the ctivtion of CDc BMDCs y TLR lignds. BMDCs were cultured in estrogen-deficient medium for 8 dys nd stimulted with TLR gonists or control ODN for the lst 24 h of culture. Nondherent cells were hrvested nd stined for FACS nlysis. Representtive plots of CDc v. MHC II nd CD4 v. CD86 (gted on CDc cells) re shown (A). Vlues represent the percentge of MHCII high nd CD4 CD86 cells. Summry of the proportion of CDc BMDCs ( SEM) tht expressed MHCII high, CD4, nd CD86 following culture with (E2 ) or without (E2 ) nm E2 nd ctivtion with the indicted TLR lignds (B). Men production of IFN- nd IL-2p4 ( SEM) y BMDCs exposed to either nm of E2 or medi lone nd ctivted with the designted TLR lignds (C). CDc BMDCs were generted y incuting cells with GM-CSF nd either nm of E2 (E2 ) or medi lone (E2 ). During the lst 24 h of the 8-dy incution, cells were ctivted with LPS, poly I:C, CpG, control ODN, or medi lone. On dy 9, cells were ssessed for surfce mrkers chrcteristic of mture cdcs y FACS nd superntnts were collected to mesure cytokine concentrtions y ELISA. Results re representtive of three independent experiments. An sterisk ( ) indictes tht E2 enhnces responses reltive to medi lone, dgger ( ) indictes tht mong E2-treted BMDCs, TLR lignds enhnced responses reltive to medi lone, p.5. Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28 B22, CD8, CD49, nd the costimultory molecules, CD4 nd CD86. In contrst to the effects on BMDCs, E2 did not significntly ffect the solute numer of CDc cells isolted from the spleen or the percentge of CDc cells determined to e cdcs sed on the high expression of CDc nd MHCII ( p.5, dt not shown). Neither incresing nor decresing concentrtions of E2 in vivo ltered the percentge of CDc CD cdcs, the percentge of CD8 cdcs, the percentge of B22 pdcs, or the expression of the costimultory molecules CD4 nd CD86 on ny of the DC susets ( p.5; Fig. 3C nd dt not shown). There is overlpping expression of surfce mrkers mong DCs, NK cells, nd IKDCs tht cn mke the precise chrcteriztion of these cell popultions complicted. Both IKDCs nd NK cells express CDc, CD49, nd NK.; thus, we sought to exmine whether these cells were responsive to E2. Removl of circulting E2 vi ovriectomy decresed, wheres sustined exposure to E2 drmticlly incresed the percentge of CDc CD49 cells in the spleen s compred with the shm controls ( p.5; Fig. 3D). To estlish whether E2 lters the numer of IKDCs in the spleen, we enriched for CDc cells nd stined for oth CD49 (i.e., integrin suunit 2) nd NK. (i.e., NK receptor PC). By gting on live CDc cells, we oserved tht sustined exposure to E2 reproducily incresed the numer of CD49 NK. low cells in the spleen s compred with shm nd ovx femle mice ( p.5; Fig. 4, A nd C). In contrst, the sence of E2 in ovx femles incresed the proportion of splenic CD49 NK. high cells s compred with ovx E2 nd shm femle mice ( p.5; Fig. 4, B nd C). To further illustrte the dependence of these chnges on iologiclly relevnt concentrtions of E2, we implnted ovx femles with lower dose of E2 (i.e., 2.5 mm of E2 in mm cpsules). Similr to ovx femles implnted with higher dose (i.e., 5 mm of
6 The Journl of Immunology 427 FIGURE 3. E2 differentilly ffects supopultions of CDc cells in the spleen. Serum, uterine horns, nd spleens were collected from intct (shm), ovriectomized (ovx), nd ovx femles tht hd E2 replced exogenously (ovx E2). Circulting E2 concentrtions were mesured y ELISA ( SEM) (A) nd uterine horns were weighed ( SEM) (B). Whole splenocytes were isolted, enriched for CDc cells, nd stined for CD (C) or CD49 (D). FACS nlysis ws performed y gting on CDc cells. Brs with different letters indicte significnt differences cross groups (n /group), p.5. E2 in mm cpsules), ovx femles exposed to low dose of E2 lso hd elevted numers of splenic CD49 NK. low cells nd lower numers of CD49 NK. high cells s compred with ovx femle mice ( p.5 in ech cse; Fig. 4). A B % CD49+/ NK. low % CD49+/ NK. hi Ovx Shm Ovx E2 Ovx Shm Ovx E2 Ovx+ 5 E2 Ovx+ 5 E2 Estrdiol conc (pg/ml) % CDc+/ CD+ Cells A C C NK Ovx Shm Ovx+E2 Ovx Shm Ovx+E2 FL4-H: NK. APC c Uterine Horn Mss (g) B % CDc+/ CD49+ Cells D Ovx Shm Ovx+E2 Ovx Shm Ovx+E2 7 -estrdiol reduces numers of splenic IKDCs IFN-producing killer DCs re cells with surfce expression chrcteristics of oth DCs nd NK cells (36). To further chrcterize the cell popultions influenced y E2 s cdcs, IKDCs, or cells tht shre oth cdc nd IKDC mrkers, we stined nd evluted CDc splenocytes from shm, ovx, nd ovx E2 mice for surfce levels of MHCII, B22, CD8, CD, CDc, CD4, CD86, Gr-, CD49, NK., CD22, nd NKG2D (36). The CD49 NK. high cells, which were reduced in numer y sustined E2 exposure, expressed pproprite levels of ll the mrkers reportedly expressed on IKDCs, including CDc, NK., CD49, CD22, MHCII, nd B22 (Fig. 5A) (36). The CD49 NK. low popultion of CDc cells, which ws incresed in numer y exposure to E2, did not express the NK cell mrkers CD22 or NKG2D, ut did express MHCII, CD, B22, CD8, Gr-, nd the costimultory molecules CD4 nd CD86 (Fig. 5A), ll of which re mrkers used to ctegorize DC susets (3, 4). The CD49 NK. high cells hd the morphologicl ppernce of IKDCs, including lrge distinct nuclei nd very smll cytoplsm (Fig. 5B) (36). Conversely, the CD49 NK. low popultion ws comprised of two predominnt phenotypes: ) cells with distinct nuclei nd lrge flowing cytoplsm, chrcteristic of cdcs (4); nd 2) cells with distinct nuclei nd very smll cytoplsm, typicl 5.6% 2% 2.8% 26% 3.5% 42% Ovx Shm Ovx + 5 E2 FIGURE 4. E2 increses numers of CDc CD49 NK. low, ut reduces numers of CDc CD49 NK. high cells ( SEM) in the spleen. Whole splenocytes were isolted from intct (shm), ovriectomized (ovx), nd ovx femles tht hd E2 replced t low (2.5 mm) nd high (5 mm) doses, enriched for CDc, nd stined for oth CD49 (i.e., integrin suunit 2) nd NK. (i.e., NK receptor PC). Using multiprmeter FACS nlyses, we gted on live CDc cells nd represent dt s the proportion of CDc cells tht expressed CD49 nd NK. low/high (A nd B). Representtive dot plots re included (C). Brs with different letters indicte significnt differences cross groups; rs tht shre letters re not significntly different from ech other (n /group), p.5. c c Downloded from y guest on Septemer, CD49
7 428 ESTROGEN AND INNATE IMMUNITY A IFNγ (ng/ml) Ovx Shm Ovx + E2 5 FIGURE 5. CDc CD49 NK. high cells hve phenotypic nd morphologicl chrcteristics of IKDCs. Whole splenocytes were isolted from the spleens of shm, ovx, nd ovx E2 femle C57BL/6 mice, enriched for CDc, nd stined for the following surfce mrkers: CD49, CD22, NKG2D, Gr-, MHCII, CD, B22, CD8, nd CD86 (A). Morphologicl nlysis using thick section microscopy illustrtes the ppernce of NK. high (i.e., IKDCs) (B) nd NK. low (i.e., cdcs nd IKDCs) (C) cells. of pdcs nd IKDCs (Fig. 5C) (36). These dt suggested tht estrogen-responsive CD49 NK. low cells re DCs tht shre mny of the clssic fetures of DC susets, including IKDCs. 7 -estrdiol increses IFN- production y CDc splenocytes Although IKDCs nd NK cells comprise only smll percentge of the CDc cells in the spleen, they re oth potent producers of IFN- (35, 36). Therefore, we hypothesized tht the effects of E2 on CD49 NK. popultions my result in functionl chnges in IFN- production y CDc cells. CDc splenocytes were isolted from ovx, shm, nd ovx E2 femles nd stimulted with either ril-2 nd ril-8 or medi lone (42). When stimulted with ril-2 nd ril-8, CDc splenocytes produced elevted concentrtions of IFN- in the presence of high E2, despite the concomitnt decrese in the percentge of CD49 NK. high cells ( p.5; Fig. 6A). These dt suggest tht the E2-induced enhncement of CD49 NK. low cells contriute to incresed IFN- production. B C IFNα (pg/ml) IL-2p4 (pg/ml) Medi Medi ril-2 + ril-8 LPS Medi poly I:C CpG FIGURE 6. Production of IFN- is enhnced y exposure to E2 in vivo. Whole splenocytes were isolted, enriched for CDc cells, nd stimulted with the indicted TLR lignds or ril-2 nd ril-8 for 24 h. Superntnts were used to mesure the synthesis of IFN- (A), IL-2p4 (B), nd IFN- (C) y ELISA. Brs (men concentrtions SEM) with different letters indicte significnt differences cross groups; rs tht shre letters re not significntly different from ech other (n /group), p.5. Becuse CDc DCs cn produce IL-2 nd IFN-, wessessed the effects of E2 on the production of these cytokines. Splenocytes were isolted from ovx, shm, nd ovx E2 femles, enriched for CDc, nd stimulted with LPS, poly I:C, CpG, or medi lone. Although CDc cells produced elevted levels of IL-2p4 following stimultion with LPS ( p.5), mnipultion of E2 did not ffect IL-2p4 production ( p.5; Fig. 6B) nd IL2p7 concentrtions were elow the limits of detection in ll tretment groups. To ensure tht the lck of effect of E2 on IL-2 production ws not the result of functionl or phenotypic chnges induced during the positive selection procedure, CDc splenocytes were isolted using negtive selection protocol. Similrly, mnipultion of E2 in vivo did not ffect production of IL-2p4 in negtively selected CDc cells ( p.5; dt not shown). Although poly I:C induced higher production of IFN- y CDc cells thn did CpG, there ws no enhncing or inhiitory effect of E2 on IFN- secretion ( p.5; Fig. 6C). These dt Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
8 The Journl of Immunology A B C CD49+/ NK. hi CD49+/ NK. low Uterine Horn Mss (g) Esr-/- Esr-/- Esr-/- indicte tht E2 does not lter the ctivity of CDc cell popultions tht produce either IL-2 or IFN- (3, 4). CDc cells do not exhiit cytolytic ctivity WT WT WT FIGURE 7. Deletion of ER (Esr / ) does not significntly ffect popultions of NK. low or NK. high cells in the spleen. Uterine horns ( SEM) from Esr / nd WT femle mice were weighed (A). Whole splenocytes were isolted from the spleens of Esr / nd WT femle mice, enriched for CDc, nd the percentge of CDc CD49 NK. low (B) or CDc CD49 NK. high (C) cells were determined ( SEM). Brs with different letters indicte significnt differences cross groups (n 5/group), p.5. To further chrcterize the functionl effects of E2 on CDc splenocytes nd to confirm tht these CDc cells were not NK cells, lytic ctivity ws ssessed. In the present study, CDc splenocytes did not engge in significnt killing of YAC- cells, regrdless of hormone tretment (dt not shown). The effects of E2 on mture CDc cells re prtilly medited y ER There re two sutypes of the ER, ER nd ER ; ER, however, is the receptor sutype tht is required for most of the known estrogenic effects (43). Both receptor sutypes re present in the thymus nd spleen s well s in circulting lymphocytes, DCs, NK cells, nd mcrophges (7 ). ER-medited trnscription cn e exmined using mice deficient in either ER (Esr / )orer (Esr2 / ) (43). To test whether the effects of E2 on CDc 429 splenocytes were medited y signl trnsduction ctivity through ER, splenocytes were isolted from Esr / nd WT C57BL/6 femle mice, enriched for CDc, nd stined for CD49 nd NK. mrkers. Esr / femles hd significntly smller uterine horns thn their WT femle counterprts, illustrting tht the iologicl effect of circulting E2 ws diminished in these femles ( p.5; Fig. 7A). Despite the effectiveness of the ER deficit on reproductive development, the sence of ER did not significntly lter popultions of CDc CD49 NK. low or CDc CD49 NK. high cells s compred with WT femles ( p.5; Fig. 7, B nd C). There ws, however, tendency for reduced numers of CDc CD49 NK. low cells in Esr / s compred with WT femles (Fig. 7). Synthesis of IFN- y CDc cells lso did not differ etween Esr / nd WT femle mice ( p.5; dt not shown). Discussion Sex-sed differences in the prevlence nd intensity of utoimmune nd infectious diseses re well documented nd likely involve the effects of sex steroids, including testosterone nd E2, on immune function (). With regrd to innte immunity, E2 hs previously een shown to influence the mturtion of BMDCs, with preferentil development of BMDCs into cdcs with chrcteristics of Lngerhns cells (4, 3), nd to fcilitte production of IFN- y NK cells (). The results of the studies reported in this study confirm tht E2 drives preferentil development of CD CDc DCs from BM precursors nd increses surfce expression of MHCII nd the costimultory molecules CD4 nd CD86. The presence of E2 did not ffect the expression of B22, CD49, or NK. on BMDCs. BMDCs lso were not responsive to IL-2/IL-8 stimultion, further illustrting tht the in vitro effects of E2 re limited to cdc popultions. Although differentition of BMDCs in the presence of E2 enhnces Ag presenttion to T cells (4), the full extent to which E2 influences the ility of DCs to medite innte immunity hs not een estlished. In the present study, only BMDCs mtured in the presence of E2 were responsive to LPS, CpG, nd, to lesser extent poly I:C, in which the expression of MHCII, CD4, nd CD86 s well s IL-2 production ws enhnced. BMDCs mtured in the sence of E2 were unresponsive to TLR4 nd TLR9 gonists, suggesting tht the presence of E2 my e required for MyD88-dependent DC ctivtion in response to microil signls. Interestingly, puttive ERE hs een identified in the promoter region of Myd88 (44). To investigte E2-dependent chnges in mture DC popultions in the spleen, we exmined the numer, phenotype, nd ctivity of CDc splenocytes from intct femles, ovx femles, nd ovx femles with E2 replcement. In contrst to the effects on BMDCs, E2 did not ffect the numer of CDc splenocytes isolted or the percentge of those cells expressing clssic cdc mrkers (e.g., CD nd CD8 ), pdc mrkers (e.g., B22), or ctivtion mrkers (e.g., MHCII, CD4, nd CD86) on ny of the exmined DC susets. Sustined elevtion of E2, however, resulted in concomitnt increse in the proportion of CDc CD49 NK. low cells nd reduction in the numer of CDc CD49 NK. high cells in the spleen. In vivo exposure to sustined E2 lso incresed production of IFN- y CDc splenocytes. IFN-producing killer DCs were distinguished y the expression of CD49, NK., CD22, MHCII, nd B22. Interestingly, the E2-enhnced popultion of CDc CD49 NK. low cells ws not redily ctegorized s DC or IKDC popultion y surfce mrker chrcteristics. The E2 enhnced NK. low cells expressed n rry of DC mrkers (e.g., CD, B22, CD8, Gr-, MHCII, CD4, nd CD86), ut did not express the definitive NK cell Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
9 43 ESTROGEN AND INNATE IMMUNITY mrker (e.g., CD22) or exhiit cytolytic ctivity, suggesting tht these cells re likely suset of DCs nd not NK cells. Microscopic nlysis of these cells lso reveled tht the E2-enhnced popultion of CDc CD49 NK. low cells hd morphologicl chrcteristics ssocited with cdcs, pdcs, nd IKDCs. Becuse of the overlpping morphologicl chrcteristics defining DC, IKDCs, nd NK cells, we ttempted to chrcterize the E2-responsive CDc cells sed on their effector function. Previous dt revel tht intct femle mice treted with dditionl E2 exogenously hve fewer IKDCs in their BM nd produce less IFN- thn intct femles not treted with E2 (45). In the present study, stimultion of CDc splenocytes with IL-2 nd IL-8 incresed production of IFN- in the presence of sustined E2 in vivo. Recent nlyses revel tht IKDCs nd NK cells re the predominnt CDc cells tht produce IFN- (46, 47). Becuse the E2-enhnced CDc cells do not express CD22 or NKG2D nd do not kill trget cells, enhnced production of IFN- likely reflects the effects of E2 on IKDC popultions. There ws no effect of E2 on IL-2 production in response to LPS or IFN- in response to either poly I:C or CpG, suggesting tht E2 does not ffect the clssic functions of either cdcs or pdcs in the spleen. The developmentl pthwys for DCs nd IKDCs re linked to common popultion of progenitor cells (45). Consequently, E2 is criticl signl in the mturtion process of lymphoid progenitor cells nd ultimtely determines which end stge cells develop. IFN-producing killer DC development from BM cells is inhiited y E2 (45). In peripherl lymphoid tissues, such s the spleen, CDc CD49 NK. low cells my represent cells tht re cple of performing DC nd IKDC functions. These cells my e expnded to compenste for the inility of IKDCs to mture in the presence of high E2. Estrogens hve their iologicl effects y inding to either ER or ER, the hormone-receptor complex then trnsloctes to the nucleus of the cell where the ER cn ind to discrete EREs in the regultory regions of trget genes (48). The lignd-receptor complex lso cn regulte the trnscriptionl ctivity of genes tht do not contin clssicl ERE in the promoter region y recruiting coregultory proteins tht cn ctivte or repress trnscription (48). Finlly, estrogens cn lter the expression of trget genes through regultion of other trnscriptionl fctors (e.g., NF- B) (49). To estlish whether E2 hs its iologicl effects through the ERs, the steroidl compound IC 82,78 (i.e., fulvestrnt) ws selected for in vitro studies ecuse it is n ER ntgonist in ll cell types (5). ICI 82,78 not only functionlly locks the ER, ut impirs dimeriztion nd nucler locliztion of the ER (5). Blocking ER nd ER with ICI 82,78 efore dministrtion of E2 in vitro inhiited differentition of DCs from BM precursor cells s illustrted y the reduced expression of CD, MHCII, CD4, nd CD86 s compred with cells treted with E2 lone. The effects of E2 on DC differentition were hypothesized to e medited y ER ecuse most of the known iologicl effects of E2 re medited y this ER sutype (48). In contrst to our prediction, deletion of ER in vivo did not significntly lter popultions of CDc splenocytes in Esr / femles s compred with WT femle mice. Although ER my medite mny of the effects of E2 on DCs nd IKDCs, if E2 concentrtions re sufficiently high, then ER my compenste nd medite the effects of E2 on DC ctivity, s noted previously (4). In the present study, Esr / femles were not ovriectomized efore experimenttion. Therefore, lthough signling through ER ws compromised, concentrtions of E2 s well s signling through ER were intct in Esr / femles. Future studies will delinete the precise roles of ER nd ER s well s the effects of ER heterodimers in mediting the effects of E2 on the functioning of DCs nd IKDCs. There currently is considerle interest in defining supopultions of DCs, NK cells, nd IKDCs sed on surfce mrker profiles nd cytokine ctivity (47, 5). Missing from current studies is n exmintion of the role tht estrogens my ply in the differentition nd ctivtion of these closely relted supopultions of cells. In the present study, notle differences were oserved etween the in vitro effects of E2 on DC differentition from BM precursor cells nd the in vivo effects of E2 on the ctivity of mture CDc splenocytes. These dt demonstrte tht the precise effects of E2 on the phenotype nd function of DCs depends on when during development these cells re exposed to E2. Exposure of BM precursors to E2 fcilittes development of these cells into clssic DCs tht synthesize IL-2. Conversely, exposure of mture splenic DCs to sustined levels of E2 results in the expnsion of n lterntive phenotype of CDc cells tht express CD49 nd NK. nd enhnce IFN- production. Notle differences were oserved in vivo etween ovx femles treted with sustined concentrtions of E2 nd intct femles with cyclicl concentrtions of E2, in which intct femles hd proportions of NK. low cells tht were similr to ovx femles. Whether there is threshold concentrtion of E2 required to lter CDc popultions requires investigtion. Heightened production of IFN- y CDc cells in response to E2 stimultion my fcilitte innte nd dptive immune responses. Previous studies illustrte tht CDc NK. cells re significnt source of innte IFN- nd innte production of IFN- y these cells is necessry for protection ginst Listeri monocytogenes (52). The oservtion tht E2 enhnces production of IFN- y CDc cells provides key mechnism regulting the downstrem differences in dptive immunity, development of utoimmune disese, nd susceptiility to microil pthogens etween the sexes. Acknowledgments We thnk Judy Esterrook, Jessic Engler, nd Michele Hnnh for technicl ssistnce, the Becton Dickinson Immune Function Lortory for ccess to FACS equipment nd softwre, nd Jnet Folmer for thick section preprtions. Disclosures The uthors hve no finncil conflict of interest. References. Klein, S. L. 28. Sex differences in infectious nd utoimmune diseses. In Sex Differences in the Brin: From Genes to Behvior. J. B. Becker, K. Berkley, N. Gery, E. Hmpson, J. Hermn, nd E. Young, eds. Oxford University Press, New York pp Jcoson, D. L., S. J. Gnge, N. R. Rose, nd N. M. Grhm Epidemiology nd estimted popultion urden of selected utoimmune diseses in the United Sttes. Clin. Immunol. Immunopthol. 84: Whitcre, C. C. 2. Sex differences in utoimmune disese. Nt. Immunol. 2: Klein, S. L. 2. The effects of hormones on sex differences in infection: from genes to ehvior. Neurosci. Bioehv. Rev. 24: Schuurs, A. H., nd H. A. Verheul. 99. Effects of gender nd sex steroids on the immune response. J. Steroid Biochem. 35: Roerts, C. W., W. Wlker, nd J. Alexnder. 2. Sex-ssocited hormones nd immunity to protozon prsites. Clin. Microiol. Rev. 4: Erlndsson, M. C., C. Ohlsson, J. A. Gustfsson, nd H. Crlsten. 2. Role of oestrogen receptors nd in immune orgn development nd in oestrogenmedited effects on thymus. Immunology 3: Cutolo, M., S. Accrdo, B. Villggio, A. Brone, A. Sulli, D. A. Coviello, C. Crio, L. Felli, D. Miceli, R. Frruggio, et l Androgen nd estrogen receptors re present in primry cultures of humn synovil mcrophges. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Met. 8: Dnel, L., G. Souweine, J. C. Monier, nd S. Sez Specific estrogen inding sites in humn lymphoid cells nd thymic cells. J. Steroid Biochem. 8: Currn, E. M., L. J. Berghus, N. J. Vernetti, A. J. Sporit, D. B. Luhn, nd D. M. Estes. 2. Nturl killer cells express estrogen receptor- nd estrogen receptor- nd cn respond to estrogen vi non-estrogen receptor- -medited pthwy. Cell. Immunol. 24: 2 2. Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
10 The Journl of Immunology 43. Nky, M., H. Tchin, nd K. Ymd. 26. Effect of estrogens on the interferon- producing cell popultion of mouse splenocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 7: Sorchi, K., S. Kumgi, M. Sugit, J. Yodoi, nd H. Imur Enhncing effect of 7 -estrdiol on humn NK cell ctivity. Immunol. Lett. 36: Fox, H. S., B. L. Bond, nd T. G. Prslow. 99. Estrogen regultes the IFN- promoter. J. Immunol. 46: Phrkov-Vtchkov, V., R. Mldondo, nd S. Kovts. 24. Estrogen preferentilly promotes the differentition of CDc CD(intermedite) dendritic cells from one mrrow precursors. J. Immunol. 72: Miller, L., nd J. S. Hunt Sex steroid hormones nd mcrophge function. Life Sci. 59: Krpuzoglu, E., J. B. Fenux, R. A. Phillips, A. J. Lengi, F. Elvinger, nd S. Ansr Ahmed. 26. Estrogen up-regultes inducile nitric oxide synthse, nitric oxide, nd cyclooxygense-2 in splenocytes ctivted with T cell stimulnts: role of interferon-. Endocrinology 47: Polnczyk, M. J., B. D. Crson, S. Surmnin, M. Afentoulis, A. A. Vndenrk, S. F. Ziegler, nd H. Offner. 24. Cutting edge: estrogen drives expnsion of the CD4 CD25 regultory T cell comprtment. J. Immunol. 73: Messinghm, K. A., S. A. Heinrich, nd E. J. Kovcs. 2. Estrogen restores cellulr immunity in injured mle mice vi suppression of interleukin-6 production. J. Leukocyte Biol. 7: Suzuki, S., C. M. Brown, C. D. Del Cruz, E. Yng, D. A. Bridwell, nd P. M. Wise. 27. Timing of estrogen therpy fter ovriectomy dicttes the efficcy of its neuroprotective nd ntiinflmmtory ctions. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 4: Nugler, W. E., T. Skuri, S. Kim, S. Med, K. Kim, A. M. Elshrkwy, nd M. Krin. 27. Gender disprity in liver cncer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science 37: Begley, K. W., nd C. M. Gockel. 23. Regultion of innte nd dptive immunity y the femle sex hormones oestrdiol nd progesterone. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microiol. 38: Verthelyi, D. 26. Femle s heightened immune sttus: estrogen, T cells, nd inducile nitric oxide synthse in the lnce. Endocrinology 47: Liv, S. M., nd R. R. Voskuhl. 2. Testosterone cts directly on CD4 T lymphocytes to increse IL- production. J. Immunol. 67: Grimldi, C. M., L. Hill, X. Xu, E. Peev, nd B. Dimond. 25. Hormonl modultion of B cell development nd repertoire selection. Mol. Immunol. 42: Beo, B. F., Jr., J. C. Schuster, A. A. Vndenrk, nd H. Offner Androgens lter the cytokine profile nd reduce encephlitogenicity of myelin-rective T cells. J. Immunol. 62: Krzych, U., H. R. Strusser, J. P. Bressler, nd A. L. Goldstein. 98. Effects of sex hormones on some T nd B cell functions s evidenced y differentil immune expression etween mle nd femle mice nd cyclic pttern of immune responsiveness during the estrous cycle. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 7: Nlndin, G., nd S. Kovts. 25. Understnding sex ises in immunity: effects of estrogen on the differentition nd function of ntigen-presenting cells. Immunol. Res. 3: Hoee, K., E. Jnssen, nd B. Beutler. 24. The interfce etween innte nd dptive immunity. Nt. Immunol. 5: Zitvogel, L., M. Terme, C. Borg, nd G. Trinchieri. 26. Dendritic cell-nk cell cross-tlk: regultion nd physiopthology. Curr. Top. Microiol. Immunol. 298: Spits, H., nd L. L. Lnier. 27. Nturl killer or dendritic: wht s in nme? Immunity 26: Mo, A., V. Phrkov-Vtchkov, J. Hrdy, M. M. Miller, nd S. Kovts. 25. Estrogen selectively promotes the differentition of dendritic cells with chrcteristics of Lngerhns cells. J. Immunol. 75: Klein, S. L., B. H. Bird, nd G. E. Glss. 2. Sex differences in Seoul virus infection re not relted to dult sex steroid concentrtions in Norwy rts. J. Virol. 74: Rissmn, E. F., A. L. Heck, J. E. Leonrd, M. A. Shupnik, nd J. A. Gustfsson. 22. Disruption of estrogen receptor gene impirs sptil lerning in femle mice. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 99: Berthois, Y., J. A. Ktzenellenogen, nd B. S. Ktzenellenogen Phenol red in tissue culture medi is wek estrogen: implictions concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 83: Lour, Y., F. S. Sutterwl, L. Gorelik, nd R. A. Flvell. 25. Trnsforming growth fctor- controls T helper type cell development through regultion of nturl killer cell interferon-. Nt. Immunol. 6: Chn, C. W., E. Crfton, H. N. Fn, J. Flook, K. Yoshimur, M. Skric, D. Brockstedt, T. W. Duensky, M. F. Stins, L. L. Lnier, et l. 26. Interferonproducing killer dendritic cells provide link etween innte nd dptive immunity. Nt. Med. 2: Becker, J. B., A. P. Arnold, K. J. Berkley, J. D. Blustein, L. A. Eckel, E. Hmpson, J. P. Hermn, S. Mrts, W. Sdee, M. Steiner, et l. 25. Strtegies nd methods for reserch on sex differences in rin nd ehvior. Endocrinology 46: Stoer, D., R. Schirmeck, nd J. Reimnn. 2. IL-2/IL-8-dependent IFN- relese y murine dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 67: Hochrein, H., K. Shortmn, D. Vremec, B. Scott, P. Hertzog, nd M. O Keeffe. 2. Differentil production of IL-2, IFN-, nd IFN- y mouse dendritic cell susets. J. Immunol. 66: Bnchereu, J., F. Briere, C. Cux, J. Dvoust, S. Leecque, Y. J. Liu, B. Pulendrn, nd K. Pluck. 2. Immunoiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 8: Dio, J., E. Winter, W. Chen, C. Cntin, nd M. S. Cttrl. 24. Chrcteriztion of distinct conventionl nd plsmcytoid dendritic cell-committed precursors in murine one mrrow. J. Immunol. 73: Cheung, H., N. J. Chen, Z. Co, N. Ono, P. S. Ohshi, nd W. C. Yeh. 25. Accessory protein-like is essentil for IL-8-medited signling. J. Immunol. 74: Couse, J. F., nd K. S. Korch Estrogen receptor null mice: wht hve we lerned nd where will they led us? Endocr. Rev. 2: Hnnh, M. F., V. B. Bjic, nd S. L. Klein. 27. Sex differences in the recognition of nd innte ntivirl responses to Seoul virus in Norwy rts. Brin Behv. Immun. In press. 45. Welner, R. S., R. Pelyo, K. P. Grrett, X. Chen, S. S. Perry, X. H. Sun, B. L. Kee, nd P. W. Kincde. 27. Interferon-producing killer dendritic cells (IKDCs) rise vi unique differentition pthwy from primitive c-kit Hi CD62L lymphoid progenitors. Blood 9: Vremec, D., M. O Keeffe, H. Hochrein, M. Fuchserger, I. Cminschi, M. Lhoud, nd K. Shortmn. 27. Production of interferons y dendritic cells, plsmcytoid cells, nturl killer cells, nd interferon-producing killer dendritic cells. Blood 9: Blsius, A. L., W. Brchet, M. Cell, nd M. Colonn. 27. Development nd function of murine B22 CDc NK. cells identify them s suset of NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 24: McDonnell, D. P., nd J. D. Norris. 22. Connections nd regultion of the humn estrogen receptor. Science 296: McKy, L. I., nd J. A. Cidlowski Moleculr control of immune/inflmmtory responses: interctions etween nucler fctor- B nd steroid receptorsignling pthwys. Endocr. Rev. 2: Howell, A., C. K. Osorne, C. Morris, nd A. E. Wkeling. 2. ICI 82,78 (Fslodex): development of novel, pure ntiestrogen. Cncer 89: Vosshenrich, C. A., S. Lesjen-Pottier, M. Hsn, O. R. Goff, E. Corcuff, O. Mndeloim, nd J. P. Di Snto. 27. CDc lo B22 interferon-producing killer dendritic cells re ctivted nturl killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 24: Plits, G., U. I. Chudhry, T. P. Kinghm, J. R. R, nd R. P. DeMtteo. 27. NK dendritic cells re innte immune responders to Listeri monocytogenes infection. J. Immunol. 78: Downloded from y guest on Septemer, 28
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Supplemental Information. Lymphocytes Negatively Regulate NK Cell Activity. via Qa-1b following Viral Infection
 Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Type II monocytes modulate T cell-mediated central nervous system autoimmunity
 Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
A critical role for interleukin 4 in activating alloreactive CD4 T cells
 A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Agilent G6825AA MassHunter Pathways to PCDL Software Quick Start Guide
 Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
FoxP3 + regulatory CD4 T cells control the generation of functional CD8 memory
 Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report July September 2018
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Comparison of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in paired human primary airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages
 Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Preliminary investigation of antimicrobial effects of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) leathery exocarp extract against some serious phytopathogens
 Preliminry investigtion of ntimicroil effects of pomegrnte (Punic grntum L.) lethery exocrp extrct ginst some serious phytopthogens Elshfie H.S. 1,*, Skr S.H. 2, Mng S.M. 1, Frisullo S. 3, Cmele I. 1 1
Preliminry investigtion of ntimicroil effects of pomegrnte (Punic grntum L.) lethery exocrp extrct ginst some serious phytopthogens Elshfie H.S. 1,*, Skr S.H. 2, Mng S.M. 1, Frisullo S. 3, Cmele I. 1 1
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
Natural killer cells determine the outcome of B cell mediated autoimmunity
 Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Consumer perceptions of meat quality and shelf-life in commercially raised broilers compared to organic free range broilers
 Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEAGRE (Argyrosomus regius) FEEDING BEHAVIOUR.
 THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEGRE (rgyrosomus regius) FEEDING EHVIOUR. Ionnis E. Ppdkis, Nikos Ppndroulkis, lkioni Sfendourki, Veronic Cmporesi 3, Mnolis Vsilkis, Constntinos C. Mylons Institute
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEGRE (rgyrosomus regius) FEEDING EHVIOUR. Ionnis E. Ppdkis, Nikos Ppndroulkis, lkioni Sfendourki, Veronic Cmporesi 3, Mnolis Vsilkis, Constntinos C. Mylons Institute
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
D14 D 10 D 7. Untreated CYTOXAN 5-FU
 Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Polymer-Coated Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles Inhibit IgE Receptor Binding, Cellular Signaling, and Degranulation in a Mast Cell-like Cell Line
 www.mterilsviews.com Polymer-Coted Metl-Oxide Nnoprticles Inhiit IgE Receptor inding, Cellulr Signling, nd Degrnultion in Mst Cell-like Cell Line Vn. Orteg, Jmes D. Ede, Dvid oyle, Jmes L. Stfford, nd
www.mterilsviews.com Polymer-Coted Metl-Oxide Nnoprticles Inhiit IgE Receptor inding, Cellulr Signling, nd Degrnultion in Mst Cell-like Cell Line Vn. Orteg, Jmes D. Ede, Dvid oyle, Jmes L. Stfford, nd
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
DNA released from dying host cells mediates aluminum adjuvant activity
 DNA relesed from dying host cells medites luminum djuvnt ctivity Thoms Mrichl 1, Keiichi Oht 2, Denis Bedoret 1, Clire Mesnil 1, Ctherine Stel 1, Kouji Koiym 2,3, Pierre Lekeux 1, Cevyir Con 2, Shizuo
DNA relesed from dying host cells medites luminum djuvnt ctivity Thoms Mrichl 1, Keiichi Oht 2, Denis Bedoret 1, Clire Mesnil 1, Ctherine Stel 1, Kouji Koiym 2,3, Pierre Lekeux 1, Cevyir Con 2, Shizuo
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
Clec4A4 is a regulatory receptor for dendritic cells that impairs inflammation and T-cell immunity
 Received 1 Oct 215 Accepted 8 Mr 216 Pulished 12 Apr 216 DOI: 1.138/ncomms11273 OPEN Clec4A4 is regultory receptor for dendritic cells tht impirs inflmmtion nd T-cell immunity Tomofumi Uto 1,, Tomohiro
Received 1 Oct 215 Accepted 8 Mr 216 Pulished 12 Apr 216 DOI: 1.138/ncomms11273 OPEN Clec4A4 is regultory receptor for dendritic cells tht impirs inflmmtion nd T-cell immunity Tomofumi Uto 1,, Tomohiro
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Health-Related Quality of Life and Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Obese Persons Seeking Bariatric Surgery
 Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Gene expression phenotypic models that predict the activity of oncogenic pathways
 3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4 + T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator
 CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF PIROXICAM
 IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Immunoregulatory cytokines in bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell products
 Bone Mrrow Trnsplnttion, (999) 23, 53 62 999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 268 3369/99 $2. http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/mt Immunoregultory cytokines in one mrrow nd peripherl lood stem cell products
Bone Mrrow Trnsplnttion, (999) 23, 53 62 999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 268 3369/99 $2. http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/mt Immunoregultory cytokines in one mrrow nd peripherl lood stem cell products
Reducing the Risk. Logic Model
 Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Local IL-21 Promotes the Therapeutic Activity of Effector T cells by Decreasing Regulatory T Cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment
 originl rticle Locl IL- Promotes the Therpeutic Activity of Effector T cells y Decresing Regultory T Cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment Seunghee Kim-Schulze, Hong Sung Kim, Qing Fn, De Won Kim nd
originl rticle Locl IL- Promotes the Therpeutic Activity of Effector T cells y Decresing Regultory T Cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment Seunghee Kim-Schulze, Hong Sung Kim, Qing Fn, De Won Kim nd
Alternative cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- mediated attraction of CTLs toward NKT cell licensed DCs
 Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
Review TEACHING FOR GENERALIZATION & MAINTENANCE
 Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Comparison of three simple methods for the
 J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression
 Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Nonpharmacologic Interventions for Treatment-Resistant Depression in Adults Executive Summary
 Comprtive Effectiveness Review Numer 33 Effective Helth Cre Progrm Nonphrmcologic Interventions for Tretment-Resistnt Depression in Adults Executive Summry Bckground Mjor depressive disorder (MDD) is common
Comprtive Effectiveness Review Numer 33 Effective Helth Cre Progrm Nonphrmcologic Interventions for Tretment-Resistnt Depression in Adults Executive Summry Bckground Mjor depressive disorder (MDD) is common
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
I n the immune response against viruses like influenza, NK cells play an important role1. NK cells express both
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: INFECTION MUCOSAL IMMUNOLOGY NK CELLS INFLUENZA VIRUS Differentil lung NK cell responses in vin influenz virus infected chickens correlte with pthogenicity Christine A. Jnsen 1, Eveline
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: INFECTION MUCOSAL IMMUNOLOGY NK CELLS INFLUENZA VIRUS Differentil lung NK cell responses in vin influenz virus infected chickens correlte with pthogenicity Christine A. Jnsen 1, Eveline
Study of Stress Distribution in the Tibia During Stance Phase Running Using the Finite Element Method
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Geographical influence on digit ratio (2D:4D): a case study of Andoni and Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delta, Nigeria.
 Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
Journl of Applied Biosciences 27: 1736-1741 ISSN 1997 5902 Geogrphicl influence on digit rtio (2D:4D): cse study of Andoni nd Ikwerre ethnic groups in Niger delt, Nigeri. Gwunirem, Isrel U 1 nd Ihemelndu,
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
